
Explore
Chapter 5. Oxygen Therapy Hypoxemia or hypoxia is a medical emergency and should be treated promptly. Failure to initiate oxygen therapy can result in serious harm to the patient. The essence of oxygen therapy is to provide oxygen according to target saturation rate, and to monitor the saturation rate to keep it within target range.
What is oxygen therapy for hypoxia?
1. Complete respiratory assessment for hypoxia. SaO 2 should be greater than 92% unless otherwise stated by the physician. The goal is to use the least amount of oxygen to maintain levels between 92% and 98%. Assess need for O 2: check SaO 2 level with a pulse oximetry device.
What should the oxygen level be in a patient with hypoxia?
Hypoxemia is a condition that occurs when there are low levels of oxygen in the blood. The blood is continuously circulating, picking up oxygen from the lungs and delivering it throughout the body to use as fuel.
What is hypoxemia (low oxygen)?
Steps 1 Complete respiratory assessment for hypoxia. 2 If a patient requires oxygen therapy, choose an oxygen delivery system based on your patient’s... 3 Once oxygen is applied, reassess your patient in 5 minutes to determine the effects on the body. 4 If required, adjust O 2 levels. 5 If hypoxia continues, contact respiratory therapist...
What are the steps involved in the treatment of hypoxia?
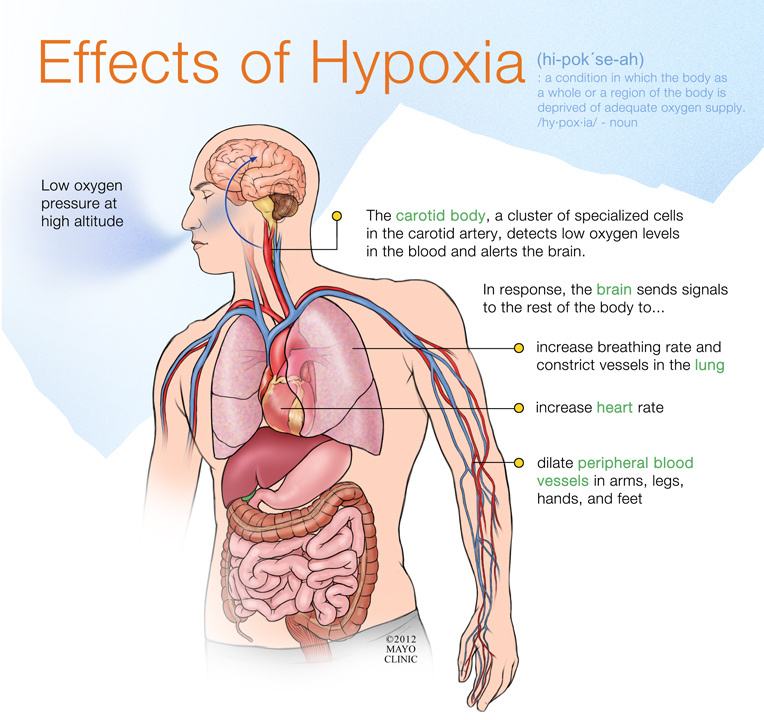
How is mild hypoxia treated?
Since hypoxemia involves low blood oxygen levels, the aim of treatment is to try to raise blood oxygen levels back to normal. Oxygen therapy can be utilized to treat hypoxemia. This may involve using an oxygen mask or a small tube clipped to your nose to receive supplemental oxygen.
What percentage of oxygen saturation is mild hypoxia?
The normal oxygen levels in a pulse oximeter usually range from 95% to 100%. Blood oxygen levels below 90% are considered low (hypoxemia).
What is the flow rate of oxygen therapy?
Arterial blood sample is immediately obtained and oxygen is started via nasal cannula or preferably via a face mask at flow rate of 4-6 L/min to achieve FiO2 of 35 to 40%. Higher flow is unlikely to improve oxygenation. Flow rate is adjusted to maintain a PaO2 of about 80 mmHg or near normal value.
At what rate oxygen should be given?
Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed with a target saturation range. The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients not at risk of type II respiratory failure is 94–98%. The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients at risk of type II respiratory failure is 88–92%.
Is 92 oxygen level OK?
If you're using an oximeter at home and your oxygen saturation level is 92% or lower, call your healthcare provider. If it's at 88% or lower, get to the nearest emergency room as soon as possible.
What is the minimum oxygen level for COVID-19 patients?
Some COVID-19 patients may show no symptoms at all. You should start oxygen therapy on any COVID-19 patient with an oxygen saturation below 90 percent, even if they show no physical signs of a low oxygen level. If the patient has any warning signs of low oxygen levels, start oxygen therapy immediately.
How many liters of oxygen do you need for a mask?
Non-rebreather face mask 10 – 15 Liters Per Minute. Pre-fill the reservoir on the mask prior to placing the mask on the patient.
Is 2 liters of oxygen a lot?
Among those who need oxygen supplement, some may require one to two litres of oxygen per minute. Factoring in wastage in oxygen supply and utilisation capacity of the lungs at the moment, this requirement may translate into three to four litres of medical oxygen per minute.
What is the recommended flow rate of oxygen via nasal cannula?
A traditional nasal cannula can only effectively provide only up to 4 to 6 liters per minute of supplemental oxygen. This equates to a FiO2 of approximately 0.37 to 0.45.
When do you give oxygen spo2?
✓ Oxygen should only be given once the airway has been cleared and at the lowest concentration necessary to achieve an oxygen saturation of 94–98% or 88–92% if the patient is at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure.
What are the guidelines for oxygen therapy?
New Guidelines for Oxygen Therapy TreatmentAcutely ill adult medical patients (with exceptions) should stop oxygen therapy no higher than 96% saturation. ... Patients with acute stroke or MI should not start oxygen therapy between 90% and 92% saturation.More items...
Is 4 Litres of oxygen too much?
Increased Oxygen Needs and Higher Oxygen Flows Rates of 4 liters/minute or greater are considered higher oxygen flow. As more scarring develops in the lungs, they become less efficient in delivering the necessary oxygen the body needs.
What are some ways to treat hypoxia?
For example, if hypoxia is caused by pneumonia, additional treatment for hypoxia may include antibiotics, increased fluid intake, oral suctioning, position changes, and deep breathing and coughing exercises. If a patient has COPD, check physician order for the amount of required oxygen and the expected saturation level.
How to help a patient with oxygen?
Deep breathing and coughing techniques help patients effectively clear their airway while maintaining their oxygen levels. Teach patients “controlled coughing” by having them take a deep breath in and cough deeply with the mouth slightly open. If they have difficulty coughing, teach the huffing technique. This involves taking a medium breath and then making a sound like “ha” to push the air out fast with the mouth slightly open. This is done three or four times, and then they are instructed to cough. If secretions are thick and tenacious, the patient may be dehydrated and require additional fluids (if medical condition does not contraindicate additional fluids).
What is the best level of oxygen to maintain a sao 2?
SaO 2 should be greater than 92% unless otherwise stated by the physician. The goal is to use the least amount of oxygen to maintain levels between 92% and 98%. Assess need for O 2: check SaO 2 level with a pulse oximetry device. Assess for underlying medical conditions or alternate causes of hypoxia (cardiovascular).
Why do people need oxygen?
The most common reasons for initiating oxygen therapy include acute hypoxemia related to pneumonia, shock, asthma, heart failure, pulmonary embolus, myocardial infarction resulting in hypoxemia, post operative states, pneumonthorax, and abnormalities in the quality and quantity of hemoglobin.
Why does oxygen cause skin breakdown?
The nose, chin, and ears may have skin breakdown due to the irritation of the tubing on the skin . Oxygen therapy tends to cause drying effects to the nares and mouth.
Is oxygen therapy short term or long term?
Oxygen therapy may be short- or long-term depending on the SaO 2 requirements of the patients and underlying diseases processes (Perry et al., 2014). Checklist 41 reviews the steps for applying and titrating oxygen therapy (see Figure 5.2).
