
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
- Coagulation and Flocculation. ...
- Sedimentation. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection.
How is water treated in water treatment plant in India?
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
- Screening. As water enters a water treatment plant, either from lakes, rivers, or the ground, it passes through a screening. ...
- Coagulation. ...
- Sedimentation. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection.
How does water get treated?
Why is water aerated in the treatment process?
What are the components of water treatment plant?
- Raw water source, for example, and impounding reservoir, lake, or river canal.
- Intake well.
- Water pumping system.
- Cascade aerator.
- Alum mixer.
- Clarifier.
- Filter bed washing system.
- Sand filters.
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
- Coagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ...
- Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Sludge Drying. ...
- Fluoridation. ...
- pH Correction.
What are the 7 stages of water treatment?
What are the 3 stages of water treatment?
What are the types of water treatment?
- Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration. Reverse Osmosis is a process where water pressure is employed to force water through a semi-permeable membrane. ...
- Ultraviolet Water Sterilization and Filtration. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Distillation.
Which type of water is generally used in the treatment of water?
Why are water treatment plants important?
Water treatment plants are critical for a municipality so that clean water can be supplied to the local community. The process of water purification in water plants requires specialists to ensure safe and effective operation. The whole procedure occurs in stages and involves a combination of technical processes.
What is the first step in water treatment?
Coagulation. When water enters a treatment plant, the first stage in the process is coagulation where chemicals are added to the water supply to enable microparticles and small solids to stick together. Polyelectrolyte, ferrous sulfate, and aluminum sulfate are examples of chemicals used in the water treatment plant process to aid coagulation.
What happens when water is flocculated?
Once the water is in the primary settling basins the large particles formed during the coagulation and flocculation stage separate and settle. This leaves cleaner water for further processing in the treatment plant. The solids form a sludge layer which forms on the bottom of the tank and is later removed via sludge thickening and reused on the land.
What is the process of coagulation of water?
These mix the chemicals and water together and enable the micro particles to form into larger pieces that are likely to stick together, making the sedimentation process in water treatment more effective. This process is known as flocculation.
What is added to water after it is clarified?
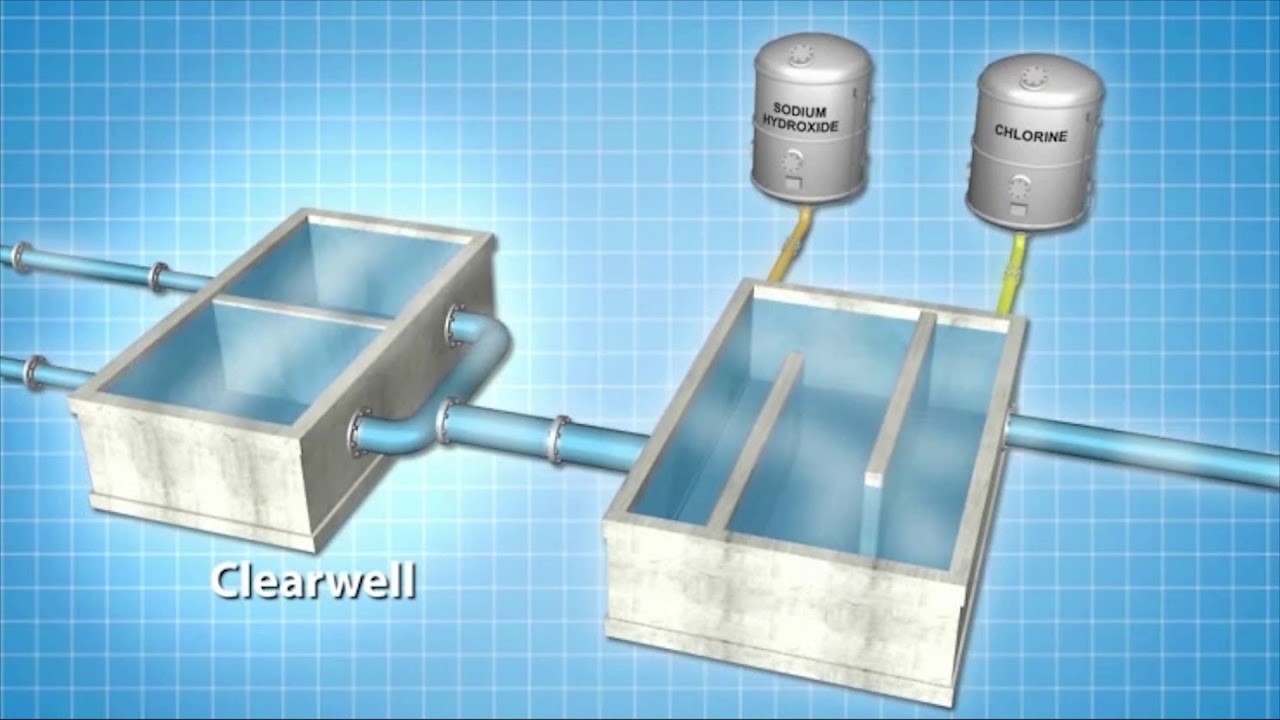
Once clarified water leaves the sedimentation basins in the treatment plant, chlorine is added during the disinfection water treatment stage. After the chlorine wastewater treatment occurs, ammonia follows which forms chloramine. This chloramine disinfected water passes through a further set of basins to complete the disinfection process.
What is the pH adjustment in water?
pH Adjustment. After the disinfection phase the water undergoes a pH treatment stage. Lime or calcium oxide makes water less acidic by adjusting the pH. It is also less corrosive to domestic water pipes. Polyphosphate solution is also added to the water at this stage to keep the lime dissolved.
