Medication
- Sputum cultures – positive yields found in 10-15% of patients with acute pulmonary histoplasmosis and 60% in patients with chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis
- Blood cultures – positive results found in 50-90% of patients with progressive disseminated histoplasmosis
- Serologic testing may indicate spreading of the disease
- Chest x-ray and CT scanning
Procedures
Can histoplasmosis be cured? For some people, the symptoms of histoplasmosis will go away without treatment. However, prescription antifungal medication is needed to treat severe histoplasmosis in the lungs, chronic histoplasmosis, and infections that have spread from the lungs to other parts of the body (disseminated histoplasmosis).
Nutrition
People with mild symptoms of histoplasmosis usually resolve the disease on their own without treatment. In more severe cases, the prognosis is good for those who receive appropriate treatment. Certain people will experience relapsing infections (chronic histoplasmosis) and may need long-term therapy with antifungal drugs.
What forms of histoplasmosis are potentially fatal?
Histoplasmosis lasts for anywhere between a few weeks to a month. If your symptoms are severe, histoplasmosis could last longer than that. This is when the lung infection is severe or when histoplasmosis spreads to other parts of the body. In such cases, it generally affects the central nervous system, particularly the brain and the spinal cord.
Can histoplasmosis be cured?
What is the prognosis of histoplasmosis?
How long does histoplasmosis last?

What is the best medicine for histoplasmosis?
Amphotericin B (Fungizone) Amphotericin B is the drug of choice for overwhelming acute pulmonary histoplasmosis, chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis, all forms of progressive disseminated histoplasmosis, meningitis, and endovascular histoplasmosis.
How long does it take to recover from histoplasmosis?
For most people, the symptoms of histoplasmosis will go away within a few weeks to a month. However, some people have symptoms that last longer than this, especially if the infection becomes severe.
Does histoplasmosis cause permanent lung damage?
Some people get better without treatment. An active infection will usually go away with antifungal medicine. But, the infection may leave scarring inside the lung. The death rate is higher for people with untreated disseminated histoplasmosis who have a weakened immune system.
What are the symptoms of histoplasmosis?
In most cases, histoplasmosis causes mild flu-like symptoms that appear between 3 and 17 days after exposure to the fungus. These symptoms include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, cough and chest discomfort. In these milder forms, most symptoms go away on their own in a few weeks.
How do you get rid of fungus in your lungs?
Antifungal drugs: These medications are generally used to treat invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Voriconazole is currently the drug of choice because it causes fewer side effects and appears to be more effective than other medications. Amphotericin B or itraconazole are also effective in treating infection.
How serious is histoplasmosis?
Severe histoplasmosis Called disseminated histoplasmosis, it can affect nearly any part of your body, including your mouth, liver, central nervous system, skin and adrenal glands. If untreated, disseminated histoplasmosis is usually fatal.
What are the long term effects of histoplasmosis?
Long-term complications of histoplasmosis include: The fibrosis may present as superior vena cava syndrome, respiratory distress, pulmonary emboli, or bronchial constriction.
Is histoplasmosis a form of COPD?
Chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis is a disorder caused by Histoplasma capsulatum infection that is classically described as cavitary disease in male smokers with underlying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Does histoplasmosis show up on xray?
After heavy exposure, radiographs may show widely disseminated, diffuse, fairly discrete nodular shadows throughout the lungs, with individual lesions measuring 1-10 mm in diameter. This form of disease is termed miliary histoplasmosis (see the image below); it is similar to miliary tuberculosis.
Is histoplasmosis related to Covid 19?
These cases suggest that COVID-19 may facilitate the development of acute pulmonary histoplasmosis and, therefore, clinicians must be aware of this differential diagnosis in patients from endemic areas with fever and coughing after recovery from COVID-19.
How is histoplasmosis diagnosed?
Histoplasmosis is usually diagnosed with a blood test or a urine test. Healthcare providers rely on your medical and travel history, symptoms, physical examinations, and laboratory tests to diagnose histoplasmosis.
What does a histoplasmosis rash look like?
Red spots on the skin (erythema nodosum) Red lumps on the skin (erythema multiforme), usually on the lower legs.
How long do you have to take antifungal medication for histoplasmosis?
Treatment usually isn't necessary if you have a mild case of histoplasmosis. But if your symptoms are severe or if you have the chronic or disseminated form of the disease, you'll likely need treatment with one or more antifungal drugs. If you have a severe form of the disease, you might need to continue to take medications for three months ...
