
Full Answer
What is outcome evaluation in evidence based practice?
Evaluation of the outcome of evidence-based practice decisions in individual patients or patient groups is step five in the evidence-based practice approach. Outcome measures are any measures that reflect patient status.
What is evidence-based treatment?
In the 1990s, the term evidence-based treatment entered the field of medicine and was used as a call for using critical thinking skills when administering a treatment method. The evidence refers to clinical studies to bolster the treatment efficacy.
What is an evidence-based approach?
An evidence-based approach involves an ongoing, critical review of research literature to determine what information is credible, and what policies and practices would be most effective given the best available evidence.
What makes evidence-based practice effective?
The exercise has been proven effective and replicated by at least two or more studies. Also, the evidence-based practice must integrate both medically-based research along with individual patient values and the experiences of the clinical provider, creating Dr. Sackett’s three-legged stool.
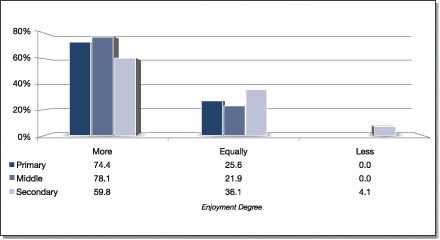
How do you evaluate EBP outcomes?
Five Steps of the Evidence-based ProcessAsk a clinical question.Obtain the best research literature.Critically appraise the evidence.Integrate the evidence with clinical expertise, patient preferences.Evaluate the outcomes of the decision.
What are evidence-based outcomes?
Evidence-based outcomes are defined as measures obtained from the assessment of quality of life domain-referenced indicators that: (a) are based on a cross-culturally validated QOL conceptual and measurement model (Schalock et al., 2005, Wang et al., 2010); (b) have utility in that they can be used for multiple ...
What is the outcome of evidence-based practice?
With the application of EBP comes better patient outcomes, which can decrease the demand for healthcare resources. Thus, healthcare organizations can reduce expenses. For example, outdated practices may have included supplies, equipment or products that are no longer necessary for certain procedures or techniques.
What is outcome in evidence based medicine?
Evidence-based medicine is fast overtaking experience-based medicine in the field of healthcare delivery. Outcomes analysis allows the assessment of the quality of care delivered and matches them against the resource costs.
How do you evaluate patient outcomes?
The Top Seven Healthcare Outcome Measures Explained#1: Mortality. Mortality is an essential population health outcome measure. ... #2: Safety of Care. ... #3: Readmissions. ... #4: Patient Experience. ... #5: Effectiveness of Care. ... #6: Timeliness of Care. ... #7: Efficient Use of Medical Imaging. ... #1: Data Transparency.More items...•
How do you evaluate clinical outcomes?
Measuring Clinical Outcomes What is your construct of interest? What is the goal(s) of your intervention? What is the population or patient/client group? What is the level of mobility or ability?
How do you evaluate the success of an intervention?
Once you have implemented a planned intervention, you can look at ways to evaluate its success.Evaluation relies on knowing the outcomes and goals of a project and testing them against results.Effective evaluation comes from measurable data and clear objectives.
How do nurses evaluate outcomes?
During the evaluation phase, nurses use critical thinking to analyze reassessment data and determine if a patient's expected outcomes have been met, partially met, or not met by the time frames established. If outcomes are not met or only partially met by the time frame indicated, the care plan should be revised.
Why is it important to measure outcomes EBP?
Measuring outcome variables before and after a practice change is essential to documenting the effect of the intervention. Deciding what to measure is directly related to why the practice change is being initiated: Improving patient health outcomes. Improving the patient experience.
What are the 5 stages of EBP?
5 steps of Evidence Based PracticeAsk a question. ... Find information/evidence to answer question. ... Critically appraise the information/evidence. ... Integrate appraised evidence with own clinical expertise and patient's preferences. ... Evaluate.
What are the 5 steps of EBM?
In this article, I have explained the five essential steps for practising EBM, which are: formulating answerable clinical questions; searching for evidence; making a critical appraisal; assessing the applicability of the evidence; and evaluating performance.
What are the 5 steps of evidence-based medicine?
Steps in EBM Generate Clinical Question. Find Best Evidence. Critical Appraisal. Appraisal of evidence for validity and usefulness. Apply the Evidence. Application of results in clinical practice. Evaluate.
What is evidence from research studies?
Evidence from research studies that includes normative data, standard error of measurement, or comparative scores for important clinical subgroups can be used to set treatment goals, monitor recovery, and compare individual patient outcomes to those reported in the literature.