Can obstructive sleep apnea cause hypoxemia?
Obstructive sleep apnea. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may be unable to maintain a patent airway. In OSA, nasopharyngeal abnormalities that cause narrowing of the upper airway produce repetitive airway obstruction during sleep, with the potential for periods of apnea and hypoxemia.
What is hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a treatment for hypoxic- and inflammatory-driven conditions, in which patients are treated with 100% oxygen at pressures greater than atmospheric pressure.
What is the subtype of hypoxia?
In this state, ischemia is a subtype of hypoxia where additional insults prevent baseline function. Both oxygen and glucose are necessary for aerobic metabolism; thus, hypoxia affects the energy cycle of the cell by creating an oxygen imbalance.
What is hypoxia in biology?
Hypoxia. The term hypoxia is quantitatively related to the organ, tissue, and even cell type. A hypoxic state indicates that an imbalance of oxygen is present and baseline function is compromised as a result of this imbalance. The imbalance of oxygen could result from a lack of oxygen or an excessive demand for oxygen.
What is hypoxic condition?
Hypoxic conditions occur with a persistent lack of oxygen. Individual tissues have differing oxygen tensions and oxygen demands; on average, tissues at rest utilize 5–6 mL of O2per deciliter of blood delivered.2–4Hypoxia could be fairly defined as a scenario when tissue fails to receive this amount of oxygen.
What are the responses of cells to hypoxia?
Cellular responses to hypoxia. As the level of oxygen drops in the blood, the body undergoes responses such as increasing respiration and blood flow. Simultaneously, individual cells experiencing hypoxia begin reacting to the decreased oxygen tension.
How much oxygen can a gram of hemoglobin carry?
One gram of hemoglobin can carry as much as 1.34 mL O2if all four binding sites are occupied on each molecule of hemoglobin.
Is ischemia a component of hypoxia?
While hypoxia is always a component of ischemia, ischemia is not always involved in hypoxia, such as in the case of CO poisoning, during which blood flow is uninterrupted but oxygen delivery is impaired. Thus, oxygen transportation within the body plays a crucial role in the effects of hypoxia. Oxygen transport.
What is hypoxemia treatment?
Treatment. Hypoxemia is typically the result of another condition that affects how your body processes oxygen. It's imperative that your physician creates a plan that treats your underlying condition in addition to treating symptoms of hypoxemia.
How to diagnose hypoxemia?
Hypoxemia is diagnosed by measuring the blood oxygen level via a blood test known as arterial blood gases (ABG) or via pulse oximetry, a noninvasive scanning probe that is usually clipped to a finger or earlobe and uses light to measure the amount of oxygen in your blood. 2
What is hypoxemia in COPD?
Though this can happen for a variety of reasons, hypoxemia appears to be relatively common in people with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD ). 1 It also may result from other conditions, such as asthma, anemia, sleep apnea, and pneumonia.
Why does COPD cause shortness of breath?
Shortness of breath. Increases in your heart rate, as your body tries to compensate for the low oxygen in your bloodstream. People with COPD who suffer from hypoxemia when they're at rest are more likely to have trouble concentrating and remembering, and those problems get worse as their hypoxemia does. 3 .
What happens if you don't have enough oxygen?
Complications. Hypoxemia often leads to hypoxia, a condition in which you don't have enough oxygen getting to your tissues. While many people confuse the two because of their similar names, they are distinct (hypoxemia only involves low oxygen in the blood itself). 2 Hypoxemia may also result in cyanosis.
What is the medical term for a person who doesn't have enough oxygen?
Sanja Jelic, MD, is board-certified in sleep medicine, critical care medicine, pulmonary disease, and internal medicine. Hypoxemia is a condition that occurs when you don't have enough oxygen in your blood. Though this can happen for a variety of reasons, hypoxemia appears to be relatively common in people with advanced chronic obstructive ...
What are the causes of hypoxemia?
Some of the most common causes of hypoxemia include: 2 . Sleep apnea. Asthma.
