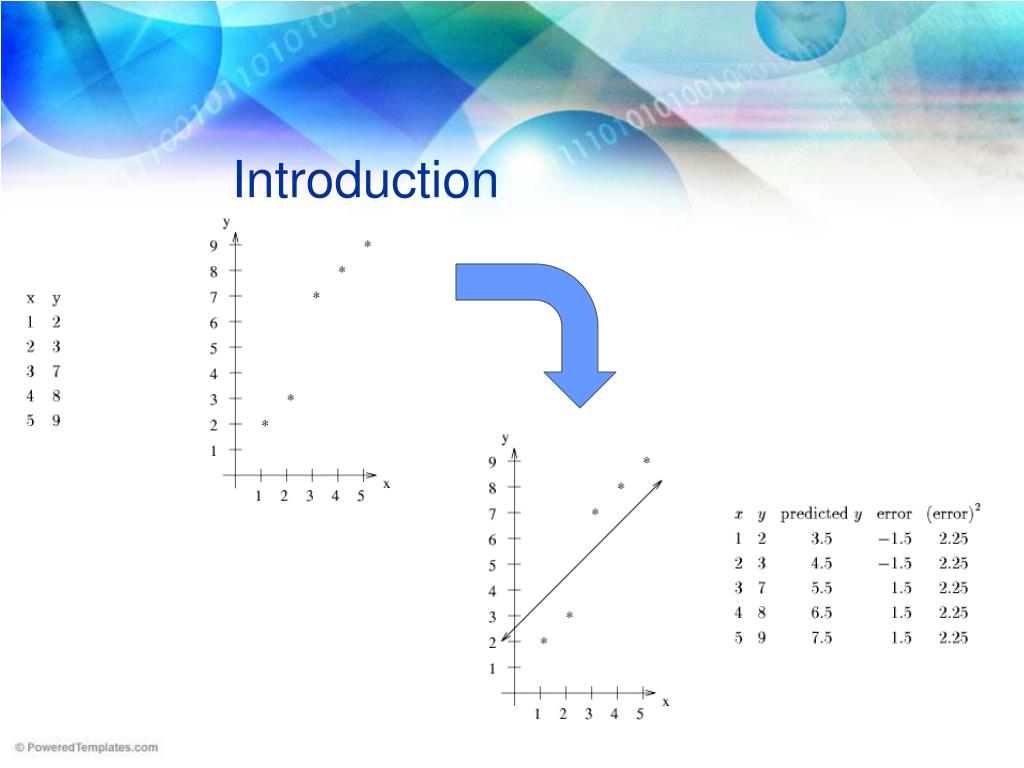
Mean squared error
In statistics, the mean squared error (MSE) or mean squared deviation (MSD) of an estimator measures the average of the squares of the errors or deviations, that is, the difference between the estimator and what is estimated. MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss or quadratic loss.
How do you calculate the mean square of treatment in Excel?
The treatment mean square is obtained by dividing the treatment sum of squares by the degrees of freedom. The treatment mean square represents the variation between the sample means. The mean square of the error (MSE) is obtained by dividing the sum of squares of the residual error by the degrees of freedom.
What is the treatment mean square of the error?
Apr 07, 2020 · MSE Calculator. The mean square error (MSE) is a metric that tells us how far apart our predicted values are from our observed values in a regression analysis, on average. It is calculated as: MSE = Σ (P i – O i) 2 / n. where: Σ is a fancy symbol that means “sum”. P i is the predicted value for the i th observation.
How do you calculate mean squares?
Mar 26, 2016 · The calculations are based on the following results: There are four observations in each column. The overall mean is 2.1. The column means are 2.3 for column 1, 1.85 for column 2 and 2.15 for column 3. After you compute SSE and SSTR, the sum of …
How do you find the treatment mean square in ANOVA?
Feb 27, 2020 · One of the most common metrics used to measure the forecast accuracy of a model is MSE, which stands for mean squared error. It is calculated as: MSE = (1/n) * Σ (actual – forecast)2. where: Σ – a fancy symbol that means “sum”. n – sample size.
What is the formula of mean square?
Mean square between is used to calculate the F ratio (sometimes called the F-value): F Ratio = MSB/MSE. For small samples, the F ratio may not be helpful. But for larger samples, MSB and MSE are usually equal and so would return an F ratio of 1.Sep 22, 2013
How is SS treatment calculated?
0:112:13The Sums of Squares Treatment in ANOVA (Module 2 2 6) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo another way we can write the sums of squares for treatment is to say the number of people in eachMoreSo another way we can write the sums of squares for treatment is to say the number of people in each group the n sub J multiplied by the deviation between the group mean for the group J.
How do you find the sum of squares treatment?
Here we utilize the property that the treatment sum of squares plus the error sum of squares equals the total sum of squares. Hence, SSE = SS(Total) - SST = 45.349 - 27.897 = 17.45 \, . STEP 5 Compute MST, MSE, and their ratio, F. where N is the total number of observations and k is the number of treatments.
