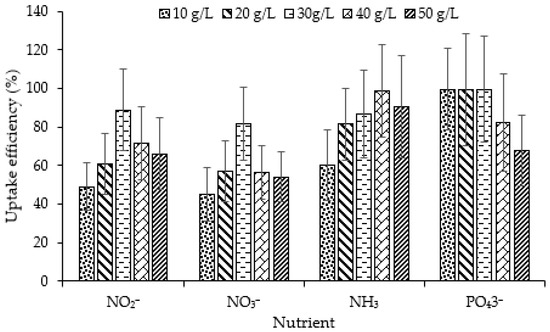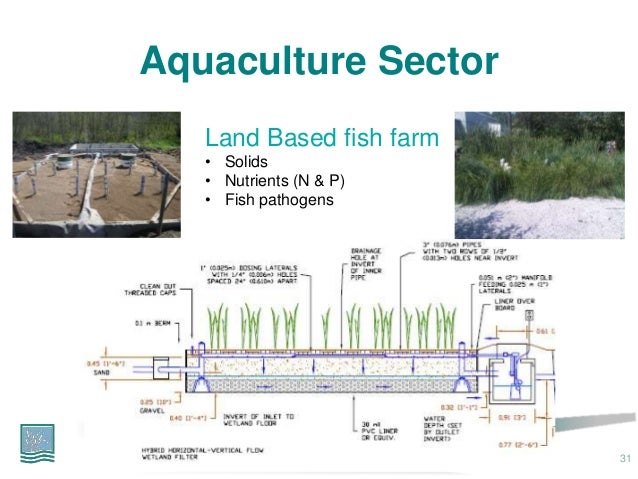
How to use anammox in wastewater treatment?
Different setups have been developed to apply Anammox in wastewater treatment. In the “two reactor nitritation-Anammox process“, ammonium is first partially oxidised to nitrite in an aerated reactor (partial nitritation). In a second stage the nitrite is reduced to elemental nitrogen using the remaining ammonium in the Anammox reactor.
What are the problems of anammox reactor?
As it is still a new technology, operation of an Anammox reactor requires a lot of knowledge. It is a high-tech system, which needs to be monitored (temperature, load, chemical compounds of wastewater, etc.). The problems that can occur are manifold and experts must be available for maintenance.
Can granular anammox biomass be used as an alternative to biofilms?
Granular anammox biomass can be used as a successful alternative to anammox biofilms when high DO concentrations are required to facilitate partial nitrification.
Do we need a nomenclature for anammox reactors?
With the experience of this first full-scale commercial Anammox reactor in operation, a consistent and descriptive nomenclature is suggested for reactors in which the Anammox process is employed.

How do you reduce TN in wastewater?
Therefore, in wastewater terms, to reduce the TN levels, the sewage first needs to be nitrified (ammonia converted to nitrates) as discussed in previous articles. Then this nitrified sewage needs to be converted to Nitrogen and Oxygen Gas. This process is called Denitrification.
How is ammoniacal nitrogen removed from wastewater?
Nitrification is the most common way to biologically remove ammonia in wastewater lagoons. In this process, ammonia treatment occurs via bacteria already present in the water. These bacteria break down the ammonia and eventually promote the release of nitrogen gas into the atmosphere.
How do you remove ammonia from water?
One of the most common methods for removal of ammonia from water is oxidation. In this work, ozonation of ammonia using microbubbles was studied in a pilot plant. The experimental results indicate that ozone microbubbles were quite effective in oxidizing ammonia.
How does anammox work?
Anammox (Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation) Bacteria combine ammonia and nitrite directly into dinitrogen gas. This allows a new and very efficient treatment possibility of wastewater. Large-scale treatment with the Anammox process is very complex in design, operation and maintenance.
How do you lower ammonia levels in wastewater treatment?
Ammonia stripping is a simple desorption process used to lower the ammonia content of a wastewater stream. Some wastewaters contain large amounts of ammonia and/or nitrogen-containing compounds that may readily form ammonia.
Does aeration reduce ammonia?
Aeration also reduces ammonia levels through physical means. Ammonia levels in wastewater can decrease through the process of desorption (Patoczka and Wilson, 1984).
How do you control ammonia?
0:571:57How to Control Ammonia in a Fish Tank | Aquarium Care - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo keeping the filtration balanced with the bio mass of the tank in other words having the rightMoreSo keeping the filtration balanced with the bio mass of the tank in other words having the right amount of fish for the right size filtration system is key to keeping your ammonia.
What chemical removes ammonia from water?
Ammonia is difficult to remove from water. It can be removed by cation exchange resin in the hydrogen form, which requires use of acid as a regenerant. Degasification can also be effective.
How do you restore ammonia from wastewater?
