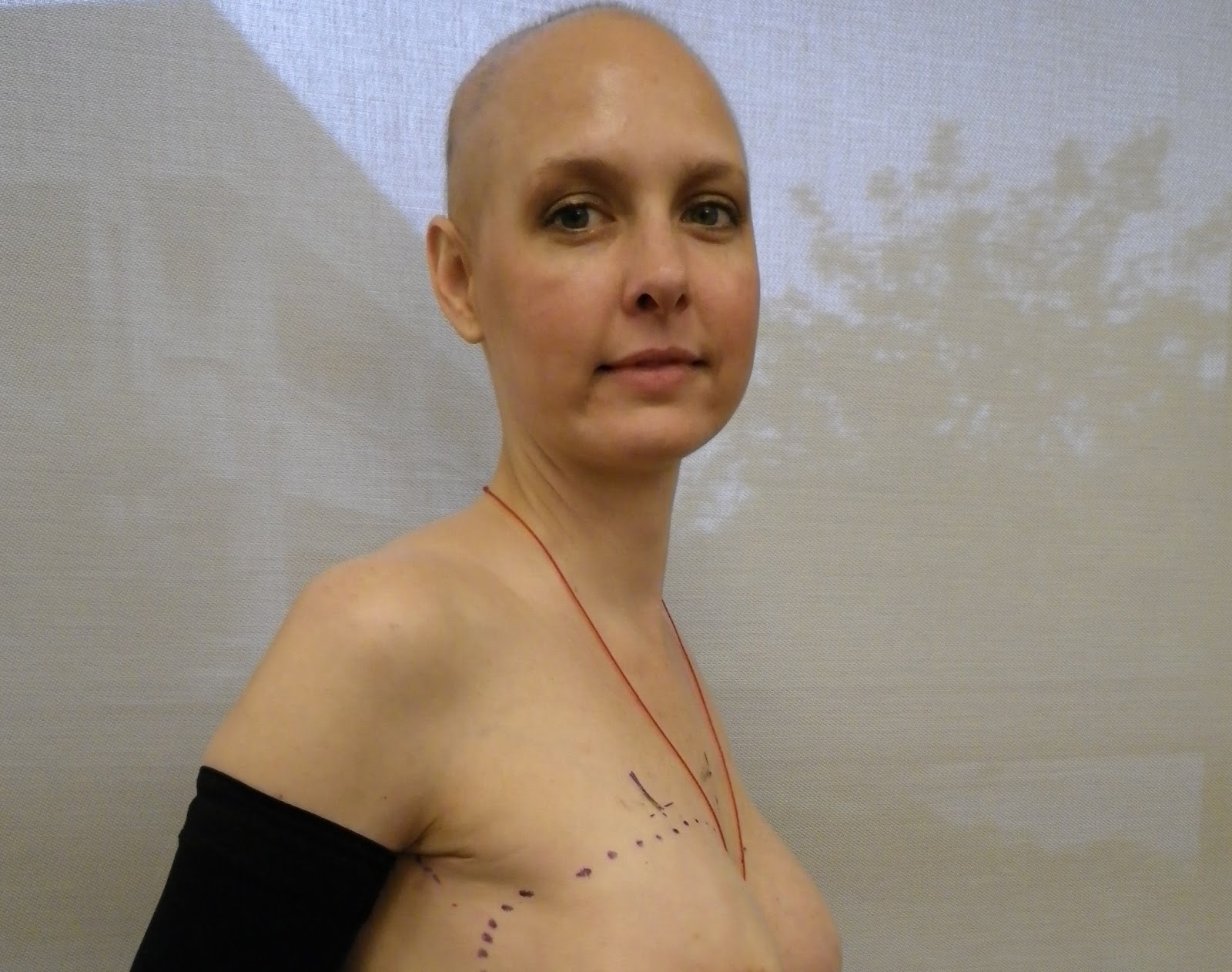
Before breast radiation is delivered, skin markings known as radiation tattoos, need to be placed on the skin. These marks help the radiation therapist aim the radiation precisely where it's needed.
What should I know about skin markings before breast radiation?
Before having breast radiation, you may need to have skin markings or radiation tattoos put on your breast skin. These marks help your radiation therapist aim the radiation precisely where it's needed.
What is the best way to mark during radiation therapy?
Tattoo is an advantageous method of marking because it ensures that the markings will not move or fade, and lessens the time it takes to set up during radiation therapy. However, it is important to note that there may be moderate pain or discomfort associated with the tattooing process.
What do you need to know about radiation for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy for breast cancer 1 Overview. Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays,... 2 Why it's done. Radiation therapy kills cancer cells. 3 Risks. Side effects from radiation therapy differ significantly depending on the type... 4 How you prepare. A doctor helps a woman prepare for radiation therapy.