What is outcome measure?
Outcome measures are any measures that reflect patient status. Status or outcome measures can be used to detect change over time (eg, treatment effects), to discriminate among clinical groups, or to predict future outcomes (eg, return to work).
Why is evidence based medicine continually being expanded upon and improved with new innovative treatment methods?
Evidence-based methods are continually being expanded upon and improved with new innovative treatment methods because science and medicine are always evolving. Doctors, therapists, and other clinicians are routinely exploring new ways to interact with and treat their clients. Evidence-based medicine, and the scientific method ...
When did evidence-based treatment become a medical term?
In the 1990s, the term evidence-based treatment entered the field of medicine and was used as a call for using critical thinking skills when administering a treatment method. The evidence refers to clinical studies to bolster the treatment efficacy. When it comes to EBPs, clinicians are urged to use therapies that are based on the scientific method.
How effective are 12-step programs?
In addition, 12-step programs are effective ways to build supportive relationships with people who also struggle with substance abuse issues.
Why is EBP less expensive?
Because these methods have been proven to work time and time again, and they are standardized, care is usually less expensive than more experimental, cutting-edge treatment methods and practices. Patients also have the added benefit of knowing that most EBP clinicians are highly-trained, experienced, and knowledgeable.
What is the purpose of EBP for substance abuse?
For people with substance abuse disorder who use an effective EBP such as CBT, they are encouraged to seek out family and peer support, learn their unique stressors and triggers, and implement plans and habits to avoid a drug or alcohol abuse relapse.
What is talk therapy?
Traditional, or talk therapy is a highly individualistic treatment method that uses the relationship between the therapist and the patient to uncover subconscious and conscious issues related to substance abuse. In many cases, clinicians will also prescribe FDA-approved medications in conjunction with talk therapy.
How does CBT work?
As a therapy, CBT works by helping people uncover the complex relationships that surround and feed into their negative thoughts, feelings, and subsequent self-destructive behaviors.
What is evidence based research?
An evidence-based approach involves an ongoing, critical review of research literature to determine what information is credible, and what policies and practices would be most effective given the best available evidence. It also involves rigorous quality assurance and evaluation to ensure that evidence-based practices are replicated with fidelity, ...
What is evidence based policymaking?
Evidence-based policymaking, which relies on rigorous analysis of program results to inform budget, policy, and management decisions, is one strategy gaining support among public leaders who want to reduce wasteful spending, expand successful programs, and strengthen accountability.".
What is EBP in Minnesota?
The 2009 Minnesota Legislature directed the Information and Supervision Services Committee’s Evidence-Based Practices (EBP) Policy Team of the Minnesota Department of Corrections (DOC) to assess the use of EBP and opportunities for greater implementation in community supervision.
What is EBP in health care?
Evidence-based Practices (EBP) Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the objective, balanced, and responsible use of current research and the best available data to guide policy and practice decisions, such that outcomes for consumers are improved. Used originally in the health care and social science fields, evidence-based practice focuses on ...
What is the National Institute of Corrections's goal?
The goal of [National Institute of Corrections'] Evidence-Based Decision Making Initiative is to build a systemwide framework (arrest through final disposition and discharge) that will result in more collaborative, evidence-based decision making and practices in local criminal justice systems.
Helpful Terms
Aspects of evidence-based practice are referred to by several similar terms. Some of these are used interchangeably, though they do have different meanings and applications.
Principles and Benefits of EBT
Evidence-based treatments are attractive options for many and offer several benefits. Some people feel more confident knowing the treatment they’re receiving has been tested and proven to be effective enough to be classified as an EBT. Below are a few of the foundational principles and benefits of evidence-based treatments.
Potential Disadvantages of EBT
Not all patients, or even behavioral health professionals, prefer evidence-based therapies. One reason for this is because the process for evaluating and classifying something as “evidence-based” is debatable and can even be seen as subjective.
Why You May Still Want to Consider Other Treatments
There are a lot of types of substance use and mental health disorder treatments that aren’t classified as EBTs. Just because their effectiveness may not necessarily be measurable or backed by large bodies of scientific evidence, doesn’t mean they aren’t still useful (or even effective).
Finding the Best Evidence-Based Addiction Treatment for You
In the field of substance use and mental health disorder treatment, there are many different approaches to recovery. What works for one person may not work for another. For some, scientific evidence is an important factor in choosing a treatment and rehab center.
