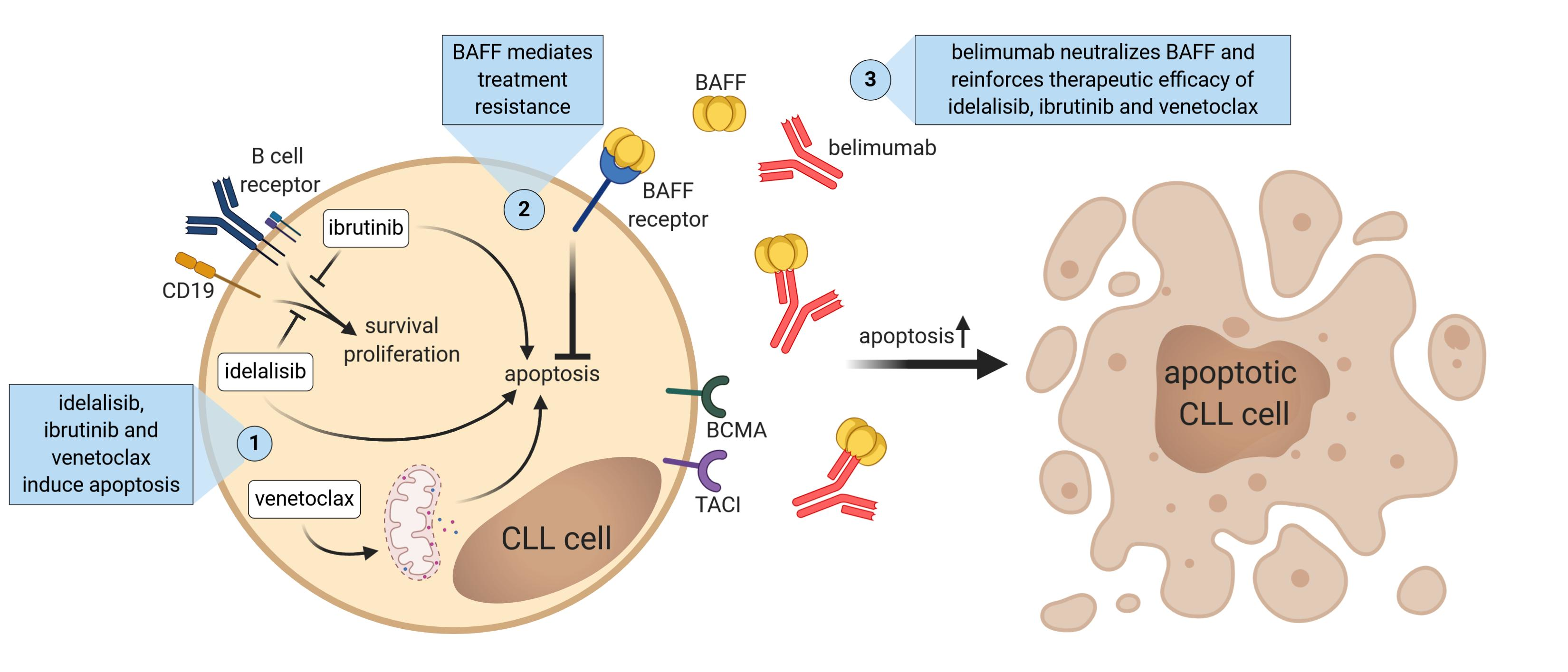
Medication
Scientists are making progress in understanding the changes in the DNA inside bone marrow stem cells that can cause them to develop into leukemia cells. Understanding these gene and chromosome changes can help explain why these cells may grow out of control, and why they don’t develop into normal, mature blood cells.
Procedures
There are five stages of chronic lymphocytic leukemia:
- stage 0: too many lymphocytes in the blood but no other symptoms
- stage I: lymph nodes are swollen because too many lymphocytes are being made
- stage II: lymph nodes, spleen, and liver are swollen because too many lymphocytes are being made
- stage III: anemia has developed because lymphocytes are crowding out red cells in the blood.
Therapy
The woman, identified by the scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases only as the “New York patient,” was diagnosed with HIV in 2013 and then leukemia in 2017. According to NBC, in order for the treatment to work ...
Nutrition
Things To Know About Leukemia. Leukemia is a cancer of the blood or bone marrow. Bone marrow produces blood cells. Leukemia can grow because of a problem with blood cell production. It normally affects the leukocytes, or white blood cells. Leukemia is the most likely to influence people over age 55 years, however, it’s also the most ...