Why is water purification important?
It is vital that the processes are quality-checked regularly to ensure that standards are being met and the public gets clean, healthy water.
What is water treatment?
The water treatment process to deliver safe and wholesome water to customers includes many steps. Coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection are the water treatment processes that make up a conventional surface water treatment plant. These water treatment processes ensure that the water consumers receive is safe ...
What is the purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rule?
The goal of the SWTR is to reduce illnesses related to pathogens in drinking water. These pathogens include coliform, Giardia, and Cryptosporidium .
How does water temperature affect coagulation?
Water temperature also impacts the coagulation process because it effects the viscosity of water. Both alum and ferric salts form flocs at a slower rate as the water temperature decreases.
Why is a coagulant injected into water?
A coagulant chemical is injected to neutralize these small negative charges and then the water is rapidly mixed. The rapid mixing disperses the coagulant and also increases the interaction of these small particles.
What is the process of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration?
The water treatment process of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration remove the pathogens. The disinfection water treatment process inactivates them. The small particles in water may consist of silt and clay, color bodies, precipitated iron or manganese oxides, and even bacteria and algae. Together, these particles make the water ...
When to backwash a plant?
A filter may be backwashed when the head loss, which is the pressure build up, reaches a certain level. The system’s domestic water supply permit may also specify that a filter be backwashed following a certain length of time, regardless if that target head loss is achieved.
When do you need to ripen a water filter?
A filter must be ripened when it is first placed into service or following a backwash. If the filter media is too clean, and the pore spaces between the sand grains and the anthracite coal too large, there are chances for particulates to pass right through the filter. The pore spaces decrease and the filter is better at removing the particulates as more water is filtered and more particles are captured. Until the filter is ripened, the water produced by it may not meet the necessary turbidity requirements. Systems must be equipped with the ability to pump this non compliant water to waste without it entering the distribution system.
How is treated raw water treated?
Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler. The mixed water flows through a reverse osmosis plant operating at a recovery of 80% and an average salt rejection of 95%. Permeate from the RO mixes with product water from both the waste RO unit and the distillate from the brine evaporator/crystalliser situated in the wastewater treatment plant. The combined flow then enters a degasifier, to remove carbon dioxide, and a mixed bed dimineraliser. The mixed bed plant consists of two 100% capacity ion exchange vessels which remove the final 5% of the dissolved salts. The ion exchange beds process 2 200 000 gallons (8327 m3) before being regenerated. Waste from the process is pH adjusted and combined with the RO reject before being pumped to the wastewater treatment plant.
