
Treatment of patients with basilar artery thrombosis includes the following:
- Hemodynamic management
- Respiratory management
- Thrombolysis
- Intra-arterial thrombolysis
- Combination therapy - The combination of IV thrombolysis with consecutive, on-demand, mechanical endovascular thrombectomy may allow for early treatment initiation with high recanalization; in one small study, recanalization was achieved ...
Will basilar artery migraine respond to Botox?
Unlike the traditional migraine, basilar migraine does respond to over-the-counter NSAIDs and hence patient education is vital. It is important to speak to a headache specialist before trying natural alternatives.
What are the symptoms of a basilar migraine?
Symptoms of a Basilar Migraine
- Headache pain on one or both sides of your head
- Vertigo
- Lack of coordination
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Nausea
- Double vision
- Temporary loss of hearing, ringing in your ears
- Loss of muscle control
- Loss of consciousness
What is narrowing of the basilar artery?
Intracranial stenosis is the narrowing of an artery inside the brain due to buildup of plaque inside the artery. The arteries most likely to be affected by stenosis are the internal carotid artery, the middle cerebral artery, the vertebral arteries, and the basilar artery.
Can ophthalmoplegia happen with basilar artery stroke?
Basilar artery stroke top of the basilar syndrome •Embolus typically lodges at the terminal bifurcation of the basilar artery and obstructs the posterior cerebral and superior cerebellar arteries, including the central branches from the proximal part of the posterior cerebrals
See more
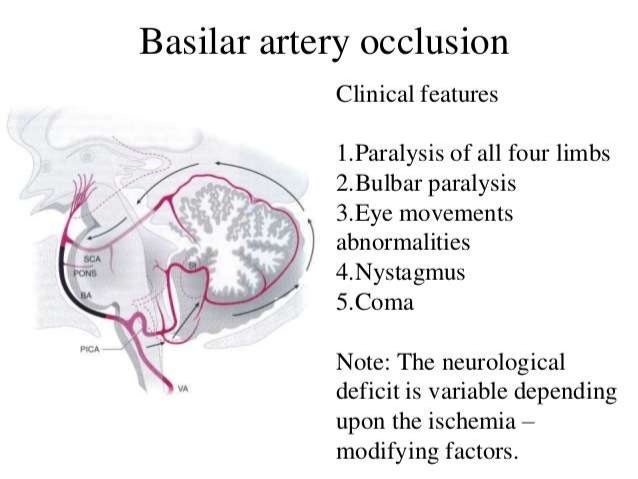
Is basilar artery thrombosis a stroke?
Basilar artery thrombosis is a devastating form of stroke with high morbidity and mortality. Its initial presentation is often extremely nonspecific and may include dizziness or blurring of vision.
What causes a blood clot in basilar artery?
The risk factors for basilar artery thrombosis are the same as those seen generally in stroke. The most common risk factor is hypertension, which is found in as many as 70% of cases. It is followed by diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, cigarette smoking, and hyperlipidemia.
Can you recover from basilar stroke?
Patients can experience a near-complete recovery if treatment is provided promptly. However, the time from onset of symptoms to diagnosis in the emergency department is often significantly delayed in basilar artery occlusion, with one study reporting an average total delay of 16 hours and eight minutes [2].
What would happen if the basilar artery were to be damaged?
The basilar artery plays a critical role in supplying blood to regions of the brain like the cerebellum, brainstem, and occipital lobes. If this vessel is compromised in some way, a stroke can occur.
What part of the brain does the basilar artery supply?
The basilar artery is the main artery that supplies blood to the back portion of your brain. It carries oxygen-rich blood to your brainstem, cerebellum and occipital lobes. Several conditions, such as blood clots or aneurysms, can disrupt blood flow in your brain.
How common is a basilar artery stroke?
Although the exact incidence of basilar artery occlusion remains unknown, it is estimated to account for 1% of all ischemic strokes. [11] Data from the center, including 129 patients with an LVO, showed that the estimated incidence was four persons per 100000/year.
What I can do to improve my basilar artery?
Treatment for vertebrobasilar insufficiencyMedication and lifestyle changes. Patients who have vertebrobasilar insufficiency, a history of stroke, or TIA (“mini-stroke”) should quit smoking immediately, attempt to lower cholesterol levels through diet, and exercise regularly. ... Open surgical repair. ... Endovascular repair.
Can the basilar artery be stented?
Conclusions—Elective stenting of the basilar artery is feasible, with minimal risk to the patient. Its impact on long-term stroke prevention and its durability are unknown and will require further study.
What causes a basilar stroke?
