The treatment involves applying a coating consisting of cobalt, to pale Tanzanites in order to give them the appearance of fine stones. The treatment is identifiable using an immersion cell and microscope which reveals areas where the coating hasn't taken completely or erosion has occurred near facet junctions.
What are the different methods of treating gemstones?
The treatment involves applying a coating consisting of cobalt, to pale Tanzanites in order to give them the appearance of fine stones. The treatment is identifiable using an immersion cell and microscope which reveals areas where the coating hasn't taken completely or erosion has occurred near facet junctions.
What is meant by dressing of stone?
– altering a gem’s appearance by applying a coloring agent like paint to the back surfaces of gems (a treatment known as “backing”), or paint applied as a coating to all or a portion of a gemstone’s surface with the effect of altering the color. 1.
What is the history of gemstone treatment?
C (Coating): The use of heat, light, and/or chemicals to lighten or remove a gemstone’s color. Coating can also be applied to the surface of a gemstone to deepen or simply alter the color of the gemstone. CR: Indicates that a particular stone is synthetic or laboratory created.
Can a gemstone be treated or enhanced?
Common treatments for amber include heat treatment, dye, and reconstitution. Coatings and fracture fillings are less common. Heat treatments darken the color and leave “sun spots.” These spots appear like glitter within the stone. The fracture spots in this piece of amber are evidence of heat treatment. Image by starbright from Pixabay.
What does coated mean on a gemstone?
What does stone treatment method mean?
Will coated topaz last?
What is coated pink topaz?
Are all gemstones treated?
Why are stones heat treated?
Heat treatment is most commonly used to alter color but is also used to increase clarity. Rubies and sapphire can require significantly higher temperature to alter color and change clarity. Heating is used to either lighten, darken or alter the color of a gem.
What is the difference between white topaz and diamond?
Who should not wear mystic topaz?
What are mystic gems?
What is the difference between pink topaz and pink sapphire?
What is pink topaz good for?
What is a pink stone?
Why is jadeite bleached?
Bleaching in jade is typically part of a two-step process: because acid bleaching causes the material to become slightly porous or susceptible to breakage along fractures, it is then subsequently treated with polymer impregnation to fill these open spaces to produce a better overall appearance.
What is the chemical used to alter / reduce a component of, or the entire color, of a por
Bleaching. – a chemical used to alter / reduce a component of, or the entire color, of a porous gem. Some gemstones are bleached and then dyed, a form of “combination treatment.”. 1. The most commonly encountered bleached gems include:
Why do people alter gemstones?
In a sense, humans alter all gem materials after they are found in the earth in order to prepare them for use in jewelry. Natural gem crystals are transformed from their rough crystallographic form into the shapes, outlines, and degrees of polish in the gemstones that we appreciate and wear in jewelry.
What is surface coating?
– altering a gem’s appearance by applying a coloring agent like paint to the back surfaces of gems (a treatment known as “backing”), or paint applied as a coating to all or a portion of a gemstone’s surface with the effect of altering the color . 1.
How do diamonds change color?
Heating diamonds at high pressures and high temperatures can remove or lessen their brownish coloration so the gem becomes colorless. Other types of diamonds may be transformed from brown to yellow, orangy yellow and yellowish green, or to blue colors by this process.
Why is it necessary to disclose gems?
Because these treatments are not always apparent to the unpracticed eye, and are sometimes difficult to distinguish even by experts, it is necessary and legally required for anyone selling a gem (including consumer to consumer trade) to disclose the treatment procedure it may have received.
Why are pearls bleached?
Pearls – All types of pearls are routinely bleached with hydrogen peroxide to lighten and improve their uniformity of color.
What is TB jade?
TB (Type B Jade): Type B jade is a natural jade that is bleached in acid to remove undesirable staining, and then impregnated with wax or polymers.
What is the F in sapphires?
F (Filling): The incorporation of colorless borax or other substances into the cracks of a gemstone that are created as a by-product of heating it. It is used only if a crack is visible at 10 times magnification.
What does a gemstone treatment code mean?
Gemstone treatment codes indicate whether a gemstone has been treated or not. An untreated gemstone will not have enhancements. However, if you see that a gemstone has been treated, you will know to ask for more information about particular enhancements.
What does "Impregnation" mean?
I (Impregnation): Introducing a colorless agent — usually plastic — into a porous gemstone to improve durability and appearance.
What is gemstone enhancement?