How does a centralized water treatment plant work?
Centralized water treatment plantsare based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water. However, they entail large infrastructure costs which is difficult to raise in rural regions of developing countries and are generally installed using government funding. Hence, centralized treatment is available only in the metros of developing countries and mainly benefit the urban population. The transportation cost of water to the centralized treatment plant and from the treatment plant to the individual households is another major expense which limits its benefits to regions which are situated away from the treatment plant. Hence centralized treatment plants are generally installed near the freshwater resources (rivers or lakes) and benefit the people living closer to these water bodies.
What is centralized water treatment?
Centralized water treatment plants are based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water.
How is brine treated?
Treatment of the brine is conducted in a vertical tube, falling film evaporator driven by vapour compression. Wastewater is pH adjusted to between 5.5 and 6 and then heated to boiling point and deaerated. Hot brine then enters the evaporator sump where it mixes with recirculating brine slurry which is pumped to the top of 2 inch (50.8 mm) heat transfer tubes. As the slurry falls a small portion of the water evaporates and condenses on the outside of the heat transfer tubes. The brine evaporator recovers 95% of the flow which is passed on to the demineralisation feed tank with a water quality of less than 10 ppm TDS. The 5% concentrated brine then enters a crystalliser where a further 95% of the remaining water is recovered. The stream is finally sent to a filter press and dewatered to a 20% moisture content sludge which is disposed of off site.
What is the Bendigo water treatment plant?
I. Bendigo water treatment plant (BWTP). The 12.54 × 10 4 m 3/day (33 MGD) BWTP has been producing drinking water for nearly 1 million people in central Victoria, Australia since 2002. It is one of the largest if not the largest MF plant in the world. The plant combines submerged microfiltration (CMF-S), ozonation and biological activated carbon (BAC) to treat a variable and difficult raw water. Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals. The coagulant dosage is typically 5–6 mg/l. The coagulant precipitate is removed by MF. The coagulant/CMF-S process removes up to 15% of the dissolved organic carbon.64
What is make up water treatment?
Make up water treatment. Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler.
What is raw water pretreatment?
The raw water pretreatment plant is designed principally for solids removal from the incoming Hanover county sewage effluent (grey water), backwash water and wastewater from the oily water collection system. Raw water enters a coagulation/flocculation chamber followed by a clarifier and dual media depth filters. Backwash water from the filters is periodically returned to the clarifier. Clarifier sludge is dosed with polymer before being thickened and then sent to the filter press for dewatering. The cake is sent to landfill and the recovered water returned to the clarifier.
What is a water treatment plant?
Drinking water treatment plant could be classified into: –. Disinfection plant which is used for high-quality water source to ensure that water does not contain pathogens. –. Filtration plant : this is usually used to treat surface water. –. Softening plant which is used to treat groundwater.
How is treated raw water treated?
Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler. The mixed water flows through a reverse osmosis plant operating at a recovery of 80% and an average salt rejection of 95%. Permeate from the RO mixes with product water from both the waste RO unit and the distillate from the brine evaporator/crystalliser situated in the wastewater treatment plant. The combined flow then enters a degasifier, to remove carbon dioxide, and a mixed bed dimineraliser. The mixed bed plant consists of two 100% capacity ion exchange vessels which remove the final 5% of the dissolved salts. The ion exchange beds process 2 200 000 gallons (8327 m 3) before being regenerated. Waste from the process is pH adjusted and combined with the RO reject before being pumped to the wastewater treatment plant.
What is a WTP plant?
WTP including an effluent treatment plant: There are three different sections in a WTP: a pretreatment (PT) plant, a posttreatment or demineralized water (DM) plant, and a waste treatment or effluent treatment (ET) plant.
What is raw water pretreatment?
