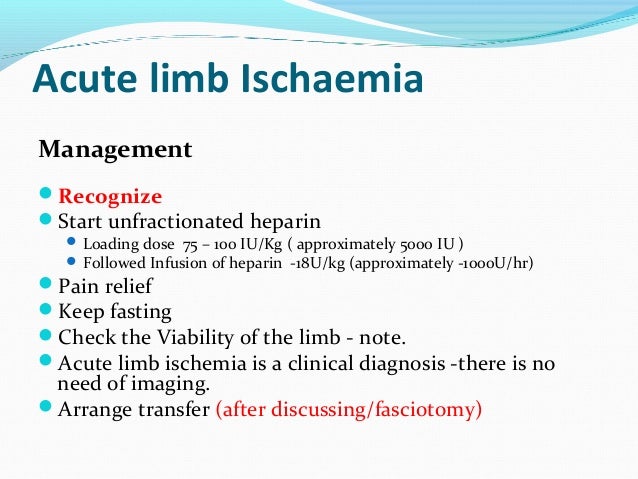
Medication
The success of your recovery after compartment syndrome surgery will highly depend on your commitment to your physiotherapy programme as well as the condition of your leg prior to the surgery. Recovery will take up to three months.
Procedures
- Pain: the most common sign that people describe as being extreme and out of proportion to the injury. ...
- Passive stretch: muscles lacking in blood are very sensitive to stretching, so extending the affected limb leads to extreme pain.
- Paresthesia: this is a weird sensation, such as tingling or pricking, sometimes described as pins and needles.
Therapy
The pressure is painful and can be dangerous. Compartment syndrome can limit the flow of blood, oxygen and nutrients to muscles and nerves. It can cause serious damage and possible death. Compartment syndrome occurs most often in the lower leg.
Self-care
Your doctor may recommend nonsurgical treatment methods first, including:
- physical therapy to stretch the muscle
- anti-inflammatory medication
- changing the type of surface you exercise on
- performing low-impact activities as part of your exercise routine
- elevating the extremity
- resting after activity or modifying the activity
- icing the extremity after activity
Nutrition
What is the recovery time for compartment syndrome surgery?
What are the early signs of compartment syndrome?
Is compartment syndrome really bad?
How do you treat treatment compartment syndrome?
What helps with compartment syndrome pain?
Doctors may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen to reduce inflammation and swelling in the affected muscle compartments and alleviate pain. These medications are available without a prescription and are taken by mouth.
Is compartment syndrome surgery painful?
You will experience pain, swelling and reduced mobility in your lower leg after compartment syndrome surgery. You will have a large wound in the area of the fasciotomy which may be covered with light dressing. It is not advised to cast, splint or compress the affected limb after the surgery.
Which type of treatment is used to treat compartment syndrome?
Surgical options. A surgical procedure called fasciotomy is the most effective treatment of chronic exertional compartment syndrome. It involves cutting open the inflexible tissue encasing each of the affected muscle compartments. This relieves the pressure.
What are 3 ways to treat compartment syndrome?
Chronic (Exertional) Compartment Syndrome Physical therapy, orthotics (inserts for shoes), and anti-inflammatory medicines may be of limited benefit in relieving symptoms and generally do not allow return to full activity.
How long does compartment syndrome surgery take to heal?
Complete recovery from compartment syndrome typically takes three or four months.
Does ice help compartment syndrome?
Chronic compartment syndrome usually responds well to rest from activities that cause pain. Ice and elevation along with anti-inflammatory medications will help to control the swelling that causes the pressure.
Is massage good for compartment syndrome?
Sports massage can reduce the tension in the muscles in the affected compartment. This, in turn, reduces the strain on the tendons attached to the bone of the compartment, allowing it to heal. It also prevents the Syndrome from re-occurring once you resume your sport.
Do you elevate leg with compartment syndrome?
If a developing compartment syndrome is suspected, place the affected limb or limbs at the level of the heart. Elevation is contraindicated because it decreases arterial flow and narrows the arterial-venous pressure gradient.