A better approach would efficiently capture ammonia directly from the wastewater. In this study, ammonia is recovered directly by using an electrically conducting gas-stripping membrane that is immersed into a wastewater reactor.
What are anammox reactions?
Anammox (anaerobic ammonium oxidation), which is a reaction that oxidizes ammonium to dinitrogen gas using nitrite as the electron acceptor under anoxic conditions, was an important discovery in the nitrogen cycle.
Where does anammox occur?
The anammox process was originally found to occur only from 20 °C to 43 °C but more recently, anammox has been observed at temperatures from 36 °C to 52 °C in hot springs and 60 °C to 85 °C at hydrothermal vents located along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
What is the purpose of Anammoxosome?
The anammoxosome membrane can be used to generate and maintain a proton motive force for ATP synthesis and to keep as much as possible of the valuable and toxic intermediates of the anammox process away from the rest of the cell.
What are the characteristics of anammox bacteria that are of particular interest for wastewater treatment?
The characteristic of anammox bacteria that is of particular interest for wastewater treatment is their ability to convert ammonium ion and nitrite ion into nitrogen gas in an anaerobic environment.
What is anammox bacteria?
The discovery of the type of bacteria now commonly called anammox bacteria is quite recent. In the mid-1990s anaerobic oxidation of ammonium ion was observed in a wastewater denitrifying pilot plant1. Subsequently the bacteria commonly called anammox bacteria were isolated and identified2. At about that time, it was also discovered that anammox bacteria are responsible for the conversion of a great deal of ammonia and nitrite nitrogen to nitrogen gas in our oceans and seas. The characteristic of anammox bacteria that is of particular interest for wastewater treatment is their ability to convert ammonium ion and nitrite ion into nitrogen gas in an anaerobic environment.
What happens if ammonia is oxidized?
If only half of the ammonia nitrogen in a wastewater flow were oxidized just to nitrite, then the remaining ammonia nitrogen and the nitrite nitrogen that has been formed could be converted to nitrogen gas by anammox bacteria in an anaerobic (absence of oxygen) environment. It turns out that this can be accomplished in a practical manner resulting ...
What is the next normal step in the nitrogen cycle?
The next normal step in the nitrogen cycle is oxidation of the ammonia nitrogen to nitrite ion (NO2-) by the appropriate aerobic bacteria and then oxidation of the nitrite ion to nitrate ion (NO3-) by another variety of aerobic bacteria. These oxidation processes taken together are called nitrification and require oxygen in order to take place.
Why is nitrification required in wastewater treatment plants?
If wastewater effluent containing ammonia nitrogen is discharged to a river, lake, or stream, nitrification will take place there, exerting a biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and using up dissolved oxygen from the water, thus affecting aquatic life. This is the reason that nitrification is required of most wastewater treatment plants.
How does nitrification work?
The nitrification that is required of most secondary wastewater treatment plants can be accomplished in a typical activated sludge wastewater treatment process by ensuring that there is adequate aeration to provide the necessary oxygen and by maintaining a long enough sludge retention time so that the slower growing nitrifying bacteria aren’t washed out of the system. With these steps the bacterial oxidation of ammonia nitrogen to nitrate (nitrification) will take place along with the bacterial oxidation of hydrocarbon BOD, as shown in the process flow diagram at the left. Nitrification, however, doesn’t remove the nitrogen from wastewater. It simply removes the oxygen demand, by converting ammonia nitrogen to nitrate nitrogen. If discharge of wastewater treatment effluent containing nitrate is a problem for the receiving body of water, then another process, denitrification, is also required.
Does nitrification remove nitrogen?
Nitrification, however, doesn’t remove the nitrogen from wastewater . It simply removes the oxygen demand, by converting ammonia nitrogen to nitrate nitrogen. If discharge of wastewater treatment effluent containing nitrate is a problem for the receiving body of water, then another process, denitrification, is also required. ...
How does anammox bacteria fulfill carbon requirements?
Anammox bacteria being chemoautotrophic, fulfill carbon requirements by fixing atmospheric CO 2 ( Gao et al., 2018 ). Hence, organic carbon is assumed to interfere with the growth of anammox bacteria. Out-competition is a form of inhibition that could occur when non-toxic organic carbon is in abundance where heterotrophic bacteria would go on to outcompete anammox bacteria. This form of inhibition is expected, primarily due to the fast growth rate exhibited by heterotrophic bacteria and the slow growth rate exhibited by anammox bacteria ( Jin et al., 2012, Mattei et al., 2015 ). The co-existence of anammox bacteria with other heterotrophic bacteria is also clearly reported in the literature ( Jin et al., 2012, Zhou et al., 2018 ). In fact, this co-existence is also known to play a crucial role in the complete removal of nitrogen from wastewater.
What pH is used for anammox?