What is the current research on leukemia?
What cells are affected by leukemia?
What is the cure for leukemia?
What to know about leukemia?
What is the most successful treatment for leukemia?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is the major form of treatment for leukemia. This drug treatment uses chemicals to kill leukemia cells. Depending on the type of leukemia you have, you may receive a single drug or a combination of drugs.
What is the new treatment for leukemia?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), a drug that targets aberrant forms of the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos™), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated ...
What is a clinical trial for leukemia?
Clinical trials are research studies that involve people. The clinical trials on this list are for acute myeloid leukemia (aml) treatment. All trials on the list are NCI-supported clinical trials, which are sponsored or otherwise financially supported by NCI.
What is the treatment protocol for leukemia?
Maintenance. If the leukemia remains in remission after induction and consolidation, maintenance therapy can begin. Most treatment plans use daily 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and weekly methotrexate, given as pills, often along with vincristine, which is given into a vein (IV), and a steroid (prednisone or dexamethasone).
Can you be fully cured of leukemia?
As with other types of cancer, there's currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience remission, a state after diagnosis and treatment in which the cancer is no longer detected in the body. However, the cancer may recur due to cells that remain in your body.
What type of leukemia is curable?
While it is similar in many ways to the other subtypes, APL is distinctive and has a specific treatment regime. Treatment outcomes for APL are very good, and it is considered the most curable type of leukemia, with cure rates as high as 90%.
What are the 4 main types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic:Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
What is the best hospital to treat AML?
Mayo Clinic doctors are respected for their expertise in diagnosing and treating acute myelogenous leukemia.
What year did the first drug trial for leukemia take place?
Abstract. The first randomized clinical trial at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), planned in 1954, commenced in 1955 for the treatment of patients with acute leukaemia.
How long is treatment for leukemia?
Coping and support. Treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia can be a long road. Treatment often lasts two to three years, although the first months are the most intense.
How long can leukemia last?
Survival rates by typeTypeAge rangeSurvival rateAcute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)This type of leukemia is most common in older adults, but it can be diagnosed at any age. Most deaths occur in people ages 65 to 84.Relative survival rate for all ages 5 years after diagnosis is about 29.5% .4 more rows•Aug 18, 2021
Why is leukemia treatment so long?
Although there may not be detectable leukemia cells in your child's blood or bone marrow at the end of induction, there still might be some leukemia cells that doctors cannot detect. This is why the treatment continues. The consolidation phase lasts for 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the ALL risk type and protocol.
What exams would be Performed?
As mentioned, your doctor will be requiring to perform series of exams to come up with the best treatment plan. Some of these exams may be anything from the following:
Treatment of Leukemia
Keep in mind that the treatment procedure for leukemia would be dictated by a number of different factors. Your doctor will be determining your options for leukemia treatment based on overall health and age, type of leukemia that you have and whether it began spreading in several parts of your body.
What is the treatment for leukemia in children?
Leukemia Treatment for Children. Standard leukemia treatments for children have been chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem-cell transplant. Despite great improvements in survival for children with some types of leukemia, some children do not respond to standard treatments or experience a relapse of their disease.
What is the drug used for chemo?
An ongoing clinical trial is adding the drug uproleselan to chemotherapy. Uproleselan targets a protein called E-selectin on non-cancerous cells that helps protect cancer cells from being killed by chemotherapy. Exploring other drugs that may have use in AML.
What drugs target the Philadelphia chromosome?
Drugs that target this abnormal protein— imatinib (Gleevec), nilotinib (Tasigna), dasatinib (Sprycel), and ponatinib (Iclusig) —have radically changed the outlook for people with CML, who now have close to a normal life expectancy.
What is the name of the gene that is used to treat AML?
About 10% of children with AML have changes in a gene called FLT3. A clinical trial is testing a drug that targets FLT3, sorafenib (Nexavar), in addition to standard chemotherapy in these children. Other trials testing drugs that target FLT3 more specifically than sorafenib are being planned.
What is the drug used for gene fusion?
One type of gene fusion can be targeted with a drug called larotrectinib (Vitrakvi). This drug is approved for the treatment of children with solid tumors that have this specific gene fusion. A clinical trial under development will test the drug in children with leukemia that harbors this gene fusion.
What is the FDA approved drug for HCL?
Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL) In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved moxetumomab pasudotox (Lumoxiti) for the treatment of HCL that has come back or progressed after earlier treatment. Originally discovered at NCI, the targeted therapy is the first non-chemotherapy drug approved for the disease.