The risk factors for basilar artery thrombosis are the same as those seen generally in stroke. The most common risk factor is hypertension, which is found in as many as 70% of cases. It is followed by diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, cigarette smoking, and hyperlipidemia.
What is basilar artery syndrome?
This syndrome is the manifestation of upper brainstem and diencephalic ischemia caused by occlusion of the rostral basilar artery; the occlusion usually results from an embolism.
What causes restricted blood flow to the brain?
Restrictions in blood flow may occur from vessel narrowing (stenosis), clot formation (thrombosis), blockage (embolism) or blood vessel rupture (hemorrhage). Lack of sufficient blood flow (ischemia) affects brain tissue and may cause a stroke.
What can cause blockages in the brain?
The narrowing is caused by a buildup and hardening of fatty deposits called plaque. This process is known as atherosclerosis. A stroke occurs when plaque causes the artery to become blocked and that area of the brain is deprived of blood, which damages and kills nerves in the brain.
How long does a patient have to be on IV thrombolysis?
Some general guidelines should be followed when treating a patient with IV or intra-arterial thrombolysis. Patients with a stuttering course of longer than 3 hours and up to 12 hours should be considered for intra-arterial thrombolysis, provided that ischemic changes are not present on the CT scan.
What is the systolic blood pressure for stroke?
However, currently available guidelines for the management of acute stroke recommend the use of antihypertensives to lower blood pressure to a systolic value of less than 185 mm Hg or a diastolic value of less than 110 mm Hg if thrombolysis is being considered.
Why do patients with brainstem, cerebellar, diencephalic, or occipital in
Patients with brainstem, cerebellar, diencephalic, or occipital infarcts secondary to basilar artery occlusion have a significant degree of disability because of weakness, ataxia, swallowing difficulties, or other cranial neuropathies or due to a combination of these.
What is the purpose of PSV in stroke?
Adding PSV during the extra breaths can minimize the patient's respiratory effort during the extra breaths. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is the only pharmaceutical agent approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke within the first 3 hours of onset.
Does heparin help basilar artery occlusion?
The role of antiplatelets, such as clopidogrel and the combination of aspirin and dipyridamole, in the treatment of acute basilar artery occlusion is not known . Angioplasty.
How to prevent basilar artery thrombosis?
To prevent thrombosis, you must follow a diet, proper nutrition. You need to eat less fatty, fried foods that contain cholesterol, fatty acids. You can not eat fast food. It is necessary to eat more seafood, garlic, berries, citrus fruits. Also need to include in the diet more vegetables, especially tomatoes, sweet peppers.
What is the cause of thrombosis of the basilar artery?
The main cause of thrombosis of the basilar artery is the formation of a thrombus in the wall of the basilar artery. The reasons for the development of thrombosis of the basilar artery may be as follows:
What is the surgical method for thrombus removal?
In the event that drug therapy and physiotherapy are ineffective, a surgical method is used. It is aimed at the mechanical elimination of thrombus and the limitation of the affected area from the total blood flow (endarterectomy). Also, the surgical method can be aimed at improving blood flow. A common type of surgical intervention is angioplasty, during which a special stent is inserted into the basilar artery, preventing the narrowing of the arteries lumen. This helps normalize blood circulation.
What are the risk factors for basilar artery thrombosis?
The likelihood of developing a basilar artery thrombosis increases with the following risk factors: Malnutrition, leading to the deposition of cholesterol plaques. Excessive consumption of food containing fat, oil, cholesterol. Fast food (fast food), lack of diet; Genetic predisposition to thrombosis;
Why is thrombosis of the basilar artery dangerous?
Thrombosis of the basilar artery is dangerous because it can have serious consequences and complications that often have a lethal outcome. Since the disease is associated with the formation of a thrombus in the basilar artery, its main danger is that it can come off and clog the vessel completely.
What is the diagnosis of basilar thrombosis?
The diagnosis of thrombosis of the basilar artery is based on a symptom complex , which includes such violations as: visual disorders (loss of visual field, agnosia, blindness, photopsy, blurred vision, the appearance of visual images); impairment of motor functions of the eye; violations of the vestibular apparatus ;
Can alternative therapy be used for basilar artery thrombosis?
Alternative agents can be very effective in treating thrombosis of the basilar artery. However, only a combination of therapy prescribed by a doctor and alternative drugs can contribute to the successful treatment and overcoming of the disease. If in doubt, it is always better to consult a doctor.
What is the basilar artery?
The basilar artery is a vital vessel contributing to the posterior cerebral circulation. It is formed at the junction of the pons and medulla by the convergence of the dual vertebral arteries. The vertebral arteries join the basilar artery to form the vertebrobasilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior portion of the circle of Willis.