What do breast radiation tattoos look like?
Your breast radiation tattoos will be tiny—about the size of a freckle, or one millimeter in diameter. There will often be four tattooed dots, each marking one corner of the area to be radiated, but some radiation centers are now only doing one or two.

How do they mark your breast for radiation?
Skin markings (tattoos) Your radiation therapists will use a felt-tipped marker to draw on your skin in the treatment area. You may also need skin markings called tattoos. If you do, your radiation therapists will use a sterile (clean) needle and a drop of ink to make them. Each tattoo will feel like a pinprick.
Where are tattoos placed for breast radiation?
What many people might not realise though is that radiographers often use small permanent black ink tattoos in order to position a patient underneath the radiotherapy machine. These small tattoos are placed on the patient's breast bone, and at points across the thorax.
What are markers for radiation therapy?
Fiducial markers are tiny metal objects (about the size of a grain of rice). They help your healthcare providers line up the beams of radiation and make sure your radiation therapy is delivered exactly the same way each time. This helps them target the tumor and avoid your nearby healthy tissue.
How long does it take to get markings for radiation?
The marks are very small and sometimes it can take up to 5-7 minutes for the radiation therapist to locate them all prior to each treatment session - longer for freckled, densely haired, or darker-toned skin.
What do breast radiation tattoos look like?
Radiation tattoos are usually blue or black in color and are very small. They may look like a freckle.
Are radiation tattoos painful?
Your care team will tattoo a few tiny dots on you in your affected area so they can line up the machine correctly with your tumor. The needle is tiny, and it doesn't hurt.
How long does it take for fiducial marker placement?
Additional images may be taken to confirm the placement of fiducial markers. This procedure is usually completed within one hour. You may be required to stay in an area for observation for several hours.
Do fiducial markers hurt?
Fiducial markers, also known as fiducials, are tiny metal implants (about 3 mm in size) that are placed in your body through a fine needle to guide radiation treatment. The markers themselves aren't painful, and you aren't able to feel them inside you.
What are the side effects of fiducial markers?
Pain, obstruction, and fever and shivers affected 3-4% of patients. Grade 3 rectal bleeding, haematuria, fever and shivers, and urinary frequency affected 0.5-1.5% of patients. Only one patient had a Grade 4 complication (i.e. fever and shivers). Overall, 9% of patients had symptoms lasting more than 2 weeks.
What should you not do during radiation?
Avoid raw vegetables and fruits, and other hard, dry foods such as chips or pretzels. It's also best to avoid salty, spicy or acidic foods if you are experiencing these symptoms. Your care team can recommend nutrient-based oral care solutions if you are experiencing mucositis or mouth sores caused by cancer treatment.
Do you lose hair with breast radiation?
Radiation treatment and hair loss If radiation is used to treat the breast, there is no hair loss on your head. But there might be loss of hair around the nipple, if you have hair there. Radiation to the brain, used to treat breast cancer that has spread (metastasized) to the brain, can cause hair loss on your head.
Do they tattoo you for radiation therapy?
During your simulation, the radiation therapist may need to put permanent (won't come off) marks on your skin. These marks are called tattoos. The therapists use these marks to line you up for treatment every day. The tattoos are often placed during simulation in the area of the body where the treatment will be given.
What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays, protons or other particles to kill cancer cells. Rapidly growing cells, such as cancer cells, are more susceptible to the effects of radiation therapy than are normal cells. The X-rays or particles are painless and invisible.
How to reduce the risk of breast cancer after surgery?
Radiation therapy is an effective way to reduce your risk of breast cancer recurring after surgery. In addition, it is commonly used to ease the symptoms caused by cancer that has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic breast cancer).
What is the most common type of radiation after a lumpectomy?
One of the most common types of radiation therapy after a lumpectomy is external beam radiation of the whole breast (whole-breast irradiation). Radiation to part of the breast. Radiation therapy to part of the breast (partial-breast irradiation) may be an option for some early-stage breast cancers.
What is radiation after a lumpectomy?
Adding radiation after a lumpectomy reduces the risk that cancer will return in the affected breast. Lumpectomy combined with radiation therapy is often referred to as breast conservation therapy. This type of treatment is as effective as having all the breast tissue removed (mastectomy).
What is the best treatment for breast cancer after lumpectomy?
Radiation after lumpectomy. If you're having an operation to remove the breast cancer and leave the remaining breast tissue intact (lumpectomy or breast-conserving surgery), your doctor may recommend radiation after your procedure to kill any cancer cells that might remain.
What is the procedure to remove breast cancer?
