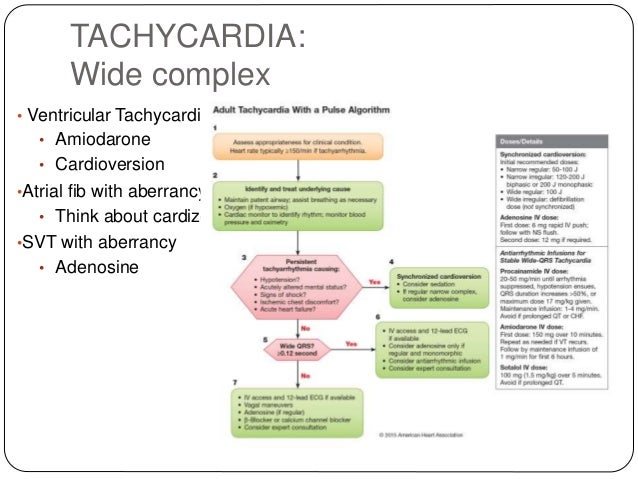
What medication is used for wide complex tachycardia?
SVT will typically be managed with adenosine, Afib with WPWS will be treated with amiodarone, and Afib with aberrancy with either diltiazem or a beta-blocker. Typically, amiodarone will be the first-line drug of choice for all ventricular arrhythmias (VT, polymorphic VT, Vfib, etc.)Jul 1, 2021
What medication should not be given when treating wide complex tachycardia?
It is so very critical to choose the right kind of medication once the decision is made to treat a patient with wide complex tachycardia. Calcium channel blockers (Diltiazem and verapamil) are strongly advised not to be used for fear of hemodynamic collapse, hypotension and cardiac arrest [4].
Is wide complex tachycardia fatal?
Despite hemodynamic stability in some patients with ventricular tachycardia, incorrect or untimely diagnosis can be dangerous, if not fatal.
What is considered a wide complex tachycardia?
A wide complex tachycardia (WCT) is simple enough to define: a cardiac rhythm with a rate >100 beats per minute and a QRS width >120 milliseconds (ms).
What causes wide-complex tachycardia?
A broad QRS complex is either caused by the ventricular conducting system not working (bundle branch block) or the electrical circuit not involving the atrioventricular (AV) node correctly. Broad complex tachycardias may be ventricular or supraventricular in origin.Oct 14, 2021
What is the initial drug of choice for SVT treatment?
Adenosine (Adenocard) Adenosine is the first-line medical treatment for the termination of paroxysmal SVT.Apr 5, 2017
Is wide QRS an emergency?
Wide QRS complex tachycardias (WCT) present significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges to the emergency physician. WCT may represent a supraventricular tachycardia with aberrant ventricular conduction; alternatively, such a rhythm presentation may be caused by ventricular tachycardia.
How serious is sinus rhythm with wide QRS?
The prognostic value of a wide QRS >120 ms among patients in sinus rhythm is well established. Aside from young patients with no underlying heart disease,7–10 a prolonged QRS clearly predicts increased morbidity and mortality for older patients and those with cardiovascular disease.Dec 23, 2013
What does a wide QRS on EKG mean?
A “wide QRS complex” refers to a QRS complex duration ≥120 ms. Widening of the QRS complex is related to slower spread of ventricular depolarization, either due to disease of the His-Purkinje network and/or reliance on slower, muscle-to-muscle spread of depolarization.
Is V fib a wide complex tachycardia?
Primary Vfib (not associated with an MI) needs evaluation by an electrophysiologist. Vtach accounts for 80% of wide complex tachycardias, while 15-30% of wide complex tachycardias may be the result of SVT with abnormal interventricular conduction.
Does adenosine block VT?
Very helpful diagnostically to distinguish VT from SVT. Adenosine will result in a transient AV block, which may terminate some re-entrant SVTs, or block conduction to the ventricles to reveal atrial activity (such as atrial tachycardia). Adenosine generally has no effect on VT.
Can IC cause aberration of SVT?
Medications: Class IA and IC can cause aberration of SVT (by their property of use dependency) QTc prolonging agents can predispose to polymorphic VT. Digoxin most commonly causes VT (monomorphic or bidirectional) Symptoms and hemodynamic status are not helpful in establishing the diagnosis in WCT. Physical Exam:
Is a WCT considered a VT?
Since a large majority of WCTs are VT (80%), especially in patients with ischemic or structural heart disease, and VT therapies are effective for both VT and SVT, it is more than reasonable to treat all WCT as VT if the diagnosis is uncertain.
Is midazolam good for blood pressure?
Generally midazolam (+/- fentanyl) is preferred in this case due to minimal effects on blood pressure. Ketamine is also an option, but is less frequently used due to emergence reactions. ***IMPORTANT NOTE: Electrical cardioversion should never be performed on a conscious patient.
Is VT a cause of WCT?
When facing a WCT, it is important to remember that VT is the cause in 80% of the cases. If the patient has ischemic heart disease, then VT is the cause in 90% of the cases. General Approach: Misdiagnosing SVT as VT would lead to treating with cardioversion and amiodarone. This is aggressive treatment for SVT, but it’s not harmful.