The raw water pretreatment plant is designed principally for solids removal from the incoming Hanover county sewage effluent (grey water), backwash water and wastewater from the oily water collection system. Raw water enters a coagulation/flocculation chamber followed by a clarifier and dual media depth filters. Backwash water from the filters is periodically returned to the clarifier. Clarifier sludge is dosed with polymer before being thickened and then sent to the filter press for dewatering. The cake is sent to landfill and the recovered water returned to the clarifier.
What is a BWTP?
I. Bendigo water treatment plant (BWTP). The 12.54 × 10 4 m 3 /day (33 MGD) BWTP has been producing drinking water for nearly 1 million people in central Victoria, Australia since 2002. It is one of the largest if not the largest MF plant in the world. The plant combines submerged microfiltration (CMF-S), ozonation and biological activated carbon (BAC) to treat a variable and difficult raw water. Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals. The coagulant dosage is typically 5–6 mg/l. The coagulant precipitate is removed by MF. The coagulant/CMF-S process removes up to 15% of the dissolved organic carbon. 64
How is brine treated?
Treatment of the brine is conducted in a vertical tube, falling film evaporator driven by vapour compression. Wastewater is pH adjusted to between 5.5 and 6 and then heated to boiling point and deaerated. Hot brine then enters the evaporator sump where it mixes with recirculating brine slurry which is pumped to the top of 2 inch (50.8 mm) heat transfer tubes. As the slurry falls a small portion of the water evaporates and condenses on the outside of the heat transfer tubes. The brine evaporator recovers 95% of the flow which is passed on to the demineralisation feed tank with a water quality of less than 10 ppm TDS. The 5% concentrated brine then enters a crystalliser where a further 95% of the remaining water is recovered. The stream is finally sent to a filter press and dewatered to a 20% moisture content sludge which is disposed of off site.
What is the name of the chemical that is added to water to neutralize particles?
Flocculation: Chemicals like alum (aluminum sulfate) are added to the water both to neutralize the particles electrically and to make them come close to each other and form large particles called flocs that could more readily be settled out
What is the purpose of water treatment plant?
Purpose of Water Treatment Plant: To remove hardness of water and purification of water. To supply water to the dye house as stander quality. To supply water to the boiler as it does not damage boiler.
What happens if you don't treat water?
If proper treatment is not done for water then Corrosion, Scaling, Microbiological contaminants and fouling will occur in the system. It is an electrochemical process by which a metal returns to its natural state. For e.g. Mild Steel is commonly used metal in cooling water systems and is very susceptible to corrosion.
What is a pretreatment plant?
Pre-treatment plant removes suspended solids like clay, salt, plants, micro-organisms, etc. form raw water to give clarified water. Suspended solids can be separable or nonseparable. Separable solids are heavier and large and can easily be removed by an aerator.
What are the four sources of water in Bangladesh?
There are mainly four source of water, such as rain water, surface water, subsoil water and deep well water. Mainly in Bangladesh deep well water is available most of the company used deep well water. The water is used in boiler, scouring, bleaching, dyeing, finishing and must be soft and clean. The water available from different water sources ...
How long does water stay in a filtration chamber?
In filtration chamber water is kept for a long duration like 22 hours which is allowed to sediment a lot of sludge remaining in the treated water.
What is a WTP plant?
Water Treatment Plant (WTP): Water is one of the most important utility used in textile industry specially in textile wet processing industry. Without water no one can imagine scouring, bleaching, dyeing, finishing etc. There are mainly four source of water, such as rain water, surface water, subsoil water and deep well water.
Can water be used in boilers?
The water available from different water sources cannot be used directly in boilers as such. The objective of water treatment plant is to produce the boiler feed water so that there shall be: The treated water is called ‘De-mineralized Water’ and the plant where it is treated is called Water Treatment Plant.
What is the most widely used water treatment technology?
Many water treatment plants use a combination of coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and disinfection to provide clean, safe drinking water to the public. Worldwide, a combination of coagulation, sedimentation and filtration is the most widely applied water treatment technology, and has been used since the early 20th century.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is residual water?