What is the NREPP program?
variety of federal initiatives are in process or underdevelopment to address some of the issues in this article.One of the most significant is the National Registry ofEvidence-Based Programs and Practices (NREPP), initiatedin 1998 by the U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental HealthServices Administration (SAMHSA) and currently underexpansion. Originally focused on substance abuse preven-tion programming, it is broadening its scope to includeinterventions to treat substance abuse disorders and toprevent and/or treat mental illness. The vision in expandingthe NREPP is that the system becomes a leading nationalresource for contemporary and reliable information on thescientific basis and practicality of interventions to preventand/or treat mental and addictive disorders. Plans areunderway to align technical assistance with this expansion.The SAMHSA obtained public comment on its plans forexpanding the NREPP and will plan to relaunch theexpanded system sometime in 2006.As of this writing (August 2005), the NREPP policiesand procedures are still being formulated, but treatment andprevention programs can apply online and achievestatus as model evidence-based programs (http://www.
Can EBT be implemented at different levels?
EBTs can be implemented at various levels. At thesimplest level, an individual practitioner may learn andprovide one or more particular EBTs as part of her or hisservice delivery. The use of EBTs is quite compatible withindividualizing treatment to patient needs and preferences,a common value among clinicians (Drake, Rosenberg,
What is a treatment with proven effectiveness in one type of setting?
A treatment with proven effectiveness in one type of setting (e.g., the home, the school, day treatment, the clinic, the office, or the institution) may vary in effectiveness when it is offered in other settings. Good guidelines specify the settings in which the treatment has been documented to be effective.
Why are guidelines important for treatment?
Good guidelines allow for flexibility in treatment selection so as to maximize the range of choices among effective treatment alternatives.
Why are guideline panels recommended?
It is recommended that guideline panels make detailed recommendations to facilitate independent evaluation of the reliability of the guidelines they produce. Ascertaining whether the guidelines are interpreted and applied consistently by health care professionals comprises one assessment of reliability.
What is a criterion 7.2?
Criterion 7.2 It is recommended that guidelines take into account the effects on treatment outcome of interactions between the patient's and the health care professional's characteristics , including but not limited to language, ethnicity, background, sex, and gender.
What is the purpose of failure to disclose scientific justification for a guideline?
Moreover, failure to disclose the scientific justification for a guideline violates a basic principle of science, which requires open scrutiny and debate. Without the disclosure of adequate scientific information, guidelines are mere expressions of opinion.
Why are guidelines promulgated?
Guidelines are promulgated to encourage high quality care. Ideally, they are not promulgated as a means of establishing the identity of a particular professional group or specialty, nor are they used to exclude certain persons from practicing in a particular area.
What factors affect outcome?
Such factors as the professional's skill, experience, gender, language, and ethnic background can affect outcome in ways that are only partly understood. Criterion 7.1 It is recommended that guidelines take into account the effect of the health care professional's training, skill, and experience on treatment outcome.
What are the five treatment approaches?
2001#N#Description: This multidimensional instrument assesses five treatment approaches: psychodynamic or interpersonal, cognitive–behavioral, family systems or dynamics, 12–step, and case management. For each of the first four modalities, items assess beliefs underlying the approach, practices appropriate in individual therapy, and practices appropriate in group therapy. Case management is an individual approach, so no group practices items were included. In addition, items were developed to tap general “group techniques” (e.g., “encouraging peer social support”) and “practical counseling” (e.g.,“developing rapport and trust”). The instrument consists of 48 items that assess 14 subscales. Construct validity was supported by the results of a confirmatory factor analysis in which subscale items loaded on the factor they were intended to assess, but not on other factors. Corresponding belief and practice subscales correlated highly, except for case management. Cronbach alphas for all subscales except psychodynamic and family systems beliefs were above 0.50 and most were over 0.70 (Kasarabada et al. 2001, p. 287). The fact that some of the subscales consist of only three items contributed to low internal consistency estimates.
What is ultimate outcome?
Ultimate outcomes (panel VIII in figure 1) refer to the end points that the treatment is supposed to effect. All treatment programs for alcohol use disorders attempt to impact drinking behavior, with many seeking to eliminate it entirely and others seeking to limit it to levels that do not cause adverse consequences. Some programs also seek to have a broader impact on patient functioning by effecting improvements in such life areas as employment, social functioning, physical health, and/or psychological functioning (for an in–depth discussion of outcome assessment, see Tonigan’s chapter in this Guide ). Treatment process models may specify different dimensions of treatment that should impact different areas of patients’ functioning.
How is quality of alcohol treatment determined?
