Explore
Progressive degeneration of the electrical conduction system of the heart can lead to third-degree heart block. This may be preceded by first-degree AV block, second-degree AV block, bundle branch block, or bifascicular block. In addition, acute myocardial infarction may present with third-degree AV block.
What causes third degree AV block?
Third-degree heart block may be caused by:
- Damage to the heart from surgery
- Damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack
- Other types of heart disease that result in heart muscle damage
- Heart valve disease
- Other diseases, including rheumatic fever and sarcoidosis
- Some medicines
What causes third degree block?
- Understand the physiology and anatomy of the cardiac conduction system and normal conduction patterns.
- Identify the different degrees and types of AV block through accurate interpretation of rhythm disturbances.
- Learn how to treat AV block patients, including the administration of atropine and transcutaneous pacing.
How do you treat third degree heart block?
Drugs that most commonly cause first-degree AV block include the following: Class Ia antiarrhythmics (eg, quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide) Class Ic antiarrhythmics (eg, flecainide, encainide, propafenone)
What medications cause AV block?
How do you treat AV blocks?
Permanent pacing is the therapy of choice in patients with symptomatic atrioventricular (AV) block with bradycardia. Temporary transcutaneous or transvenous pacing is required if a slow heart rate (or asystole) caused by AV block requires correction and permanent pacing is not immediately indicated or not available.
What is the pacemaker in 3rd degree AV block?
Third-degree heart block: The electrical signal from the atria to the ventricles is completely blocked. To make up for this, the ventricle usually starts to beat on its own acting as a substitute pacemaker but the heartbeat is slower and often irregular and not reliable.
Do you give atropine for 3rd degree heart block?
There may be some action at the AV-node with atropine, but the effect will be negligible and typically not therapeutic. In most cases, atropine will not hurt the patient with 3rd-degree block unless they are unstable and cardiac pacing is delayed in order to administer atropine.
Can heart block be treated with medicine?
You treatment depends on the type of heart block you have: With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment. With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen. With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.
What is the best treatment for third-degree heart block?
Transcutaneous pacing is the treatment of choice for any symptomatic patient. All patients who have third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block (complete heart block) associated with repeated pauses, an inadequate escape rhythm, or a block below the AV node (AVN) should be stabilized with temporary pacing.
Is atropine used for heart block?
Atropine is indicated for the treatment of bradycardia associated with hypotension, second- and third-degree heart block, and slow idioventricular rhythms. Atropine is no longer recommended for asystole or PEA.
What medication do you give for complete heart block?
Medications that may be used in the management of third-degree AV block (complete heart block) include sympathomimetic or vagolytic agents, catecholamines, and antidotes.
When do you give atropine vs epinephrine?
Epinephrine provides a greater amount of hemodynamic support. Patients dying with bradycardia aren't truly dying from bradycardia itself, but rather from cardiogenic shock (low cardiac output). Atropine offers these patients an increased heart rate, nothing more.
What drugs are contraindicated in heart block?
Topic OutlineNonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aspirin.Calcium channel blockers.Drugs that may cause hyperkalemia.Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.Antidepressants.Oral hypoglycemic agents. Thiazolidinediones. Metformin.Phosphodiesterase inhibitors. PDE-3 inhibitors. PDE-5 inhibitors.Antiarrhythmic agents.More items...•
How do you treat a blocked heart without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Which fruit juice is good for arteries?
Researchers found that pomegranate juice not only appears to prevent hardening of the arteries by reducing blood vessel damage, but the antioxidant-rich juice may also reverse the progression of this disease.
Who needs a pacemaker?
The most common reason people get a pacemaker is their heart beats too slowly (called bradycardia), or it pauses, causing fainting spells or other symptoms. In some cases, the pacemaker may also be used to prevent or treat a heartbeat that is too fast (tachycardia) or irregular.
How does atropine help with heart rate?
The goal of atropine therapy is to improve conduction through the AVN by reducing vagal tone via receptor blockade. Atropine often improves the ventricular rate if the site of block is in the AVN. The peak increase in heart rate occurs in 2-4 minutes after IV administration; the half-life is 2-3 hours.
What is a third degree block?
New-onset third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block (complete heart block) is a medical emergency. Treatment of third-degree AV block is based on the level of the block. A common misconception of an inexperienced clinician is to gauge a patient’s stability according to the heart rate and blood pressure rather than according to the symptoms and level of the block.
What drugs cause AV block?
Common drugs that induce AV block include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics, and digoxin. Withdrawal of the offending drugs is the first treatment for heart block. Cases in which complete heart block results from a calcium channel blocker should be managed in much the same fashion as cases involving other causes ...
What is the treatment for heart block?
The first, and sometimes most important, medical treatment for heart block is the withdrawal of any potentially aggravating or causative medications. Many antihypertensive, antianginal, antiarrhythmic, and heart failure medications cause AV block that resolves after withdrawal of the offending agent.
Can hemodynamically unstable patients be treated with atropine?
