
Medication
- Educate patients with migraine about the risk of MOH with frequent overuse of acute medication.
- Manage established MOH by explanation and withdrawal of the overused medication; abrupt withdrawal is preferred, except for opioids.
- Recognize and, when possible, modify risk factors for the transformation of episodic migraine to chronic migraine.
Therapy
- Tension-type headaches. Daily prescription medications, including tricyclic antidepressants, might manage chronic tension-type headaches.
- Migraines. Migraines are another common type of headache. ...
- Recognize emergency symptoms. These symptoms suggest a more serious condition, so it's important to get a prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- Take control. ...
Self-care
- Confusion or trouble understanding speech
- Fainting
- High fever, greater than 102 F to 104 F (39 C to 40 C)
- Numbness, weakness or paralysis on one side of your body
- Stiff neck
- Trouble seeing
- Trouble speaking
- Trouble walking
- Nausea or vomiting (if not clearly related to the flu or a hangover)
Nutrition
When to Go to the ER. For many patients, visits to the ER are only necessary if the headache or migraine is severe and lasts for a period of days or weeks. This is usually because the patient no longer has the patience or desire to deal with the headache anymore, so by going to the ER, it allows them to be treated by a doctor who will be able to “fix them.”.
What is the first line treatment for a migraine?
What is the best treatment for a chronic migraine?
What kind of doctor should I See for migraines?
Should you go to the emergency room for a migraine?
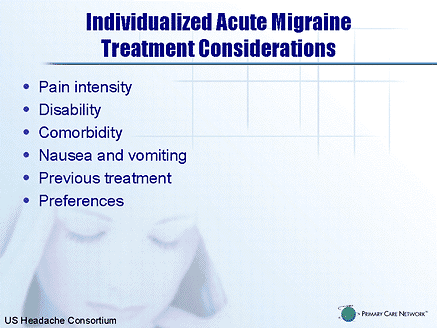
What are the migraine guidelines?
They recommend intravenous metoclopramide, intravenous prochlorperazine, and subcutaneous sumatriptan to treat these patients (level B recommendation). Dexamethasone should be offered to these patients to prevent recurrence of headache (level B). Opioids (injectable morphine and hydromorphone) should be avoided.
What is the best treatment for migraine?
Many people who have migraines find that over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol, aspirin and ibuprofen, can help to reduce their symptoms. They tend to be most effective if taken at the first signs of a migraine attack, as this gives them time to absorb into your bloodstream and ease your symptoms.
What is the fastest way to resolve a migraine?
Hot packs and heating pads can relax tense muscles. Warm showers or baths may have a similar effect. Drink a caffeinated beverage. In small amounts, caffeine alone can relieve migraine pain in the early stages or enhance the pain-reducing effects of acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) and aspirin.
What foods cure a migraine?
Following are some foods that fight migraines, tension headaches, cluster headaches, caffeine headaches, and headaches in general.Leafy greens. Leafy greens contain a variety of elements that contribute to headache relief. ... Nuts. ... Fatty fish. ... 4. Fruits. ... Seeds. ... Whole grains. ... Legumes. ... Hot peppers.More items...•
What is new migraine medicine?
On September 28th, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a once-daily oral medicine, Qulipta (atogepant), for preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults. It is the second FDA-approved, oral anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) drug for preventing migraine.
What causes migraine?
The exact cause of migraines is unknown, but they're thought to be the result of abnormal brain activity temporarily affecting nerve signals, chemicals and blood vessels in the brain.
What is the strongest headache medicine?
Aymen: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are more powerful compared to acetaminophen because NSAIDs reduce inflammation. Examples of NSAIDs include Motrin, Aleve or Advil.
Is coffee good for migraine?
Caffeine can provide relief for a headache. This brings on the headache. Caffeine has vasoconstrictive properties, meaning that blood vessels narrow to restrict blood flow, thereby alleviating the pain.
How to get rid of migraines?
When symptoms of migraine start, try heading to a quiet, darkened room. Close your eyes and rest or take a nap. Place a cool cloth or ice pack wrapped in a towel or cloth on your forehead or at the back of your neck.
What is the best way to diagnose migraines?
Diagnosis. If you have migraines or a family history of migraines, a doctor trained in treating headaches (neurologist) will likely diagnose migraines based on your medical history, symptoms, and a physical and neurological examination. If your condition is unusual, complex or suddenly becomes severe, tests to rule out other causes ...
How long does dihydroergotamine last?
Available as a nasal spray or injection, this drug is most effective when taken shortly after the start of migraine symptoms for migraines that tend to last longer than 24 hours. Side effects can include worsening of migraine-related vomiting and nausea.
What are the two types of medications used to treat migraines?
Medications used to combat migraines fall into two broad categories: Pain-relieving medications. Also known as acute or abortive treatment, these types of drugs are taken during migraine attacks and are designed to stop symptoms. Preventive medications.