What causes compartment syndrome after surgery?
Abstract. Purpose: Acute compartment syndrome is known to develop after trauma or after postischemic revascularization. It also can occur when a patient has been lying in the lithotomy position during prolonged surgery.
Can compartment syndrome heal itself?
To diagnose chronic compartment syndrome your doctor will measure the pressures in your compartment, after ruling out other conditions like tendinitis or a stress fracture. This condition can resolve itself after discontinuing activity. Other treatment options are nonsurgical: Physical therapy.
Will stretching help compartment syndrome?
Stretching techniques can be used to help restore motion in these joints to minimize undue muscle tension. Muscle Strengthening. Hip and core weakness can influence how your lower body moves, and can cause imbalanced forces through the lower-leg muscle groups that may contribute to compartment syndrome.
How do you get rid of leg pain fast?
If you have leg pain from cramps or overuse, take these steps first:Rest as much as possible.Elevate your leg.Apply ice for up to 15 minutes. ... Gently stretch and massage cramping muscles.Take over-the-counter pain medicines such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome occurs when excessive pressure builds up inside an enclosed muscle space in the body. Compartment syndrome usually results from bleeding or swelling after an injury. The dangerously high pressure in compartment syndrome impedes the flow of blood to and from the affected tissues. It can be an emergency, requiring surgery ...
What does exertional compartment syndrome feel like?
Exertional compartment syndrome can feel like shin splints and be confused with that condition. Abdominal compartment syndrome usually develops in people who are hospitalized and critically ill on life support. They usually cannot describe their symptoms.
How long does it take for compartment syndrome to develop?
Compartment Syndrome Symptoms. Acute compartment syndrome usually develops over a few hours after a serious injury to an arm or leg. Some symptoms of acute compartment syndrome include: A new and persistent deep ache in an arm or leg. Pain that seems greater than expected for the severity of the injury.
What is the most common type of compartment syndrome?
Acute compartment syndrome is the most common type of compartment syndrome. About three-quarters of the time, acute compartment syndrome is caused by a broken leg or arm. Acute compartment syndrome develops rapidly over hours or days.
How long does it take for cramps to go away after exercise?
Symptoms of chronic compartment syndrome (exertional compartment syndrome) include worsening aching or cramping in the affected muscle (buttock, thigh, or lower leg) within a half-hour of starting exercise. Symptoms usually go away with rest, and muscle function remains normal.
What happens to the fascia after injury?
After an injury, blood or edema (fluid resulting from inflammation or injury) may accumulate in the compartment. The tough walls of fascia cannot easily expand, and compartment pressure rises, preventing adequate blood flow to tissues inside the compartment.
Can steroids cause compartment syndrome?
Taking anabolic steroids can also contribute to developing compartment syndrome. Another form of compartment syndrome, called chronic compartment syndrome, develops over days or weeks. Also called exertional compartment syndrome, it may be caused by regular, vigorous exercise.
What is compartment syndrome?
COMPARTMENT syndrome is a potentially devastating postoperative complication that can occur during or after surgery. It is a tissue injury that causes pain, erythema, edema, and hypoesthesia of the nerves in the affected area. In general, fasciotomy must follow clinical diagnosis quickly ...
Can compartment syndrome occur in a supine position?
Compartment syndrome is considered to occur primarily in patients who undergo procedures while in the lithotomy position. Our data confirm that compartment syndrome is more likely to develop with no apparent cause when the patient is in the lithotomy position than in a supine position. However, we were surprised by three of our findings: (1) patients in lateral decubitus positions unexpectedly had a high frequency of compartment syndrome, (2) compartment syndromes necessitating fasciotomies of the upper extremities developed in three patients (23%), and (3) nearly half of the patients in whom compartment syndromes developed in the lower extremities underwent procedures while in the supine position. There are few case reports of upper extremity compartment syndrome with causes other than trauma or vascular surgery. With the exception of a few reports of compartment syndrome developing in the lower extremities of patients who were positioned prone in “tucked,”“kneeling,” or “knee-chest” positions for lumbar spine surgery, 13–15 nearly all other reports of position-related compartment syndrome of the lower extremities occur in patients undergoing procedures while in the lithotomy position.