Hemodynamically unstable patients for whom timely cardiologic consultation is unavailable should undergo temporary transvenous pacemaker insertion in the emergency department (ED). Hemodynamically unstable patients may be treated with atropine. This should be done with a degree of caution.
Does atropine increase ventricular rate?
However, if the block is in the His bundle, atropine may lead to an increased atrial rate, and a greater degree of block can occur with a slower ventricular rate. Atropine is unlikely to be successful in wide-complex bradyarrhythmias where the level of the block is below the level of the AVN.
Is isoproterenol a contraindication?
Isoproterenol is more likely to facilitate conduction with a distal level of block, but patients with a block at the distal level are more likely to have a contraindication, such as active ischemic heart disease.
What is AV block?
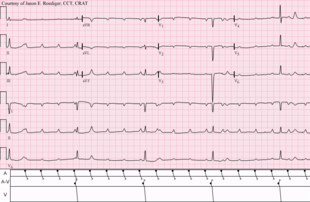
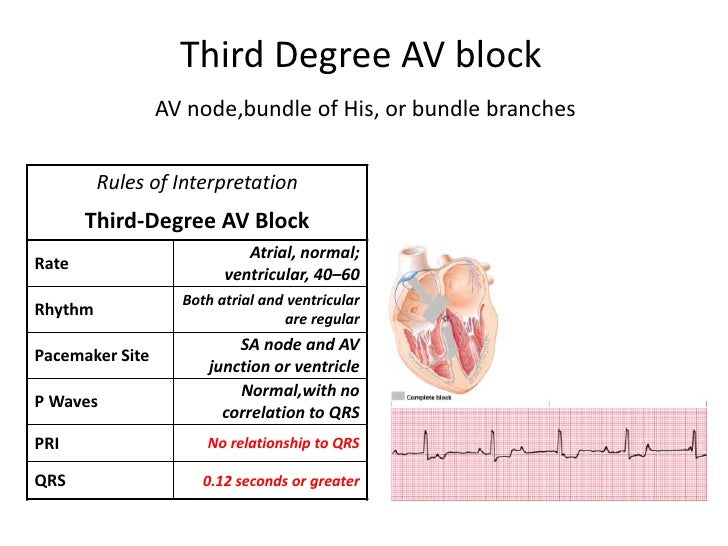
In third-degree AV block no atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles. The atria and the ventricles are electrically dissociated from each other. This condition is referred to as atrioventricular (AV) dissociation.
What is the third degree AV block?
Third-degree AV block causes cardiac arrest unless an escape rhythm occurs. The escape rhythm may have narrow or wide QRS complexes, depending on from where the impulses are discharged and whether there is concomitant bundle branch block.
Where do P waves occur?
P-waves may occur on the ST-T segment ( Figure 1, upper panel). The atrial rate is typically faster than the ventricular rate. It may be very difficult to establish a diagnosis of third-degree AV block if the atrial and ventricular rate is equal and the P-waves occur right before the QRS complexes.
Do P waves have a relation to QRS?
On the ECG P-waves have no relation to the QRS complexes. The QRS complexes may be normal or wide. P-waves have constant PP interval and ride straight through the strip, without any relation to QRS complexes. P-waves may occur on the ST-T segment ( Figure 1, upper panel).
Is AV block a second degree or first degree?
If no escape rhythm occurs, cardiac arrest will ensue. Third-degree AV block may be preceded by second-degree or (rarely) first- degree AV block.
Can a transcutaneous pacemaker be withdrawn?
Transcutaneous pacemaker is a painful method which mandates sedation but should not be withdrawn if the situation is life-threatening. Any medications causing or aggravating the block must be withdrawn. AV blocks due to reversible causes does not need permanent pacemaker.
Is Holter ECG necessary?
Holter ECG may be valuable if the diagnosis is uncertain. Otherwise, no further examination is needed beyond the 12-lead ECG. Echocardiography is generally not necessary. Management of AV blocks aims to restore atrioventricular conduction either pharmacologically or by means of artificial pacemakers. Both methods may be used in the acute setting, ...
Does atropine block AV node?
Atropine will have effect if the block is located in the AV node. Note that atropine may aggravate the block if it is located distal to the AV node. Isoprenaline (isoproterenol, 5 micrograms per minute) may also be administered (with caution in case of acute coronary syndromes, as isoprenaline may trigger ventricular tachycardia).
What is the clinical significance of a third degree heart block?
They require urgent admission for cardiac monitoring, backup temporary pacing and usually insertion of a permanent pacemaker.
What is a complete heart block?
In complete heart block, there is complete absence of AV conduction, with none of the supraventricular impulses conducted to the ventricles. The perfusing rhythm is maintained by junctional or ventricular escape rhythm. Alternatively, the patient may suffer ventricular standstill leading to syncope (if self-terminating) or sudden cardiac death ...
What does marked inferior ST elevation mean?
Rhythm is maintained by a junctional escape rhythm. Marked inferior ST elevation indicates that the cause is an inferior STEMI. Example 2.
How to keep pacemaker ready?