What is the goal of oxygen delivery?
The goal of oxygen delivery is to maintain targeted SpO 2 levels in children through the provision of supplemental oxygen in a safe and effective way which is tolerated by infants and children to:
How to reduce hypothermia?
Ensure adequate clearance of secretions and limit the adverse events of hypothermia and insensible water loss by use of optimal humidification (dependent on mode of oxygen delivery). Maintain efficient and economical use of oxygen.
What is CO2 narcotics?
CO2 Narcosis - This occurs in patients who have chronic respiratory obstruction or respiratory insufficiency which results in hypercapnea (i .e. raised PaCO 2 ). In these patients the respiratory centre relies on hypoxaemia to maintain adequate ventilation. If these patients are given oxygen this can reduce their respiratory drive, causing respiratory depression and a further rise in PaCO 2.
Can oxygen be delivered through a high flow system?
Oxygen therapy can be delivered using a low flow or high flow system. All high flow systems require humidification. The type of humidification device selected will depend on the oxygen delivery system in use, and the patient's requirements. The humidifier should always be placed at a level below the patient's head.
Does cyanosis require oxygen?
Tachycardia, cyanosis) may not routinely require oxygen therapy in most cases. The threshold for oxygen therapy can vary with the child’s general state and point in the illness. There is no physiological basis for the application of low flow oxygen therapy to a child with normal SpO2 and increased work of breathing.
Can oxygen be used in neonatal intensive care?
At the RCH, oxygen therapy via an isolette is usually only for use in the Butterfly neonatal intensive care unit. (See Isolette use in paediatric wards, RCH internal link only.)
Is Airvo 2 safe to use?
On device start up, a green traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 is safe for use on a new patient. An orange traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 has not been cleaned and disinfected since last use, and is not safe for use on a new patient. Follow the instructions in the disinfection kit manual :
How to increase oxygen levels in the lungs?
In addition to supplemental oxygen, making these lifestyle changes will help increase oxygen levels. Exercise regularly to help the respiratory system improve its functionality by increasing the lungs’ capacity. This will allow more oxygen into the lungs, and increase the blood oxygen level, even while asleep.
What is the most accurate way to measure blood oxygen levels?
Bluish tint to lips, earlobes, or nails. Death. The most accurate way to measure blood oxygen levels is to have an arterial blood gas test, or ABG. However, a physician must perform this test, and it is uncomfortable for patients.
What causes a person to breathe slowly?
Hypoxemia can also occur as a result of health conditions that cause hypoventilation, or breathing at a slow rate, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and bronchitis. Other health conditions that decrease the amount of oxygen in the body while sleeping consist of sleep apnea, various lung diseases, heart disease, ...
What causes hypoxemia in the sleep cycle?
Several conditions can cause sleep-related hypoxemia, including environmental factors, health conditions, and even pain medications. Environmental factors that can trigger this sleep-related breathing disorder include, not having enough available oxygen in the air, for example, places with high altitudes, flying on a plane, or smoke inhalation.
How to measure oxygen saturation?
The alternative, most common way to measure oxygen saturation is with the use of a pulse oximeter. A pulse oximeter is a device that is clipped onto a finger and connected to a small device that records the percentage of oxygen saturation at certain intervals.
How do you know if you have hypoxemia?
Symptoms of sleep-related hypoxemia range from mild to severe depending on how low oxygen levels drop. Mild symptoms of hypoxemia include: Rapid heart rate. Fast breathing. Restlessness, snoring. Daytime drowsiness. Shortness of breath. If left untreated, symptoms can become severe and can lead to: Confusion .
Can you take oxygen while sleeping?
If an individual has been diagnosed with sleep-related hypoxemia, their physician may recommend supplemental oxygen use while sleeping. This is the most effective way to increase blood oxygen levels and treat conditions that cause hypoxemia, like lung disease, COPD, and sleep apnea. If nighttime use of oxygen does not improve the condition, ...
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-466865156-56b7615b3df78c0b13600698.jpg)