The pH for optimum growth and anammox activity ranges from 6.5 to 9.0 ( Pereira et al., 2017 ). The inhibitory effects caused by a change in pH on anammox are mostly a result of toxic chemical formation ( Cho et al., 2020 ). For example, when pH is low, ammonia concentrations reduce, and free nitrous acid concentrations increase, and vice versa ( Tomaszewski et al., 2017 ). Accordingly, the anammox process is best carried out at neutral pH. There is an overall increase of pH during the anammox process, and hence pH control is critical to enable a stable operation of the reactor.
What is the most common species of anammox?
Kuenenia stuttgartiensis is the most commonly occurring species of anammox bacteria; therefore, it is extensively studied to unravel the metabolic pathway and genomic studies ( Almeida et al., 2015, Frank et al., 2018 ).
What temperature is anammox?
Temperature is one of the critical operating parameters that substantially impact anammox activity and efficiency in nitrogen removal. The temperature in anammox bioreactors poses a significant impact on anammox growth and activity by affecting the nitrogen removal, activating inhibitory factors that produce detrimental effects to the microbial community, and enhancing the stability of organic chemicals effluent water ( Li et al., 2018 ). Naturally, anammox bacteria occur under different temperature conditions ranging from 4 °C − 80 °C, which indicates utilizing an anammox process under various temperature ranges. However, in the practical scenarios, the best tolerable temperature for anammox bacteria lies between 20 °C − 45 °C ( Pereira et al., 2017 ).
What are the toxic metals in wastewater?
Industrial wastewater and landfill leachate are familiar sources of toxic metals in wastewater treatment plants. Metal ions are toxic to microorganisms due to cell accumulation and cell death/inhibition resulting from their impact on cell metabolism ( Cho et al., 2020, Jin et al., 2012, Yu et al., 2016 ). The most commonly identified toxic metals in anammox systems include Cu, Cr, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cd, and Mn. As reported in Val del Río et al., (2017), the concentration of these heavy metals that lead to a 50% loss in anammox activity lies between 19.3 mg/L to 175.8 mg/L, where Cu 2+ reports to have the lowest inhibitory concentration and Mn 2+ reports to have the highest inhibitory concentration concerning the anammox activity.
What are the two compounds that bacteria use to remove nitrogen?
These bacteria mostly utilize organic compounds as electron donors in reducing nitrate (NO3–) and nitrite (NO 2–) to form gaseous N compounds such as NO, N 2 O, and N 2 ( Du et al., 2019 ). The use of the anammox process as a biological method of nitrogen removal is a recent discovery.
How do anthropogenic activities contribute to nitrogen emissions?
Anthropogenic activities contribute to nitrogen emissions through multifaceted ventures with the rising world population. Excess nitrogen discharges into natural waterways leading to environmental issues such as soil acidification and eutrophication. In the last decade, the law and the community have placed stricter effluent criteria for nutrient effluent.
What is anammox in water?
Anammox stands for Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation. The process was discovered in the early nineties and has great potential for the removal of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater. The responsible bacteria transform ammonium (NH4+) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) into nitrogen gas (N2) and water (H2O). This saves costs as less energy for aeration ...
Why is Anammox important?
Because autotrophic bacteria carry out Anammox, there is no need for organic carbon sources, which saves on chemical dosage costs.
What is the process of denitrification called?
This process is called DEAMOX and stands for Denitrifying Ammonium Oxidation. It is the coupling of denitrification and Anammox processes. Research is still ongoing. It can be applied to the treatment of wastewater with high nitrogen concentrations and high organic carbon levels, e.g. landfill leachate and wastewater from digested animal waste (e.g. large anaerobic digestion reactor ).
What is the one step reactor process?
A common name is the CANON Process for ‘Completely Autotrophic Nitrogen removal Over Nitrite’ where aerobic ammonium oxidising bacteria (nitrifiers) and Anammox bacteria simultaneously perform a two-step reaction under oxygen-limited conditions in one reactor. However, this process is limited to the laboratory and pilot-plant scale due to the complex controlling conditions and the slow growth of Anammox bacteria (HUMBERT 2011).
What is the process of oxidizing ammonium?
In the “two reactor nitritation-Anammox process“, ammonium is first partially oxidised to nitrite in an aerated reactor (partial nitritation). In a second stage the nitrite is reduced to elemental nitrogen using the remaining ammonium in the Anammox reactor.
Is Anammox a low yield?
The biomass yield of Anammox is very low, which saves on sludge treatment costs. However, the long start-up time and the high sensitivity of the bacteria to oxygen concentration and nitrite accumulation limit the application of the Anammox process (LI et al. 2008).
Is Anammox a high tech reactor?
As it is still a new technology, operation of an Anammox reactor requires a lot of knowledge. It is a high-tech system, which needs to be monitored (temperature, load, chemical compounds of wastewater, etc.). The problems that can occur are manifold and experts must be available for maintenance.