How is SSE and MSE calculated?
MSE = [1/n] SSE. This formula enables you to evaluate small holdout samples.
How is SS total calculated?
How to calculate sum of squaresCount the number of measurements. The letter "n" denotes the sample size, which is also the number of measurements.Calculate the mean. ... Subtract each measurement from the mean. ... Square the difference of each measurement from the mean. ... Add the squares together and divide by (n-1)Oct 28, 2021
How is Grand mean calculated?
If you choose the first method (calculate weights), multiply the mean by the number of data points, then divide by the total number of points: (2 * 2 + 5 * 6 + 9 * 11)/ 19 = 7....Grand Mean Examples(6, 6, 3, 3)(1, 5, 0, 14)(9, 10, 11, 12)(0, 4, 0, 20).Apr 20, 2021
How do you calculate SSTr and MSTr?
Scaled versions of the treatment and error sums of squares (the sums of squares divided by their associated degrees of freedom) are known as mean squares: MSTr = SSTr/(a−1) and MSE = SSE/(n − a).
What is SSR in statistics?
In statistics, the residual sum of squares (RSS), also known as the sum of squared residuals (SSR) or the sum of squared estimate of errors (SSE), is the sum of the squares of residuals (deviations predicted from actual empirical values of data).
How do you calculate F?
Calculate the F value. The F Value is calculated using the formula F = (SSE1 – SSE2 / m) / SSE2 / n-k, where SSE = residual sum of squares, m = number of restrictions and k = number of independent variables. Find the F Statistic (the critical value for this test).
How do you calculate mean square by hand?
How do I calculate MSE by hand?Compute differences between the observed values and the predictions.Square each of these differences.Add all these squared differences together.Divide this sum by the sample length.That's it, you've found the MSE of your data!Feb 15, 2022
How is SSE calculated?
To calculate the sum of squares for error, start by finding the mean of the data set by adding all of the values together and dividing by the total number of values. Then, subtract the mean from each value to find the deviation for each value. Next, square the deviation for each value.
How is MSE sample calculated?
General steps to calculate the MSE from a set of X and Y values: Find the regression line. Insert your X values into the linear regression equation to find the new Y values (Y')....Step 2: Find the new Y' values:9.2 + 0.8(43) = 43.6.9.2 + 0.8(44) = 44.4.9.2 + 0.8(45) = 45.2.9.2 + 0.8(46) = 46.9.2 + 0.8(47) = 46.8.
What is the p-value of 0.071?
This provides a permutation-based p-value of 0.071 and suggests marginal evidence against the null hypothesis of no difference in the true means. We would interpret this as saying that there is a 7.1% chance of getting a SS A as large or larger than we observed, given that the null hypothesis is true.
Can total variation change?
In a permutation situation , the total variation (SS Total) cannot change - it is the same responses varying around the grand mean. However, the amount of variation attributed to variation among the means and in the residuals can change if we change which observations go with which group.
Need more help understanding mean squares?
2. The manager of the purchasing department of a large company would like to develop a regression model to predict the average amount of time it takes to process a given number of invoices. Over a 30-day period, data...
Get the most out of Chegg Study
In math there are many key concepts and terms that are crucial for students to know and understand. Often it can be hard to determine what the most important math concepts and terms are, and even once you’ve identified them you still need to understand what they mean.
Data and Sample Means
Suppose we have four independent populations that satisfy the conditions for single factor ANOVA. We wish to test the null hypothesis H0: μ 1 = μ 2 = μ 3 = μ 4. For purposes of this example, we will use a sample of size three from each of the populations being studied. The data from our samples is:
Sum of Squares of Error
We now calculate the sum of the squared deviations from each sample mean. This is called the sum of squares of error.
Sum of Squares of Treatment
Now we calculate the sum of squares of treatment. Here we look at the squared deviations of each sample mean from the overall mean, and multiply this number by one less than the number of populations:
Degrees of Freedom
Before proceeding to the next step, we need the degrees of freedom. There are 12 data values and four samples. Thus the number of degrees of freedom of treatment is 4 – 1 = 3. The number of degrees of freedom of error is 12 – 4 = 8.
Mean Squares
We now divide our sum of squares by the appropriate number of degrees of freedom in order to obtain the mean squares.
The F-statistic
The final step of this is to divide the mean square for treatment by the mean square for error. This is the F-statistic from the data. Thus for our example F = 10/6 = 5/3 = 1.667.
What is the ratio of MST to MSE?
If the null hypothesis is true, that is, if all of the population means are equal, we'd expect the ratio MST / MSE to be close to 1. If the alternative hypothesis is true, that is, if at least one of the population means differs from the others, we'd expect the ratio MST / MSE to be inflated above 1.
What are the assumptions for equality of means?
If you go back and look at the assumptions that we made in deriving the analysis of variance F -test, you'll see that the F -test for the equality of means depends on three assumptions about the data: 1 independence 2 normality 3 equal group variances