Residuals are the by-products that remain in the water after substances are added and reactions occur within the water. The particular residuals depend on the coagulant that is used. If ferric sulphate is used, iron and sulphate are added to the water. If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added.
Why are pathogens removed from water?
Usually, the pathogens that are removed from the water are removed because they are attached to the dissolved substances that are removed by coagulation. In the picture below, the coagulants have been added to the water, and the particles are starting to bind together and settle to the bottom.
How is fine sand removed from water?
Particles with a diameter greater than 100 microns (or 0.1 millimetre), such as fine sand, are removed through sand filtration. As the pore size decreases, a greater proportion of material is retained as the water passes through the filter.
Does DOC remove suspended particles?
Organic Carbon (DOC). Coagulation can also remove suspended particles, including inorganic. precipitates, such as iron. A large amount of DOC can give water an unpleasant taste and odour, as well as a brown discolouration.
Does sand filtration remove bacteria?
Rapid sand filtration removes suspended particles, which may have bacteria attached, but in. general does not remove bacteria, protozoa, or viruses. In water treatment plants, filtration. removes a large number of contaminants, but still requires disinfection to produce drinking water that is safe.
How is groundwater treated?
The water may be treated as it is pumped from the ground to remove certain contaminants or it may be chlorinated if there is concern of bacterial or parasitic infection.
What was the main goal of water providers?
Nearly a century ago, controlling water-borne disease was the main treatment goal of water providers. Today, water agencies large and small provide their customers with the highest quality drinking water in the world. Before disinfection became a common practice, widespread outbreaks of cholera and typhoid were frequent throughout the United States. These diseases are still common in less developed countries, but largely disappeared in the United States when chlorine and filtration became widely used 80 years ago.
What are the contaminants in water?
Contaminants fell into several categories: those that occur naturally, such as arsenic and uranium, those that are manmade, such as solvents or pesticides; and those that derive primarily from the materials used in supplying water, most notably disinfection byproducts (DBPs). The byproducts emerge from the treatment process when chlorine reacts with naturally occurring organic compounds found in the water supply. Public health experts note the possible risks from DBPs are limited compared to inadequate disinfection of drinking water.
Why is fluoride added to water?
In some systems, fluoride is added to reduce tooth decay. California law requires fluoridation of water in systems with 10,000 or more connections if outside funding is provided. According to the state, 30 percent of all public water providers in California fluoridate their water.
What is the purpose of the Safe Drinking Water Act?
Passed by Congress in 1974, the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) regulates drinking water quality in the United States. Under the SDWA, the U.S. Environmental protection Agency (EPA) can delegate implementation of drinking water regulations to states that have developed programs at least as stringent as the federal one. Such states, including California, have primary enforcement responsibility for administering their own programs.
How often is a water system tested?
Monthly monitoring for microbial contaminants is required for both surface water and groundwater systems, while organic chemical monitoring must be conducted annually by surface systems and every three years by groundwater systems.
What is the driving force behind the development of drinking water standards and regulations?
The driving force behind the development of drinking water standards and regulations is the protection of public health. Many laws have been adopted concerning water quality standards, going as far back as the Interstate Quarantine Act of 1893, which sought to control the introduction of communicable diseases from other countries.
How is wastewater pumped?
Wastewater is pumped or carried by gravity along our sewer mains through to our wastewater treatment plants . Once it reaches the treatment plant, we begin our rigorous treatment processes. In this article we explain how we treat wastewater and where the water goes once it's treated.
Why do we heat water tanks?
We heat the tanks to encourage the growth of bacteria. The bacteria, in turn, breaks down the sludge into water and biosolids —this process is called anaerobic digestion.
What is the process of sludge being broken down into water and biosolids called?
The bacteria, in turn, breaks down the sludge into water and biosolids —this process is called anaerobic digestion. The biosolids are trucked off site to be made into fertilizer or used for agriculture. Methane gas is a primary by-product of the anaerobic digestion process.
How much sludge is in a sedimentation tank?
These tanks are 8 meters high and go down another 8 meters into the ground. Each tank holds around 4 million litres of sludge.
