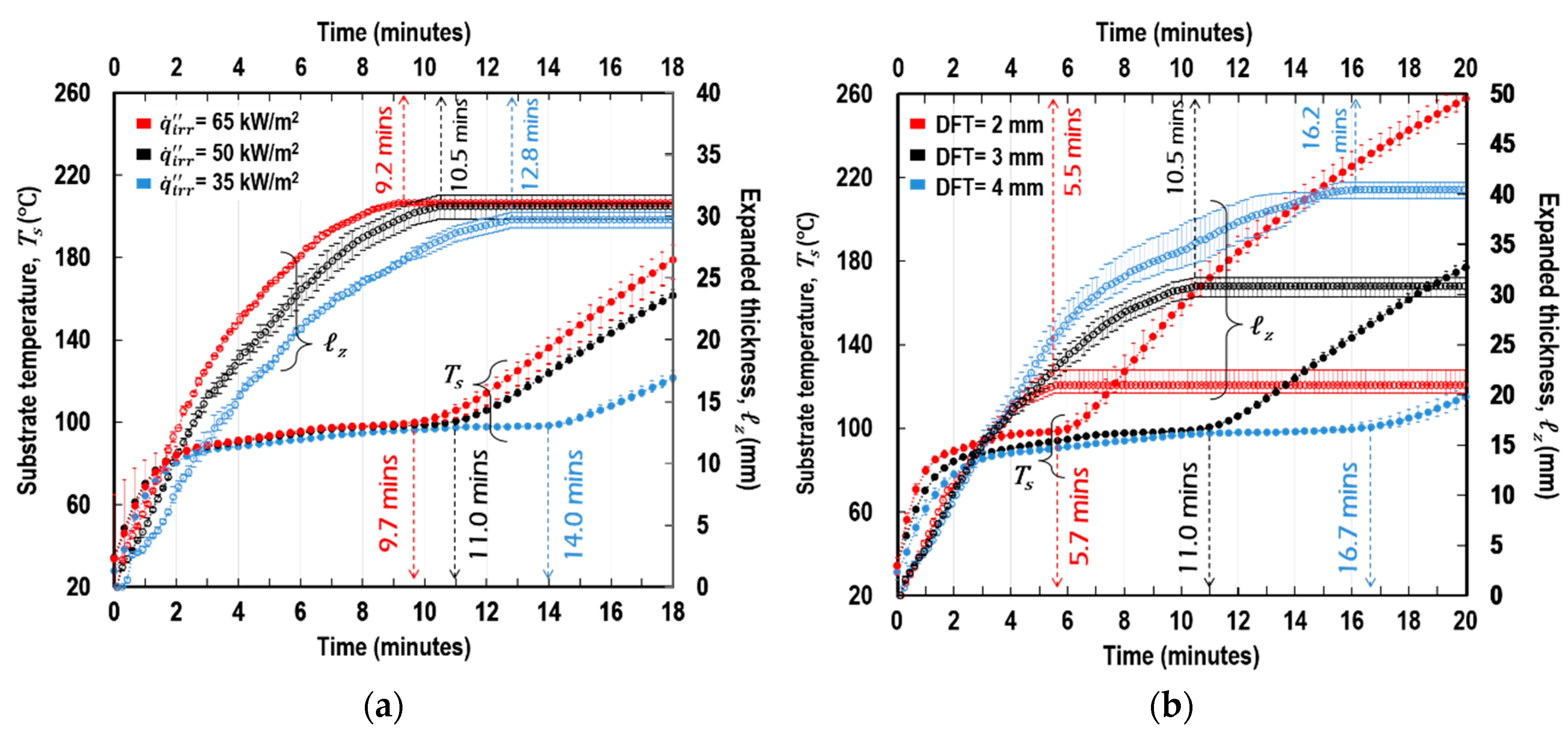
Indirect heat exchangers utilize hot water, air or steam to indirectly heat the polymers by conduction. A small amount of crossflow air also can be incorporated to carry away moisture. The heated medium does not directly contact the polymer, but the heat is transferred indirectly through walls of the heat exchanger.
Full Answer
How does heat affect polymers?
The effect that heat has on polymers depends in part on what type of polymer it is. A thermoplastic polymer will be a crystalline solid below a certain temperature, then undergo a glass transition when it softens, then melts, and finally burns. A thermoset, or cross-linked, polymer will remain solid until it begins to char and burn.
How to control polymer temperatures before processing?
A highly efficient solution to control polymer temperatures prior to processing is the use of an indirect heat exchanger. This new technology allows for accurate control of the polymer temperature regardless of ambient conditions and variable input temperatures.
How do you Dry hygroscopic polymers?
To ensure the highest quality final product, it is important to dry hygroscopic polymers. There are a variety of traditional processes used to dry polymers: Dehumidifying dryers eliminate moisture from the plastic prior to processing by using a hygroscopic substance known as a desiccant.
How can plastic polymers be made more environmentally friendly?
