Procedures
Treatment for a pneumothorax usually involves inserting a needle or chest tube between the ribs to remove the excess air. However, a small pneumothorax may heal on its own. The main symptoms of a pneumothorax are sudden chest pain and shortness of breath. Severity of symptoms may depend on how much of the lung is collapsed.
What is the treatment for a pneumothorax?
The medical provider needs to be keenly aware that there is a high probability of a tension pneumothorax if the patient has an open trauma to the chest wall. Good assessment skills, proper equipment, and the training to effectively relieve a tension pneumothorax are vital to save patients from this critical condition.
What to do if there is a high probability of pneumothorax?
D: All of the options listed should be assessed by the nurse in a patient with pneumothorax. A: Tracheal alignment should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax. B: Expansion of the chest should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax. C: Breath sounds should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax.
Which options should the nurse assess in a patient with pneumothorax?
The patient in this condition will die if treatment is not provided. For an open pneumothorax, treatment requires sealing the open wound with an occlusive dressing. This is often taught by using Vaseline gauze and securing the gauze to the patient's chest with tape.
What happens if a patient with a pneumothorax is not treated?

What is the first line treatment for pneumothorax?
If confirmed by other studies, the first line of treatment in a first episode of spontaneous pneumothorax has definitely to be observation, or needle aspiration if some treatment has to be offered to the patient.
What is right sided pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is an extrapulmonary air accumulation within the pleural space between the lung and chest wall. Once pneumothorax acquires tension physiology, it turns into a potentially lethal condition requiring prompt surgical intervention.
How do you treat a pneumothorax injury?
Treatment of Traumatic Pneumothorax The goal of treatment is to remove the air from the pleural space and allow the lung to reinflate. Usually, a tube ( thoracostomy. The procedure is done... read more or chest tube) is inserted into the chest between two ribs.
Which position is best for pneumothorax?
Probably the most widely accepted postbiopsy techniques used to reduce the incidences of pneumothorax and of pneumothorax that requires treatment are the recumbent position and the puncture-site–dependent position (,5,,10,,14–,17).
What are 3 signs and symptoms of a pneumothorax?
What are the Symptoms of Pneumothorax?Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens when trying to breath in.Shortness of breath.Bluish skin caused by a lack of oxygen.Fatigue.Rapid breathing and heartbeat.A dry, hacking cough.
How is a partially collapsed lung treated?
Your doctor treats a collapsed lung by basically getting rid of the pressure outside the lung so it can inflate again. In cases so minor that no symptoms show up, the lung may expand again on its own. Some people may need to temporarily breathe oxygen from a container to help.
Can pneumothorax be treated with medication?
Medication Summary A tension pneumothorax requires treatment with rapidity. However, anesthetics and analgesics should be used if the patient is not in distress. The goals of pharmacotherapy are to reduce morbidity and to prevent complications.
What are the three types of pneumothorax?
What are the different types of collapsed lung?Primary spontaneous pneumothorax: Collapsed lung sometimes happens in people who don't have other lung problems. ... Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: Several lung diseases may cause a collapsed lung. ... Injury-related pneumothorax: Injury to the chest can cause collapsed lung.More items...•
How do you inflate a collapsed lung?
This is called aspiration. using a chest drain. This is a flexible plastic tube that's inserted through the chest wall, after the area is numbed. The drain allows air out but not back in, so your lung can re-inflate.
How is pneumothorax managed?
Treatment options may include observation, needle aspiration, chest tube insertion, nonsurgical repair or surgery. You may receive supplemental oxygen therapy to speed air reabsorption and lung expansion.
How do you treat a spontaneous pneumothorax at home?
How can you care for yourself at home?Get plenty of rest and sleep. ... Hold a pillow against your chest when you cough or take deep breaths. ... Take pain medicines exactly as directed. ... If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed.More items...
What size pneumothorax needs a chest tube?
Large (> 25% or apex to cupula distance > 3 cm) pneumothorax requires chest tube placement.
