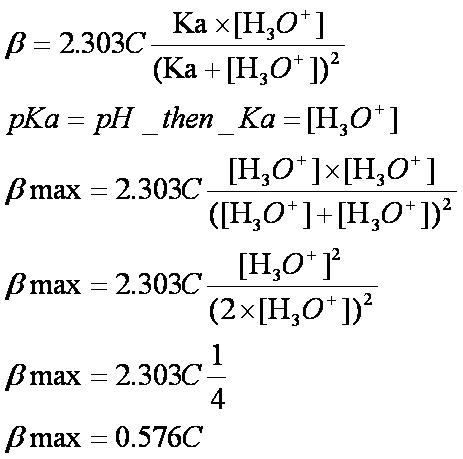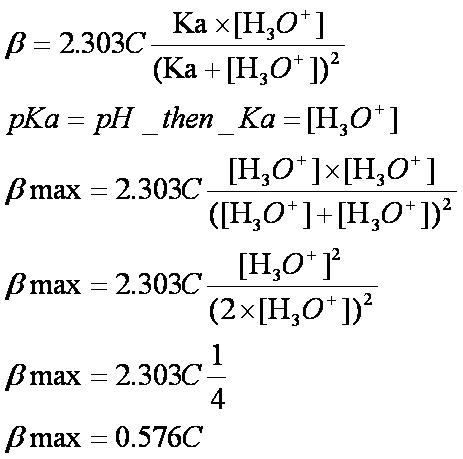
Minimize volume change due to evaporation by covering loosely. Cool to room temperature. Set pH to 9.0 again. Boil until colorless. Repeat this cycle until the solution remains at pH 9.0 after boiling and cooling. Bring up to the initial volume with water.
Full Answer
How do you determine the volume of buffer for dialysis?
The volume of buffer for dialysis is determined by two factors; how high dilution you should like to reach and how many steps you would like to employ. In general, if dilution higher than 100-fold is the aim, you should plan more than one dilution step.
What is the recommended buffer volume for YUO assay?
My general rule is that buffer volume has to be 10X-20X the sample. Dialysis duration (O/N rather than few hours), temperature (I assume yuo operate at about 4°C) and buffer changes affect the buffer exchange and are to be taken into consideration. In general, the more the better.
What is the recommended range of sample volumes for purification?
The recommended range of sample volumes is 0.1 to 1.5 mL when complete removal of low molecular weight components is desired. The separation is not affected by the flow rate, in the range of 1 to 10 mL/min.
What is the recommended Stacker volume of equilibration buffer?
† For sample volumes less than 0.10 mL it is recommended to apply a stacker volume of equilibration buffer to reach a total of 0.10 mL after the sample has fully absorbed. For sample volumes ranging from 0.1 to 2.5 mL, it is possible to run multiple samples in parallel with PD-10 Desalting, PD MidiTrap™ G-25, and PD MiniTrap™ G-25 columns.
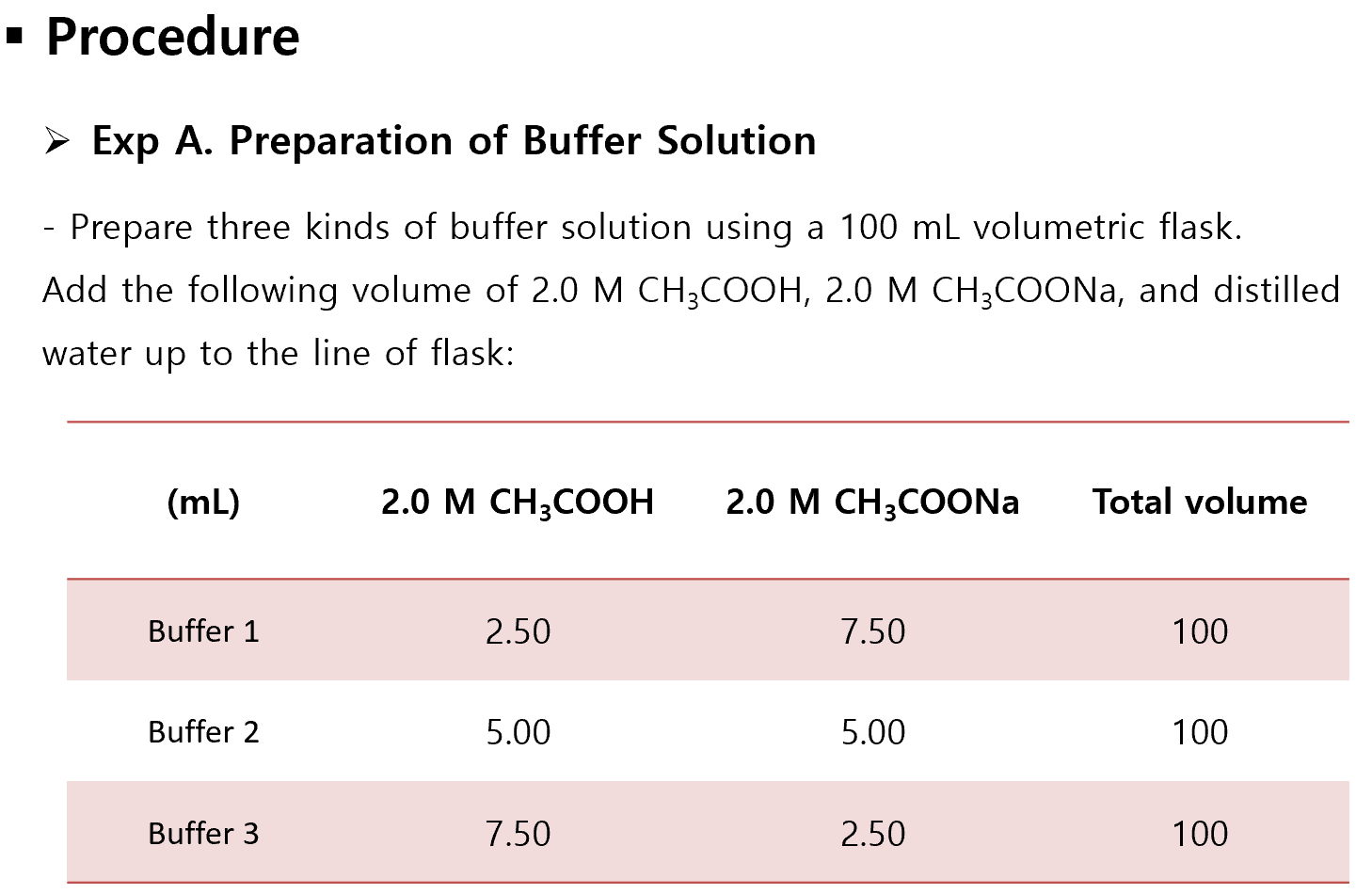
How do you normalize sample data?
Here are the steps to use the normalization formula on a data set:Calculate the range of the data set. ... Subtract the minimum x value from the value of this data point. ... Insert these values into the formula and divide. ... Repeat with additional data points.
How do you calculate normalized volume?
The equation for normalization is derived by initially deducting the minimum value from the variable to be normalized. The minimum value is deducted from the maximum value, and then the previous result is divided by the latter.
