
What is secondary wastewater treatment?
Apr 08, 2022 · Secondary treatment of wastewater is a process that follows the primary treatment of sewage. Secondary treatment aims to remove the remaining organic matter and suspended solids from the wastewater. The secondary sewage treatment is not as efficient in removing the contaminants as the primary treatment of sewage. If the secondary treatment is …
What are the available options in the biological treatment processes of sewage?
Oct 16, 2009 · The secondary treatment is designed to remove soluble organics from the wastewater. Secondary treatment consists of a biological process and secondary settling is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage such as are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent.
What is the role of organic solids in biological wastewater treatment?
In secondary treatment of sewage, which removes organic matter? A) chlorine B) ozone C) aluminum sulfate and lime D) aerobic bacteria
What is the purpose of sewage treatment?
In secondary treatment, biological treatment is done on the wastewater to remove the organic matter present. This treatment is performed by indigenous and aquatic micro-organisms like bacteria and protozoa which consume biodegradable soluble contaminants like sugar, fat, detergent, and food waste.
How is organic matter removed from wastewater?
Oily wastewater treatment is achieved by various methods which include flotation, chemical treatment, gravity and centrifugal separations, membrane processes, filtration, evaporation, biological treatment, activated carbon adsorption and integrated or hybrid processes.
Which process is involved in the secondary treatment of sewage water?
(i) Physical removal of large and small particles through filtration and sedimentation is called primary sewage treatment. (ii) Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
How does secondary sewage treatment work?
Secondary wastewater treatment processes use microorganisms to biologically remove contaminants from wastewater. Secondary biological processes can be aerobic or anaerobic, each process utilizing a different type of bacterial community.
Which phase of sewage treatment removes organic matter by biodegradation?
secondary treatmentIn most cases, secondary treatment follows primary treatment and involves the removal of biodegradable dissolved and colloidal organic matter using aerobic biological treatment processes.
What is removed in secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment removes the soluble organic matter that escapes primary treatment. It also removes more of the suspended solids. Removal is usually accomplished by biological processes in which microbes consume the organic impurities as food, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and energy…
Which is part of the secondary sewage treatment?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What is a secondary treatment system?
Secondary treatment systems(STS) are wastewater treatment systems which produce treated effluent of secondary standard, i.e. 20 mg/L of Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD), 30 mg/L of Total suspended solids (TSS) and 10 cfu/100 mL of Escherichia (E) coli.Dec 7, 2021
Why secondary treatment is known as biological treatment?
Secondary treatment removes the dissolved organic matter by the use of biological agents and hence, known as biological treatment. This is achieved by microbes which can consume and degrade the organic matter converting it to carbon dioxide, water, and energy for their own growth and reproduction.
What is the process of secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is a step in wastewater treatment that involves the use of biological processes in order to capture all the dissolved organic materials that were not caught during the initial treatment. Microbes take these organic substances as food, transforming them to water, energy and carbon dioxide.Oct 29, 2017
What is primary and secondary treatment for sewage?
The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended.Jun 26, 2018
Why is BOD reduced in secondary sewage treatment?
During the secondary treatment of primary effluents, the BOD level decreases because useful microbes consume a major part of the organic matter. Reduction in the organic matter leads to lowering of BOD.
What is primary and secondary wastewater treatment?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.Nov 19, 2020
What is secondary wastewater treatment?
Secondary Wastewater treatment is the second stage of wastewater treatment. In primary treatment, suspended solids, colloidal particles, oil, and grease are removed. In secondary treatment, biological treatment is done on the wastewater to remove the organic matter present. This treatment is performed by indigenous and aquatic micro-organisms like ...
What is a membrane bioreactor?
Membrane Bioreactor – MBR is the combination of ultrafiltration (UF) and activated sludge process. MBR produces effluent of high quality which can be discharged to surface water for reuse. It can be retrofitted in existing installations.
What is SBR treatment?
It is used to reduce the organic matter (BOD and COD), oxygen is bubbled with a mixture of wastewater and activated sludge. After this treatment, the treated water can be discharged on surface water.
What is MBBR in biofilm?
A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) consists of an aeration tank which is similar to an activated sludge tank with special plastic carriers that provide a higher surface area where a biofilm can grow.
What is the process of dissimilation?
