
How do you find the treatment effect in an RCT?
Mar 28, 2018 · Within epidemiology a randomised controlled trial (RCT) is considered to be the best way to investigate the effect of a new treatment. Regarding the analysis of RCT data there is a debate in the epidemiological and biostatistical literature, whether an adjustment for the baseline value of the outcome variable should be made [ [1] , [2] , [3 ...
What are the key features of an RCT?
With the Brute Force Design, you can recover the average effect of the treatment on the whole population. This parameter is generally called the Average Treatment Effect (ATE). In this section, I am going to detail the assumptions required for the Brute Force Design to identify the ATE, how to form an estimator of the ATE and how to estimate its sampling noise.
What are randomised controlled trials (RCT)?
Jun 01, 2014 · Objective Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are often considered as the gold standard for assessing new health interventions. Patients are randomly assigned to receive an intervention or control. The effect of the intervention can be estimated by comparing outcomes between groups, whose prognostic factors are expected to balance by randomisation. …
How do you interpret dichotomous outcomes in an RCT?
Jun 01, 2018 · Within epidemiology a randomised controlled trial (RCT) is considered to be the best way to investigate the effect of a new treatment. Regarding the analysis of RCT data there is a debate in the epidemiological and biostatistical literature, whether an adjustment for the baseline value of the outcome variable should be made [ [1] , [2] , [3 ...
What is average treatment effect on the treated?
The average treatment effect (ATE) is a measure used to compare treatments (or interventions) in randomized experiments, evaluation of policy interventions, and medical trials. The ATE measures the difference in mean (average) outcomes between units assigned to the treatment and units assigned to the control.
How do you estimate treatment effect in RCT?
To estimate a treatment effect in an RCT, the analysis has to be adjusted for the baseline value of the outcome variable. A proper adjustment is not achieved by performing a regular repeated measures analysis (method 2) or by the regular analysis of changes (method 3).Mar 28, 2018
What is conditional average treatment effect?
Abstract We consider a functional parameter called the conditional average treatment effect (CATE), designed to capture heterogeneity of a treatment effect across subpopulations when the unconfoundedness assumption applies.
How do you calculate average causal effect?
Using conditional expectations we have Average causal effect=E(Yi|Xi=1)−E(Yi|Xi=0), Average causal effect = E ( Y i | X i = 1 ) − E ( Y i | X i = 0 ) , where Xi is a binary treatment indicator.
How is treatment treated calculated?
However, we can figure out the TOT by using the formula: TOT = ITT/(difference in percentage treated). In this case we have $21/. 3 = $70. The average person who picked up the money received $70.
How do you calculate treatment effect?
When a trial uses a continuous measure, such as blood pressure, the treatment effect is often calculated by measuring the difference in mean improvement in blood pressure between groups. In these cases (if the data are normally distributed), a t-test is commonly used.
What is population average treatment effect?
Often the target causal parameter is the population average treatment effect (PATE): the expected difference in the counterfactual outcomes if all members of some population were exposed and if all members of that population were unexposed.Apr 18, 2016
What is the difference between average treatment effect and average treatment effect on the treated?
ATE is the average treatment effect, and ATT is the average treatment effect on the treated. The ATT is the effect of the treatment actually applied.Oct 25, 2017
What is treatment effect size?
What is an effect size? In medicine, a treatment effect size denotes the difference between two possible interventions. This can be expressed in point change on a rating scale or the percentage of people who meet the threshold for response.Oct 3, 2019
How do you calculate average treatment effect in Excel?
0:023:053.2 (a) Average Treatment Effect (ATE) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis means within each group for by T treatment. And control summarize. The variable X dot. TheMoreThis means within each group for by T treatment. And control summarize. The variable X dot. The average expenditures of households in the control group where T equals zero.
What is the average causal effect?
In this article, the authors review Rubin's definition of an average causal effect (ACE) as the average difference between potential outcomes under different treatments. The authors distinguish an ACE and a regression coefficient.
