Alternative treatments for MRSA in patients with a vancomycin allergy include bactrim, doxycycline, linezolid, daptomycin, tigercycline, and synercid. CLINDAMYCIN. Clindamycin is an antibiotic with gram-positive and anaerobic coverage, which is also sensitive to MRSA with good bone and joint coverage (31).
Can you be allergic to vancomycin?
Aug 31, 2021 · Vancomycin is a medication used in the treatment of serious Gram-positive bacterial infections. It is in the cell wall synthesis inhibitor class of antimicrobial medications. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for vancomycin as a valuable antimicrobial in treating Gram-positive bacterial infections. This activity will highlight the …
How often can you give vancomycin IV?
Sep 27, 2021 · INTRODUCTION. Vancomycin causes several different types of hypersensitivity reactions, ranging from localized skin reactions to generalized cardiovascular collapse. The most common adverse reaction, vancomycin infusion reaction (VIR). VIR is a rate-dependent infusion reaction, not a true allergic reaction. Vancomycin hypersensitivity will be ...
What should I know about vancomycin before using it?
Mar 05, 2022 · low potassium level - leg cramps, constipation, irregular heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, increased thirst or urination, numbness or tingling, muscle weakness or limp feeling. Side effects on the kidneys may be more likely in older adults taking this medicine. Common vancomycin side effects may include:
What antibiotics can you take if allergic to penicillin?
Nov 30, 2018 · red man syndrome is a nonimmunologically-mediated pseudoallergic reaction to vancomycin that may resemble IgE-mediated anaphylaxis, but is characterized by rapid onset of flushing and pruritus, and typically resolves with a reduction in the …

What antibiotics can you take if you are allergic to vancomycin?
Tetracyclines (e.g. doxycycline), quinolones (e.g. ciprofloxacin), macrolides (e.g. clarithromycin), aminoglycosides (e.g. gentamicin) and glycopeptides (e.g. vancomycin) are all unrelated to penicillins and are safe to use in the penicillin allergic patient.
Can you give clindamycin if allergic to vancomycin?
Instead, vancomycin and clindamycin are recommended alternatives, especially in patients with severe allergy or true anaphylaxis. However, clindamycin alone is only bacteriostatic, and vancomycin alone has reduced Gram-negative coverage and may thus be associated with increased infection rates.Dec 21, 2015
Is clindamycin in the same family as vancomycin?
Cleocin and vancomycin hydrochloride belong to different antibiotic drug classes. Cleocin is a lincomycin antibiotic and vancomycin hydrochloride is a glycopeptide antibiotic.
How do you treat red man syndrome?
If you experience red man syndrome, your doctor will stop vancomycin treatment immediately. They will give you an oral dose of an antihistamine to help manage your symptoms. In more severe cases, such as those involving hypotension, you may need IV fluids, corticosteroids, or both.
Can you give vancomycin with erythromycin allergy?
No interactions were found between erythromycin and vancomycin. However, this does not necessarily mean no interactions exist. Always consult your healthcare provider.
Can you take doxycycline if allergic to vancomycin?
by Drugs.com Tetracyclines are unrelated to penicillins and therefore are safe to take in hypersensitive patients. Other unrelated antibiotics include quinolones (e.g. ciprofloxacin), macrolides (e.g. clarithromycin), aminoglycosides (e.g. gentamicin) and glycopeptides (e.g. vancomycin).Oct 26, 2020
Can you be allergic to vancomycin?
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
Why is clindamycin given with vancomycin?
Vancomycin Combined With Clindamycin for the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin-Structure Infections.Oct 1, 2015
What class drug is vancomycin?
Vancomycin is in a class of medications called glycopeptide antibiotics. It works by killling bacteria in the intestines. Vancomycin will not kill bacteria or treat infections in any other part of the body when taken by mouth. Antibiotics will not work for colds, flu, or other viral infections.May 15, 2016
How do you administer vancomycin IV?
Vancomycin shall only be administered as slow intravenous infusion of at least one hour duration or at a maximum rate of 10 mg/min (whichever is longer) which is sufficiently diluted (at least 100 ml per 500 mg or at least 200 ml per 1000 mg) (see section 4.4).
