Medication
To treat a mild infection at home:
- Stay hydrated. Drink water and clear liquids if you’re experiencing vomiting or diarrhea.
- Switch between acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce any fever or muscle aches.
- Try the BRAT diet. While your intestines return to normal, eating foods that are easy to process can help. ...
Are there any home remedies for Listeria?
Listeria infections are associated with a high mortality rate, and thus effective antibiotic treatment is essential. Although a variety of antibiotics have activity against the organism, ampicillin alone or in combination with gentamicin remains the treatment of choice.
How to cure Listeria?
Method 1 Method 1 of 3: Treating Listeriosis On Your Own Download Article
- Recognize the signs and symptoms of a Listeria infection. Fever, muscle aches, nausea and diarrhea are all common symptoms of listeriosis.
- Allow your immune system to combat the infection naturally. [2] ...
- Get plenty of rest. ...
- Drink plenty of fluids. ...
- Boost your immune system. ...
How do doctors treat Listeria infection?
Treatment of listeria infection varies, depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms. Most people with mild symptoms require no treatment. More-serious infections can be treated with antibiotics. During pregnancy, prompt antibiotic treatment might help keep the infection from affecting the baby.
Is there a cure for a Listeria infection?

Can antibiotics help listeria?
Treatment of listeria infection varies, depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms. Most people with mild symptoms require no treatment. More-serious infections can be treated with antibiotics.
Can Listeria be treated with amoxicillin?
Amoxicillin is the keystone of listeriosis treatment and should be swiftly prescribed when L. monocytogenes is isolated during pregnancy. In addition, some experts recommend empiric amoxicillin therapy in the presence of high-level clinical suspicion, without consensus on treatment dosage and duration [4].
Does penicillin treat Listeria?
Despite early reports of penicillin resistance in L monocytogenes, more recent work and much clinical experience have shown that ampicillin and penicillin, given in daily doses of more than 6 g, are probably equally effective against L monocytogenes.
What antibiotics treat Listeria in pregnancy?
Penicillin, ampicillin, and amoxicillin have been used most extensively in the treatment of listeriosis. Most experts recommend 6 g or more per day of ampicillin for treatment during pregnancy. This dosage provides adequate intracellular penetration and crosses the placenta in adequate amounts.
Does azithromycin treat Listeria?
Antibiotics effective against Listeria species include ampicillin, vancomycin, ciprofloxacin, linezolid and azithromycin. However, early diagnosis is the exception rather than the rule, since the first signs of a case or an outbreak are reports of stillbirth or serious infections resembling listeriosis.
Can ciprofloxacin treat Listeria?
Among food-related infections, listeriosis has a high case-fatality rate (∼25%) [1]. Ciprofloxacin has been demonstrated to be bacteriostatic against Listeria [4] in usual concentrations. Of the “older” quinolones, ciprofloxacin is the most effective against L.
Does doxycycline treat Listeria?
When penicillin is contraindicated, doxycycline can be used to treat: Syphilis caused by Treponema pallidum. Yaws caused by Treponema pertenue. Listeriosis due to Listeria monocytogenes.
Does ceftriaxone treat Listeria?
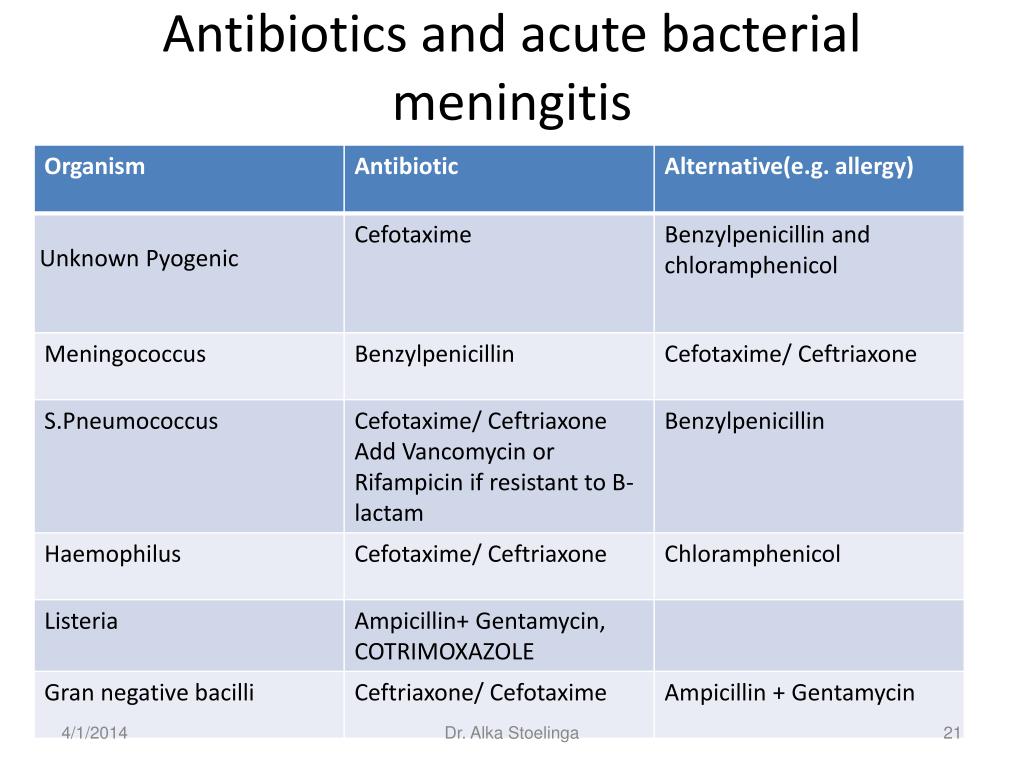
Selected Drug Comments Ceftriaxone/cefotaxime. Cephalosporins do not have activity against Listeria. This is important to remember in the empiric selection of drugs for pyogenic meningitis. Often added to ampicillin to achieve synergy.