What is complier average causal effect analysis?
The complier average causal effect (CACE) parameter measures the impact of an intervention in the subgroup of the population that complies with its assigned treatment (the complier subgroup).Apr 4, 2014
3.1 Brute Force Design
In the Brute Force Design, eligible individuals are randomly assigned to the treatment irrespective of their willingness to accept it and have to comply with the assignment. This is a rather dumb procedure but it is very easy to analyze and that is why I start with it.
3.2 Self-Selection design
In a Self-Selection design, individuals are randomly assigned to the treatment after having expressed their willingness to receive it. This design is able to recover the average effect of the Treatment on the Treated (TT).
3.3 Eligibility design
In an Eligibility design, we randomly select two groups among the eligibles. Members of the treated group are informed that they are eligible to the program and are free to self-select into it. Members of the control group are not enformed that they are eligible and cannot enroll into the program.
3.4 Encouragement Design
In an Encouragement Design, we randomly select two groups among the eligibles, as in Randomization After Eligibility. Treated individuals randomly receive an encouragement to participate in the program and decide whether they want to comply with the encouragement and join the program.
What is a RCT?
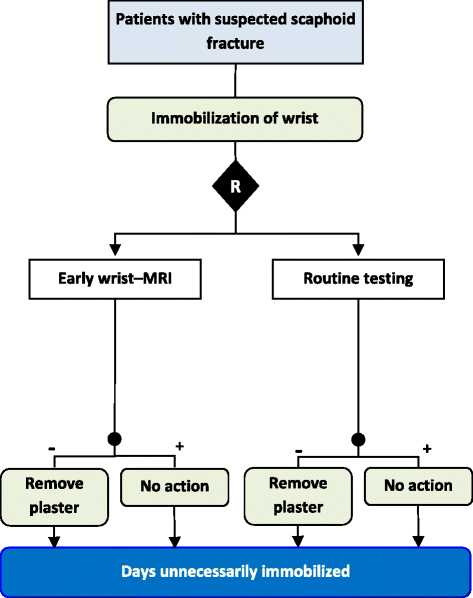
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are often considered as the gold standard for assessing new health interventions where patients are randomly assigned to receive an intervention or control (eg, placebo). Since patients’ prognostic factors are expected to balance by randomisation patients’ outcomes can be directly compared between groups to infer the effect of a treatment. In many cases, patients may not fully comply with their assigned treatment according to the protocol. Such protocol violation compromises the ‘fair’ comparison, which is protected by randomisation, and will potentially bias the estimate of treatment effect. Analysing RCTs subject to non-compliance can be challenging. While different analyses have been proposed to deal with non-compliance, the bias of treatment effect estimate is rarely compared among different approaches. Result interpretations also vary depending on the nature of non-compliance and the objective of a trial. Some RCTs, known as pragmatic trials, 1–3 are primarily designed to guide clinical practice. Their goal is often to assess whether an intervention will work in routine practice. In contrast, non-pragmatic trials usually focus on the biological efficacy of an intervention. Despite the objective, an analysis that provides an unbiased or less biased estimate of treatment effect is always desirable. In this study, we compare common approaches to analyse non-compliant data in RCTs. The results will provide useful knowledge in choosing optimal methods for different non-compliant scenarios.
How is the ITT approach analysed?
In the ITT approach, patients are analysed by how they were randomised regardless of their actual compliance with treatment. The treatment effect was estimated by where and were the mean outcome scores of the intervention and usual care groups, respectively.
What is an objective controlled trial?
Objective Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are often considered as the gold standard for assessing new health interventions. Patients are randomly assigned to receive an intervention or control. The effect of the intervention can be estimated by comparing outcomes between groups, whose prognostic factors are expected to balance by randomisation.
What is pragmatic trial?