How do you normalize a protein sample?
Idea 1: make an equal concentration of protein using protein extraction buffer what you have used previously. For sample 3 protein 1.176 / 0.462 = 2.545 time dilution possible, you will take 1 fold protein (1µl) sample of stock and 1.545 (1.545 µl) fold of extraction buffer = 2.454 µl.
How do you normalize a sample in western blot?
There are two approaches to normalization when evaluating a western blot: single protein detection and total protein normalization. By far the most common approach to single protein detection is to use housekeeping proteins. Their abundance within a sample serves as a proxy for the entire protein population.
What is Normalised volume?
To normalize audio is to change its overall volume by a fixed amount to reach a target level. It is different from compression that changes volume over time in varying amounts. It does not affect dynamics like compression, and ideally does not change the sound in any way other than purely changing its volume.
What is the formula for Normalisation?
SummaryNormalization TechniqueFormulaLinear Scalingx ′ = ( x − x m i n ) / ( x m a x − x m i n )Clippingif x > max, then x' = max. if x < min, then x' = minLog Scalingx' = log(x)Z-scorex' = (x - μ) / σJun 13, 2021
What is normalization of protein?
Total protein normalization (TPN) is a technique that can be used to quantify the abundance of the protein of interest without relying on housekeeping genes. Traditionally, TPN is performed by incubating the membrane with a total protein stain, either before or after detection with antibodies.
How do you normalize protein to loading control?
To normalize expression, multiply the density of the target protein in each lane by the ratio of loading control density from the control sample (lane 1) to the loading control density of other lanes.
What is Normalisation?
What Does Normalization Mean? Normalization is the process of reorganizing data in a database so that it meets two basic requirements: There is no redundancy of data, all data is stored in only one place. Data dependencies are logical,all related data items are stored together.
How do you quantify and normalize Western blot data?