Does levofloxacin cover Listeria?
We report a case of acute bacterial meningitis due to Listeria monocytogenes whose successful treatment was mainly attributable to high-dose levofloxacin therapy (500 mg iv bid). This supports the hypothesis that levofloxacin may be an effective option for the treatment of listerial meningitis.
How long do you take antibiotics for listeria?
In either case, if the diagnostic test comes back positive for a listeria infection, the “standard” treatment is a 14- to 21-day course of intravenous (IV) antibiotics using the drugs ampicillin and gentamicin, which provide more protection against the harmful bacteria than oral doses.
Can cephalexin treat listeria?
Listeria is not susceptible to cephalosporins of any generation. Therefore, cephalosporins should not be used to treat Listeria infections.
What happens if I get listeria while pregnant?
During the first trimester of pregnancy, listeriosis may cause miscarriage. As the pregnancy progresses to third trimester, the mother is more at risk. Listeriosis can also lead to premature labor, the delivery of a low-birth-weight infant, or infant death.
What is the treatment for listeria?
In higher-risk individuals (including those who are pregnant or have compromised immune systems) treatment for a listeria infection typically means intravenous antibiotics administered in a hospital. Shutterstock. A listeria infection can be a life-threatening condition — one that requires urgent medical attention.
How long does it take to recover from a listeria infection?
Patients treated early on for listeriosis — and who don’t develop sepsis, meningitis, or any of the infection’s more serious systemic complications — tend to recover quickly and completely; usually within a matter of weeks, according to a report published in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases. ( 5 ) Anyone who takes an antibiotic may experience some side effects, including an upset stomach or other gastrointestinal symptoms. But these usually subside within a month, noted a study published in September 2017 in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine. ( 6)
What test can you take to confirm a listeria infection?
If you are experiencing symptoms and think you may have been exposed to listeria and you are pregnant, elderly, or immunocompromised, your doctor may pursue diagnostic testing to confirm a listeria infection — usually a blood test or other fluid test . Your doctor may also start you on a course of oral antibiotics.
How long does it take for Listeria to show up?
(1) It’s important to note that while symptoms usually show up within 24 hours, they may take up to two months to emerge.
What to do if pregnant woman has a fever?
If a pregnant woman has a fever coupled with other listeriosis symptoms, her doctor will likely start her on a course of intravenous antibiotics while ordering blood or placenta testing to check for the infection. (4) RELATED: What All Pregnant Women Should Know About the Risks of Listeria.
Can you get rid of Listeria on its own?
People Exposed to Listeria Who Do Have Symptoms Should See a Doctor. If you and your doctor believe you’ve been exposed to listeria and you have symptoms — stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea — your immune system will likely get rid of the infection on its own . For these individuals, doctors typically do not recommend testing or treatment.
Do you need to see a doctor if you ate Listeria?
You’re pretty sure you ate something contaminated with listeria bacteria, and you noticed some symptoms. But before you had the chance to see a doctor, your symptoms went away. Good news: You don’t require any testing or treatments, according to the CDC.
How to treat Listeria?
Treatment of listeria infection varies, depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms. Most people with mild symptoms require no treatment. More-serious infections can be treated with antibiotics. During pregnancy, prompt antibiotic treatment might help keep the infection from affecting the baby.
What to do if you have eaten listeria?
Preparing for your appointment . If you have eaten food that has been recalled because of listeria contamination, see a doctor only if you have signs and symptoms of a listeria infection.
What is the best treatment for listeriosis?
Treatment of listeriosis. Ampicillin is currently the drug of choice for treating L. monocytogenes infections. Many antibiotics have been shown to be effective and are used as second-line agents. However, further study is required for some of the most recently introduced antibiotics, such as the fluoroquinolones, to determin ….
What is the second line for Listeria?
Some patients may require alternative therapies due to allergies or certain disease states. Second-line agents for these cases include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole , erythromycin, vancomycin, and the fluoroquinolones. Cephalosporins are not active against Listeria.
Is Listeria a high mortality disease?
