- NSAIDs . Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. ...
- Steroids. Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, reduce inflammation and pain and slow joint damage. ...
- Conventional DMARDs . ...
- Biologic agents. ...
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs .
Medication
The optimal treatment of RA requires a comprehensive program that combines medical, social, and emotional support for the patient. It is essential that the patient and the patient’s family be educated about the nature and course of the disease. Treatment options include medications, reduction of joint stress,...
Procedures
Since then, new drugs have hit the market, older drugs have been reassessed, and there’s more evidence for the role of nondrug treatments for RA. Of 44 recommendations, only seven were considered strong, meaning there’s clear evidence that the benefits of the treatment outweigh the risks and most patients endorse them.
Therapy
The rheumatologist will work with the patient and the patient’s primary care physician to reach a RA diagnosis and provide treatment. Because there is no exact known cause of RA, doctors look at a number of different factors before reaching a diagnosis.
Self-care
The ACR updates its guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) every few years. The last changes appeared in 2015. Since then, new drugs have hit the market, older drugs have been reassessed, and there’s more evidence for the role of nondrug treatments for RA.
Nutrition
What is the optimal treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
Is there more evidence for non-rug treatments for RA?
How does a rheumatologist diagnose and treat RA?
How often does the ACR update its guidelines for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?

When should you start treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Once it is clear that a patient has developed rheumatoid arthritis (RA), disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy should be introduced immediately. This controls synovitis and slows the rate of subsequent disease progression.
What is the first line treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Methotrexate. Methotrexate is now considered the first-line DMARD agent for most patients with RA. It has a relatively rapid onset of action at therapeutic doses (6-8 weeks), good efficacy, favorable toxicity profile, ease of administration, and relatively low cost.
What is the safest way to treat RA?
There is no one drug that is the safest or best – all drugs have benefits and side effects. The main types of drugs used to treat RA include: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
What is the newest treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Official Answer. The newest drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis are the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which are FDA approved under the brand names Rinvoq, Olumiant, and Xeljanz.
What are the 4 stages of rheumatoid arthritis?
The four stages of rheumatoid arthritis are known as synovitis, pannus, fibrous ankylosis, and bony ankylosis.Stage I: Synovitis. During stage I, you may start having mild symptoms, including joint pain and joint stiffness. ... Stage II: Pannus. ... Stage III: Fibrous Ankylosis. ... Stage IV: Bony Ankylosis.
Can rheumatoid arthritis go away?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong disease. When it's treated, it may go away for a little while, but it usually comes back. It's important to see your doctor as soon as symptoms begin. The earlier you start treatment, the better your outcome.
What triggers rheumatoid arthritis?
Researchers think it's caused by a combination of genetics, hormones and environmental factors. Normally, your immune system protects your body from disease. With rheumatoid arthritis, something triggers your immune system to attack your joints. An infection, smoking or physical or emotional stress may be triggering.
What is the best vitamin for rheumatoid arthritis?
For people with RA, vitamin D can have additional benefits: RA is an autoimmune disorder, and vitamin D plays a role in the immune system. People with RA also have high levels of inflammation, and vitamin D helps mediate this condition.
What are the different types of rheumatoid arthritis drugs?
There are three general classes of drugs commonly used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). NSAIDs and corticosteroids have a short onset of action while DMARDs can take several weeks or months to demonstrate a clinical effect. DMARDs include methotrexate, sulfasalazine, leflunomide (Arava®), etanercept (Enbrel®), infliximab (Remicade®), adalimumab (Humira®), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®), golimumab (Simponi®), abatacept (Orencia®), rituximab (Rituxan®), tocilizumab (Actemra®), anakinra (Kineret®), antimalarials (e.g. Plaquenil®). Other immunomodulators are occasionally used including azathioprine (Imuran) and cyclosporine. Because cartilage damage and bony erosions frequently occur within the first two years of disease, rheumatologists now move aggressively to a DMARD agent early in the course of disease, usually as soon as a diagnosis is confirmed. Analgesic drugs are also sometimes helpful in decreasing pain until DMARDs take effect. A summary table of how to monitor drug treatment in rheumatoid arthritis is included.