What is the goal of pneumothorax treatment?
The goal of treatment is to relieve the pressure on the lung and allow it to re-inflate. The type of treatment selected will depend on the cause and severity of the collapse, and on the patient’s overall health. For a minor pneumothorax, your doctor may simply keep an eye on you, as the lung may re-inflate on its own, ...
What are the Symptoms of Pneumothorax?
Symptoms normally come on almost immediately and commonly begin with chest pain. Other signals that the problem may be a collapsed lung are:
How to remove air from a collapsed lung?
During a needle aspiration, a needle attached to a syringe is inserted between the ribs into the air-filled space that is pressing on the collapsed lung and is used to suction out the excess air. A chest tube involves a similar insertion that involves a one-way valve device that continuously removes air until the lung re-inflates. The tube may need to stay in for a few hours, or even a few days, to ensure that the lung does not collapse again.
How long does a chest tube stay in?
The tube may need to stay in for a few hours, or even a few days, to ensure that the lung does not collapse again.
What is the next step in a lung leak?
In cases that involve an accident, or repeated collapsed lungs, the next step is a non-surgical repair of the leak. This can be done in several ways and is sometimes called pleurodesis.
Can you go to the hospital after a lung collapse?
Avoiding air travel for the first week after a collapse is often suggested. Diving puts patients at high risk, so most doctors suggest permanently avoiding it . Also, people who smoke are at increased risk of a pneumothorax, so quitting is highly recommended.
How old is too old to have pneumothorax?
The type of pneumothorax caused by ruptured air blisters is most likely to occur in people between 20 and 40 years old, especially if the person is very tall and underweight.
How to tell if you have a collapsed lung?
On some occasions, a collapsed lung can be a life-threatening event. Treatment for a pneumothorax usually involves inserting a needle or chest tube between the ribs to remove the excess air. However, a small pneumothorax may heal on its own.
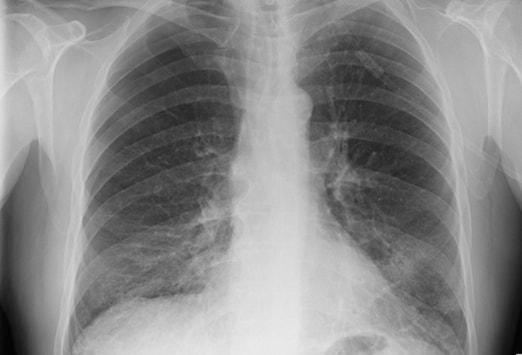
What happens when a lung collapses?
In a collapsed lung, air from the lung leaks into the chest cavity. The example shown is a complete left pneumothorax.
Do pneumothorax run in families?
Genetics. Certain types of pneumothorax appear to run in families.
Can pneumothorax be mechanical?
Mechanical ventilation. A severe type of pneumothorax can occur in people who need mechanical assistance to breathe. The ventilator can create an imbalance of air pressure within the chest. The lung may collapse completely.
How to treat an open pneumothorax?
For an open pneumothorax, treatment requires sealing the open wound with an occlusive dressing. This is often taught by using Vaseline gauze and securing the gauze to the patient's chest with tape. However, this can be a difficult process in the field depending on the size of the wound, the patient's condition, and the area the dressing is applied.
What to do if tension pneumothorax is not improving?
If there is no improvement, the procedure will need to be repeated with another needle placed adjacent to the first needle. Monitor, then reassess the patient. A tension pneumothorax is a life-threatening situation.
What is the condition called when air is trapped in the pleural cavity?
Tension pneumothorax is a life threatening condition that can occur with chest trauma and is more likely to happen with trauma involving an opening in the chest wall. Apr 14, 2021. Tension pneumothorax is a critical condition that can occur with chest trauma when air is trapped in the pleural cavity leading to rapid deterioration ...
What happens when a patient cannot compensate for a pneumothorax?