Where is the basilar artery located?
It is located on the ventral surface of the neuronal "bridge" also known as the pons (Latin for "bridge") that connects the forebrain to the cerebellum.
What is the purpose of the thalamus?
Its crucial purpose is to serve the cerebellum, brainstem, thalamus, occipital and medial temporal lobes of the brain with oxygen-rich blood. With an average diameter of 3 to 4 millimeters, it furnishes 20 paramedian and circumflex perforating arteries thus providing a robust collateral network to the pons and midbrain.
What is the best treatment for basilar artery thrombosis?
Recanalization of the basilar artery is key to the successful treatment of basilar artery thrombosis and to improving prognosis. This can be accomplished by systemic thrombolysis (IVT), intra-arterial thrombolysis (IAT), or mechanical endovascular thrombectomy.
What is the basilar artery?
The basilar artery is a vital vessel contributing to the posterior cerebral circulation. It is formed at the junction of the pons and medulla by the convergence of the dual vertebral arteries. The vertebral arteries join the basilar artery to form the vertebrobasilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior portion of the circle of Willis.
How long does basilar thrombosis last?
The commonly accepted time window is at least 12 hours and potentially up to 24 hours.
What causes a vascular dissection in the basilar artery?
The cause can occur from thromboembolism , atherosclerotic disease , or vascular dissection. The mechanism differs depending on the affected segment. The atherosclerotic disease more commonly affects the mid-portion of the basilar artery, followed by the vertebrobasilar junction. Lodging of an embolic source is much more frequent in the distal third of the basilar artery especially at the top of the basilar artery and the vertebrobasilar junction. Arterial dissection is more common in the extracranial vertebral artery and has been associated with neck injuries and cervical chiropractic adjustments. Intracranial dissections are exceedingly rare. [1]
When is basilar artery occlusion most prevalent?
Distal basilar artery occlusion is usually secondary to embolism and is most prevalent in the fourth decade of life. [3] [4] [5]
Where is the basilar artery located?
It is located on the ventral surface of the neuronal "bridge" also known as the pons (Latin for "bridge") that connects the forebrain to the cerebellum . [1] [2] Overall, the basilar artery is one of the most important arteries of the human body.
What is the purpose of the thalamus?
Its crucial purpose is to serve the cerebellum, brainstem, thalamus, occipital, and medial temporal lobes of the brain with oxygen-rich blood. With an average diameter of 3 to 4 millimeters, it furnishes 20 paramedian and circumflex perforating arteries thus providing a robust collateral network to the pons and midbrain.
What is the basilar artery?
The basilar artery is located at the base of the brain, where the two vertebral arteries come together.
How long does it take to remove a clot from a stroke?
Ideally, this procedure should be performed within six hours of stroke symptoms, but can be beneficial if performed within 24 hours. 8.
What is the name of the stroke that occurs when blood vessels to the brain are blocked or damaged?
Basilar Artery Stroke Symptoms. Strokes occur when blood vessels to the brain are blocked or damaged. Nearly 90% of strokes are ischemic; of these, fewer than 5% occur in the basilar artery . 2. A basilar artery stroke is a type of posterior stroke, which means it affects circulation at the back of the brain. Because the basilar artery supplies ...
What causes a brainstem stroke?
In some cases, a brainstem stroke may be the result of an injury to an artery as a result of sudden head or neck movement.
How can a patient with risk factors for stroke reduce their risk of stroke?
While certain risk factors as age, gender, heredity, and ethnicity are uncontrollable, a patient with risk factors for a stroke can reduce their risk of stroke by beginning treatment that controls their risk factors and adjusts their lifestyle choices.
How to lower your risk of stroke?
Taking steps to adjust lifestyle choices can help you control your risk. You can lower your risk of stroke by: Quitting smoking.
What is the role of the brainstem?
The brainstem coordinates movement and balance and plays a major role in sleep, digestion, swallowing, breathing, vision, and heart rate. A basilar artery stroke can impact the brainstem, which can be devastating and lead to long-term disabilities or even death. 1.
What is the best treatment for acute BAO?
IVT represents probably the best treatment that can be offered to victims of acute BAO in such hospitals. Approximately one fifth of ischemic strokes occur in the posterior circulation supplied by vertebrobasilar arteries, where basilar artery occlusion (BAO) tends to cause the most desolate strokes.
Is alteplase used in intravenous studies?
The intra-arterial studies used preferentially urokinase, whereas all intravenous protocols used alteplase like in anterior circulation stroke trials. All patients treated intravenously had heparin as an adjuvant antithrombotic therapy, which is comparable to the 81% rate of heparin use in the intra-arterial studies.