0:293:36Total Protein Normalization - Basic Tutorial - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis is done by selecting Blaine. And bands in analysis toolbox. Then under the normalization.MoreThis is done by selecting Blaine. And bands in analysis toolbox. Then under the normalization.
Why do we normalize data in Western blot?
The overall goal of normalization is to minimize effects arising from variations in experimental errors, such as inconsistent sample preparation, unequal sample loading across gel lanes, or uneven protein transfer, which can compromise the conclusions that can be obtained from Western blot data.
What is a normalizing control?
Normalization uses an internal loading control to correct for unavoidable sample-to-sample and lane-to-lane variations. Without Western blot normalization, you can't know if changes in band intensity reflect biological change in your samples or variability in sample preparation, loading, and transfer.
How do you calculate normalized revenue?
Divide your total earnings by the number of years of the business cycle to calculate your normalized earnings. Continuing the example, divide $430,000 by 5 to get $86,000 in normalized earnings. This means that your business generates an average of $86,000 in a typical year of business.
What dB should I normalize to?
So you can use normalization to reduce your loudest peak by setting the target to just under -3 dB, like say -2.99 dB.
What is a normalized value?
What is Normalization? Normalization is a scaling technique in which values are shifted and rescaled so that they end up ranging between 0 and 1. It is also known as Min-Max scaling.
What does normalize volume in Spotify mean?
A louder song generally has a different impact on listeners than a softer, quieter song. To help even this out, Spotify uses something called volume normalization. This helps to ensure that the volume levels for any song or audio file you play using Spotify remains at the same level.
Most recent answer
For Vivek, Regarding Buffer exchange: Dialyzing against water will precipitate out many proteins..which protein did you try this with?
All Answers (23)
The volume must be enormous if compared to that of the sample. This, is the main rule to follow. At least three changes are recommended for successful dialysis.
Similar questions and discussions
What should be the ideal dialysis buffer composition for a His-tagged purified protein to remove imidazole salts?
Which is more efficient, continuous or discontinuous diafiltration?
In general, continuous diafiltration is more efficient than discontinuous diafiltration. In discontinuous diafiltration, the permeate flux decreases as the sample concentration increases, which can contribute to membrane fouling and cause increased retention of microsolutes that would otherwise pass through the membrane.
Why is the macrosolute concentration achieved during ultrafiltration?
During ultrafiltration, the desired macrosolute concentration is achieved because the concentration of non-permeating species is increased while the fluid volume is reduced. Furthermore, the concentration of membrane-permeating species such as salts and microsolutes remains unchanged.
What buffers are used for desalting?
All commonly used aqueous buffers can be used for desalting/buffer exchange. Often a buffer with 25 to 50 mM concentration of the buffering substance is sufficient. A salt concentration of at least 25 mM is recommended to prevent possible ionic interactions with the chromatography medium. Sodium chloride is often used for this purpose. At salt concentrations above 1 M, hydrophobic substances may be retarded or may bind to the chromatography medium. At even higher salt concentrations (> 1.5 M ammonium sulfate), the column packing shrinks.
What is desalting at the laboratory scale?
Desalting at laboratory scale is a well-proven, simple, and very fast method that will rapidly remove low molecular weight contaminants at the same time as transferring the sample into the desired buffer in a single step.
What is the salt concentration of a chromatography?
A salt concentration of at least 25 mM is recommended to prevent possible ionic interactions with the chromatography medium. Sodium chloride is often used for this purpose. At salt concentrations above 1 M, hydrophobic substances may be retarded or may bind to the chromatography medium.
Why is the equilibration buffer left in the resin?
Because the solution carrying the sample into the column displaces the solution the resin is equilibrated in, the macromolecules that emerge from the column will be carried in the equilibration buffer. The original buffer is left in the resin, hence the term, buffer exchange.
What is sample preparation and clean up?
In the context of protein science and proteomics research, sample preparation and clean-up refers to an eclectic set of techniques aimed at making extracted or purified protein samples suitable for long-term storage or compatible with downstream applications. Dialysis, diafiltration and gel filtration (desalting) are the most broadly applicable methods for sample preparation. These techniques are based on well-understood principles of size exclusion and have been used in laboratory research for many decades. Advances in the quality of materials and designs used to make dialysis, diafiltration and desalting devices have kept pace with the changes in scale, refinement and convenience that modern research experiments require.
What is diafiltration used for?
