
Therapy
Sleep Related Low Thyroid Symptoms
- Insomnia
- Poor Sleep Quality
- Waking Up Feeling Unrested
- Difficulty Getting Out of Bed in the Morning
- Frequent Nightmares
- Sleep Apnea
- Excessive Snoring
- Night Sweats
Self-care
The most usual ones are:
- Dry skin
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to cold
- Forgetfulness
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Voice changes
Nutrition
This may occur for a number of reasons, including:
- Graves' disease. Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies produced by your immune system stimulate your thyroid to produce too much T4. ...
- Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules (toxic adenoma, toxic multinodular goiter or Plummer's disease). ...
- Thyroiditis. ...
What are some symptoms of low thyroid levels?
Signs and Symptoms of Low TSH Levels
- General. Fatigue, nervousness, restlessness and weakness are common symptoms of low TSH. ...
- Heart and Lungs. People with low TSH commonly feel their heart pounding hard. ...
- Skin. ...
- Digestive System. ...
- Personality and Thinking. ...
- Call the Doctor. ...
What are the effects of low thyroid?
What causes the thyroid to secrete too much hormone?
What symptoms might you have if your TSH level is too low?
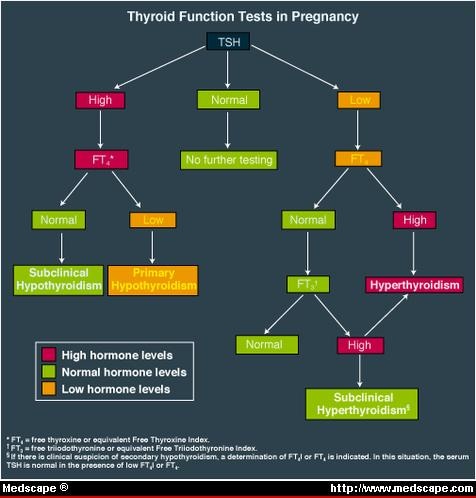
Does low TSH need to be treated?
If your TSH levels are low but still detectable and you don't have complications, you may not receive immediate treatment. Instead, your doctor may choose to retest your TSH levels every few months until they return to normal or your doctor is satisfied that your condition is stable.
At what level do you treat a low TSH?
The American Thyroid Association and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommend treating patients with thyroid-stimulating hormone levels less than 0.1 mIU per L if they are older than 65 years or have comorbidities such as heart disease or osteoporosis.
What happens if your TSH hormone is low?
TSH is a hormone made by the pituitary gland that tells the thyroid gland how much thyroid hormone to make. Symptoms of low TSH include weight loss, fatigue, confusion, heat intolerance, fast heartbeat, high blood pressure and other symptoms.
Should I worry if my TSH is low?
Low TSH levels can mean your thyroid is making too much of the hormones, a condition called hyperthyroidism. A TSH test does not explain why TSH levels are too high or too low.
How do you know if thyroid medicine is working?
You and your doctor should set up a plan to test and measure thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) every few weeks after beginning medication. This is the best way to know whether it is working.
Why is my TSH level dropping?
In cases of hyperthyroidism, your TSH level will be decreased, because there is too much thyroid hormone in your blood. Your TSH levels will be decreased, if: You have Grave's hyperthyroidism. This is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
Does low TSH cause weight gain?
According to Dr. Kitahara, if someone has low thyroid function, their TSH is high, and the thyroid hormones known as T3 and T4 are low—and weight gain often occurs. If someone has an overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism, TSH is usually low, the T3 and T4 are high, and weight loss occurs.
How can I raise my TSH level?
Eating a portion of Essential Fats at every meal which includes extra virgin olive oil, flaxseed oil, raw unsalted nuts and seeds, avocados and oily fish, will improve thyroid hormone levels as our cell receptors become more able to take up thyroid hormone.
Does low TSH always mean hyperthyroidism?
A high TSH level indicates that the body does not have enough thyroid hormone. A TSH level lower than normal indicates there is usually more than enough thyroid hormone in the body and may indicate hyperthyroidism.
What is a critical TSH level?
The standard reference range for the TSH level is anywhere between 0.30 and 5.0 uIU/mL. If your TSH level is higher than 5.0 uIU/mL, then the lab will flag you as “high,” and you may experience the symptoms listed above 5.0 uIU/mL. Values of the TSH level more than 10.0 uIU/mL need long-term thyroid supplements.