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome is an elevation of intracompartmental pressure to a level that impairs circulation. While the most common etiology is trauma, other less common etiologies such as burns, emboli, and iatrogenic injuries can be equally troublesome and challenging to diagnose. The sequelae of a delayed diagnosis of compartment syndrome may be ...
Is parasthesia a symptom of compartment syndrome?
Further, parasthesias may occur as an early symptom in acute compartment syndrome, represent ing a potentially reversible state because peripheral nerves are more sensitive to ischemia than muscle [26]. It is thought that irreversible ischemic changes begin approximately 8 h after the onset of ischemia [15].
How to prevent compartment syndrome?
Load up on anti-inflammatory foods to help flood your body with as many healing nutrients as possible. 2. Remove Constricting Casts or Bandages.
What are the symptoms of compartment syndrome?
When someone experiences compartment syndrome symptoms can include: ongoing, deep pains or aches (especially in the limbs or abdomen, depending on where the condition develops) numbness, tingling, light shocks, or the feeling of “pins and needles”. high levels of swelling, pressure, tightness and bruising around the injury.
What is a shin split?
Shin splits are very similar to exertional compartment syndrome and cause a lot of pains and aches in the muscles, tissue and bones of the lower legs after high levels of repetitive movements or exercise.
How long does compartment syndrome last?
While acute compartment syndrome is much more common, longer-term cases of compartment syndrome called chronic compartment syndrome can develop that last for up to several weeks. This type is sometimes caused from ongoing vigorous exercise that the body cannot adjust to, called exertional compartment syndrome.
What to do if fascia doesn't work?
If this doesn’t work, removing part of the fascia (fasciectomy) is also sometimes needed. If fascia cannot stretch far enough to enclose the compartment, a skin graft might be needed to cover the wound so it can heal. Your doctor might also recommend taking anti-inflammatory medicines while you heal.
How long does it take for a nerve to heal in a muscle?
Luckily, the muscles and nerves inside the compartment recover well if they aren’t left cut off from blood flow for too long — however, if it takes a while for a diagnosis to be made, permanent nerve injury and loss of muscle function are possible within just 12–24 hours (called Volkmann’s ischemia ).
Why do you wear a bandage after surgery?
wearing a tight cast or bandage in order to heal a wound (which keeps the compartment from moving at all) a limb being cut off from blood flow during a period of unconsciousness (such as after fainting or getting in an accident) following surgery, especially if the surgery involved blood vessels.
How to treat acute compartment syndrome?
The treatment for acute compartment syndrome is surgery (fasciotomy). The surgeon (either an orthopedic or general surgeon) will perform a fasciotomy (see last reference for video of procedure), an operation where the thick, fibrous bands that line the muscles are filleted open, allowing the muscles to swell and relieve the pressure within the compartment (similar to splitting open the casing of a sausage). Depending upon the amount of swelling (edema), a second operation may be required later to close the skin after the swelling has resolved.
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome is a condition that occurs when injury causes generalized painful swelling and increased pressure within a compartment to the point that blood cannot supply the muscles and nerves with oxygen and nutrients. Muscles in the forearm, lower leg and other body areas are surrounded by fibrous bands of tissues.
What happens when you compress a muscle group?
The weight of an object (or the weight of the body itself) compressing a muscle group can cause rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown). Compartment swelling may occur after the blood supply is re-established (reperfusion swelling) to an area that has lost it for a period of time.
How long does compartment syndrome last after exercise?
Chronic or exercise induced compartment syndrome rarely requires any treatment; the pain and other symptoms usually stop minutes to hours after the activity is stopped.
What is the high index of suspicion for acute compartment syndrome?
While it is uncommon, the health care practitioner has to have a high index of suspicion for acute compartment syndrome if a patient presents with excessive pain, numbness, and a tense extremity after an injury. The patient’s history of an injury to the extremity often is all that is necessary for a diagnosis.
