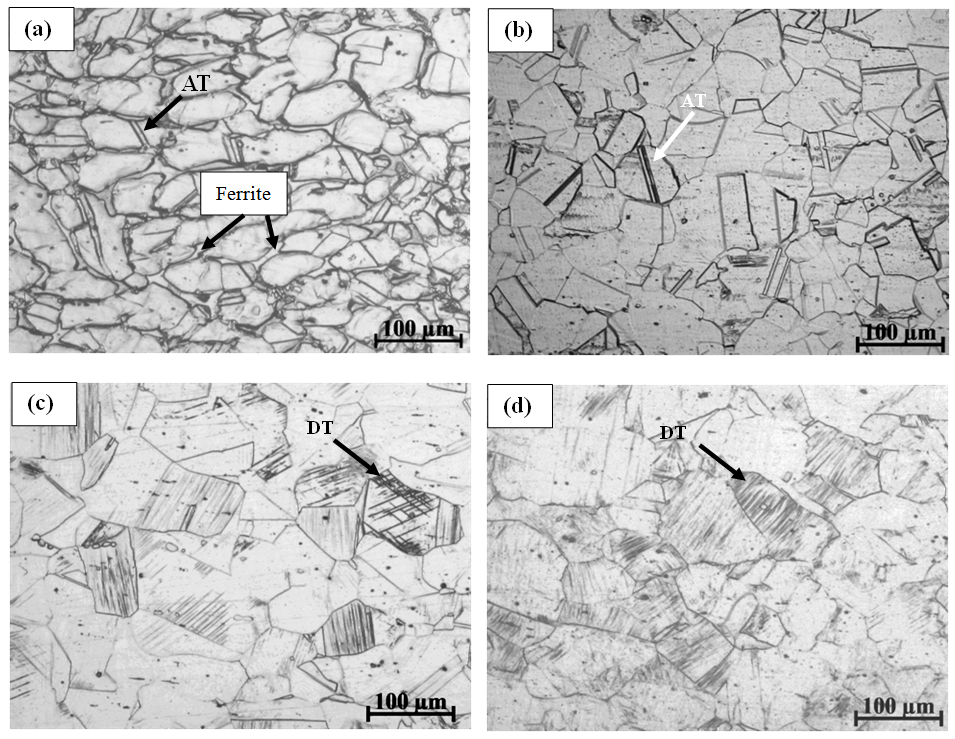
In the low carbon MnB steel, the air-cooled microstructure is ferrite and granule bainite. With the increasing of carbon content, ferrite was replaced by bainite, and martensite comes into being. By this reckoning, one would expect medium carbon MnB cast steel to form bainite/martensite to obtain high wear-resistance.
Full Answer
What is the effect of heat treatment on corrosion?
4. The optimal heat treatment process for laser solid forming of 34CrNiMo6 steel was as follows: 830 °C quenching and holding for 1 h followed by oil cooling +540 °C tempering and holding for 2 h after air cooling. The tensile strength and yield strength of LSFed sample was greatly improved after the optimized heat treatment process.
Do post weld heat treatment temperatures affect corrosion performance of weld overlay?
Based on the initial X6CrNiMoVNb11-2 steel of the casting-rolling disk, achieved by pre-heat treatment and the hot-rolling process, the identification of microstructure evolution and mechanical properties is urgently needed to reveal the reinforcement mechanism of phase transformation after the heat-treatment process (quenching at 1040 °C and tempering at …
Why are the mechanical properties of different types of steel different?
Experimental results have shown that the microstructure of these steels can be changed and significantly improved by varying the cooling rate. Thus, heat treatment (heating and cooling) is used to obtain desired properties of steels such as improving the toughness, ductility or removing the residual stresses, etc.
Does heat treatment affect the corrosion resistance of Inconel 625?
Effect of Heat Treatment Temperatures on Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Inconel 625 Weld Overlay Deposited by ... The AISI 4130 steel plate having dimensions of 150×150×25mm was used as substrate. It was ... After heat treating, the samples were cooled in air to room temperature. Table 3.