Heating, cooling, and drying plastic polymers can be a resource intensive process using traditional processes, but newer thermal technologies allow manufacturers to increase their efficiencies and limit their impact on the environment. What are plastic polymers?
Can polymers be heat treated?
Heat treatment of the polymers is considered one of the most effective methods of modification to widen their applications. Heat treatment of polymers improves their mechanical and tribological properties.
What are the steps in heat treatment?
Stages of Heat TreatmentThe Heating Stage.The Soaking Stage.The Cooling Stage.
What are the three main methods of heat treatment?
The 4 Types of Heat Treatment Steel UndergoesHeat Treatment Steel: Annealing.Heat Treatment Steel: Normalizing.Heat Treatment Steel: Hardening.Heat Treatment Steel: Tempering.
Can you heat treat plastic?
Heat treating plastics is a cheap way to produce resistant plastics. Certain processes can prolong the plastics' lifespan, as well as relieve internal stresses caused by manufacturing methods. Ovens should heat the polymers to a specific degree to introduce new properties.
What are the five main types of heat treatment?
Types of Heat TreatmentAnnealing. Annealing is one of the most important processes of heat treatment. ... Normalizing. Normalizing: The main aim of normalizing is to remove the internal stresses developed after the cold working process. ... Hardening. ... Tempering. ... Nitriding. ... Cyaniding. ... Carburising. ... Case Hardening or Surface Hardening.
Why do we do heat treatment?
Heat treating can improve wear resistance by hardening the material. Metals (including steel, titanium, inconel, and some copper alloys) can be hardened either on the surface (case hardening) or all the way through (through hardening), to make the material stronger, tougher, more durable and more resistant to wear.
What are the four types of heat treatment?
What are the 4 Types of Heat Treating Processes? Common types of heat treating methods include annealing, hardening, quenching, and stress relieving, each of which has its own unique process to produce different results.
What is critical temperature in heat treatment?
Critical temperature of steel defines phase transition between two phases of steel. As the steel is heated above the critical temperature, about 1335°F (724°C), it undergoes a phase change, recrystallizing as austenite.
What is annealing used for?
Annealing is used to reverse the effects of work hardening, which can occur during processes such as bending, cold forming or drawing. If the material becomes too hard it can make working impossible or result in cracking.
How do you flame treat plastic?
Flame Treating Plastic to Improve Adhesion Flame treatment is applying the exhaust from a gas flame to the surface of a material to improve adhesion. To flame treat a plastic surface, hold a propane torch so the flame just touches the surface and move it across the surface at a rate of 12 to 16 inches per second.
Can polymers be annealed?
Annealing of conjugated polymers and poly- mer blend films is a widely used process that achieves optimal film morphology and therefore improves material properties, such as electrical mobility for photovoltaic devices and other appli- cations.
How do you temper plastic?
Cold bending or temper shaping This technique involves forcing a plastic sheet into the desired shape in its cold state. The sheet is then heated up to a lower temperature (max. 70 degrees) in a tempering oven. This removes the tension from the material, which retains the desired shape after cooling.
Why is it important to heat treat both the base material and finished component?
To ensure component stability, it is important to heat treat both the base material and finished component to ensure that they are stress free and will remain stable over a long period of time.
Why is heat treatment important?
The heat treatment of plastics (known as Annealing and Normalising) is essential to ensure tight tolerances are maintained during precision machining, bonding and polishing and to avoid cracking and crazing. Heat treating also eliminates internal stresses and ensures better mechanical and thermal properties.
Why is annealing used?
Typically, annealing is used to reduce the hardness and helps eliminate internal stresses and ensures better mechanical and thermal properties. The correct heat treatments of the initial plastic materials along with the finished machined components are essential to ensure a long and reliable component life and performance.
How does heat affect polymers?
A thermoplastic polymer will be a crystalline solid below a certain temperature, then undergo a glass transition when it softens, then melts, and finally burns.
What happens to thermoplastic polymers when they melt?
With more heat, a thermoplastic polymer will reach the melting temperature. The melting only affects the crystalline regions. The polymer chains become unstructured. With all of the polymer chains, amorphous and moving, the polymer behaves like a liquid and can be recycled into new shapes.
Why is it important that polymers in finished products remain above or below the glass transition?
It is important that polymers in finished products remain above or below the glass transition over the expected temperature range of use so that the properties do not change.
What happens to polymers after time?
After time the polymer will be reduced to ash. The glass transition, melting and degradation temperatures of a polymer depend on the type of polymer. All polymers are long chains of carbon atoms, but different types contain other chemical groups within the chain, which alters the expected behaviour.
What is a solid polymer?
Solid polymers are usually semicrystalline. The long chains arrange themselves so portions are structured in crystals and others are loose. At a low temperature the loose, or amorphous, regions are glassy and brittle. As the heat increases, the polymer passes through the glass transition temperature and the chains in the amorphous regions are free ...
What happens when a polymer has a short chain?
A polymer with short chains branching from the main chain will also behave differently than a linear polymer.