Internal radiation (brachytherapy). After you have surgery to remove the cancer, your doctor temporarily places a radiation-delivery device in your breast in the area where the cancer once was. A radioactive source is placed into the device for short periods of time over the course of your treatment.
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy. External beam radiation uses high-powered beams of energy to kill cancer cells. Beams of radiation are precisely aimed at the cancer using a machine that moves around your body. Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays, protons or other particles to kill cancer cells.
How many tattoos can a radiographer make?
Tattoo marks. During your radiotherapy planning session, your radiographer (sometimes called a radiotherapist) might make between 1 to 5 permanent pin point tattoo marks on your skin. For some types of radiotherapy, for example, electron treatments, you might not have tattoo marks.
Can a radiographer draw on tattoos?
Ink markings. Your radiographer might also draw marks around the tattoos with permanent ink pen. This helps to highlight the tattoos so they can be seen more easily in the room where you have treatment, which can be dark. Don't try to wash them off. The pen marks will start to rub off in time.
What are the techniques used to mark skin during radiation?
Common marking techniques include marker pen, henna, and tattoo.
Why do tattoos have blue dots?
These are the markings that our organization refers to “My Blue Dots.”. Tattoo is an advantageous method of marking because it ensures that the markings will not move or fade, and lessens the time it takes to set up during radiation therapy . However, it is important to note that there may be moderate pain or discomfort associated with ...
Is radiation tattooing painful?
However, it is important to note that there may be moderate pain or discomfort associated with the tattooing process. A less common method of radiation marking is henna. In this method, leaves from the henna tree are broken down and used as ink to stain the skin surface.
Is henna less invasive than tattoos?
Compared to tattoo, henna is slightly less invasive as it is not injected to the skin. However, henna is very time-consuming and may fade during the course of radiation therapy. The last method is marker pen. This is the easiest method of radiation marker, but also has its drawbacks.
What is the radiation called after breast cancer?
After that, you may receive an extra dose of radiation called a “boost.”. The boost directs radiation to the area where the lump or cancer cells were located, instead of at your whole breast. Before your boost, your radiation oncologist will make more skin markings with a felt-tipped marker to outline the boost field.
How to protect yourself from radiation?
Talk with others. When people try to protect each other by hiding their feelings, they can feel very alone. Talking can help the people around you know what you’re thinking. It might help to talk about your feelings with someone you trust. You may choose your spouse or partner, a close friend, family member, chaplain, nurse, social worker, or psychologist. You may also find it helpful to talk to someone who’s going through radiation therapy, or a cancer survivor or caregiver who has been through a similar treatment. Through our Patient-to-Patient Support Program, you have a chance to speak with former patients and caregivers. To learn more about this service, please call 212-639-5007.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to treat cancer. It works by damaging the cancer cells and making it hard for them to reproduce. Your body is then naturally able to get rid of these damaged cancer cells. Radiation therapy also affects normal cells.
How long does it take for a breast to feel swollen?
Your breast or chest may feel heavy or swollen. You may also have some shoulder stiffness on your affected side. These sensations may begin within the first few days of treatment and go on for many months after your treatment is done. Below are suggestions to help you reduce this discomfort.
Does radiation therapy affect normal cells?
Radiation therapy also affects normal cells. However, your normal cells are able to repair themselves in a way that cancer cells can’t. During treatment, a machine will aim beams of radiation directly to the tumor. The beam passes through your body and destroys cancer cells in its path.
Can you have radiation before surgery?
You can have it to your breast or chest wall and to the lymph nodes near your collarbone or under your arm. Back to top.
Can you pass radiation to someone else?
You might have concerns about how cancer and your treatment can affect your sexuality. You aren’t radioactive. You can’t pass radiation to anyone else, so it’s safe to be in close contact with other people.
Technical Advancements For Late Complication Risk Reduction
Several radiation techniques for delivering dose to the breast and regional lymphatics while sparing healthy tissue have been developed, including: 3D conformal radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiation therapy , deep-inspiration breath hold , prone positioning, accelerated partial breast radiation , hypofractionation and proton beam radiotherapy .
What Are The Physical Side Effects
Receiving the radiation will not be painful. Side effects vary from person to person and depend on the site being treated. The most common side effects in the treatment of breast cancer are:
What Side Effects Occur With Radiation Therapy To The Breast And Chest
Radiation treatment to the chest may cause several changes. You will notice some of these changes yourself, and your treatment team will keep an eye on these and others. For example, you may find swallowing to be difficult or painful. You may develop a cough.
How Does Radiation Therapy Work
Radiation therapy uses special high-energy X-rays or particles to damage a cancer cells DNA. When a cancer cells DNA is damaged, it cant divide successfully and it dies.