A tension pneumothorax occurs when the patient cannot compensate, and several events begin to occur that can lead to death. As air fills the pleural space on inspiration through the opening with an open pneumothorax, the wound can act as a one-way valve and not allow the air to exit.
What is a closed pneumothorax?
It is called a closed pneumothorax when the chest wall is intact. With an intact chest wall, a pneumothorax can be caused by several things, but the most frequently encountered cause is from trauma resulting in a rib fracture that punctures a lung, releasing air into the pleural space. The signs and symptoms for a closed pneumothorax are:
When to use needle decompression?
A needle decompression should only be performed if the patient has a tension pneumothorax. When inserting the needle, it should be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the chest wall. This is a critical point as this will position the needle straight into the pleural space. If any other angle is used, there may be a chance of hitting other structures in the area such as major blood vessels or even the heart.
Can pneumothorax be caused by trauma?
This is particularly true for combat and tactical team medics who are working in tactical environments and may often encounter thoracic trauma. Tension pneumothorax is more likely to occur with trauma involving an opening in the chest wall.
Which alignment should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax?
A: Tracheal alignment should be assessed in a patient with pneumothorax.
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is one of the disorders of the chest and lower respiratory tract.
What is the term for a pleural space that is exposed to positive atmospheric pressure?
Pneumothorax occurs when the parietal or visceral pleura is breached and the pleural space is exposed to positive atmospheric pressure.
What is a traumatic pneumothorax?
A traumatic pneumothorax occurs when air escapes from a laceration in the lung itself and enters the pleural space or from a wound in the chest wall.
What are the different types of pneumothorax?
Types of pneumothorax include simple, traumatic, and tension pneumothorax. Simple pneumothorax. A simple or spontaneous pneumothorax occurs when air enters the pleural space through a breach of either the parietal or visceral pleura. Traumatic pneumothorax. A traumatic pneumothorax occurs when air escapes from a laceration in ...
What does chest x-ray show?
Chest x-ray: Reveals air and/or fluid accumulation in the pleural space; may show a shift of mediastinal structures (heart).
What is pleuritic pain?
A: Pleuritic pain is a clinical manifestation of pneumothorax.
How to diagnose pneumothorax?
Diagnosis of pneumothorax is done by thorough clinical examination and investigations. However, clinical interpretation of the presenting signs and symptoms is crucial for correctly diagnosing and treating the condition.
What is pneumothorax in a patient?
A pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air between parietal and visceral pleural cavity .[4] Tension pneumothorax is the accumulation of air under pressure in the pleural space. This condition develops when injured tissue forms a 1-way valve, allowing air to enter the pleural space and preventing the air from escaping naturally. This condition rapidly progresses to respiratory insufficiency, cardiovascular collapse, and ultimately death if, unrecognized and untreated. Favorable patient outcomes require urgent diagnosis and immediate management.
What causes iatrogenic pneumothorax?
The leading cause of iatrogenic pneumothorax is transthoracic needle aspiration. Two factors may be responsible for it, depth and size of the lesion. If the lesion is deeper and the size is smaller chances of traumatic pneumothorax increases.
How does a pneumothorax occur?
A traumatic pneumothorax can result from either penetrating or nonpenetrating chest trauma. With penetrating chest trauma, the wound allows air to enter the pleural space directly through the chest wall or through the visceral pleura from the tracheobronchial tree. With non penetrating trauma, a pneumothorax may develop if the visceral pleura is lacerated secondary to a rib fracture, dislocation. Sudden chest compression abruptly increases the alveolar pressure, which may cause alveolar rupture. Once the alveolus is ruptured, air enters the interstitial space and dissects toward either the visceral pleura or the mediastinum. A pneumothorax develops when either the visceral or the mediastinal pleura ruptures, allowing air to enter the pleural space.[11]
How does pneumothorax cause hypoxia?
