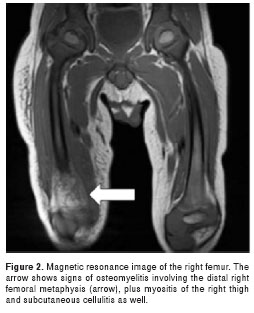
Current standard therapies for toxoplasmic encephalitis often cause severe adverse events. A 57-year-old HIV-positive man in Japan who had toxoplasmic encephalitis but was intolerant to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, pyrimethamine, sulfadia-zine, and atovaquone was successfully treated with the combi-nation of clindamycin and azithromycin. This drug combination can be an alternative treatment for this condition.
What are some good alternatives to clindamycin?
Clindamycin Amoxicillin Doxycycline Clindamycin is an antibiotic that is usually reserved for treating anaerobic infections or other serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria in penicillin-allergic people. The risk of C... more Amoxicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic that may be used to treat infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Is clindamycin stronger than amoxicillin?
· Clindamycin is approved for use in dogs and cats suffering from bacterial infections caused by events like bite wounds, toxoplasmosis, pyoderma, abscesses, and bone and dental infections. It’s not indicated in cats and dogs with allergies to clindamycin and should be used with caution in pets with liver and kidney damage.
What are the adverse effects of clindamycin?
· Clindamycin topical Alternatives Compared Clindamycin topical Doxycycline Spironolactone Prescribed for Perioral Dermatitis, Bacterial Vaginosis, Acne. clindamycin topical may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide. Doxycycline is an effective antibiotic that treats a wide range of infections.
How long does clindamycin stay good for?
In conclusion, clindamycin is an alternative for treatment of several head and neck infections, including dental infections, recurrent pharyngitis and chronic sinusitis. The indications for its use in these conditions remains largely undefined, although level 1 evidence exists for its efficacy in preventing recurrence and tonsillectomy in patients with recurrent group A streptococcal …

What conditions does clindamycin treat?
What Conditions does CLINDAMYCIN HCL Treat?serious symptoms of malaria.pneumonia caused by the bacteria anthrax.bacterial stomach or intestine infection due to anthrax.acne.treatment to prevent anthrax after exposure to disease.blood poisoning caused by anaerobic bacteria.More items...
What is clindamycin most commonly used for?
Clindamycin is used to treat certain types of bacterial infections, including infections of the lungs, skin, blood, female reproductive organs, and internal organs.
Does clindamycin treat bronchitis or pneumonia?
Clindamycin has an antimicrobial spectrum which makes this antibiotic a possible alternative in community-acquired pneumonia, and its efficacy in pneumococcal pneumonia has been documented.
Does clindamycin treat sepsis?
Clindamycin treats many categories of bacterial infection, including: Severe respiratory infections. Severe skin and soft tissue infections. Bloodstream infection (sepsis)
Does clindamycin treat chlamydia?
Clindamycin may be helpful in treating Chlamydia infections, but there are more popular antibiotics for this condition. The mainstay of therapy for chlamydia includes appropriate antibiotic treatment such as tetracyclines, azithromycin or erythromycin.
Can clindamycin treat yeast infection?
Clindamycin is used to treat certain vaginal infections. It belongs to the class of medicines known as macrolide antibiotics. It works by killing bacteria or preventing their growth. This medicine will not work for vaginal fungus or yeast infections.
Can clindamycin be used for Covid 19?
Firstly, common orthopaedic antibiotics including penicillin and clindamycin can continue to be used for soft tissue and bony infections in COVID-19 patients.
Can I take clindamycin for a upper respiratory infection?
A doctor may prescribe clindamycin in the form of oral capsules or dissolvable granules for: respiratory infections with streptococci, pneumococci, and staphylococci bacteria.
Can clindamycin cure bronchitis?
It is concluded that clindamycin fails to eradicate Haemophilus influenzae from the sputum of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, irrespective of in vitro sensitivity.
Is clindamycin safe for heart patients?
Serious heart problems could develop later if your infection is not cleared up completely. Also, if you stop taking this medicine too soon, your symptoms may return. This medicine works best when there is a constant amount in the blood. To help keep the amount constant, do not miss any doses.