How long does it take for thyroid medication to work?
You should start to feel better a few days after you begin taking medicine. But it may take a few months for your thyroid hormone levels to get back to normal. If your levels get better, but you still have symptoms like fatigue and weight gain, your doctor may need to change your treatment.
Can hypothyroidism go away?
For those with particularly low levels of thyroid hormones, hypothyroidism is a life-long condition that will need to be controlled with medication on a regular schedule. It can be controlled very well and you can live a normal life with hypothyroidism.
What is the best test for low TSH?
The most common and effective test for low TSH is a blood test . In addition to analyzing your TSH level, your doctor is looking for T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine), which the thyroid produces. These three hormones give doctors an indication of which gland they should focus on, the thyroid or the pituitary.
How does low TSH affect your health?
Low TSH levels can affect your health, quality of life, and your relationships. The signs of the conditions caused by a low TSH level are essential to know so that you can recognize that you might have a health issue and discuss it with your doctor to get the proper treatment.
What happens if your thyroid is not producing TSH?
If the pituitary gland is not functioning to produce TSH as it should, then the thyroid will not make the level of hormones it should be. This reduction of hormones from the thyroid can lead to many health problems. Low TSH levels can affect your health, quality of life, and your relationships.
What is it called when you have a thyroid gland that is too large?
Other autoimmune disorders. A goiter is an enlarged thyroid. Thyroids can grow nodules on them, and if more than one grows, it is called a multinodular goiter, which produces too much thyroid hormone. These nodules can also be toxic and cause the thyroid not to function as it should.
What is the TSH hormone?
TSH is a hormone made by the pituitary gland that tells the thyroid gland how much thyroid hormone to make. Symptoms of low TSH include weight loss, fatigue, confusion, heat intolerance, fast heartbeat, high blood pressure and other symptoms. The endocrine system is responsible for regulating the function of organs in your body.
Why does TSH drop?
The pituitary gland is signaled to stop producing TSH when there is enough thyroid hormones, like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), in the blood. When something other than the pituitary gland causes excess thyroid hormone production, TSH levels will drop. The conditions associated with low TSH levels produce a lot of symptoms, including: ...
What causes hyperthyroidism?
Autoimmune disorders are the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Of these disorders, Grave's disease is the most well-known. Other conditions that can cause hyperthyroidism include: 1 Multinodular goiter (enlarged thyroid) 2 Thyroid inflammation (thyroiditis) 3 Toxic nodules on your thyroid 4 Thyroid gland dysfunction due to a medication 5 Excess thyroid hormone therapy 6 Other autoimmune disorders
Why does my thyroid have low TSH?
Because an overactive thyroid secretes too much thyroid hormones, signals are sent to your pituitary gland to secrete lower TSH levels. This can cause symptoms of low TSH or hyperthyroidism such as weight loss, nervousness, difficulty sleeping, or light periods (in women).
What causes low TSH levels?
The causes of low TSH can be Graves’ disease, nodules that stimulate the thyroid, or inflammation. In this article, you will learn how low levels of TSH affect the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). I will also look at what should be the normal levels of TSH, T3, and T4 and how you can spot symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
How does TSH affect T3?
How TSH Affects T3 and T4 Levels. TSH affects levels of T3 and T4 in the bloodstream by stimulating the thyroid to produce these hormones. Doctors from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry say that the TSH mainly stimulates the production of T4 and this is converted into T3 by other tissues in the body. 4.
What is free T4?
It contains 4 iodine molecules. 3. Levels of free T4 (FT4) refer to the amount of thyroxine that is biologically active and not bound to protein. Doctors usually test for FT4 levels to help identify possible causes of thyroid issues. Free T4 is the active form of thyroxine.
How does TSH affect thyroid hormones?
Doctors from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry say that TSH affects levels of T3 and T4 hormones by stimulating the thyroid to produce these hormones. Checking for normal or low TSH levels can help to diagnose thyroid disorders. 2.
What is the normal TSH level?
According to the British Thyroid Foundation the normal range of TSH is as follows: 21. 0.4 – 4.0 mIU/L (milliunits per liter) However, recent studies into thyroid activity and what should be classed as normal TSH levels put the upper range somewhat lower.