The quality of alcohol treatment is determined, not only by the therapeutic techniques applied, but also by the characteristics of individual treatment providers (panel III in figure 1). In particular, this domain of variables refers to within–program variation in provider characteristics (aggregate, program–level staff characteristics are considered in panel II). Gerstein (1991) argued that “the competence, quality, and continuity of individual caregivers are likely to be critical elements in explaining the differential effectiveness of [substance abuse] treatment programs” (p. 139). In the alcohol treatment field, the few studies that have been conducted (e.g., W.R. Miller et al. 1980; Valle 1981; McLellan et al. 1988; Sanchez–Craig et al. 1991; Project MATCH Research Group 1998; for reviews, see Najavits and Weiss 1994; Najavits et al. 2000) indicate that therapist characteristics play an important role in determining clients’ treatment retention and outcomes.
What is the National Drug and Alcoholism Treatment Unit Survey?
Measure: National Drug and Alcoholism Treatment Unit Survey (NDATUS)#N#Citation: Office of Applied Studies 1991#N#Description: The NDATUS is a brief questionnaire (five pages) that covers (a) the overall organization and structure of programs (ownership, funding sources and levels, organizational setting, capacity in different treatment settings using different treatment modalities, hours of operation, etc.), (b) staffing and staff characteristics, (c) services (e.g., methadone dosages), (d) policies, and (e) clients and client characteristics. The 1989 NDATUS was augmented in 1990 by the Drug Services Research Survey (DSRS) (Office of Applied Studies 1992 a, 1992 b) to obtain additional data in the areas of facility organization and staff, client data, services, and costs and charges. Using data from the 1991 NDATUS, Rodgers and Barnett (2000) found that private, for–profit substance abuse treatment programs tended to be smaller and more likely to provide treatment in only one setting. Public programs and nonprofit programs generally had more treatment staff; Federal and for–profit programs had more psychologists and physicians. In 1992, the NDATUS evolved into the Uniform Facility Data Set (UFDS), sponsored by the Office of Applied Studies.
What are proximal outcomes?
Proximal outcome variables (Rosen and Proctor 1981; panel VII in figure 1) refer to cognitions, attitudes, personality variables, or behaviors that, according to the treatment theory under investigation, should be affected by the treatment provided, and should , in turn, lead to positive ultimate outcomes (e.g., abstinence or reduced alcohol consumption). An Institute of Medicine (1989) panel found that “little research has been devoted to the short–term impact of specific [alcoholism treatment] program components” (p. 159), and suggested that such short–term gains could be studied quite readily. Proximal outcome variables can be assessed at any point between treatment entry and the assessment of ultimate outcomes. When assessed during treatment, proximal outcomes constitute an important method that clinicians can use to assess patients’ treatment progress. For researchers, proximal outcomes, assessed during or after treatment, are key components in treatment process analyses.
What is alcohol treatment?
Alcohol treatment programs typically provide psychosocial and/or pharmacologic interventions to patients. To the extent that it is constant across all patients, treatment provided is a program–level characteristic (panel II in figure 1). In most programs, however, the treatment provided varies across patients (panel V).
What are the factors that affect the impact of alcohol treatment?
Therapeutic Alliance. One of the key factors affecting the impact of alcohol treatment, especially psychosocial treatments, is the quality of the alliance or relationship that is developed between the therapist and client (panel IV in figure 1).
What is community based juvenile justice?
Increasingly, community-based juvenile justice practitioners are required to validate that they are engaging in evidence-based practice—proof that they are delivering the services their clients require and that the program yields the desired outcomes for youth in their care. While this expectation is a good one, many practitioners understandably feel overwhelmed as they contemplate the task; they often do not know where to begin or how to lay the foundation. In addition, conducting an outcome evaluation is a resource-intensive task that takes an appropriate amount of funding, planning, and data.
What is the goal of a program?
Goals are broad, general statements about what the program expects to accomplish and are usually long term. Objectives are precise actions that move the program closer to achieving its goal. For example, an objective of a program whose goal is to reduce juvenile crime may be to help kids to avoid reoffending.
Do social service providers have evidence based practices?
In recent years, social service providers of all kinds have felt a growing pressure to demonstrate that what they do is an “evidence-based practice.” People who provide community-based services for youth involved in the juvenile justice system are not exempt. They, too, are being asked to provide evidence-based assessments of their work with ever-increasing frequency. Contracts and funding often can depend on a program’s ability to produce such evaluations. Not surprisingly, this trend has many service providers in the juvenile justice field wondering what, exactly, it means and how they can qualify.