Based on the given set of vital signs and level of consciousness, you decide to keep the pacer ready by using combination#N#(monitor/defibrillator/pacing/cardioversion) pads to monitor the patient. You establish IV access as you provide transport to the patient's medical facility.#N#No change in the patient's status occurred during transport and the patient is received by the emergency department's team. Shortly after arriving, the emergency physician decides to place an intravenous pacemaker and calls cardiology to continue the admission of this patient for the placement of a permanent, implantable pacemaker.
What is an EKG club?
The EKG Club expert panel accepts 12-lead ECG and EKG cases for review and discussion. The EKG Club expert panel provides an opportunity for EMTs, paramedics, nurses, physicians and other health care providers learn from real patient-based case studies.
What is external pacing?
External pacing to increase ventricular pulse rate. There are three types of pacemakers: Transcutaneous. Transvenous. Implantable (permanent) The road to a permanent, implanted pacemaker begins with a temporary pacemaker (transcutaneous or transvenous).
Does a transcutaneous pacemaker require analgesia?
This can be noted when the TCP is no longer capturing the ventricles and requires the user to increase the energy level in order to maintain capture. A transcutaneous pacemaker will produce an electrical stimulus to the patient’s skeletal muscles that may be painful for the patient and requires analgesia and sedation.
What is a Mobitz II block?
Mobitz II, or Type II, second degree AV block, can be confused with a nonconducted premature atrial complex. In Mobitz II block, the electrocardiogram (EKG) shows a constant P–R interval, followed by a sudden failure of a P wave to be conducted to the ventricles.
What is the P–R interval of AV block?
First-degree AV block, with a P–R interval greater than 200 ms , is rarely found in young, healthy adults during activity. However, a longer P–R interval, and even Mobitz I (Wenckebach) block can be seen in young, well-conditioned individuals at rest and during sleep. The P–R interval decreases and the Wenckebach block disappears with increased activity, and is considered normal vagal influence on the AV node.
What is surface EKG?
The surface EKG is our most important tool for the diagnosis of AV block and intraventricular conduction disturbances. First-degree AV block is seen as a P–R interval >200 ms and each P wave is followed by a QRS complex with a constant, prolonged interval (Figure 2).
How long can you keep anticoagulant for atrial fibrillation?
Patients on anticoagulants who need temporary or permanent pacemaker placement are at increased risk of bleeding complications. If the procedure is not emergent, and the patient is on warfarin for atrial fibrillation, the drug can be withheld for 3 to 5 days, and restarted postprocedure when the risk of bleeding is acceptable.
What is a slowed conduction?
Slowed conduction, or blocked conduction, can occur anywhere along the path of conduction fibers, and can generally be identified by EKG analysis. Infra-Hisian block is the most important to identify, since it is the cause of most cases of symptomatic complete heart block.
Why is my heart block reversible?
Reversible causes of complete heart block can be due to metabolic abnormalities, drug effects, Lyme disease, or vasovagal episodes. In these cases, the complete heart block resolves once the abnormality has been treated. In true complete heart block, the sinus rate is faster than the ventricular rate.
What causes AV block?
Acquired AV block is most commonly caused by idiopathic fibrosis, acute myocardial infarction, or drug effects. AV block can also be congenital. If AV block is symptomatic, and determined to be permanent, pacing is the only effective long-term therapy. Conduction Terminology.
What medications slow the heart's electrical impulses?
You take medications that slow the conduction of the heart’s electrical impulses including some heart medications (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin), high blood pressure drugs, antiarrhythmics; muscle relaxants and sedatives; antidepressants and antipsychotics; diuretics; lithium.
What is the difference between type 2 and type 2?
The electrical signal gets slower and slower until your heart actually skips a beat. Type II, also called Mobitz Type II: While most of the electrical signals reach the ventricles every so often , some do not and your heartbeat becomes irregular and slower than normal.
What is an electrophysiology test?
Electrophysiologists are physicians who specialize in the electrical activity of the heart. Tests you might undergo include: An ECG: An electrocardiogram (ECG) records your heart’s electrical activity – its heart rate and rhythm and the timing of electrical signals as they move through your heart.
What is the name of the block that makes your heart beat?
Heart Block. Heart block, also called AV block, is when the electrical signal that controls your heartbeat is partially or completely blocked. This makes your heart beat slowly or skip beats and your heart can’t pump blood effectively. Symptoms include dizziness, fainting, tiredness and shortness of breath. Pacemaker implantation is ...
What is the purpose of an electrophysiology study?
An electrophysiology study: An electrophysiology study involves inserting a long, thin tube called a catheter through a blood vessel and guiding it to your heart to measure and record electrical activity from inside your heart. If you need this test, you’ll get more detailed information.
How to keep your heart healthy?
Steps you can take to keep your heart and body as healthy as possible include: Lead a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a heart healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting an adequate amount of sleep each night, reducing stress, limiting alcohol and stopping smoking and use of illicit drugs.
What is the mildest heart block?
First-degree heart block: The electrical impulse still reaches the ventricles, but moves more slowly than normal through the AV node. The impulses are delayed. This is the mildest type of heart block. Second-degree heart block is classified into two categories: Type I and Type II.
