
Medication
Studies on long-term outcomes and comparison to other well-known treatment modalities such as laparoscopic Heller myotomy (LHM) and pneumodilation have recently been published. POEM and LHM both have excellent 2-year success rates for relieving achalasia symptoms, but reflux disease and erosive esophagitis are more prevalent following POEM.
Procedures
Jun 23, 2017 · Traditionally, the treatment modalities employed for this purpose included pharmacological therapy (e.g. calcium channel blockers, long-acting nitrates), endoscopic interventions (e.g. endoscopic botulinum toxin injection to LES, pneumatic dilation), and possibly surgical interventions (surgical myotomy, esophagectomy). 10 In recent years ...
Self-care
Oct 20, 2021 · Surgical myotomy has a success rate of 88% to 95% for up to 10 years. However, a common side effect is the development of GERD. To reduce this effect, they can combine LHM with Partial or Dor Fundoplication. An additional technique, called Dor Fundoplication may be combined with myotomy.
Nutrition
Mar 15, 2019 · However, several groups have since reported on stenting as a primary treatment for achalasia based on two general strategies: long-term (months) implantation of a regular-sized stent (20 to 25 mm) or short-term (< 1 week) implantation of a …
What is the prognosis of achalasia?
Laparoscopic myotomy should be the initial treatment for most patients with achalasia. Pneumatic dilatation is the most cost-effective alternative but its long-term efficacy is less than that of surgical myotomy. Endoscopic botulinum toxin injection can be considered when other forms of treatment ar …
What are the treatment options for achalasia in adults?
Unfortunately, there are no medications available to treat achalasia that offer significant or sustained responses. The three ways achalasia is treated are by: Dilatation of the lower esophageal sphincter. Injection of botulinum toxin. Surgery. Most patients require an endoscopy, an upper GI series and an esophageal motility test.
What are the secondary endpoints of treatment for end-stage achalasia?
For people with achalasia, these medications relax the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing food and liquid to pass more easily into the stomach. Calcium channel blockers and nitrates are taken by mouth 10 to 30 minutes before a meal. They are available in tablets that can be absorbed under the tongue.
Is pneumatic dilatation an effective treatment for achalasia?
In group A, the estimated 20-year survival rates in patients with achalasia [76% (95% confidence interval (CI): 66-85%)] did not significantly differ from those in controls 80% (95% CI: 71-89%). In group B, 25-year survival rates were also similar in patients [87% (95% CI: 78-97%)] and controls [86% (95% CI: 76-97%)].
Is there a cure for achalasia?
There is no known cure for achalasia. But several treatments can provide good to excellent relief from symptoms for a number of years. When treatment needs to be repeated, it can be as successful as initial treatment.
What is the test for achalasia?
Manometry is a key test in diagnosing achalasia. A thin tube will be passed through your nose into your stomach. Pressure in your esophagus and at the sphincter will be recorded while you drink sips of water . The tube will be slowly withdrawn.
What are the symptoms of a syringe?
Make an appointment to see your doctor for an evaluation if you experience: 1 Unexplained weight loss 2 Nighttime cough or pain 3 Difficulty swallowing solid food
How do you know if you have achalasia?
They may take years to progress. Symptoms can include: Difficulty swallowing solid food. Swallowing liquids is not affected in the early stages. Regurgitation or vomiting of undigested food.
What is the disorder of the esophagus?
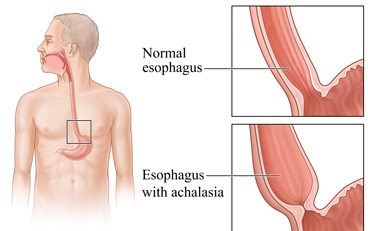
Achalasia is an uncommon disorder of the esophagus. The disorder makes it difficult for food to pass from the esophagus into the stomach. The esophagus is a muscular tube. It carries food from the mouth to the stomach. Normally, coordinated contractions of smooth muscle move food through the esophagus. These contractions are called peristaltic ...
What is the muscle between the esophagus and stomach called?
Between the esophagus and stomach is a muscle called the esophageal sphincter (LES). The sphincter surrounds the esophagus. It keeps the esophagus closed. This prevents food and acid from splashing back up into the esophagus from the stomach. When you swallow, this sphincter relaxes.
What happens when you swallow?
When you swallow, this sphincter relaxes. It opens to allow food to pass into the stomach. At the same time, nerves coordinate the contractions of the esophagus. This moves food into the stomach when the sphincter opens. In achalasia, the nerve cells in the lower two-thirds of the esophagus and the sphincter are abnormal.

What Is Achalasia?
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Expected Duration
Specialist to consult
Treatment
- Achalasia is an uncommon disorder of the esophagus. The disorder makes it difficult for food to pass from the esophagus into the stomach. The esophagus is a muscular tube. It carries food from the mouth to the stomach. Normally, coordinated contractions of smooth muscle move food through the esophagus. These contractions are called peristaltic waves. Between the esophagu…
When to Call A Professional
- The symptoms of achalasia come on gradually. They may take years to progress. Symptoms can include: 1. Difficulty swallowing solid food. Swallowing liquids is not affected in the early stages. 2. Regurgitation or vomiting of undigested food 3. Chest pain, discomfort, or fullness under the breastbone, especially following meals 4. Difficulty belching 5. Difficulty swallowing solids and li…
Prognosis
- Tests will be done to diagnose achalasia. These tests will also look for other conditions that could be causing the symptoms. Tests include: 1. Esophagography (barium swallow). You will swallow a thick liquid (barium) that can be seen on an X-ray. The test can show whether the esophagus is enlarged or dilated. It will also show whether the barium is able to empty properly into the stoma…
Further Information
- Achalasia generally worsens unless treated. Even after successful treatment, symptoms may still return five to 10 years later. They may require repeat treatments.