Does heat treatment change the microstructure?
Heat treatment is the process of heating and cooling metals to change their microstructure and to bring out the physical and mechanical characteristics that make metals more desirable. The temperatures metals are heated to, and the rate of cooling after heat treatment can significantly change metal's properties.Oct 7, 2019
What effect does heat treatment have on steel microstructure?
This is due to the formation of huge amounts of martensite, from austenite, as observed in the microstructure. Tempering after heat treatment of EN 8 steel always leads to a reduction in hardness. The reduction in surface hardness is the most in normalizing (almost 48%), while it is the least in annealing (17%).
What happens when steel is heated then cooled?
The metal is heated to a predefined temperature then cooled by air. The resulting metal is free of undesirable impurities and exhibits greater strength and hardness. Normalising is often used to produce a harder and stronger steel, albeit one that is less ductile than that produced by annealing.Sep 9, 2015
What will happen to the steel when cooled?
In principle, when steel cools quickly, there is less time for carbon atoms to move through the lattices and form larger carbides.
What happens to steel when heat treated?
Heat Treating of steel and other metals can lead to: Improved wear resistance. Increased resistance to deformation and warpage and. Increased strength or toughness.Oct 29, 2019
What happens to microstructure during tempering?
During tempering, the particles coarsen and become large enough to crack, thus providing crack nuclei which may then propagate into the matrix. As a consequence, untempered low--carbon martensitic steels sometimes have a better toughness than when they are tempered, even though the untempered steel is stronger.
What happens to the molecules of metal when the metal is heated and then cooled down slowly?
It is a physical change because metal expands on heating and also contracts on cooling, so it is a reversible change and can be considered as physical change.Jun 3, 2019
When a heated metal is cooled it expands?
When it is cold the kinetic energy decreases, so the atoms take up less space and the material contracts. Some metals expand more than others due to differences in the forces between the atoms / molecules.
How does the rate of cooling affect the hardness of steel?
The higher the cooling rate of the quenching, the smaller the size of the grain size. Hence, it will increase the hardness of the steel. When the cooling rate is very high, it will increase the strength of the steel but it will reduce the toughness and the ductility of the steel.
What temperature was stainless steel annealed?
The Duplex stainless steel (DSS) was solution annealed at 1100 °C and subsequently furnace or air cooled, and oil or water quenched. After characterization using the optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled with Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and the microhardness testing the following conclusions were drawn:
What is the OM 3D microstructure?
2 a, 2b, 2c, and 2d respectively. The OM 3D microstructures revealed the dominant presence of both, the austenitic and the ferritic phases but with considerable changes in the morphology as compared to the morphology of the as-received sample. It is noticed that the austenitic phases in all three directions (rolling, longitudinal and transverse) looked similar in all the samples collected after the furnace, water, and oil cooling methods. The continuous lamellae austenite observed in the as-received sample in the rolling and the longitudinal direction and the elongated in the transverse direction are appearing in the heat-treated sample in the form clustered-like dispersed in the all DSS matrix. An exception was noticed in the case of the air cooling method where instead of forming a pronounced clustered structures of austenite, these were relatively continuous, but characterized with the apparition of a metastable phase noticed by intermediate color between the grey whitish and the grey darkish which is assimilated to the secondary austenite dispersed in the ferrite. However, looking at the OM microstructures generated after air cooling and furnace cooling, it can be noticed the presence of precipitates at the flexural austenite-ferrite grain boundaries as small black dots. These precipitates appear in the form of σ-phase, χ-phase, and secondary austenite as shown by the arrows in the micrograph. The formation of intermetallic observed in the case of the furnace cooling and air cooling may be attributed to the relatively low and fast cooling rate respectively.
What is DSS stainless steel?
The Duplex stainless steel (DSS) is required to maintain its exceptional mechanical and corrosion resistance properties during its utilization. It is a dual micro-structured material consisting of δ-ferrite and γ-austenite in almost equal proportion as established by the international quality standards. It owes its exceptional properties ...