Why is T3 called T4?
The thyroid hormone triiodothyronine is referred to as T3 because it contains one less iodine molecule than T4. Dr. Irizarry explains that thyroxine converts to triiodothyronine when it reaches the cells in the body. T3 is 4 times more active than the more abundant T4. 3.
Why is it important to control thyroid levels during pregnancy?
These hormones help develop the brain and nervous system. If you have hypothyroidism, it’s important to control your thyroid levels during pregnancy. If your baby doesn’t get enough thyroid hormone during development, the brain may not develop correctly and there could be issues later.
How to prevent a serious form of hypothyroidism?
If you experience any of the symptoms of hypothyroidism, the best thing to do is talk to your healthcare provider .
What is it called when your metabolism slows down?
Hypothyroidism is a condition where there isn’t enough thyroid hormone in your bloodstream and your metabolism slows down. Hypothyroidism happens when your thyroid doesn’t create and release enough thyroid hormone into your body. This makes your metabolism slow down, affecting you entire body. Also known as underactive thyroid disease, ...
How to diagnose hypothyroidism?
The main way to diagnose hypothyroidism is a blood test called the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test. Your healthcare provider may also order blood tests for conditions like Hashimoto’s disease. If the thyroid is enlarged, your provider may be able to feel it during a physical exam during an appointment.
What causes thyroid to be damaged?
In Hashimoto’s disease, the body’s immune system attacks and damages the thyroid. This prevents the thyroid from making and releasing enough thyroid hormone. The other primary causes of hypothyroidism can include: Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid).
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
Primary causes of hypothyroidism are much more common. The most common of these primary causes is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto’s disease. Also called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, this condition is hereditary (passed down through a family).
What happens if you don't treat hypothyroidism?
If you are not treated, your symptoms can become more severe and can include: Developing mental health problems. Having trouble breathing.
What is the best treatment for hyperthyroidism?
A person may need to take beta-blockers and antithyroid medications.
What does a doctor do if you have high TSH?
If a person has abnormally high or low TSH levels, the doctor needs to run at least one other diagnostic test to identify the underlying cause. These tests look at levels of specific thyroid hormones and antibodies.
What is TSH test?
Summary. The thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test measures the amount of TSH in the blood. The results convey how well the thyroid is functioning. Doctors can use TSH test results to diagnose thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. The pituitary gland produces TSH, which is a hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland.
What is the normal TSH range?
Reference ranges remain controversial, but for most people, the normal range falls between 0.4 and 4.0 mU/l. Having an overactive or underactive thyroid can cause health issues that interfere with daily life.
Why do doctors use lower reference ranges for pregnant women?
the levels of certain thyroid hormones in the blood. This is essential for the development of the fetal brain and nervous system. At the same time, the levels of TSH in the blood decrease. As a result, doctors use lower reference ranges for pregnant women.
How many women have thyroid problems?
report that 1 in 8 females experience thyroid problems at some point. This includes hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. The risk of thyroid problems increases during pregnancy and around menopause. Research has not shown a consistent difference in TSH levels between males and females.
Which gland produces TSH?
The pituitary gland produces TSH, which is a hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the throat. It produces hormones that help regulate many bodily functions, such as metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. In this article, we describe the TSH test and results.
What hormones are released when TSH levels are low?
The pituitary gland releases the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is responsible for stimulating the release of the thyroid hormones namely thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These two thyroid hormones are necessary for various body functions.
What does it mean when your thyroid is low?
Keep in mind that the pituitary gland plays a role in the production of eight hormones, including the TSH and thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). When a patient has low levels of TSH, it indicates that a patient has a health problem. The common causes are: Hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism is a medical condition wherein a patient will have high levels ...
Why is my TSH low?
What are Symptoms: The most common cause of low TSH level is a hyperactive thyroid gland. Because the thyroid hormones help regulate various body functions such as metabolism, an increase in these hormones can lead to the following symptoms: General Symptoms.
Why is my thyroid gland weak?
When both the thyroid hormones and TSH levels are low, it indicates that the patient’s pituitary gland is either weak or damaged because of a disease, head injury, or tumor.
Why do I have a high TSH level?