What is car T cell therapy?
Using CAR T-cell therapy. CAR T-cell therapy is a type of treatment in which a patient’s own immune cells are genetically modified to treat their cancer. Currently, CAR T cells are approved for the treatment of some children and young adults with ALL. They are now being explored for use in older adults with B-cell ALL.
What is HPSCT?
A bone marrow transplant, or HPSCT, is the process of replacing blood cells in the body. To do this, healthy blood stem cells are injected into the body. These stem cells travel to the bone marrow where they replace the current stem cells called hematopoietic stem cells.
How is it done?
Receiving stem cells is similar to receiving a blood transfusion. A needle may be inserted into a large vein in your arm, or you may have a central venous catheter placed in a blood vessel in the right side of your chest and the stems cells will flow into your heart.
What are the side effects and risks?
Complications may occur, but not everyone will experience them. Complications may include:
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy uses strong drugs or chemicals, sometimes in combination, to damage or kill cancer cells. This treatment is systemic, which means chemotherapy drugs attack cancer cells, which tend to be fast-growing. However, these drugs can also affect healthy cells.
How is it given?
Chemotherapy can be given orally as a pill, capsule, or liquid, but most of the time, the drugs are given intravenously, through a catheter or central line. This is a port-like device attached to one of your veins that allows you to receive intravenous drugs.
Which types of leukemia may be treated with this?
All four main types of leukemia may be treated with chemotherapy. In ALL, AML, and CLL, it’s the first and main treatment. For CML, targeted therapies are typically used first, followed by chemotherapy.
What are the side effects and risks?
As with any medical treatment, there are side effects with chemotherapy depending on the drug used, dosage, and how long you take it.
What is the treatment for childhood leukemia?
Other treatments might also be used in special circumstances. Surgery for Childhood Leukemia. Radiation Therapy for Childhood Leukemia.
What happens after leukemia diagnosis?
After leukemia is diagnosed and tests have been done to determine its type and subtype, your child’s cancer care team will discuss the treatment options with you. The most important factor in choosing a treatment is the type of leukemia, but other factors also play a role.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. Sometimes they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments (although there is no guarantee that newer treatments will be better). They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat these cancers.
What are the services that help with cancer?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. For children and teens with cancer and their families, other specialists can be an important part of care as well.
Why is it important to discuss your child's treatment options?
It’s important to discuss your child’s treatment options as well as their possible side effects with the treatment team to help make the decision that’s the best fit for your child. If there is anything you don’t understand, ask to have it explained.
What to do if your child has leukemia?
It’s important to weigh the benefits of each treatment option against the possible risks and side effects.
What to talk to your child's cancer care team about?
Be sure to talk to your child's cancer care team about any method you are thinking about using. They can help you learn what is known (or not known) about the method, which can help you make an informed decision. Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
What is the treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia?
The main treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) in adults is typically long-term chemotherapy (chemo). In recent years, doctors have begun to use more intensive chemo regimens, which has led to more responses to treatment. But these regimens are also more likely to cause side effects, such as low white blood cell counts.
How to tell if you have leukemia?
Other common symptoms from leukemia are low blood counts and fatigue. Medicines or blood transfusions may be needed to help correct these problems. Nausea and loss of appetite can be treated with medicines and high-calorie food supplements. Infections that occur may be treated with antibiotics.
What is the goal of induction chemo?
The goal of induction chemo is to get the leukemia into remission (complete remission). This means that leukemia cells are no longer found in bone marrow samples (on a bone marrow biopsy ), the normal marrow cells return, and the blood counts return to normal levels.
How long does imatinib last?
Maintenance usually lasts for about 2 years.
How long does chemo last for leukemia?
This typically lasts for a few months. Usually the drugs are given in high doses so that the treatment is still fairly intense.
How many people have complete remission from leukemia?
Response rates to ALL treatment. In general, about 80% to 90% of adults will have complete remissions at some point during these treatments. This means leukemia cells can no longer be seen in their bone marrow. Unfortunately, about half of these patients relapse, so the overall cure rate is in the range of 40%.
What is the best treatment for B cell ALL?
Monoclonal antibodies such as blinatumomab (Blincyto) or inotuzumab ozogamicin (Besponsa) may be an option for patients with B-cell ALL. A stem cell transplant may be tried if the leukemia can be put into at least partial remission. Clinical trials of new treatment approaches may also be considered.
Why is T-LGL leukemia treated?