Enhancements are the specific changes that have been applied to treated gemstones. Both gemstone treatments and gemstone enhancements have codes that indicate what has been done to the gemstone’s appearance. These codes are usually indicated on jewelry product pages if you’re shopping for jewelry online. If you’re shopping for jewelry in brick and mortar stores, the employees will be able to tell you more about how a gem has been treated.
What does the E symbol mean on a gemstone?
Treatment Code E: The “E” symbol indicates the gemstone has undergone an enhancement procedure.
What is the purpose of oiling a gemstone?
O (Oiling): Also known as resin infusion, oiling fills surface-breaking cavities and cracks with a colorless oil, wax, resin, or other substance to improve the gemstone’s appearance.
What are some ways to enhance gemstone color?
If you’re unfamiliar with gemstone treatments, check out our articles on heat treatment and radiation treatment, two of the most common gemstone treatments for enhancing color.
What are the treatments for amber?
Common treatments for amber include heat treatment, dye, and reconstitution. Coatings and fracture fillings are less common. Heat treatments darken the color and leave “sun spots.”. These spots appear like glitter within the stone. The fracture spots in this piece of amber are evidence of heat treatment.
How long have humans treated gemstones?
Common Gemstone Treatments Cheat Sheet. Humans have treated gemstones for thousands of years. Much of the gem material currently on the market has been treated in some way before it reaches the consumer.
What is lapis lazuli dye used for?
Lapis Lazuli. Dyes are commonly used to hide white calcite inclusions in lapis lazuli. In addition to dye treatment, most specimens contain a coating of wax or plastic to seal in the dye. In some cases, plastic or wax may even be present in undyed specimens.
What is the best treatment for morganite?
Heat treatment enhances the pink color in morganite. This common treatment is undetectable.
What is jade treated with?
In addition, some jade is treated with acid and dyed polymer. This is sometimes called “B+C” jade.
What is reconstituted amber?
Reconstituted amber consists of several pieces pressed or melted together. In some cases, the people creating reconstituted pieces add modern insects to the mix. Artificial resins as well as copal may also be added to the mix. Reconstituted gems often exhibit a mosaic structure, which may only be visible under high magnification.
What is the trickiest gemstone to separate?
Two of the trickiest gemstone separations to make are scapolite from citrine and apatite from tourmaline . Learn some tips for distinguishing…
What gems are more prone to treatment than other stones?
Corundum gems receive more types of treatments than any other stones. Learn how to test rubies and sapphires for signs of these enhancements.
What is a gem coating?
Gemstone coatings are a simple way to enhance color and luster. Learn about commonly coated gems, different coating techniques, and how to detect…
Do cut emeralds have clarity enhancements?
Almost all cut emeralds have had clarity enhancements. Learn how these emerald enhancements work, what substances are used, and how to detect…. Emerald Treatments and Alternatives. Emerald treatments, such as oiling, are very common.
Is aquamarine blue or green?
There’s more to aquamarine color than blue. Most natural stones start blueish green and are he ated to blue. Learn the pros and cons of this treatment.…
How is a 0.55 ct diamond treated?
This 0.55-ct brownish orangey-red round brilliant cut synthetic diamond was treated by irradiation and annealing to produce its red color.
How to lighten dark inclusions?
Laser drilling: Diamond manufacturers can employ lasers to remove or lighten a dark-appearing inclusion by drilling a tiny hole to the site of the inclusion. The laser may cause the inclusion to vaporize or the treater may apply bleach or acid to lighten the inclusion further.
What colors can you use for silica?
Silica coatings can be applied to polished colorless or near-colorless diamonds to produce a variety of natural-looking fancy colors, including pinks, oranges, yellows, blues, and purples. The coating is fairly durable but not permanent.
What are the treatments for enhancing diamonds?
Sometimes this process will be followed by annealing. Irradiated diamonds are sensitive to heat and jewelry repair procedures, recutting, and repolish ing can change their colors. Annealing:
What color are brownish diamonds?
The HPHT process can turn some brownish diamonds colorless or transform these brownish stones into other colors like yellow, greenish yellow or green. This process is also associated with pink, blue, and orange-yellow diamonds. HPHT is considered a permanent process.
Why are diamonds treated?
A relatively small percentage of gem-quality diamonds are treated and they are treated for two reasons: to improve clarity or to alter color.
What is the most common diamond treatment used to enhance clarity?
Fracture filling: Infusing molten leaded glass-like substance into a diamond’s fractures – is the most common diamond treatment used to enhance clarity.