The common causes are: Hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism is a medical condition wherein a patient will have high levels of thyroid hormones and a low TSH level. When a patient has hyperthyroidism or Grave’s diseases, he will have an overactive thyroid wherein there is an increase in the levels of thyroid hormones.
Why is it important to keep TSH levels within normal range?
It is vital that person must keep their TSH levels within the normal range because it can affect the production of thyroid hormones. However, various factors can result in a low TSH leading to several health problems.
How to increase TSH levels?
Exercise. One way to stimulate your pituitary gland and boost the levels of TSH is through daily exercises such as yoga, breathing exercises, and meditation . On the plus side, doing regular exercises can help balance your hormones and improve your overall health condition. Tweet.
What happens if your thyroid doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone?
If your thyroid doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone, your pituitary triggers your thyroid to make more. (This might happen in cases of illness, stress, or surgery, for example.) If your thyroid is overactive and producing too much thyroid hormone, your pituitary senses that and slows or shuts down TSH production.
What is the normal TSH level for adults with thyroid disease?
The reasoning behind this is that the vast majority of adults without thyroid disease have a TSH value between 0.45 and 4.12 mU/l. 2. In addition, some physicians believe older patients should have a TSH level that is greater than 4.0 mU/l or 5.0 mU/l, since TSH normally increases with age. 3.
Why do TSH levels vary?
That's because TSH levels vary depending on numerous factors, including your age, your thyroid condition, and possibly even how well you sleep at night or when you last ate. To gauge the optimal level for you, your doctor should consider these factors along with any symptoms you are experiencing.
Why is free T4 checked?
For instance, free T4 in addition to TSH is usually tested if a doctor suspects thyroid dysfunction due to disease of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus. 1. Likewise, if the TSH is normal, but a person still has symptoms of being hyperthyroid or hypothyroid, free T4 may be checked.
What does a high TSH level mean?
A high TSH level can mean a new diagnosis of hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid. A low TSH might mean hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid.
What is the TSH level for pregnancy?
In contrast, someone who has health risks—such as heart disease or osteoporosis—may benefit from having a goal TSH that is higher, perhaps around 5.0 mU/l or 6.0 mU/l. In pregnancy, TSH should not be allowed to rise above 3.0 mU/l for the health of both the baby and mother. 4.
Why does hypothyroidism occur?
This is by far the most common form of hypothyroidism, and it occurs because the thyroid gland produces an inadequate amount of thyroid hormones. 5 The pituitary gland senses these low levels and increases the production of TSH.
When was the thyroid threshold lowered?
Plus, he points out, the threshold of what’s considered a normal thyroid range was lowered in 2002, and that lower number is what labs use today when they look at thyroid hormones in the blood.
What does it mean when your body has antibodies to your thyroid?
These antibodies would indicate a hypothyroid condition called Hashimoto’s disease, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid. if there is evidence of heart disease or risk for it.
How many prescriptions for levothyroxine were there in 2006?
Maybe that’s why prescriptions of levothyroxine increased in the U.S. from about 50 million in 2006 to about 70 million in 2010. Researchers found a similar increase in England and Wales, with prescriptions jumping from 17 million in 2006 to 23 million in 2010. What’s wrong with giving people who have a borderline underactive thyroid ...
What are the problems caused by the thyroid gland?
I’m always amazed to see just how many problems a slowdown in the output of the thyroid gland can cause: extreme fatigue, intolerance to cold, weight gain, dry skin, and dry hair, to name a few. Millions of Americans have an underactive thyroid, a condition known as hypothyroidism.
Does levothyroxine cause heart problems?
They run the risk of experiencing side effects from taking levothyroxine, which include irregular heart rhythms, insomnia, and loss of bone density, without reaping any benefit from it. The best way to check for hypothyroidism is to look at the level of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood.
Does soy cause hypothyroidism?
The main bioactive compounds of soy are isoflavones and those can induce hypothyroidism. Other countries as Brazil also have these increase of thyroid problems. Is urgent that we found the cause to prevent this situations in the future, and probably for some people this could be reversible. A. Greenwell.
Does TSH test the thyroid?
TSH tests the pituitary gland, not the thyroid and while yes, there is a feedback mechanism between the two glands, testing TSH production is only an indirect indication of the function of the thyroid.