Side Effects Of Radiotherapy For Breast Cancer
Radiotherapy can cause side effects in the area of your body that is being treated. You may also have some general side effects, such as feeling tired.
Travelling To Radiotherapy Appointments
You might have to travel a long way each day for your radiotherapy, depending on where your nearest cancer centre is. This can make you very tired, especially if you have side effects from the treatment.
D Techniques And Imrt
One of the first major advancements in radiotherapy that resulted in reduced doses to normal tissues is the use of 3D imaging for the design of the radiation plan.
How long does radiation treatment last?
Radiation treatment can span 4-6 weeks and if the marks fade or wash off, the patient will need to be re-simulated. Patients may be instructed to limit activities that may cause the marks to wear off.
What is temporary mark?
Temporary marks are small pinpoint or linear marks made with a semi-permanent marker. The main upside to temporary marks is that they are temporary and act as a counterbalance to many of the downsides that permanent marks represent. These marks disappear over time.
How long does it take for a tattoo to be visible?
As alluded to above, there are times where the tattoo is not easily visible. The marks are very small and sometimes it can take up to 5-7 minutes for the radiation therapist to locate them all prior to each treatment session - longer for freckled, densely haired, or darker-toned skin.
Do cancer marks stay in place?
Not only will the marks remain in place and be easily visible (in most cases) throughout the treatment process, they also serve as a permanent record of radiation exposure should additional radiation be required due to recurrence or the development of a new cancer near the original site.
Is radiation therapy permanent or temporary?
So as you can see, the choice between permanent and temporary marks for radiation therapy can be difficult and rely on a variety of factors, but in the end it comes down to what's going to be best for your patient's well-being, both clinically and emotionally.

Size and Appearance
Process
- Although each radiation treatment center may have some differences, the process of placing radiation tattoos is likely to be similar at most locations. The first step after radiation has been prescribed is a simulation process. During simulation, a CT scan of the area getting radiation is done. This helps the radiation specialists make a map of where exactly the radiation beams nee…
Types
- Many radiation treatment centers use a dark ink for the tattoo, often India ink. The use of dark ink can make it easy for the radiation technologist to properly line up the radiation treatment. However, although the spots are small, they are still visible on the skin. For some people with breast cancer, seeing these spots after treatment can be a constant reminder of their cancer an…
Side Effects
- There are very few side effects related to the use of tattoos for breast cancer radiotherapy. In extremely rare cases, people have had allergic reactions to the dye.5
Alternatives
- In addition to the traditional dark ink tattoo or the newer UV dye, some radiation centers have used henna to temporarily mark the skin of someone getting radiation. Henna is not permanent, but it may only last up to two weeks. It may require frequent touch-ups to continue to be accurate in marking the skin for radiation.6 Henna application can also be a lengthy procedure, with the dye …
Removal Options
- If chances of cancer recurrence are very low and the oncologist agrees, radiation tattoos may be removed. Options include surgery, dermabrasion, and cryotherapy. A dermatologist should be able to provide guidance on the best method to use.
A Word from Verywell
- Coping with radiation tattoos is easier if you understand their purpose and importance. Some women see their radiation tattoos as marks of survival and strength, rather than something they want to have removed. If you wish to have your tattoos removed after treatment, talk with your oncologist.
Overview
Why It's Done
- Radiation therapy kills cancer cells. It's often used after surgery to reduce the risk that the cancer will come back. It can also be used to provide relief from pain and other symptoms of advanced breast cancer.
Risks
- Side effects from radiation therapy differ significantly depending on the type of treatment and which tissues are treated. Side effects tend to be most significant toward the end of your radiation treatment. After your sessions are complete, it may be several days or weeks before side effects clear up. Common side effects during treatment may include: 1. Mild to moderate fatigu…
How You Prepare
- Before your radiation treatments, you'll meet with your radiation therapy team, which may include: 1. A radiation oncologist,a doctor who specializes in treating cancer with radiation. Your radiation oncologist determines the appropriate therapy for you, follows your progress and adjusts your treatment, if necessary. 2. A radiation oncology medical physicist and a dosimetrist,who make c…
What You Can Expect
- Radiation therapy usually begins three to eight weeks after surgery unless chemotherapy is planned. When chemotherapy is planned, radiation usually starts three to four weeks after chemotherapy is finished. You will likely have radiation therapy as an outpatient at a hospital or other treatment facility. A common treatment schedule (course) historically has included one ra…
Results
- After you complete radiation therapy, your radiation oncologist or other medical professionals will schedule follow-up visits to monitor your progress, look for late side effects and check for signs of cancer recurrence. Make a list of questions you want to ask members of your care team. After your radiation therapy is completed, tell your medical professional if you experience: 1. Persiste…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.