Why is topaz pink?
This is also mostly a structural effect. Heating repairs crystal structural damage, reducing the yellow component, and turning the topaz pink.
What gemstones are heated?
Some of the more commonly heated gemstones and the impact of heat upon them are: Amber : Gentle heating oxidizes and darkens Amber . Some Amber also contains gas bubbles that can make it appear cloudy. The bubbles can be removed by slow heating, generally whilst immersed in rape or linseed oil.
How do humans treat gemstones?
Humans have been enhancing and treating gemstones for centuries. This article explores the two of the most common methods used – Heating and Irradiation.
What happens when you heat rubies?
Heat causes structural changes in “silk” inclusions in ruby and sapphire. The rutile which forms the silk dissolves into the stone at high temperature (usually around 1800 degrees centigrade). Leaving a more transparent and therefore more beautiful gemstone. A large percentage of ruby and sapphire on the market today is heated and it is a fairly routine treatment. Unheated rubies and sapphires will contain microscopic rutile needles or tiny gas bubbles in pockets of liquid which are evidence that laboratories can use to guarantee that these stones have not been heated. If these gems are the finest color they will command premium prices due to their extreme rarity.
What is the process of changing a gemstone's color?
Irradiation is the process of using electromagnetic radiation to alter a gem’s color. Irradiation has been with us since the early 1900’s when scientists like Bordas and Crookes used radium salts to change blue sapphires and diamonds green. In today’s world, irradiation is routinely used to color a number of gemstones.
How does irradiation change the color of a gemstone?
The process by which irradiation changes color is fairly straightforward. Radiation causes electrons to be knocked off some atoms, leaving them free to be absorbed by others. This has the effect of creating “color centers” which in turn alter the light-absorbing pattern of the gem stone and by extension its color.
What color is Beryl?
Beryl : The blue-green variety of Beryl - Aquamarine is a routinely heated gemstone. Color in Aquamarine is caused by iron impurities and it generally has 2 colors – yellow and blue. The 2 colors together make green which is why most unheated aquamarine is a greenish blue color.
What is irradiated gem?
Sometimes irradiation is followed by heating to produce a better or new color for the gem. Blue topaz is the most common example. Although blue topaz occurs in nature, it is quite rare and pale in color. In the United States irradiated gems are regulated by the Nuclear Regulatory Agency to in an attempt to insure there is no harmful residual radiation.
What color is chalcedony?
Without dyeing there would little, if any, black onyx: although natural black chalcedony has been claimed to be found in Namibia and Iran, I am at the time of this writing skeptical. Chalcedony or more commonly known as agate, is often dyed blue, green, or orange and carved into bowls, statues, or cut into beads. This is fine, as there are some lovely pieces around using this stuff, especially carved animals and the like and no one minds that it's not "natural". Japanese cultured pearls, which are grown in an Akoya oyster that produces pearls up to about l0 millimeters, grow into a limited selection of colors with various overtones of colors. If they are dark gray, bluish, violet, nearly black, or intense bronze, assume they are dyed. To meet current demand for pearls with rose overtones, some cultured pearls have been given a pink tint; this can be detected by looking for concentrations of dye around drill holes or around blemishes. On the other hand, South Sea cultured pearls which are generally larger than the Japanese cultured pearls, may grow into a variety of exotic colors naturally because they are grown in a different variety of oyster.
What would happen if tanzanite was not treated?
If it was not for treatments the stone would be far more expensive than it is! Tanzanite in shades of violet and blue depends on heat treatment to produce enough supply to meet the demands of the public. Pink topaz is another example of a gem that would not be available without heat treatment.
What stones are treated with oils?
Recently, I have read articles that other colored stones such as rubies, alexandrite, other varieties of chrysoberyl, and demantoid garnets have been treated with oils and resins to make surfacing inclusions less visible. Occasionally colored oils are used on emeralds and rubies.
What is the color of cultured pearls?
If they are dark gray, bluish, violet, nearly black, or intense bronze, assume they are dyed.
What is synthetic resin used for?
Synthetic resins can be used to fill in fractures in emeralds and other stones with fractures that reach the surface of the gem. Hardeners are often applied to make the process more permanent. The use of these resins, with hardeners (Like Opticon) are NOT acceptable treatments. Irradiation.
Why does a gemstone need heating?
In most cases the heating enhances the gemstone to make it more beautiful; the price premium is the result of the rarity of being unheated!. Heating. Heating is the most common treatment available. It can cause the color of a stone to lighten, darken, or change completely.