What happens if vancomycin is given too fast?
If vancomycin injection is injected too fast, a condition known as “red man syndrome” may occur (symptoms include flushing of the upper body, dizziness, low blood pressure, or muscle pain/spasms of the chest and back).Apr 30, 2020
Why does red man syndrome occur with vancomycin?
Red man syndrome, an anaphylactoid reaction, is caused by the degranulation of mast cells and basophils, resulting in the release of histamine independent of preformed IgE or complement. The extent of histamine release is related partly to the amount and rate of the vancomycin infusion.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not take this medication if you are allergic to vancomycin.To make sure vancomycin is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have: 1. an...
How Should I Take Vancomycin?
Take vancomycin exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take this medicine in larger or smal...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Vancomycin?
Other drugs may interact with vancomycin, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell each of your h...
What is the most common adverse reaction to vancomycin?
VANCOMYCIN FLUSHING SYNDROME. The most common adverse reaction to vancomycin is "vancomycin flushing syndrome (VFS)," previously known as "red man syndrome," although we will avoid further use of this term. (See 'Terminology' above.)
What is the red man syndrome?
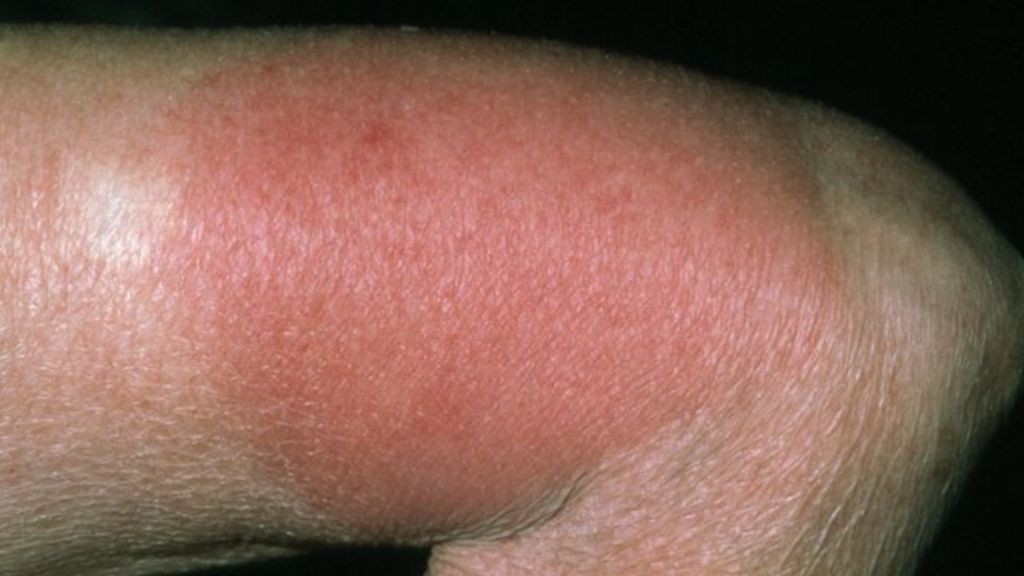
The terms "red man syndrome" or "red neck syndrome" have commonly been used to describe vancomycin flushing syndrome. This terminology originated from the dramatic erythema that develops in some patients in response to infusion of vancomycin, but the terms could be misconstrued as insulting to specific groups of people in the United States [ 1,2 ]. Thus, the terms "vancomycin flushing syndrome (VFS)" or "vancomycin infusion reaction" are preferred. The term "vancomycin flushing reaction" has also been suggested, although using the term "syndrome" as opposed to "reaction" better reflects that clinical manifestations other than flushing can occur.
What are the side effects of vancomycin?
Certain side effects may occur if your body absorbs vancomycin through the intestinal walls. Call your doctor at once if you have: 1 increased diarrhea that is watery or bloody; 2 hearing loss, ringing in your ears; 3 kidney problems - swelling, rapid weight gain, pain in your side or lower back, little or no urination; or 4 low potassium level - leg cramps, constipation, irregular heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, increased thirst or urination, numbness or tingling, muscle weakness or limp feeling.