Listeria infections are associated with a high mortality rate , and thus effective antibiotic treatment is essential. Although a variety of antibiotics have activity against the organism, ampicillin alone or in combination with gentamicin remains the treatment of choice.
How does Listeria get rid of food?
Listeria is a resilient bacteria that is hard to get rid of once it has contaminated food products. Even freezing is not enough to get rid of the bacteria. Listeria is killed by by cooking, so make sure all meats are thoroughly cooked all the way through. [8]
Where can I find Listeria bacteria?
It is generally improperly processed deli meats or unpasteurized dairy products that are responsible for carrying Listeria bacteria, but it is also found in soil and on vegetables. Pay attention to any outbreaks of listeriosis that are reported in your area, or to any products that have been recalled from the supermarket due to concern ...
How do you know if you have Listeria?
Recognize the signs and symptoms of a Listeria infection. Fever, muscle aches, nausea and diarrhea are all common symptoms of listeriosis. In more severe cases, the infection may spread to your nervous system, leading to a stiff neck, a headache, loss of balance, convulsions, and/or an altered level of consciousness.
Why do they give antibiotics to newborns?
Normally, a few different antibiotics will be given to your newborn in order to provide the maximum treatment possible. Your newborn will also be monitored (usually in the hospital setting) where the doctors can keep track of his or her vital signs and overall health.
How to boost your immune system when you are sick?
Boost your immune system. Consuming vitamin C may also help to boost your immune system when you are sick. Echinacea tablets or teas and zinc may also help as natural ways to boost your immune system; however, neither have been validated in official medical trials.
Is Listeria dangerous to a newborn?
If Listeria infects a newborn, it can be especially dangerous . As such, it requires prompt medical treatment and ongoing monitoring, usually in a hospital setting. If your newborn appears ill and has any of the symptoms mentioned above, seek prompt medical attention for diagnosis.
Do you need antibiotics for Listeria?
Antibiotics are generally not needed in healthy adults with a mild infection, whose immune systems are competent enough to fight off the infection; however, antibiotics are generally offered to: People in whom the Listeria bacteria has spread to infect their nervous system, which always requires emergency medical care.
What is Listeria infection?
Overview. Listeria infection, also known as listeriosis, is caused by the bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. These bacteria are most commonly found in foods that include: unpasteurized dairy products. certain deli meats. melons. raw vegetables. Listeriosis isn’t serious in most people.
How does listeria develop?
Listeriosis develops after you come into contact with the bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. Most commonly, a person contracts listeria after eating contaminated food. A newborn can also get it from their mother.
How long does it take for a baby to recover from a bacterial infection?
If your infection becomes invasive, recovery may take up to six weeks. You may also need to stay in the hospital during part of your recovery so you can have IV antibiotics and fluids. An infant born with the infection may be on antibiotics for several weeks while their body fights the infection.
What to do if you have listeriosis while pregnant?
If you’re pregnant and have listeriosis, your doctor will want to begin treatment with an antibiotic. They’ll also monitor your baby for signs of distress. Newborn babies with an infection will receive antibiotics as soon as they’re born.
What foods are not killed by Listeria?
unpasteurized dairy products, including soft cheeses and milk. some processed dairy products, including ice cream. raw vegetables and fruit. Listeria bacteria are not killed in the cold environments of refrigerators and freezers.
How long does it take for a symtom to show after eating contaminated food?
Symptoms can begin within one to three days after eating contaminated food. The mildest symptom is a flu-like illness with diarrhea and fever. Some people don’t experience the first symptoms until days or weeks after exposure. Symptoms will last until the infection is gone.
How to know if you have listeriosis?
If you have a compromised immune system, it’s important you check in with your doctor.
MICROBIOLOGY
Sero-types 1/2a, 1/2b, and 4b cause almost all human infections and serotype 4b is associated with outbreaks.
Infections
If started as empiric therapy and patient found to have Listeria- stop dexamethasone.
Prevention: High Risk Persons
Asymptomatic: no testing or treatment. Instruct to report sx of fever, GI disease, etc. within next 2 months as at risk.
OTHER INFORMATION
Although part of its name, human monocytosis uncommon--seen in experimental animal studies in rabbits.
Class Summary
These agents are used for suspected bacterial infections. Ampicillin in combination with an aminoglycoside such as gentamicin is the therapy of choice. Listeria is not susceptible to cephalosporins of any generation. Therefore, cephalosporins should not be used to treat Listeria infections.
Ampicillin (Marcillin, Omnipen, Polycillin, Principen)
DOC. Interferes with synthesis of cell wall mucopeptide during active multiplication, resulting in bactericidal activity.
Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim (Bactrim, Cotrim, Septra)
Second-line DOC for non-neonatal penicillin-allergic patients. Inhibits bacterial growth by inhibiting synthesis of dihydrofolic acid.
Penicillin G (Pfizerpen)
Can be used as an alternative to ampicillin. Interferes with synthesis of cell wall mucopeptide during active multiplication, resulting in bactericidal activity.