Some RCTs, known as pragmatic trials, 1–3 are primarily designed to guide clinical practice. Their goal is often to assess whether an intervention will work in routine practice. In contrast, non-pragmatic trials usually focus on the biological efficacy of an intervention.
What is the assumption advantage of repeated measures analysis?
An assumed advantage of repeated measures analysis is that subjects with only a baseline value, but with missing data at all the follow-up measurements are still part of the analysis. When applying longitudinal analysis of covariance (method 1), individuals with only a baseline measurement are not part of the analysis.
Does regression increase or decrease blood pressure?
Because in the example dataset, the treatment group has a lower mean blood pressure at baseline, regression to the mean tend to increase blood pressure for the treatment group and tend to decrease blood pressure for the control group.
What is external validity in RCT?
An RCT may give an unbiased estimate of the Sample Average Treatment Effect (SATE), but external validity is an issue when the individuals in the RCT are unrepresentative of the actual population of interest. For example, the participants in an RCT in which individuals volunteer to sign up for health insurance may be in poorer health at baseline than the overall population. External validity is particularly relevant to policymakers who want to know how the treatment effect would generalize to the broader population.
Does the Patt C estimator outperform its unadjusted counterpart?
The simulation results presented in Section 4 show that the PATT-C estimator outperforms its unadjusted counterpart when the compliance rate is low. Of course, the simulation results depend on the particular way we parameterized the compliance, selection, treatment assignment, and response schedules.
What is treatment effect in RCTs?
Treatment effect in RCTs may be reported in various ways including absolute risk, relative risk, odds ratio, and number needed to treat . These measures of treatment effect and their advantages and disadvantages have recently been reviewed. 21 A large treatment effect may be more important than a small one.
What to consider when reading an RCT article?
When you are reading an RCT article, the answers to a few questions will help you decide whether you can trust the results of the study and whether you can apply the results to your patient or population. Issues to consider when reading an RCT may be condensed into three important areas 8:
Why is randomization important in RCT?
Randomisation ensures that known and unknown baseline confounding factors would balance out in the treatment and control groups. However, after randomisation, it is almost inevitable that some participants would not complete the study for whatever reason. Participants may deviate from the intended protocol because of misdiagnosis, non-compliance, or withdrawal. When such patients are excluded from the analysis, we can no longer be sure that important baseline prognostic factors in the two groups are similar. Thus the main rationale for random allocation is defeated, leading to potential bias.
What is the most rigorous scientific method for evaluating the effectiveness of health care interventions?
An RCT is the most rigorous scientific method for evaluating the effectiveness of health care interventions. However, bias could arise when there are flaws in the design and management of a trial.
Why is RCT important?
It is important for people reading medical reports to develop the skills for critically appraising RCTs, including the ability to assess the validity of trial methodology, the magnitude and precision of the treatment effect, and the applicability of results.
What is triple blind study?
When, rarely, study participants, data collectors, and data evaluators such as statisticians are all blinded, the study is referred to as “triple blind”. 5. Recent studies have shown that blinding of patients and health care professionals prevents bias.
How does allocation concealment work?
Allocation concealment is a technique that is used to help prevent selection bias by concealing the allocation sequence from those assigning participants to intervention groups, until the moment of assignment . The technique prevents researchers from consciously or unconsciously influencing which participants are assigned to a given intervention group. For instance, if the randomisation sequence shows that patient number 9 will receive treatment A, allocation concealment will remove the ability of researchers or other health care professionals from manoeuvring to place another patient in position 9.
Is the compliance rate imperfect?
In reality, however, the compliance rate is often imperfect, which prevents researchers from identifying the ATE. In such cases, estimating the LATE becomes the more feasible option.
Can ATE be recovered?
In the presence of non-compliance, the ATE can no longer be recovered. Instead, what is recovered is the average treatment effect for a certain subpopulation known as the compliers, which is the LATE. When there may exist heterogeneous treatment effects across groups, the LATE is unlikely to be equivalent to the ATE.