Is it necessary to test for histoplasmosis?
While testing might not be necessary for mild cases of histoplasmosis, it can be crucial in treating life-threatening cases.
What is the best treatment for histoplasmosis?
Options for therapy include amphotericin B or one of its lipid formulations, and ketoconazole, itraconazole, or fluconazole. Recently, newer antifungal agents have been evaluated in animals models of histoplasmosis. Of these, a new triazole, posaconazole (SCH56592) appears most promising.
What is the causative organism of histoplasmosis?
The causative organism is a dimorphic fungus, Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasmosis can present as a self-limited disease or cause life-threatening diseases resulting in considerable morbidity and mortality.
Is itraconazole used for severe histoplasmosis?
The role of intravenous formulation of itrac onazole for severe histoplasmosis is unknown because studies comparing it with amphotericin B have not been conducted. Copyright 2001 by W.B. Saunders Company.
What is the best treatment for histoplasmosis?
Itraconazole ( Sporanox, Onmel), fluconazole ( Diflucan ), and amphotericin B ( Ambisome, Amphotec; drug of choice for severe disease) are antifungal drugs that treat histoplasmosis. A person may need to continue treatment for a period of several months.
What is the cause of histoplasmosis?
Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by an infection with a fungus known as Histoplasma capsulatum, which is common in the environment, most frequently in association with bird or bat droppings. Some people also refer to the disease as "cave disease.". The infection can cause a lung disease similar to pneumonia in some people.
How many people infected with histoplasma capsulatum each year?
The airborne spores can travel hundreds of feet. Estimates indicate that around 250,000 people are infected each year in the U.S. Histoplasma capsulatum exists throughout the world, but it is most commonly located in North and Central America.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary histoplasmosis?
The symptoms of pulmonary histoplasmosis are similar to those of pneumonia and include flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, sweats, a dry cough, malaise, and chest pains. Some affected people also experience joint pains. If the disease progresses without treatment, those affected may develop weight loss, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Can anyone develop histoplasmosis?
Anyone may develop histoplasmosis. However, the illness is more likely to occur in infants, young children, and the elderly. Risk factors for developing severe or widespread disease include having a suppressed immune function or chronic lung disease.
Is histoplasmosis a disease?
The disease is most severe in people with a decrease d function of the immune system. Symptoms of histoplasmosis are similar to those of pneumonia. Mild cases of histoplasmosis do not require specific treatment, and more severe or disseminated infections require antifungal medications.
How long does it take for histoplasmosis to go away?
How Histoplasmosis Is Treated. Most cases of histoplasmosis go away on their own in a few weeks without treatment. However, for chronic or disseminated histoplasmosis, antifungal medication is recommended.
Is histoplasmosis a long term disease?
For most people, there are no long-term consequences of histoplasmosis. Reoccurrence is possible, however, especially for people with weakened immune systems. So, it is important to take precautions to avoid infection in the future.
How to know if you have histoplasmosis?
Most people who have histoplasmosis don’t know it. Have your eyes examined for histo spots if you ever lived somewhere with high rates of histoplasmosis.
How does histoplasmosis enter the air?
It enters the air when people disturb soil when plowing fields, sweeping chicken coops, or digging holes. Histoplasmosis starts as a lung infection. Doctors think that the infection, even if mild, can later move to the eye through the blood stream.
Can you have histoplasmosis without a cold?
Histoplasmosis infection is often so mild that it produces no clear symptoms. Any symptoms are often like those from a common cold. In fact, if you had histoplasmosis symptoms, you might think you just had a cold or flu . This is because the body’s immune system normally beats the infection in a few days without treatment.
Do histo spots affect vision?
Histo spots do not generally affect vision. Although ophthalmologists don’t know why, they can cause complications years or even decades later. We do know that there is a connection between histo spots and the growth of abnormal blood vessels underneath the retina.
How to prevent histoplasmosis?
Avoid exposure. Avoid projects and activities that might expose you to the fungus, such as cave exploring and raising birds, such as pigeons or chickens. Spray contaminated surfaces. Before you dig soil or work in an area that could harbor the fungus that causes histoplasmosis, soak it with water.
What is the most severe form of histoplasmosis?
Severe histoplasmosis. The most severe variety of histoplasmosis occurs primarily in infants and in people with compromised immune systems. Called disseminated histoplasmosis, it can affect nearly any part of your body, including your mouth, liver, central nervous system, skin and adrenal glands.