The volume of this nonabsorbable intrapleural air increases with each inspiration. As a result, pressure rises within the affected hemithorax; ipsilateral lung collapses and causes hypoxia. Further pressure causes the mediastinum shift toward the contralateral side and compresses both, the contralateral lung and the vasculature entering the right atrium of the heart. This leads to worsening hypoxia and compromised venous return. Researchers still are debating the exact mechanism of cardiovascular collapse but, generally the condition may develop from a combination of mechanical and hypoxic effects. The mechanical effects manifest as compression of the superior and inferior vena cava because the mediastinum deviates and the intrathoracic pressure increases. Hypoxia leads to increased pulmonary vascular resistance via vasoconstriction. If untreated, the hypoxemia, metabolic acidosis, and decreased cardiac output lead to cardiac arrest and death.[9,10]
What is the presence of air and fluid in the chest?
Presence of air and fluid with in the chest might have been documented as early as Fifth Century B.C. by a physician in ancient Greece, who practiced the so-called Hippocratic succession of the chest. This is due to a development of communication between intrapulmonary air space and pleural space, or through the chest wall between the atmosphere and pleural space. Air enters the pleural space until the pressure gradient is eliminated or the communication is closed. Increasing incidence of road traffic accidents, increasing awareness of healthcare leading to more advanced diagnostic procedures, and increasing number of admissions in intensive care units are responsible for traumatic (noniatrogenic and iatrogenic) pneumothorax. Clinical spectrum of pneumothorax varies from asymptomatic patient to life-threatening situations. Diagnosis is usually made by clinical examination. Simple erect chest radiograph is sufficient though; many investigations are useful in accessing the future line of action. However, in certain life-threatening conditions obtaining imaging studies can causes an unnecessary and potential lethal delay in treatment.
What happens when you get stuck in air at 3050 m?
Since the volume of given mass of gas at a constant temperature is inversely proportional to its pressure, so a given volume of air saturated at body temperature expand to 1.5 times the volume at sea level, if it is placed at an altitude of 3050 m, the trapped air in the pleural bleb may rupture resulting in a pneumothorax as seen in air crew members.[12] Similarly in scuba divers, compressed air is delivered to lung by a demand regulators and during ascent barotraumas may occur as ambient pressure falls rapidly, gas contain in the lung expand and cause pneumothorax.[13]
How to treat hemopneumothorax?
The main treatment for hemopneumothorax is called chest tube thoracostomy. This procedure involves placing a hollow plastic tube between the ribs into the area around the lungs in order to drain the air and blood. The tube may be connected to a machine to help with the drainage.
What is the difference between hemothorax and pneumothorax?
Hemopneumothorax is a combination of two medical conditions: pneumothorax and hemothorax. Pneumothorax, which is also known as a collapsed lung, happens when there is air outside the lung, in the space between the lung and the chest cavity. Hemothorax occurs when there is blood in that same space. Only about 5 percent of patients ...
Why do doctors order chest X-rays?
If you have an injury or trauma to your chest, your doctor may order a chest X-ray to help see if fluid or air is building up within the chest cavity.
What causes hemopneumothorax?
Hemopneumothorax is most frequently caused by a trauma or blunt or penetrating injury to the chest.
What to do before thoracostomy?
Before the thoracostomy procedure, depending on the cause of your condition, your doctor may also give you prophylactic antibiotics to help prevent bacterial infections . Your doctor may also prescribe pain medications to help with any pain before and after your surgery.
Does hemopneumothorax have a prognosis?
If the condition was caused by a trauma or injury to the chest, the outlook will depend on the severity of the injury. Spontaneous cases of hemopneumothorax have an excellent prognosis once the fluid and air is removed from the chest. In one small study, all four patients with spontaneous hemopneumothorax recovered completely and their lungs expanded fully after the episode.
Is hemopneumothorax a medical emergency?
Hemopneumothorax is a medical emergency, so it’s important to recognize its symptoms right away.
Why do you give extra oxygen to a pneumothorax?
Extra oxygen may be given if your oxygen level is too low. Oxygen may help the pneumothorax get better faster.