What is the best antibiotic for sepsis?
The majority of broad-spectrum agents administered for sepsis have activity against Gram-positive organisms such as methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, or MSSA, and Streptococcal species. This includes the antibiotics piperacillin/tazobactam, ceftriaxone, cefepime, meropenem, and imipenem/cilastatin.
Is clindamycin a powerful antibiotic?
Yes, Clindamycin is a strong broad-based antibiotic doctors prescribe to treat severe infections, including the fatal MRSA infection. It has a positive effect on various bacterial infections, including those which survive without air.
What to take if you can't take penicillin?
These options include glycopeptides, such as vancomycin.
What are the different types of penicillins?
For Penicillin Allergy. Penicillins include amoxicillin, nafcillin, ticarcillin, and penicillin G and penicillin V. Some people with penicillin allergies are also allergic to a class of drugs called cephalosporins, which include cephalexin (Keflex).
What is the best medicine for strep throat?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), penicillin or amoxicillin are generally the first medications prescribed for strep throat. Experts consider them a good way to reduce symptoms and reduce the amount of time a person is sick.
What is the best antibiotic for tonsillitis?
The antibiotic erythromycin is an effective drug for chronic tonsillitis as well as for after a tonsillectomy in order to treat post-operative infections.
What is the best acne treatment without a prescription?
Benzoyl peroxide is considered the most effective acne-fighting medication available without a prescription. Both medications are desirable alternatives for people with acne who cannot or do not need to take antibiotics for any other reason. There are other antibiotics and other medications available for acne.
Is salicylic acid good for acne?
For Acne. Both salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide are effective medications that can treat acne. Better yet, both are available in over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription products. Salicylic acid may reduce acne by helping to shed the outer, older layer of dead skin cells.
Is clindamycin good for ear infections?
Clindamycin is effective for ear infections. But penicillins, including Augmentin (amoxicillin / clavulanic acid) and amoxicillin, may be more appropriate, depending on the type of bacteria causing the infection. NOTE: Antibiotics are prescribed on a case by case basis and different antibiotics cover different bacteria.
What is the half life of a drug?
The half-life of a drug is the time taken for the plasma concentration of a drug to reduce to half its original value.
Is doxycycline a topical antibiotic?
Remove Doxycycline from your drug comparison. Spironolactone. Remove Spironolactone from your drug comparison. Prescribed for Bacterial Vaginitis, Perioral Dermatitis, Acne. clindamycin topical may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide. Doxycycline is an effective antibiotic that treats a wide range of infections.
Is doxycycline safe for children?
Doxycycline is an effective antibiotic that treats a wide range of infections. However, it is not usually recommended for children aged less than eight nor in pregnant women in the last half of... View. more.
When was clindamycin invented?
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic, developed in 1966 by chemically modifying the naturally occurring lincomycin. In vitro, its spectrum of activity includes staphylococci, streptococci and pneumococci, most anaerobic bacteria (including over 90% of Bacteroides fragilis), Chlamydia trachomatisand certain protozoa.
What is the best antibiotic for acne vulgaris?
Levine et al (7), in the evidence-based publication Drugs of Choice, recommended topical clindamycin for moderate to severe acne vulgaris, and oral clindamycin as an alternative to the penicillins and cephalosporins for cellulitis and furunculosis in patients with drug allergies. (These constitute level 3 evidence.)
Is clindamycin a penicillin?
Clindamycin is an alternative to penicillin for treatment of dental abscesses (7). Indications include allergy, failure of penicillin treatment or immune-compromised status. Clindamycin is an alternative to amoxicillin, cephalexin, azithromycin or clarithromycin for the prophylaxis of bacterial endocarditis in patients undergoing dental procedures. For recurrent tonsillitis, clindamycin may be indicated (1), although reviewers remain concerned about its potential for inducing C difficile-associated diarrhea and for inducing erythromycin or clindamycin-resistant pneumococci.
Is clindamycin a quinolone?
In conclusion, clindamycin is an alternative to penicillin and cephalosporin derivatives for the treatment of osteomyelitis and septic arthritis (level 3 evidence, case series), and may be the drug of choice in combination with a quinolone for diabetic osteomyelitis (level 3 evidence, expert opinion).