Why is the end of a wastewater pipe important?
The end of the pipe contains small holes to ensure the wastewater is evenly dispersed into the sea. This is the most cost effective option as the process uses very little energy, instead relying on gravity to transport the water. Sunlight, oxygen and ocean currents combine to continue the wastewater treatment process.
What is the purpose of aeration in wastewater?
The microbes form ‘activated sludge’ flocks and feed on the organic matter remaining in the wastewater. The microbes remove contaminants and convert organic matter into carbon dioxide, nitrogen gas and more activated sludge. The aeration process is a natural alternative to chemical processing.
What is aeration process?
The aeration process is a natural alternative to chemical processing. If we relied on chemicals to treat wastewater, we'd also need a process to remove them before returning the water back to the environment. When the activated sludge flocks have done their job, the water flows through to secondary sedimentation tanks.
Coagulation
Flocculation
- Once water has been treated with the coagulation chemicals it enters a tank with giant paddles. These mix the chemicals and water together and enable the micro particles to form into larger pieces that are likely to stick together, making the sedimentation process in water treatmentmore effective. This process is known as flocculation.
Sedimentation
- Once the flocculation process is complete the water enters the sedimentation phase. Once the water is in the primary settling basins the large particles formed during the coagulation and flocculation stage separate and settle. This leaves cleaner water for further processing in the treatment plant. The solids form a sludge layer which forms on the bottom of the tank and is lat…
Disinfection
- Once clarified water leaves the sedimentation basins in the treatment plant, chlorine is added during the disinfection water treatment stage. After the chlorine wastewater treatment occurs, ammonia follows which forms chloramine. This chloramine disinfected water passes through a further set of basins to complete the disinfection process.
Ph Adjustment
- After the disinfection phase the water undergoes a pH treatment stage. Lime or calcium oxide makes water less acidic by adjusting the pH. It is also less corrosive to domestic water pipes. Polyphosphate solution is also added to the water at this stage to keep the lime dissolved.
Fluoridation
- Once water exits the sedimentation basins, fluorosilicic acid is added in small quantities. This helps fluoridate the water supply to help in the prevention of dental decay.
Filtration
- Finally, water goes through a filtration process using rapid gravity filters. Sand is commonly used in this type of filter and it removes any further sediment or particles in the water. During this final stage water is passed through a filter in a regulated manner. Any particles stick to the filter, leaving clean water to be piped into the municipal supply. Pumping stations pump water to dom…
Coagulation
Flocculation
- Following the coagulant chemical addition and the rapid mix processes, the raw water will continue on to a flocculation basin. The goal of the flocculation treatment process is to increase the size of the flocs in order to increase their ability to settle out.
Sedimentation
- The water continues on to the sedimentationbasin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. The goal of this stage of the treatment process is to reduce the amount of solids in the water before the water is filtered in the next treatment step. The large flocs will settle out of suspension via gravity. Clarifiers can remove a very large percentage of the suspended materials in water. I…
Filtration
- The final water treatment process in removing particulates is filtration. The sedimentation process will have already removed a large percentage of the suspended solids. Sedimentation is unable to remove many small particles in water though. Filtration will remove these microorganisms and other suspended material that did not settle out previously.
Disinfection
- As discussed previously, the surface water treatment rule requires both the filtration and disinfection of surface water sources. The water must be disinfected now that it has been filtered.
Chlorination Operations
- Chlorination was one of the first drinking water disinfection methods. It is still the most commonly used disinfection method used today. The filtered water is injected with either liquid sodium hypochlorite, gaseous chlorine, or solid calcium hypochlorite. Chlorine is a strong oxidant. It is used to both disinfect and also to remove color, taste and odor compounds, iron and manganes…
Conclusion
- In order to meet the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule, a water system must both remove and inactivate the pathogens in the water. This process begins with coagulation, which destabilizes the particles in the water. Then, during flocculation, the destabilized particles bump into each other and form larger and larger flocs. These large flocs are given adequate time to se…