What is the best antiarrhythmic?
Which of the following is the best course of action? 1 A. Amiodarone would be the best long-term antiarrhythmic to suppress further arrhythmias such as this. 2 B. For immediate treatment, intravenous (IV) esmolol is a reasonable option. 3 C. For immediate treatment, a 0.5 mg IV dose of digoxin is a reasonable option. 4 D. Immediate cardioversion is necessary. 5 E. For immediate treatment, IV procainamide should be given.
What is the treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
This is a classic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome ECG. The treatment of choice is IV procainamide, probably the only time you'll reach for this agent. Amiodarone would not be the agent to use long term given its side effects.
What is wide complex tachycardia?
A wide-complex tachycardia can arise from a ventricular or a supraventricular origin with a regular or irregular QRS complex (table 1). Brugada criteria and the Vereckei algorithm or the simplified avR algorithm [3] are helpful in correctly identifying ventricular tachycardia. Nonetheless, 10% of cases remain misdiagnosed.
What are the first steps in tachycardia?
The first steps are maintenance of the patient’s airway with assisted breathing if necessary, cardiac monitoring to identify the heart rhythm, monitoring of blood pressure and oximetry, and establishing intravenous access [4, 5].
Is tachycardia polymorphic or polymorphic?
The morphology of the tachycardia also give hints concerning the origin. If a wide-complex tachycardia is monomorphic , its origin can be ventricular tachycardia in a structurally abnormal heart, most commonly scar re-entry in coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathies such as hypertrophic or dilated cardiomyopathy, or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (table 2). In polymorphic wide-complex tachycardia, the QT interval has to be analysed firstly. If it is normal ( cave: the Bazzet formula is not valid for correcting the QT interval during tachycardia), ischaemia or electrolyte imbalance should be considered. Torsade des pointes tachycardia results from QT interval prolongation and originates from inherited long QT syndrome, drugs, intoxication or electrolyte imbalance, to name the most common causes.
Can tachycardia be detected in the ED?
Patients with wide-complex tachycardia can present at the emergency department (ED) haemodynamically stable or unstable. ECG algorithms, as well as knowledge about pre-existing cardiac diseases, can help to identify ventricular tachycardia.
Is tachycardia considered ventricular tachycardia?
In the emergency setting, a wide-complex tachycardia always should be considered as ventricular tachycardia unlike proven otherwise, as treatment has to be initiated immediately to avoid degeneration into ventricular fibrillation.
Is tachycardia a wide complex condition?
Regular wide-complex tachycardia can be either ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. Ventricular tachycardia originates from the left ventricle, the left ventricular outflow tract, the right ventricle or the right ventricular outflow tract.
What causes WCT?
Three main possible causes of WCT should be considered: VT. SVT with aberrancy (i.e. reentry tachycardia with a Bundle Branch Block) Antidromic AVRT (requires an accessory pathway) There are multiple criteria to differentiate VT from SVT with aberrancy.
Is VT tolerated by a patient with a cardiac history?
One important reason this should be our train of thought is that VT is less likely to be tolerated by a patient with a cardiac history or structural heart disease compared to a younger individual without these mitigating factors.
Is adenosine good for tachycardia?
Adenosine can be used initially for stable regular wide complex tachycardia. This is because a WCT caused by SVT with aberrancy (and right ventricular outflow tract ventricular tachycardia) are responsive to adenosine. Synchronized Cardioversion is the preferred treatment for unstable WCT.
Which pathway is most common in reentry tachycardia?
Mechanism 2: Reentry ( most common) – Reentry tachycardia can occur from the spontaneous discharge of a terminal Purkinje cell if its subsequent propagation encounters a branch in its pathway: Branch I – Normally conducted (Antegrade) pathway. Branch II – Refractory pathway (Antegrade signal is blocked)
What is the most important recognition of V tach?
What is most important is the recognition of V Tach and differentiating it from wide complex SVT. It is clearly true that V Tach is a more life threatening rhythm and that the treatment mode is very different from SVT.
What is a spontaneous focus of irritably of the atrium?
Spontaneous focus of irritably of Atrium (supraventricular) that discharges at a rapid rate. (Please note that although Atrial Fibrillation on page 28 is supraventricular in origin, the term SVT is typically reserved for regular rhythms (either atrial, with p-wave often hidden, or junctional).
ECG Challenge
A 66-year-old woman with a history of hypertension and persistent atrial fibrillation was referred to the Arrhythmia Clinic. Before her visit, a routine 12-lead ECG was ordered ( Figure 1 ). The patient was asymptomatic except for minor palpitations.
Response to ECG Challenge
The ECG shows a very wide QRS complex tachycardia (QRS duration 280 ms) with variation in morphology. Following a pause of 700 ms, there are repeating sequences of 6 to 7 beats with cycle lengths of 400 to 415 ms.
Footnotes
Correspondence to: G. Neal Kay, MD, Division of Cardiovascular Disease, Department of Medicine, 921 Faculty Office Tower, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL 35294. E-mail [email protected]