What medications can help with migraines?
Blood pressure-lowering medications. These include beta blockers such as propranolol (Inderal, InnoPran XL, others) and metoprolol tartrate (Lopressor). Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil (Verelan) can be helpful in preventing migraines with aura. Antidepressants .
Can you take ubrogepant with a CYP3A4 inhibitor?
Ubrogepant should not be taken with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor drugs . CGRP antagonists. Ubrogepant (Ubrelvy) and rimegepant (Nurtec ODT) are oral CGRP antagonists recently approved for the treatment of acute migraine with or without aura in adults.
Is ubrogepant good for migraines?
It's the first drug of this type approved for migraine treatment. In drug trials, ubrogepant was more effective than placebo in relieving pain and other migraine symptoms such as nausea and sensitiv ity to light and sound two hours after taking it . Common side effects include dry mouth, nausea and excessive sleepiness.
How to manage migraines?
One of the important parts in managing patients with migraine is to help them learn how to manage their own illness. This includes educating them about the cascade of events that occurs with each attack. Understanding that early treatment will improve response to therapy is an important component to also realizing that this approach will lead to less medication use and less disability. Learning how to recognize migraine versus other headache types (e.g., tension-type headache) will also help the patient to know when to take a migraine-specific medication or other analgesic. Preliminary studies have been done that assess the efficacy of giving triptans during an aura. When given during an aura, triptans do not show consistent efficacy in aborting or preventing the migraine. Therefore, until further studies are done, it is also helpful to educate the patient to not take their triptan during the aura phase but rather early in the pain phase of the attack.
How is migraine treated?
Pharmacologic treatment of migraine can involve both acute and preventive interventions. Patients with frequent headache may require both approaches. Acute treatment is aimed at aborting the headache, whereas preventive treatment is geared toward reducing the frequency and severity of anticipated attacks.
How long does it take for triptans to work?
Triptans, relative to nonspecific therapies, including analgesics and NSAIDs, provide rapid onset of action (between 15 minutes and 1 hour, depending on the formulation), are highly effective in relieving migraine pain symptoms, and have a favorable side effect profile.
What is the pharmacologic treatment for migraine?
The pharmacologic treatment of migraine encompasses several stages. Choice of initial acute therapy depends on the severity and intensity of the migraine, the presence of comorbid conditions, patient preferences, and past therapeutic response profile.
What are nonspecific treatments?
Nonspecific treatments are those effective for any pain disorder and include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), combination analgesics, opioids, neuroleptics/antiemetics, and corticosteroids. Specific therapies, such as ergotamine-containing compounds, DHE, and triptans, are effective only for the treatment of migraine ...
What are the triggers of migraines?
Dietary factors are also frequently reported triggers, although few have been scientifically validated. Although the impact of food triggers probably is not great for the population, their impact could be for the individual. Oversleeping and sleep deprivation are commonly recognized triggers. Patients should maintain a routine bedtime and avoid sleeping in.Hormonal headaches are triggered by variations in female estrogen levels and possibly other hormonal factors. Noise, bright lights, and fumes are commonly identified migraine triggers. Physical exertion can cause headache of the subtype, exercise-induced migraine.
What is the first strategy for therapy?
There are two strategies for initial therapy: step care and stratified care. Step careis the use of medications in a sequential order, based on a predetermined plan. Therapy starts with the lowest level of treatment, independent of the characteristics of the attack.
Is KP Washington a headache medication?
KP Washington and national headache guidelines advise against the use of opioids and butalbital-containing medications (e.g., Fiorinal, Floricet) for treatment of headaches. Print out and share or encourage your patients to view the Choosing Wisely guide on the low value and risks of using opiates for headache:
Does yoga help with headaches?
The more recent published literature on the effects of yoga on headache includes a systematic review with meta-analysis (Anheyer 2019) that investigated the effect of yoga on headache disorders, and an RCT(Kumar 2020) that evaluated the effectiveness of yoga as an adjuvant to conventional medical management on clinical outcomes in patients with migraine.
Is Cefaly more effective than sham?
One high-quality randomized controlled trial indicates that transcuta neous supraorbital stimulation using the Cefaly device may be more effective than sham procedure in the short term as prevention therapy.
Is butterbur safe for migraines?
Very low-strength evidence suggests that butterbur may be effective in the prophylactic treatment of migraine headaches; however, there is insufficient evidence to determine its long-term efficacy or safety, and there are concerns regarding the association between butterbur and liver toxicity. According to the literature, it is unclear if hepatotoxicity is due to alkaloids in the formulation or in the butterbur itself.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Migraine treatment is aimed at stopping symptoms and preventing future attacks. Many medications have been designed to treat migraines. Medications used to combat migraines fall into two broad categories: 1. Pain-relieving medications.Also known as acute or abortive treatment, these types of drugs are taken during migraine attacks and are designed to stop sym…