Do polymers change temperature?
It is important that polymers in finished products remain above or below the glass transition over the expected temperature range of use so that the properties do not change. With more heat, a thermoplastic polymer will reach the melting temperature.
What is the process of depolymerization?
Depolymerization (unzipping) is a free radical process reverse to polymerization, in which polymer chains are degraded to monomers, dimers, and/or oligomers at high temperature. This reaction generally starts at chain ends where the free radical is formed (initiation).
What is the process of removing monomers from the chain ends?
Except for random scission, the end-chain scission process, in which monomers are effectively removed from the chain ends, is another possible pathway for the polymer thermal degradation. Chain scission processes drastically decrease the molecular weight and mechanical strength of polymer.
Why do chemical mechanisms occur?
The chemical mechanisms occur because of the thermal degradation of polymer into volatile species—pyrolysis. The physical mechanisms involve diffusion of the volatile species to the surface of the compact, as well as changes in the polymer distribution within the green body.
What is thermal degradation?
A thermal treatment is defined as a treatment of a compound in a device, when the temperature is elevated as the primary means to change the composition or characters (chemically, physically, and biologically) of the compound.
What are the three main reactions during nonoxidative thermal degradation?
Three main reactions during nonoxidative thermal degradation of polymers are depolymerization, random chains scission, and side-group elimination . In some cases, a recombination process that leads to cross-linking or cyclization may occur during degradation [7]. Usually, more than one degradation mechanism take place simultaneously.
Why are thermal properties important?
Thermal properties are relevant to the potential use of polymeric materials in many consumer-oriented applications . A detailed understanding of the thermal degradation of polymers is important in the design of materials with improved properties.
Is carbon fiber oxidative stabilization a chemical or physical process?
Thermal oxidative stabilization process in a carbon fiber production is a chemical-physical process. Although, the physical features, such as heat and tow tension, are important, the chemical structure has the ability to control the final properties and applications. Being familiar with this part of reaction can help the researchers and designers to find better viewpoints and knowledge regarding the stabilization process. Chemical kinetics is one method used to investigate chemistry changes during the process. Moreover this kinetic modelling is an applicable instrument to forecast the results of a series of chemical reactions in an industrial chemical process [223].
How does a polymer separate from water?
The polymer separates from water as an insoluble phase, and the ensuing deposited layer becomes as an insulator that determines the rate of heat extraction from the quen ched part. “The polymer slows the cooling compared to water, and controls the heat treating process” Steiger says.
How does induction hardening work?
Induction hardening uses a shorter time to harden the targeted section of the part instead of using an atmosphere furnace to heat treat the entire part.
What is a polyalkylene glycol quenchant?
There are several different types of organic polymer quenchants, including polyalkylene glycol (PAG), sodium polyacrylate (ACR), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), and polyethyl oxazoline (PEO). The polyalkylene glycol (PAG) polymer is one of the most widely used in the heat treating industry and provides an ideal uniform cooling for minimizing ...
What are the advantages of polymer quenchants?
The advantage of polymer solutions is that they have widely variant properties, which give a heat treater flexibility in how they use the product compared to just water or oil.
What is the viscosity of Daphne plastic quench?
The Daphne Plastic Quench HF has a viscosity (at 104°F/40°C) of 29.5 mm2/s , which bests its two top competitors at 536.1 and 301.7. The lower viscosity improves handling and production efficiency, and also reduces or eliminates sticky build-up on machines, gauges, fixtures and parts.
Is polyalkylene glycol soluble in water?
Polyalkylene glycols utilize inverse solubility in water; while they are completely soluble at room temperature, they become insoluble at higher temperatures from 140°F to 195°F, depending upon chemical structure. Inverse solubility controls the cooling and quenching mechanism. The ability to vary the concentration of a polymer quench provides great flexibility of the cooling rate. The polymer separates from water as an insoluble phase, and the ensuing deposited layer becomes as an insulator that determines the rate of heat extraction from the quenched part.
What Is Heat Treatment of Plastics?
Types of Heat Treatment
- As mentioned, heat treating has two main types. 1. Normalizing Normalizing gives plastic material a higher resistance to internal stresses and makes a uniform structure. The material must heat to a specific temperature to change its properties. After heating, the polymer is cooled down at a controlled rate. Industries use normalizing to get a calcu...
Why Do You Need to Heat Treat Plastics?
- Heat treating plastics is a cheap way to produce resistant plastics. Certain processes can prolong the plastics’ lifespan, as well as relieve internal stresses caused by manufacturing methods. Ovens should heat the polymers to a specific degree to introduce new properties. The heat softens the ingredients so you can shape or cut them more easily. What’s more, it improves the …
Need A Heat-Treating oven?
- You can find plastics in different industries, ranging from technology and healthcare to industrial manufacturing of consumer goods. Heat treatment of plastics is necessary for most industries that work with polymers and similar synthetic materials. Despatch manufacturesplastic tempering and plastic annealing ovens in both batch and conveyor style. If you need more information abo…