What are the benefits of DMARD?
Although both NSAIDs and DMARD agents improve symptoms of active rheumatoid arthritis, only DMARD agents have been shown to alter the disease course and improve radiographic outcomes. DMARDs have an effect upon rheumatoid arthritis that is different and may be slower. In most cases, when the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is confirmed, DMARD agents should be started. The presence of erosions or joint space narrowing on x-rays of the involved joints is a clear indication for DMARD therapy, however one should not wait for x-ray changes to occur. The currently available drugs include: 1 Methotrexate (Rheumatrex®, Trexall®) 2 Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ®) 3 Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine®) 4 Leflunomide (Arava®) 5 Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors — etanercept (Enbrel®, adalimumab (Humira ®), and infliximab (Remicade®), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®), golimumab (Simponi®) 6 T-cell Costimulatory Blocking Agents —abatacept (Orencia®) 7 B cell Depleting Agents —rituximab (Rituxan®) 8 Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors– tocilizumab (Actemra®) 9 Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Receptor Antagonist Therapy —anakinra (Kineret®) 10 Intramuscular Gold 11 Other Immunomodulatory and Cytotoxic agents — azathioprine (Imuran®) and cyclosporine A (Neoral®, Sandimmune®)
What is a DMARD?
Disease Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDS) Although both NSAIDs and DMARD agents improve symptoms of active rheumatoid arthritis, only DMARD agents have been shown to alter the disease course and improve radiographic outcomes. DMARDs have an effect upon rheumatoid arthritis that is different and may be slower.
How long does it take for folic acid to work after methotrexate?
These side effects can often be overcome by increasing folic acid or using an activated form of folic acid known as folinic acid (leukovorin®) given as a 5mg dose 12 hours and sometimes 24 hours after methotrexate is given. Some patients complain of GI upset (nausea or diarrhea) with oral methotrexate.
How long does it take for NSAIDS to work?
Usual Time to Effect: The onset of action is seen in as early as 4 to 6 weeks.
When did TNF antagonists start being used?
TNF antagonists were the first of the biological DMARDS to be approved for the treatment of RA. These drugs began to enter the market for rheumatoid arthritis in 1999 and are now considered a part the ACR recommendations for treatment of RA.
What is the mechanism of action of antimalarials in the treatment of patients with rheumato
Dosage: Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil®) is the drug of choice among antimalarials.
Medications that slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis
Medications that slow the progression of RA can help reduce your symptoms while preventing joint damage and disability. Options include:
Medications to reduce the inflammation and pain of rheumatoid arthritis
Many people with RA also take medications to help manage pain. You might take these medications temporarily, during a flare-up, or every day depending on your condition and the treatment plan you discuss with your doctor. Pain-relieving options include:
Physical therapy
A physical therapist can also provide pain relief through massages and muscle stimulation. They can teach you exercises to do at home that will build your strength and reduce your pain.
Occupational therapy
An occupational therapist can help you maintain your ability to do everyday tasks on your own. They can also recommend supports and devices to assist you and teach you how to use them. These can include:
What is DMARDs for arthritis?
DMARDs, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, are long-term medications meant to slow or alter the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by stopping the immune system from attacking healthy tissue. These drugs protect joints and tissues from permanent damage and gradually reduce daily pain.
How do NSAIDs work?
NSAIDs can be taken orally or applied directly to the joint as a patch or cream. Corticosteroid medications or another form of drug used in the treatment of RA. They work in your body similar to hormones as they try to slow the progression of the disease and stop the immune system from attacking healthy tissue.
What are the side effects of methotrexate?
Methotrexate (Trexall) leflunomide (Arava) Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) Side effects are different for each patient and medication, but the most serious are liver damage and susceptibility to infections. There is a subset of DMARD medications called biologic response modifiers.