The dissimilation process of breaking down the nitrate molecule to make it chemically-bound oxygen requires both an electron donor and an electron acceptor. Nitrate gains (accepts) electrons and is reduced to nitrogen gas and a carbon source loses (donates) electrons and is oxidized to carbon dioxide.
Can anaerobic bacteria use oxygen?
However, anaerobic bacteria can and will use oxygen that is found in the oxides introduced into the system or they can obtain it from organic material within the wastewater. Anaerobic treatment technology is Up-flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor (UASB)
What is primary treatment of sewage?
Primary treatment of sewage by quiescent settling allows separation of floating material and heavy solids from liquid waste. The remaining liquid usually contains less than half of the original solids content and approximately two-thirds of the BOD in the form of colloids and dissolved organic compounds.
What happens when biocide concentrations exceed the secondary treatment?
BOD reduction normally accomplished by that species temporarily ceases until other species reach a suitable population to utilize that food source, or the original population recovers as biocide concentrations decline.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage which are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent. The majority of municipal plants use aerobic biological processes as a secondary treatment step. To be effective, the biota require both oxygen and food to live.
How is primary clarifier effluent discharged?
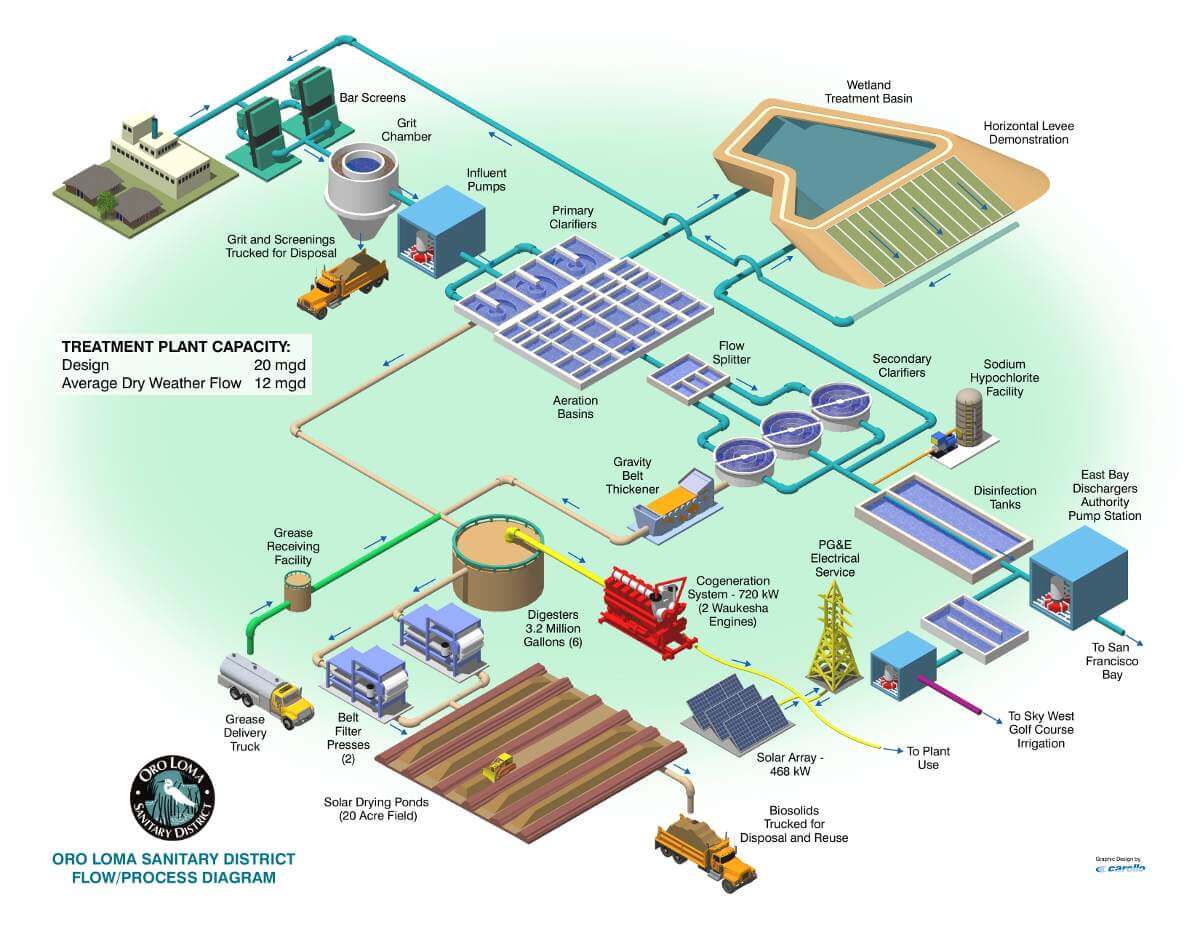
Primary clarifier effluent was discharged directly to eutrophic natural wetlands for decades before environmental regulations discouraged the practice. Where adequate land is available, stabilization ponds with constructed wetland ecosystems can be built to perform secondary treatment separated from the natural wetlands receiving secondary treated sewage. Constructed wetlands resemble fixed-film systems more than suspended growth systems, because natural mixing is minimal. Constructed wetland design uses plug flow assumptions to compute the residence time required for treatment. Patterns of vegetation growth and solids deposition in wetland ecosystems, however, can create preferential flow pathways which may reduce average residence time. Measurement of wetland treatment efficiency is complicated because most traditional water quality measurements cannot differentiate between sewage pollutants and biological productivity of the wetland. Demonstration of treatment efficiency may require more expensive analyses.