Is clindamycin effective for osteomyelitis?
No comparative studies for clindamycin versus alternative regimens were found. Clindamycin was effective for septic arthritis or osteomyelitis in an open study of 48 children, who were treated with a regimen of intravenous administration until afebrile for three days, followed by oral medication for one week (cellulitis) or up to six months (chronic osteomyelitis) (15).
Which antibiotic is used for osteomyelitis?
Falagas and Gorbach (3) recommended clindamycin for the treatment of osteomyelitis due to S aureusand anaerobes, particularly if associated with diabetes or decubitus ulcers. Steigbigel (1) recognized that clindamycin is effective for many of the organisms that cause osteomyelitis, and achieves drug concentrates in bone, but states that there is “no established advantage for osteomyelitis”.
Can you use penicillin and clindamycin together?
In conclusion, clindamycin and penicillin should be used together for severe streptococcal and possibly clostridial soft tissue infections ( level 3 evidence, expert opinion). Given the rarity of these infections and their severe sequelae, combined therapy is the treatment of choice.
What is clindamycin used for?
People use clindamycin to treat bacterial infections. Clindamycin is an antibiotic drug. People use antibiotics to treat bacterial infections. Antibiotics, including clindamycin, do not work for infections caused by viruses. Clindamycin is in the lincosamide family.
Why do doctors prescribe clindamycin?
They prescribe it when they cannot use penicillin and when they have determined the type of bacteria involved in the infection.
What happens if you take clindamycin and you get a CDAD?
If a person develops CDAD while taking clindamycin, the doctor will immediately stop their treatment with the antibiotic.
Can colitis be treated with clindamycin?
People with a history of colitis should not use clindamycin creams or suppositories.
Can pregnant women use clindamycin?
Pregnant people should not use clindamycin vaginal suppositories. Researchers have yet to confirm the safety of suppositories during pregnancy.
Does clindamycin dissolve in water?
For people who have difficulty swallowing, clindamycin comes in granules that dissolve in water.
Can clindamycin cause esophageal irritation?
Clindamycin capsules may irritate the esophagus, which is the tube that runs from the mouth to the stomach. To prevent this irritation, people may wish to take clindamycin capsules with a full glass of water.
What is the treatment for toxoplasmic encephalitis?
A 57-year-old HIV-positive man in Japan who had toxoplasmic encephalitis but was intolerant to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and atovaquone was successfully treated with the combination of clindamycin and azithromycin.
Is trimethoprim a sulfamethoxazole?
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (10 mg/kg/d trimethoprim) was first initiated because of limited availability of pyrimethamine plus sulfadiazine at the time, but acute liver toxicity developed on treatment day 6 (increases in levels of aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase from 24/20 IU/L to 127/145 IU/L [ (reference 10–42 IU/L]). Pyrimethamine plus sulfadiazine was started on treatment day 7. However, on day 9, acute renal failure developed because of obstructive urolithiasis caused by sulfadiazine crystals. After the patient was switched to pyrimethamine plus clindamycin, his renal function persistently worsened, and a drug-induced lymphocyte stimulation test suggested that pyrimethamine was responsible for the acute renal failure. A switch to atovaquone on treatment day 12 resulted in thrombocytopenia by day 17.
Is clindamycin effective against TE?
Clindamycin has in vitro activity against Toxoplasma gondii, inhibitory effects in vivo at lower concentrations ( 6 ), and the ability to penetrate into CSF ( 7 ), suggesting that it is a promising alternative agent for TE treatment. More important, clindamycin causes far fewer adverse events than sulfadiazine ( 2, 4 ). Although the potency of clindamycin monotherapy has not been assessed, some case reports suggested its effectiveness ( 8 ). Therefore, a clindamycin-containing combination with potent agents other than pyrimethamine may be a reasonable treatment option for TE treatment.
Is clindamycin safe for macrolides?
Our results suggest that the combination of clindamycin and macrolides could be a safer and potent alternative therapy for patients who are intolerant of current standard regimens.
What is clindamycin used for?