Where does vancomycin work?
Oral vancomycin works only in the intestines and will not treat infections in other parts of the body. Follow all directions on your medicine label and package. Tell each of your healthcare providers about all your medical conditions, allergies, and all medicines you use.
What is the purpose of vancomycin?
Oral (taken by mouth) vancomycin fights bacteria in the intestines. Vancomycin is used to treat an infection of the intestines caused by Clostridium difficile , which can cause watery or bloody diarrhea.
Can you take vancomycin if you are allergic to it?
You should not vancom ycin if you are allergic to it. To make sure vancomycin is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had: an intestinal disorder such as inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis; if you are receiving any intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
Can you take vancomycin with a viral infection?
Skipping doses can increase your risk of infection that is resistant to medication. Vancomycin will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold.
Does vancomycin cause kidney problems?
Side effects on the kidneys may be more likely in older adults taking this medicine. Common vancomycin side effects may include: low potassium; nausea; or. stomach pain. This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
How long does Clostridium difficile take to treat diarrhea?
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: 125 mg orally 4 times a day#N#-Duration of therapy: 10 days#N#Enterocolitis: 500 mg to 2 g orally per day, given in divided doses 3 to 4 times a day#N#-Maximum dose: 2 g/day#N#-Duration of therapy: 7 to 10 days#N#Comment: Formulations administered by injection will not treat colitis.#N#Uses:#N#-Treatment of C difficile-associated diarrhea#N#-Treatment of enterocolitis caused by S aureus (including MRSA)#N#Society of Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) and IDSA Recommendations:#N#Initial treatment of severe C difficile infection (CDI): 125 mg orally 4 times a day#N#-Duration of therapy: 10 to 14 days#N#Severe, complicated CDI: 500 mg orally 4 times a day AND 500 mg (in 100 mL normal saline) rectally every 6 hours with/without IV metronidazole#N#Comments:#N#-Rectal formulations should be administered as a retention enema.#N#-The first recurrence of CDI may be treated with the initial treatment regimen; a second recurrence of CDI may be treated with a tapered/pulsed regimen of this drug.#N#Uses:#N#-Initial treatment of patients with severe CDI#N#-Initial treatment of patients with complicated, severe CDI
What is the most common reaction to vancomycin?
vancomycin hypersensitivity reactions are adverse drug reactions mediated by pseudoallergic or allergic responses, and include red man syndrome, which is the most common hypersensitivity reaction to vancomycin and, more rarely, immediate anaphylaxis and delayed reactions, such as skin rashes, cytotoxicity, or vasculitic syndromes 1, 4, 5, 6
What are the symptoms of anaphylaxis?
symptoms are similar to anaphylaxis and may include pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, cardiovascular instability and gastrointestinal symptoms. pseudoallergic reactions can occur without prior exposure to the drug. sometimes called an anaphylactoid reaction.
Why are references used in DynaMed?
The references listed below are used in this DynaMed topic primarily to support background information and for guidance where evidence summaries are not felt to be necessary. Most references are incorporated within the text along with the evidence summaries.
How long does it take for an IgE reaction to occur?
immediate IgE-mediated responses such as urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylaxis typically occurs within 1 hour but may present up to 1 day after exposure. delayed (or nonimmediate) allergic reactions to vancomycin occur > 2 days and up to several weeks after vancomycin exposure and include.
When to use strong recommendations?
Strong recommendations are used when, based on the available evidence, clinicians (without conflicts of interest) consistently have a high degree of confidence that the desirable consequences (health benefits, decreased costs and burdens) outweigh the undesirable consequences (harms, costs, burdens).
What is red man syndrome?
red man syndrome is a nonimmunologically-mediated pseudoallergic reaction to vancomycin that may resemble IgE-mediated anaphylaxis, but is characterized by rapid onset of flushing and pruritus, and typically resolves with a reduction in the rate of vancomycin infusion 1, 5, 6. vancomycin may also be associated with allergic reactions, ...
What is a type A reaction?
adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are classified as type A or type B 1, 2. type A reactions are much more common, accounting for about 80% of ADRs. type A reactions are predictable reactions due to pharmacologic action of the drug, and are usually dose dependent. type A reactions include side effects of the drug, toxicity, and drug interactions.