What is the best treatment for RA?
Blocking TNF inhibitors or the activation of T cells is one method of preventing the joint damage that frequently occurs in patients who suffer from RA. This greatly reduces the risk of further damage or infection. Biologic agents are typically prescribed in combination with other medications to fight RA symptoms.
How does surgery help with RA?
However, surgery potentially enables patients to regain function by repairing the joint damage that frequently occurs with this condition . The overall goal of surgery, when deemed appropriate, is to improve the quality of life of those affected. There are three surgical procedures that RA patients typically receive.
How does a physical therapist help with RA?
Physical therapists can help patients learn appropriate exercises and new ways of approaching tasks that minimize the strain on affected joints while improving overall body strength.
What is tight control for RA?
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, the goals of treatment will be to gain “tight control” of RA, meaning the disease’s activity is kept steadily at a low level. Keeping RA in “tight control” can prevent long-term joint damage. These goals primarily focus on:
How does optimism help with arthritis?
Optimism Helps With Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis. After coping with rheumatoid arthritis for nearly 20 years, Guillory offers these words of wisdom: "Try to be careful in your everyday activities. Don't do anything that will damage your joints. Take medications as you're supposed to. Also, take things day by day.
What kind of arthritis did Guillory have?
Right away, doctors suspected she had rheumatoid arthritis. Guillory was tenacious about finding the right doctor -- one who would treat her aggressively. She knew she had to tackle this thing head-on, she says. And that she did -- with disease-modifying drugs that helped curb the damaging inflammation at her joints.
How many people with RA quit working?
About half the people with RA had to quit working within 10 years," says Stephen Lindsey, MD, chairman of rheumatology at the Ochsner Clinical Foundation in Baton Rouge, La. More than two million Americans suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, also known as RA. About 75% of them are women, according to the American College of Rheumatology.
What drugs were used in the 1960s and 1970s to treat other diseases?
For example, methotrexate, a drug that Guillory took early on, was first used as a form of cancer chemotherapy.
What is DMARDs in medicine?
The key is early diagnosis, then aggressive treatment with the right medicine.". To protect joints from damage, doctors turn to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These include several drugs used in the 1960s and 1970s to treat other diseases -- and were discovered to also work with rheumatoid arthritis.
What biologics are approved by the FDA?
Biologics approved by the FDA include Actemra, Cimzia, Enbrel, Humira, Kineret, Orencia, Remicad e, Rituxan, and Simponi. Very often, patients are switched to different drugs -- and often take multiple drugs -- during the course of treatment, he points out.
Is rheumatoid arthritis an autoimmune disease?
New research has revealed more about the disease itself. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body mistake nly identifies certain cells as foreign and attacks them -- triggering the inflammation that damages healthy joints.
How are biosimilars created?
Biosimilars are created by slightly changing the manufacturing process used for the original or reference drug. The 2020 guideline acknowledges the safety and efficacy of biosimilars and encourage their use — a shift from the ACR stance in 2015. One hurdle to broader use of biosimilars is that insurers have been reluctant to pay for them. In 2019, insurers approved a biosimilar before a biologic just 14% of the time. Plus, copays for biosimilars are often about the same as for the reference drug. Whether biosimilars will really make biologics more affordable remains to be seen.
What is the best treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Methotrexate. Methotrexate is a conventional disease-modifying anti-inflammatory drug (DMARD). It works to lower inflammation and slow an overactive immune system, which occurs in rheumatoid arthritis. The new guidelines strongly recommend methotrexate alone (monotherapy) as the first treatment for people with moderate to high disease activity who ...
What is the most important factor in all treatment considerations?
The most important factor in all treatment considerations is shared decision-making, where patients are informed of all their options, including nondrug ones, and have a full voice in their own care. “Patients were involved in every step of the process [of creating the update], and the recommendations truly reflect their perspectives,” Dr. Fraenkel says.