The majority of these patients eventually need treatment because of severe or symptomatic neutropenia, anemia, or RA. No standard therapy has been established because of the absence of large prospective trials.
How are LGLs identified?
LGLs are identified by their specific morphology and phenotype. They display a large size (15-18 μm), an abundant cytoplasm containing typical azurophilic granules, and a reniform or round nucleus (Figure 2).
Can methotrexate be used for neutropenia?
No standard therapy has been established because of the absence of large prospective trials. The authors use low-dose methotrexate initially for T-LGL leukemia patients with neutropenia and/or RA. We recommend either methotrexate or oral cyclophosphamide as initial therapy for anemia.
Is apoptosis a T cell or NK cell?
Dysregulated apoptosis has been shown to be an important mechanism in the pathogenesis of LGL leukemia either of T- or NK-cell origin. Unlike their normal counterparts, leukemic LGLs are activated cytotoxic cells that escaped Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
Traditionally, leukemia is primarily treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Stem cell transplants may also be used in conjunction with chemotherapy, particularly in children. Immunotherapy and targeted therapies are newer treatments for certain types of leukemia.
How does immunotherapy help with leukemia?
Depending on the type of immunotherapy, treatment may help: boost your T-cells (T-cell transfer therapy) preserve the integrity of immune cells by helping prevent them from responding too strongly to leukemia cells ( immune checkpoint inhibitors)
What are the treatments for cancer?
For this reason, standard treatments tend to include: chemotherapy (sometimes with stem cell transplant) radiation therapy. Due to the risk of lifelong side effects, researchers are looking into other options, such as targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
How does targeted therapy work?
As the name suggests, this treatment approach works by targeting genes or proteins that may be helping cancerous cells grow.
What is car T cell therapy?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a newer type of immunotherapy for childhood ALL. Your body already has T-cells, but when you have cancer, they may not work as they should. With CAR T-cell therapy, some T-cells are removed and genetically modified with receptors to fight cancer more effectively.
What is the survival rate for leukemia?
The overall 5-year survival rate for leukemia is estimated at 63.7 percent. Trusted Source. . As new, earlier treatments have emerged, the death rate for this type of cancer is also declining. In 2020, leukemia made up only 3.8 percent.
Is CLL faster than HCL?
Both CLL and HCL progress slower than any other types of leukemia. To prevent side effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, a doctor may try targeted therapies first. Another option may include “watchful waiting” to see how initial treatments work before attempting more aggressive treatments.
How to cope with chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Explore ways to cope with the nagging, chronic nature of the disease. If you have chronic lymphocytic leukemia, you'll likely face ongoing tests and ongoing worries about your white blood cell count. Try to find some activities that help you relax, whether it's yoga, exercise or gardening.
What test is used to diagnose chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Blood tests . Tests and procedures used to diagnose chronic lymphocytic leukemia include blood tests designed to: Count the number of cells in a blood sample. A complete blood count may be used to count the number of lymphocytes in a blood sample. A high number of B cells, one type of lymphocyte, may indicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
What kind of doctor would you see for lymphocytic leukemia?
If your doctor determines you may have chronic lymphocytic leukemia, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood and bone marrow (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to be well-prepared.
What test is used to determine if a person has an increased number of lymphocytes?
Determine the type of lymphocytes involved. A test called flow cytometry or immunophenotyping helps determine whether an increased number of lymphocytes is due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia, a different blood disorder or your body's reaction to another process, such as infection.
What is targeted drug?
Targeted drugs are designed to take advantage of the specific vulnerabilities of your cancer cells. Your cancer cells are tested to determine which targeted drugs may be helpful. Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses your body's immune system to fight cancer.
Does green tea help with leukemia?
A green tea extract has shown some promise in initial clinical trials for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Laboratory research determined that a compound in green tea extract, called EGCG, can kill chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. A study of people with early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia found that EGCG in pill form reduced some signs of the disease. But green tea trials haven't been conclusive, and this subject requires more study before doctors can agree on the merits of this treatment.
Can bone marrow transplants help with leukemia?
As new and more-effective drug combinations have been developed, bone marrow transplant has become less common in treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Leukemia Treatment For Adults
Leukemia Treatment For Children
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Nci-Supported Research Programs
- A diagnosis of leukemia may be devastating — especially for the family of a newly diagnosed child. With time you'll find ways to cope with the distress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn enough about leukemia to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your leukemia, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As …
Leukemia Research Results
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you have signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have leukemia, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood and bone marrow (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared. Here's some information to …