What is the name of the antibiotic that is used to treat a staphylococcal infection?
Intravenous Vancomycin. Vancomycin is an antibiotic originally isolated from the bacteria Streptococcus orientalis. It was discovered in the 1950’s but became a preferred treatment against infections resistant to other antibiotics, particularly penicillin-resistant staphylococcal infections. Vancomycin is a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic ...
What is the red man syndrome?
Red skin rash on the upper body, face, and neck. Between 3.7% to 47% of patients develop red man syndrome. The faster the infusion of vancomycin, the more likely someone is to develop the syndrome. The most severe cases occur in children and patients who are 40 years old or younger.
Does vancomycin cause kidney damage?
In some cases, ototoxicity induced by vancomycin treatment may be irreversible. Vancomycin also exhibits nephrotoxicity and has been found to cause acute kidney injury (AKI). The most likely explanation is that vancomycin induces oxidative effects on the renal tubules, restricting blood flow and oxygen to the organ.
How long does it take for red man syndrome to develop?
When intravenous vancomycin is administered too quickly, red man syndrome can develop. Symptoms that often begin 4 to 10 minutes after administration include: Between 3.7% to 47% of patients develop red man syndrome. The faster the infusion of vancomycin, the more likely someone is to develop the syndrome.
Is vancomycin good for diarrhea?
Oral vancomycin is given to treat Clostridiodes ( Clostridium) difficile infections and infection-induced diarrhea. However, the drug has poor oral bioavailability and is broken down in the stomach and intestines before it can enter the bloodstream to treat systemic infections.
What is the main component of bacterial cell walls?
Vancomycin is a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic that prevents synthesis of peptidoglycan, the main component of bacterial cell walls. It is an effective antibiotic treatment against Gram-positive bacteria that contain peptidoglycan in their walls.
Is MRSA resistant to beta-lactam?
Enterococcus faecalis. MRSA and MRSE are both resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics (for example, oxacillin), which are commonly used to treat most staph infections. Intravenous vancomycin can also be used for a variety of other serious or severe infections, including: Skin and soft tissue infections. Lower respiratory tract infections.
How to tell if you are allergic to antibiotics?
Ask a pharmacist if you are not sure. Tell all healthcare providers about your allergy. Always tell your healthcare providers the names of medicines that you are allergic to and the symptoms of your allergic reactions. Ask if you need to avoid other medicines. You may be allergic to other medicines if you had an allergic reaction to an antibiotic. ...
What is an antibiotic allergy?
What is an antibiotic medication allergy? An antibiotic medication allergy is a harmful reaction to an antibiotic. The reaction can start soon after you take the medicine, or days or weeks after you stop. Healthcare providers cannot know ahead of time if you will have an allergic reaction. Your immune system may become sensitive to ...
What are the symptoms of a swollen swollen swollen swollen
Mild symptoms include red, itchy, flaky, or swollen skin. You may have a flat, red area on your skin that is covered with small bumps. You may also have hives. Severe symptoms include skin that blisters or peels, vision problems, and severe swelling or itching.
How long does epinephrine last?
You may need a second shot, because epinephrine only works for about 20 minutes and symptoms may return. Your healthcare provider can show you and family members how to give the shot. Check the expiration date every month and replace it before it expires. Create an action plan.
What are the symptoms of anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis symptoms include throat tightness, trouble breathing, tingling, dizziness, and wheezing. Anaphylaxis is a sudden, life-threatening reaction that needs immediate treatment. Anaphylaxis may occur if you exercise after exposure to a trigger, such as after you take an antibiotic.
How to know if you have anaphylaxis?
Stop exercising right away if you start to develop any signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis. You may first feel tired, warm, or have itchy skin. Hives, swelling, and severe breathing problems may develop if you continue to exercise. Carry medical alert identification.
Do steroids help with inflammation?
Steroids reduce inflammation. Desensitization may be done after you have a reaction, if you need to be treated with the antibiotic again. Your healthcare provider will give you small doses of the antibiotic over a few hours. He will treat any allergic reaction that you have.