What happens if you don't treat a muscle injury?
If the condition is not recognized and treated, the whole muscle can die, scar down, and contract. Similarly, nerve cells that are damaged may fail causing numbness and weakness in the structures beyond the injury site. If infection or necrosis develops, the individual may need the limb amputated to prevent death.
Can compartment pressure be measured before exercise?
Chronic compartment syndrome may be diagnosed clinically but compartment pressures may be measured before and after exercise to confirm the diagnosis. The health care professional should also explore other potential causes of pain due to exercise, including stress fractures, shin splints, or tendon inflammation.
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome (SIN-drohm) is a condition that occurs when pressure increases within a compartment (closed space) in the body. Inside this compartment are muscle tissues, nerves, and blood vessels that are enclosed by a fascia. The fascia is a thick layer of special protective tissue that does not expand (grow).
What tests are used to diagnose compartment syndrome?
Blood and urine tests, muscle compartment measurement, and laser doppler flowmetry may be used to diagnose compartment syndrome. Treatment may include removing a tight cast, medicines for pain, or surgery to decrease the pressure and swelling.
Why do you put a splint on your arm?
Caregivers may put a splint on your arm or legs to stop your injured limb from moving while it heals. It may also be used to decrease pain. A splint is made of plaster or fiberglass. Ask your caregiver for more information on brace or splint care.
What does it mean when your splint is soaked in blood?
You have trouble breathing, pain in your chest, or confusion. Your injured limb or the area around it turns blue or white, or feels cold and numb. Your bandages, splint, or wound becomes soaked with blood. Your pain or swelling is not relieved or is getting worse even after taking medicine.
How does physical therapy help with pain?
These exercises help improve movement and decrease pain. Physical therapy can also help improve strength and decrease your risk for loss of function . Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy (OT) uses work, self-care, and other normal daily activities to help you function better in your daily life.
What to do when you feel like you need to rest?
Rest when you feel it is needed. Walking: You may need to use a cane, walker or crutches. This may help you get around and decrease your chances of falling or getting hurt. Ask your caregiver how to use your cane, walker, or crutches correctly.
How to make sure you're getting the best possible treatment for your post-surgical pain?
In order to make sure you’re getting the best possible treatment for your post-surgical pain, experts advise taking an active role and keeping the channels of communication open between you and your doctor -- starting before your operation.
What to do after surgery?
After your surgery, it’s important that you communicate openly with your doctors and nurses about what you’re feeling while you recover. Talk about your pain. Now is not the time to tough it out. If you have pain -- whether it's at the site of the incision or elsewhere in your body -- tell your doctors and nurses.
Why do people with sleep apnea need a CPAP machine?
He recommends that people with sleep apnea bring their continuous positive airway pressure ( CPAP) machine to the hospital to assist their breathing while they sleep. Anxiety and depression can make pain worse and much more difficult to manage. Understandably, both are very common in people having surgery.
What does it mean when a doctor says "We're going to have to operate"?
Hearing your doctor utter the words, "We’re going to have to operate," can send a shiver down your spine. Immediately, questions about the seriousness of your condition, the procedure itself, and the likelihood that it will cure what ails you flood the mind. Then, there is the prospect of post-surgery pain. How badly is this going to hurt?
Can chronic pain medication be used long term?
In addition, people with chronic pain conditions often take medication to manage it. Long-term use of pain medication can lead to medication tolerance, meaning the drugs don’t work as well as they once did to block pain and that greater dosages are needed to get the same effect.
Can pre-existing conditions cause pain after surgery?
Pre-existing medical conditions can complicate pain management after surgery. According to Fraifeld, there are a few conditions that commonly interfere with post-surgical pain management.
Can you wait too long to take pain medicine?
A common mistake people make, according to Fraifeld, is waiting too long to take pain medication. By the time you’re in pain, you’re starting from behind the eight ball. "It takes a lot more medicine to control pain after it’s started as opposed to starting it ahead of time," he says.