How does histoplasmosis spread?
The infection is most commonly spread when these spores are inhaled after taking to the air, such as during demolition or cleanup projects. Soil contaminated by bird or bat droppings also can spread histoplasmosis, putting farmers and landscapers at a higher risk of the disease. In the United States, histoplasmosis commonly occurs in ...
What are the most common causes of disseminated histoplasmosis?
Other factors that can weaken your immune system include: HIV or AIDS. Cancer chemotherapy. Corticosteroid drugs, such as prednisone.
What are the complications of histoplasmosis?
Complications can include: Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Histoplasmosis can damage lungs to the point that the air sacs begin filling with fluid. This prevents good air exchange and can deplete the oxygen in your blood.
Can histoplasmosis spread from person to person?
It's particularly common in chicken and pigeon coops, old barns, caves, and parks. Histoplasmosis isn't contagious, so it can't be spread from person to person.
What is the best treatment for histoplasmosis?
If central nervous system (CNS) involvement occurs, or if the person is compromised by other diseases or has severe histoplasmosis (progressive disseminated histoplasmosis), either itraconazole or amphotericin B is recommended.
What causes histoplasmosis?
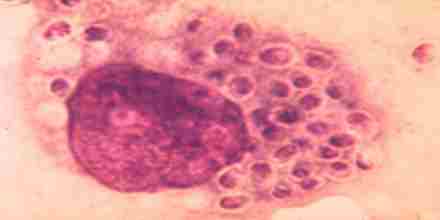
Histoplasmosis is caused by a dimorphic (two forms) fungus named Histoplasma capsulatum. The dimorphic fungus has a branching (mycelial) phase consisting of branches and spores that can be inhaled while they are airborne and may reach the lung alveoli. Macrophages (immune system cells that protect the body by engulfing foreign invaders) surround and engulf H. capsulatum. The fungus then changes inside the macrophages to the yeast form in about 15-18 hours. In most cases, the macrophage response kills the yeast. When macrophages fail to kill all the yeast, different forms of the disease develop because the yeast form multiplies and invades other cells. The larger the number of mycelia and spores the person is exposed to, the more likely the person will develop symptomatic disease. Severe histoplasmosis occurs when the yeast forms are spread by the blood and lymphatic systems to other organs. Histoplasmosis is sometimes referred to according to the severity of the disease: 1 Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis; asymptomatic and symptomatic 2 Chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis causing chronic lung symptoms 3 Ocular histoplasmosis syndrome, causing ocular (eye) symptoms 4 Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis: causes mouth and throat lesions or ulcers 5 Subacute progressive disseminated histoplasmosis causes intestinal, adrenal, cardiac, or central nervous system ( CNS) involvement. 6 Acute progressive disseminated histoplasmosis causes encephalopathy (alteration of brain function), meningitis, mass lesions, and cutaneous lesions.
How long does it take for histoplasmosis to incubate?
Histoplasmosis has an incubation period of about three to 17 days. Histoplasmosis is not contagious; it is not transmitted person to person. Definitive diagnosis is made by culturing and identifying Histoplasma capsulatum from biopsy, ...
What is progressive disseminated histoplasmosis?
Histoplasmosis is sometimes referred to according to the severity of the disease: Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis: causes mouth and throat lesions or ulcers. Subacute progressive disseminated histoplasmosis causes intestinal, adrenal, cardiac, or central nervous system ( CNS) involvement.
Where is histoplasmosis most common?
Risk factors for histoplasmosis include immunocompromised people and association with airborne particles containing the fungi (caves containing bats, bird feces, construction sites). Histoplasmosis is most common in North and Central America. In North America, the fungus is known to live in the soil in the central and eastern states, ...
How long does it take for a person to die from histoplasmosis?
Acute progressive disseminated histoplasmosis, if not treated quickly and appropriately, can lead to death in a few weeks. Even with lifelong antifungal treatment, about 10%-20% of people with disseminated disease will relapse.
Which type of patient is at the highest risk for histoplasmosis?
Immunosuppressed patients (for example, cancer or AIDS patients) are at the highest risk for severe histoplasmosis. Histoplasma capsulatum lives in acidic, damp environments that contain organic material. High concentrations of the fungus occur in caves where bats or birds reside, and the fungi are in the soil.
Drugs used to treat Histoplasmosis
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.