What is the treatment to target approach?
Although there’s not much evidence to support it, a treat-to-target approach is strongly recommended for patients who haven’t taken biologics or small molecule drugs. In treat-to-target, doctors and patients decide on a goal and adjust treatment until the goal is reached. Though everyone hopes for remission, many patients may not be able to achieve it. A more realistic aim is low disease activity, which keeps symptoms under control and helps maintain a good quality of life. Still, the guideline states the goal should be tailored to each patient and remission can be the target when possible.
How many recommendations are there for non-drug treatment for RA?
Since then, new drugs have hit the market, older drugs have been reassessed, and there’s more evidence for the role of nondrug treatments for RA. Of 44 recommendations, only seven were considered strong, meaning there’s clear evidence that the benefits of the treatment outweigh the risks and most patients endorse them.
Why are the remaining recommendations called conditional?
The remaining recommendations are called conditional because they lack good evidence one way or the other. The new guidelines don’t address vaccinations — particularly relevant right now — or nondrug therapies like diet and exercise. Those are expected in a later update. Here are some of the main takeaways:
Is methotrexate a biologic?
It’s conditionally recommended over methotrexate combined with a TNF blocker. Methotrexate plus a biologic is preferred over triple therapy (combined methotrexa te, hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine), mainly because it’s faster-acting.
What are the most common DMARDs?
Commonly prescribed DMARDs include Plaquenil, Ridaura, Azulfidine and Rheumatrex. Immunosuppressants keep your immune system from attacking healthy tissue and eliminate the defective cells causing the condition. These medications make you more susceptible to infection. Common ones include Arava, Neoral and Sandimmune.
What is the procedure to remove a joint?
You might undergo one or more of the following procedures during your operation. Arthroplasty removes the joint and replaces it with a prosthesis. If inflammation and joint damage have affected the surrounding tendons, your surgeon will fix them. Synovectomy involves removing the lining of the joint if it is inflamed.
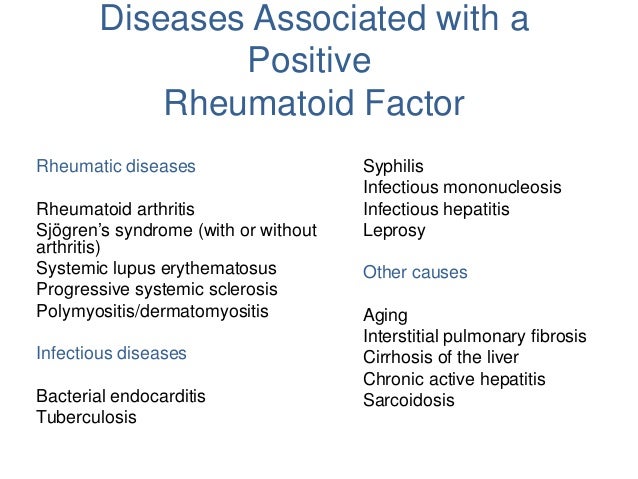
What is rheumatoid factor?
Share on Facebook. Rheumatoid factor is a protein in your body that attacks healthy tissue. A high rheumatoid factor is indicative of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a painful condition that causes stiff, swollen, painful joints and fatigue. You have many treatment options available to you to treat this condition.
How to reduce inflammation in the body?
Avoid refined, white flour foods and foods high in table sugar like cookies and ice cream. They promote inflammation. Reduce your consumption of red meat and aim for healthier protein sources like whole soy foods, beans and cold-water fish rich in inflammation-fighting omega-3 fatty acids.
How to treat RA?
Adequate rest is also important for easing inflammation. A good exercise routine is an important part of treatment for RA.
How effective are corticosteroids?
If they are unsuccessful, other treatments are available. Corticosteroids quickly reduce pain and inflammation, slowing joint damage. They are most effective for short-term relief. Their power diminishes with long-term use, and they can cause many serious side effects.