What happens when you have a tension pneumothorax?
With a tension pneumothorax, the injured lung and trapped air push against your uninjured lung. A tension pneumothorax can lead to low blood pressure, decreased oxygen in your blood, and heart problems. Treatments that require cuts in your skin to reach your lung may lead to an infection in the lung area.
How is a traumatic pneumothorax diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and examine you. He or she will listen to your lungs. You may also need any of the following:
What is traumatic pneumothorax?
What is a traumatic pneumothorax and what causes it? A traumatic pneumothorax is when part of your lung collapses. A traumatic pneumothorax is caused by an injury that tears your lung and allows air to enter the pleural space. This is the area between your lungs and your chest wall. The air trapped in your pleural space prevents your lung ...
How does a needle aspiration work?
Needle aspiration: During needle aspiration, a needle covered with a tube is put through your skin and into your pleural space.
Can a small pneumothorax be removed on its own?
If your pneumothorax is small, it may resolve on its own. The goal of treatment is to remove the air from your pleural space. Once your lung is able to fill with air, you will be able to breathe easier. You may need any of the following:
Can you get better with a small pneumothorax?
Treatment will depend on the size of your pneumothorax. If your pneumothorax is small, it may get better on its own. The goal of treatment is to remove the air from your pleural space. When your lung is able to fill with air, you will be able to breathe easier. You may need any of the following:
What do you do when you have a hemothorax?
If you go to the emergency room for hemothorax, your doctor or emergency medical staff will use emergency tools, such as a ventilator with a tube inserted through your nose into your windpipe, to support your breathing and make sure you’re getting enough oxygen . The most important treatment for hemothorax is draining the blood out ...
What causes a hemothorax?
Other possible causes of hemothorax include: 1 blood not clotting properly and leaking into the chest cavity 2 cancer in the lungs 3 fluid and cancer around the lungs, called malignant pleural effusion 4 cancerous tumors in your chest wall 5 large vein torn open when a catheter is inserted while you’re in the hospital 6 tissue around your lungs dying, called pulmonary infarction 7 Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) type 4, a condition that affects your connective tissues
Why does hemothrax happen?
Hemothorax also commonly happens as a complication of a major heart or lung surgery that requires a surgeon to open the chest wall. Blood can leak into the chest cavity if the blood doesn’t clot properly after the surgeon closes the incisions, or if an organ or vessel is cut open and leaks blood.
Why does my chest pool?
The pooling of blood in your chest can have numerous causes. It’s most common after major chest injuries or surgeries that include opening your chest wall, especially heart or lung surgery. Certain conditions that cause your blood not to clot properly can also cause hemothorax.
What is the term for the tissue around the lungs that dies?
tissue around your lungs dying, called pulmonary infarction. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) type 4, a condition that affects your connective tissues. In rare cases, especially outside of the United States and other developed countries, hemothorax can be caused by tuberculosis (TB).
How do you know if you have hemothorax?
The most common symptoms of hemothorax include: pain or feeling of heaviness in your chest. feeling anxious or nervous. dyspnea, or having trouble breathing. breathing quickly. abnormally fast heartbeat. breaking out in cold sweats. skin turning pale. high fever over 100°F (38°C)
How long does a lung tube stay in your chest?
The tube may remain in your chest for several days if your lung has collapsed so that it can expand again. If the bleeding continues even as the tube drains the blood, you may need chest surgery to treat the cause of the bleeding. Chest surgery is also known as thoracotomy.

What Is Pneumothorax?
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Specialist to consult
Clinical Manifestations
- A pneumothorax (noo-moe-THOR-aks) is a collapsed lung. A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This air pushes on the outside of your lung and makes it collapse. A pneumothorax can be a complete lung collapse or a collapse of only a portion of the lung. A pneumothorax can be caused by a blunt or penetra...
Assessment and Diagnosis
Medical Management
Surgical Management
Practice Quiz: Pneumothorax