What is the process of dressing stone?
The Dressing of stone is defined as “The process of giving a proper size, shape and finish to the roughly broken stones as obtained from the quarry.”
Why is dressing stones important?
The dressing of stones is important so that they are dressed in suitable shapes and polished to give a smooth surface if desired. The stones are used in different types of masonry; therefore, it has to be cut and shaped to fit in the type of work needed.
Why are stones rubbed?
In this method of dressing of stone, The surfaces of stones are rubbed to get a smoother finish.
How many types of dressing of stones are there?
16 Types of Dressing of Stones; Its Methods, Objectives.
What is a boaster stone?
It is a very common type dressing of stone, in which the surface of the stone is covered with parallel marks that may run in any direction. A boaster, which is actually a wide-edged chisel, is used for this purpose. These marks may be horizontal or at any angle.
Why are stones used in construction?
(c) To obtain an appealing finish. In a residential building, stones are used not only because of their extra strength, hardness, and durability but also because of their aesthetic value.
How many cm are sunk in a stone dressing?
In this method of dressing of stone, about 1 cm vertical or horizontal grooves are sunk with a chisel having it’s shaped as a hollow semi-circle. The sides of the rock are kept chamfered or sunk.
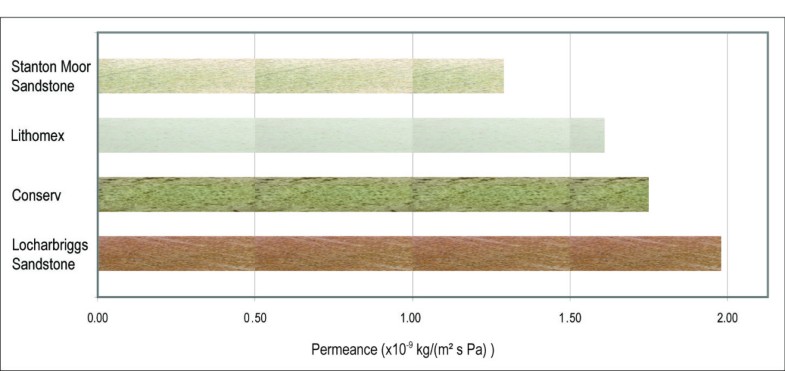
What is topcoat sealer?
These types of stone can have coatings inside only. These stones are very rough, hard to clean, and porous. Topcoat sealers#N#Designed to lay on top of the stone and change appearance ranging from a low to high shine. Prevents liquids from soaking into the stone. This type of sealer is prone to scratching, dulling and peeling. Regular maintenance is required to keep the sealer intact and looking good. More#N#are helpful in sealing the pores, making it easier to maintain, and will give shine because these stones cannot be buffed naturally to a shine as can travertine, marble or limestone. Of course, you don’t have to use a topcoat sealer but it is an option if you want some shine. Keep in mind that topcoat sealers#N#Designed to lay on top of the stone and change appearance ranging from a low to high shine. Prevents liquids from soaking into the stone. This type of sealer is prone to scratching, dulling and peeling. Regular maintenance is required to keep the sealer intact and looking good. More#N#need to be re-applied every couple of years before they wear thin and require stripping.
What is impregnating sealer?
Penetrating or Impregnating Sealers#N#Designed to penetrate the pores of the stone and prevent liquids from soaking into the stone. Helpful in keeping liquids out and lessen the severity of etching When an acidic solution comes in contact with the stone, a dull spot is the result. The acid “eats” the stone leaving dullness, or etching behind. Penetrating sealers help to reduce severity of etches, but cannot eliminate them. Depending on acidity, some liquids can etch immediately, such as wine, where milder acidic solutions may not etch with proper penetrating sealing. More, but will not prevent etching When an acidic solution comes in contact with the stone, a dull spot is the result. The acid “eats” the stone leaving dullness, or etching behind. Penetrating sealers help to reduce severity of etches, but cannot eliminate them. Depending on acidity, some liquids can etch immediately, such as wine, where milder acidic solutions may not etch with proper penetrating sealing. More. This type of sealer will not alter the appearance of the stone in any way if applied properly.#N#: common in the industry, they are intended to SOAK INTO THE STONE and leave no trace. They have no visual impact on the stone unless over applied. Penetrating sealers will slow water absorption and minimize severity of etches. But they do not make your stone waterproof or etch proof.