Clindamycin is an antibiotic that is usually prescribed to treat anaerobic infections mainly caused by gram positive bacteria in penicillin-allergic people . The risk of diff. Continue Reading. First off all, I want you to know that the following descriptions are for information purpose only.
How long does clindamycin last?
Clindamycin half-life is up to 4 hours. Amoxicillin and Clindamycin are Category B antibiotics, meaning that they should be avoided during pregnancy. Again, before to take any drugs (antibiotics especially) talk to your doctor or dentist !!! Learn to make nutritional assessments and dietary analyses.
What is the best antibiotic for diarrhea?
CLINDAMYCIN. Clindamycin is an antibiotic that is usually prescribed to treat anaerobic infections mainly caused by gram positive bacteria in penicillin-allergic people. The risk of difficile colitis often associated with diarrhea may be higher with clindamycin compared with Amoxicillin. Prescription only.
What is the best antibiotic for tooth infection?
They know you and your health status so they know what works best for you. AMOXICILLIN. Amoxicillin belongs to penicillin family of antibiotics.
What is the best treatment for acne?
Topical erythromycin is used to control acne by applying it on the skin.
Is C diff in the wild?
It’s a miserable, and potentially lethal diarrhea, especially in debilitated patients, which I was. AND, C. Diff is now in the wild.
Does clindamycin cause diarrhea?
The risk of difficile colitis often associated with diarrhea may be higher with clindamycin compared with Amoxicillin.
What is clindamycin used for?
Clindamycin is a medication used for the treatment of numerous infections, including but not limited to septicemia, intra-abdominal infections, lower respiratory infections, gynecological infections, bone and joint infections, and skin and skin structure infections. Clindamycin is also used in the treatment ...
How to administer clindamycin?
When administered intramuscularly, the sites must require rotation with no dose exceeding 600 mg in a single injection. Clindamycin is administered by intravenous (IV) intermittent infusion over at least 10 to 60 minutes at a maximum rate of 30 mg/minutes. The final concentration of the IV solution should not exceed 18 mg/mL. Pediatric dosing for neonates is 15 to 20 mg/kg per day, given IM/IV divided over 6 to 8 hours. Infants, children, and adolescents are treated with 8 to 40 mg/kg per day orally divided over 3 to 4 doses. For IM/IV administration, 20 to 40 mg/kg per day can be given over 3 to 4 doses. [8]
What are the side effects of clindamycin?
The most common side effects experienced with topical use include pruritis, xeroderma, erythema, burning, exfoliation, or oily skin. The most common side effects of intravaginal administration are vaginal candidiasis, pruritis, vulvovaginal disease, and vulvovaginitis. The primary adverse effects of clindamycin with systemic administration are pseudomembranous colitis, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, resulting from clindamycin destroying much of the GI tract’s healthy flora. Clostridium difficileis allowed to overgrow in this environment. Toxins A and B, which are produced by C. difficile, cause Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD). If suspected, a stool antigen test should is in order. Severe cases that result from hypertoxic-producing strains occur in an increase in morbidity and mortality, which may require colectomy for definitive treatment. Other adverse effects include thrombophlebitis or metallic taste with IV administration, azotemia, agranulocytosis, anaphylactic shock, abscess formation, induration, or irritation at the site of IM injection. [9][10][11][12]
How is clindamycin administered?
Administration. Clindamycin can be administered into the body by multiple routes. It is available topically as a foam, gel, lotion, or solution for the treatment of acne vulgaris. A thin film needs to be applied twice a day.
How long does clindamycin stay in your system?
When given intramuscularly (IM), the drug achieves peak concentrations in 1 to 3 hours. The half-life of clindamycin is approximately 3 hours in adults and approximately 2.5 hours in children. At this point, it is excreted in the urine (major) and feces (minor) as active and inactive metabolites.
How long does it take for clindamycin to metabolize?
When administered orally, the antibiotic peaks within 60 minutes.
Can clindamycin penetrate the meninges?
Clindamycin cannot efficiently penetrate meninges very well and is therefore not an antibiotic of choice for infections of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). As it travels through the bloodstream, clindamycin is primarily bound to protein.