What determines the most appropriate medication for a patient?
Medications. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate medications based on several factors. They include the severity of your condition, the length of time symptoms have been manifesting, blood tests, your overall health and the presence of any other medical problems . The most commonly prescribed treatments are listed below.
What is the best way to treat RA?
Probiotics are bacteria that benefit your health. You can find them in foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi. Probiotic supplements may also be effective for treating RA. A 2014 study found that taking probiotic supplements daily for 8 weeks decreased disease activity and inflammation.
What is the best treatment for arthritis?
Products that contain capsaicin, salicylates, camphor, or menthol are standard for treating arthritis. There’s limited current research on using these treatments for RA. Still, a 2017 study found that a gel containing menthol, benzocaine, and procaine hydrochloride resulted in temporary pain relief in people with RA.
How to help RA?
6. Massage. Massage can be done by a trained therapist, a family member, or by yourself, and may improve RA symptoms. found that after one month, people with RA who received moderate pressure massage had less pain, more grip strength, and increased range of motion over those who received light pressure massage.
What are some ways to make your hands easier?
Special household tools can make working with your hands easier. For example, grab bars and handrails in bathrooms and on stairs can help you navigate your home safely. 16. Creams, gels, and lotions. Topical creams, gels, and lotions can be rubbed directly onto the skin to help ease painful joints.
How to relieve RA pain?
Keep reading to find out more about these and other ways to relieve your RA pain. 1. Sleep. Getting enough sleep is important for everyone, but it’s especially important for those with RA. A 2018 study suggested that poor sleep quality influences levels of pain and your ability to move.
How to reduce RA?
Still, a healthy diet, stress management, regular exercise, and other remedies can help improve your quality of life.
What to do if you don't get enough sleep?
If you don’t get enough sleep at night, taking a nap during the afternoon may also help. If you’re experiencing insomnia or if you think you may have sleep apnea, talk to your doctor for diagnosis and a treatment plan. 2. Exercise.
What doctor treats RA?
If a patient is showing early signs and symptoms of RA, a doctor can refer the patient to a rheumatologist – a physician who specializes in arthritis and other diseases of the joints, muscles and bones. The rheumatologist will work with the patient and the patient’s primary care physician to reach a RA diagnosis and provide treatment.
How long does it take to show signs of RA?
That being said, the main criteria for diagnosing RA do not change. The patient must exhibit symptoms for greater than six weeks, symmetrical symptoms, as well as multiple joints being affected including fingers and hands.
What does it mean if a patient tests positive for anti-CCP?
If a patient tests positive for anti-CCP this is a strong indicator of RA. The anti-CCP antibodies can exist in a person’s system long before they ever exhibit symptoms of RA.
What does a physical exam show?
A full physical examination helps doctors find these symptoms and look at joints for tenderness, swelling, soreness, warmth, and redness. They will ask about difficulties moving joints and decreases in range of motion. Symptoms may come and go but typically, they do not. They remain noticeable and possibly progressive.
What are the conditions that doctors rule out?
Some of these conditions include: Other forms of arthritis including osteoarthritis. Lup us.
What is specific blood test?
The specific tests identify a specific set of antibodies that are known contributors of RA symptoms. The general blood tests look for overall inflammation levels in the body. When these results are placed together, they create an overall picture of a patient with RA (or without). These tests include:
What scans are needed for RA?
When a patient has strong and clear symptoms of RA, a doctor may also order a series of imaging scans. These include x-rays, CTs, MRIs, and possibly ultrasounds. In these imaging scans, doctors look for signs of joint damage. Bone and cartilage erosion as well as narrowing joint spaces can be signs of RA.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
- Rheumatoid arthritis can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages because the early signs and symptoms mimic those of many other diseases. There is no one blood test or physical finding to confirm the diagnosis. During the physical exam, your doctor will check your joints for swelling, r…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. But clinical studies indicate that remission of symptoms is more likely when treatment begins early with medications known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).