Diafiltration, similar to dialysis, uses a semi-permeable membrane to separate macromolecules from low molecular-weight compounds. Unlike dialysis, which relies on passive diffusion, diafiltration involves forcing solutions through the membrane by pressure (i.e., reverse osmosis, syringe tip sterilization cartridges) or centrifugation. A variety of different types of protein concentrators are commercially available.
How are target proteins concentrated?
Target proteins are concentrated when they bind to the chromatography medium at low ionic strength, and elute differentially in a purified, concentrated form by increasing salt concentration or by changing pH in a gradient. Learn more. Protein Sample Preparation eLearning Course. Select products.
How to separate small molecules from large proteins?
Small molecules may be separated from large proteins in a sample via precipitation with acetonitrile. When used in combination with 96-well centrifuge filter plates, this method is ideal for processing many samples at once. Protocol for removing substances that interfere with colormetric protein assays.
How to remove interfering substances?
One method used to remove interfering substances is to selectively precipitate proteins using trichloroacetic acid (TCA) or acetone. The solution containing the interfering substance is removed and the protein is then resolubilized in an assay-compatible buffer.
What is the matrix used in affinity purification?
The support or matrix in affinity purification is any material to which a biospecific ligand is covalently attached. Typically, the material used as an affinity matrix is insoluble in the system in which the target molecule is found. Usually, but not always, the insoluble matrix is a solid.
Flow cytometry buffers for sample preparation
Sample preparation is an important step for obtaining statistical value from flow cytometry experiments. Sample preparation reagents for flow cytometry include cell surface staining, intracellular and transcription factor staining buffer sets, cell lysis assays, blocking reagents, and magnetic cell isolation beads.
Flow cytometry buffers for intracellular and cytoplasmic staining
Fixatives are necessary for saving samples to be used later or for looking at intracellular or intranuclear targets. Ready-to-use fixation kits are optimized for flow cytometry applications. Benefits of using these kits include the following:
Cytoplasmic and cytokine staining reagent kits
Activated cells often express higher levels of transcription factors, cytokines, chemokines, and other mediators detected by flow cytometry.
Nuclear staining reagent kits
Flow cytometry permits the detection of transcription factors within discrete immune cell subsets among a heterogeneous population and provides a sensitive approach to analyzing an immune response. Refer to the following section on intracellular staining buffers prior to any transcription factor staining analysis. Benefits include:
Resources
Flow Cytometry Learning Center —Access flow cytometry educational resources for better experiment planning and execution.
Support
Flow Cytometry Support Center —Find technical support recommendations for your flow cytometry workflows, including tips for experimental setup and in-depth troubleshooting help.
How to achieve cell lysis with detergent free buffer?
Cell lysis with detergent-free buffer is achieved by mechanical shearing, often with a Dounce homogenizer or by passing cells through a syringe tip. In these cases, a simple Tris buffer will suffice, but as noted above, buffers with detergents are required to release membrane- or cytoskeleton-bound proteins.
What is lysis buffer?
Lysis buffers. Lysis buffers differ in their ability to solubilize proteins, with those containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and other ionic detergents considered to be the harshest and therefore most likely to give the highest yield. The main consideration when choosing a lysis buffer is whether the chosen antibody will recognize denatured ...
How to denature a protein?
To denature, use a loading buffer with the anionic detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and boil the mixture at 95–100°C for 5 min. Heating at 70°C for 5–10 min is also acceptable and may be preferable when studying multi-pass membrane proteins.
How long does deoxycholate buffer stay at 4°C?
0.5% deoxycholate. All four of these buffers will keep at 4°C for several weeks or for up to a year if divided into aliquots and stored at -20°C. Protease and phosphatase inhibitors. As soon as lysis occurs, proteolysis, dephosphorylation and denaturation begin.
What temperature can you freeze bovine serum albumin?
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is a frequently used protein standard. Once you have determined the concentration of each sample, you can freeze them at -20°C or -80°C for later use or prepare for immunoprecipitation or for loading onto a gel. . Preparation of samples for loading into gels.
What is the protocol for RIPA?
Nuclear. RIPA or use nuclear fraction protocol*. Mitochondria. RIPA or use mitochondrial fraction protocol*. *Proteins that are found exclusively or predominantly in a sub-cellular location will be more enriched in a lysate of the sub-cellular fraction compared with whole cell or tissue lysates.
What is the pH of SDS?
Check the pH and bring it to pH 6.8. When SDS is used with proteins, all of the proteins become negatively charged by their attachment to the SDS anions. SDS binds to proteins fairly specifically in a mass ratio of 1.4:1. In doing so, SDS confers a negative charge to the polypeptide in proportion to its length.