What is suspended growth?
Suspended-growth systems include activated sludge, which is an aerobic treatment system, based on the maintenance and recirculation of a complex biomass composed of micro-organisms able to absorb and adsorb the organic matter carried in the wastewater. Constructed wetlands are also being used.
How does an aerated lagoon work?
Aerated lagoons are a low technology suspended-growth method of secondary treatment using motor-driven aerators floating on the water surface to increase atmospheric oxygen transfer to the lagoon and to mix the lagoon contents. The floating surface aerators are typically rated to deliver the amount of air equivalent to 1.8 to 2.7 kg O 2 / kW·h. Aerated lagoons provide less effective mixing than conventional activated sludge systems and do not achieve the same performance level. The basins may range in depth from 1.5 to 5.0 metres. Surface-aerated basins achieve 80 to 90 percent removal of BOD with retention times of 1 to 10 days. Many small municipal sewage systems in the United States (1 million gal./day or less) use aerated lagoons.
What is a trickling filter bed?
In older plants and those receiving variable loadings, trickling filter beds are used where the settled sewage liquor is spread onto the surface of a bed made up of coke (carbonized coal), limestone chips or specially fabricated plastic media. Such media must have large surface areas to support the biofilms that form.
How does secondary treatment remove organic matter?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria that is naturally found in it. Increased oxygen encourages the growth of bacteria, which consume and breakdown the complex organic compounds.
What is the main objective of wastewater treatment?
The main objective of Wastewater Treatment is to separate solids from liquid then to treat both turning the solids into nonhazardous Bio-solids and water into non-threatening environmentally safe water to add back to the environment where it came from with the intention of using it again. 1. Primary Wastewater Treatment.
What is organic solid?
The organic solids are material that can be processed at the treatment facility through separating these solids from the rest of the wastewater we use simple gravity. Suspended solids that pass through screens and grit chambers are removed from the sewage in sedimentation tanks.
How much BOD is removed from sewage?
Weekly averages may be up to 50 percent higher. A sewage treatment plant providing both primary and secondary treatment is expected to remove at least 85 percent of the BOD and suspended solids from domestic sewage.
What is stage 2 of wastewater treatment?
Stage 2. – Includes Secondary Treatment using different methods of Biological Oxidation to further purify wastewater. The Conventional Activated Sludge Process is the most popular, using Aeration in a long, but effective process that entails mixing and aerating wastewater in a solution of microorganisms grown in the system that breakdown organic material and separates dissolved solids. This can be accomplished by:
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the part of the Wastewater Treatment process that breaks down organic matter, removes dissolved and colloidal solids. This organic waste material would create a high Oxygen demand on the receiving stream if it were let go into the environment. Secondary treatment is traditionally applied to the liquid portion of sewage after initial Preliminary and Primary treatment has removed settleable solids and inorganic floating material.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic Digestors. Most large Wastewater Treatment Plants use 2 Stage Anaerobic Digestion to treat the solids removed from the Primary and Secondary Treatment facilities. Treatment is needed for the Solids to be deemed safe for landfills.