Primary wastewater treatment usually involves gravity sedimentation of screened, degritted wastewater to remove settleable solids; slightly more than one-half of the suspended solids ordinarily are removed. BOD in the form of solids removable by sedimentation (typically about one-third of total BOD) is also removed.
Full Answer
How does a sewage treatment plant work?
Primary Treatment As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
How is sewage treated to comply with the Clean Water Act?
Many sewage treatment processes may be used for complying with Clean Water Act (CWA) requirements. Most municipalities use a series of unit processes to treat wastewater prior to discharge including the following: primary clarification (or preliminary sedimentation) to remove floating and settleable solids,
How is wastewater treated and discharged into the environment?
Pretreated wastewater is discharged through piping onto porous surfaces that allow wastewater to filter though the soil. The soil accepts, treats, and disperses wastewater as it percolates through the soil, ultimately discharging to groundwater.
What is the importance of sewage collection and treatment?
The collection and treatment of domestic sewage and wastewater is vital to public health and clean water. It is among the most important factors responsible for the general level of good health enjoyed in the United States.

What are the 4 steps of sewage treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
How does a sewage treatment plant work?
As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What are the 7 steps of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What are the 3 steps to wastewater treatment?
The three stages of wastewater treatment are known as primary, secondary and tertiary. Each stage purifies water to a higher level. In some applications, only one or two stages are necessary. The level of treatment necessary depends on the water's intended use case, and what environment it will be discharged into.
Where does human waste go after a sewage treatment plant?
The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What happens to poop at the water treatment plant?
During the first stage, all of the waste that accumulates in the city's pipes just sits in a tank for hours. This stage allows the solids to settle at the bottom of the tank. The water at the top of the tank is skimmed off and sent off to be processed. Your poop remains in the sludge that's left over.
What are the 5 stages of water purification?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
How is wastewater treatment done?
Primary Treatment As wastewater enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen. This removes large floating objects, such as rags and sticks, which clog pipes or damage equipment. Once the wastewater has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What are the steps in water treatment process?
They typically consist of several steps in the treatment process. These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What are the methods of sewage treatment?
Majorly, four methods of sewage water treatment are followed – physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment. By following these methods, the wastewater is disinfected from all the sewage materials and converted into treated water that is safe for both human usage and the environment.
What bacteria is used in sewage treatment?
Anaerobic bacteria are used in wastewater treatment on a normal basis. The main role of these bacteria in sewage treatment is to reduce the volume of sludge and produce methane gas from it.
What can sewage treatment not remove?
Biological stages in wastewater treatment plants are not able to remove substances such as drugs, found in the wastewater of medical centers, or halogenated compounds and cyanides from industrial wastewater.
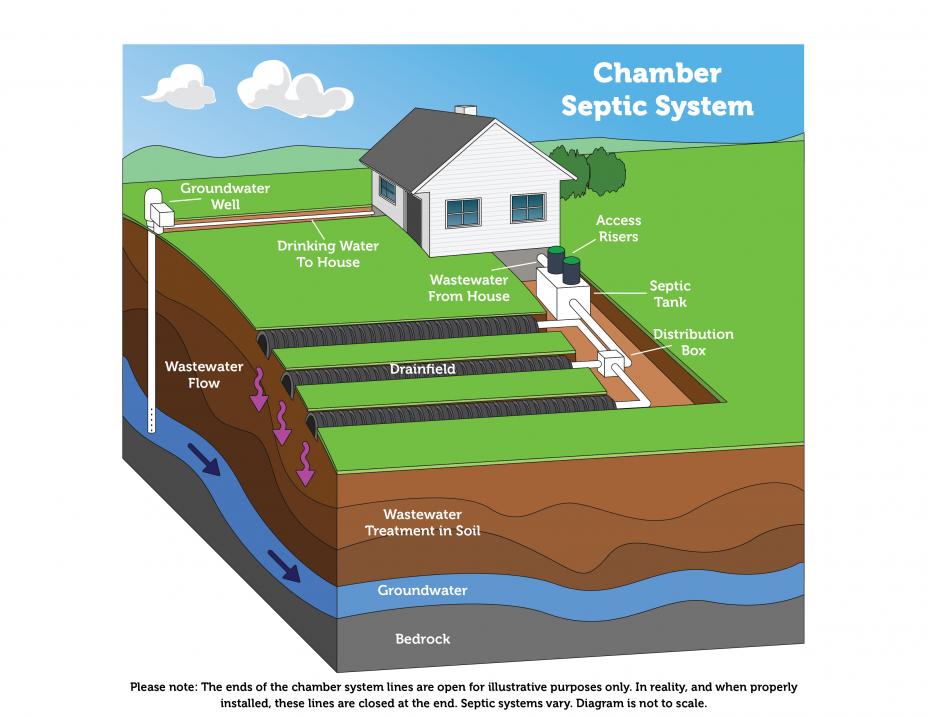
Specifically, This Is How A Typical Septic System Works
1. All water runs out of your house from one main drainage pipe into a septic tank. 2. The septic tank is a buried, water-tight container usually m...
Do You Have A Septic System?
You may already know you have a septic system. If you do not know, here are tell-tale signs that you probably do: 1. You use well water. 2. The wat...
How to Find Your Septic System
Once you have determined that you have a septic system, you can find it by: 1. Looking on your home’s “as built” drawing. 2. Checking your yard for...
Failure Symptoms: Mind The Signs!
A foul odor is not always the first sign of a malfunctioning septic system. Call a septic professional if you notice any of the following: 1. Waste...
How does a septic system work?
Specifically, this is how a typical conventional septic system works: All water runs out of your house from one main drainage pipe into a septic tank. The septic tank is a buried, water-tight container usually made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene. Its job is to hold the wastewater long enough to allow solids to settle down to ...
What exits the tank into the drainfield?
The liquid wastewater (effluent) then exits the tank into the drainfield.
What is a typical septic system?
A typical septic system consists of a septic tank and a drainfield, or soil absorption field.
Does wastewater percolate into the soil?
Finally, the wastewater percolates into the soil, naturally removing harmful coliform bacteria, viruses and nutrients. Coliform bacteria is a group of bacteria predominantly inhabiting the intestines of humans or other warm-blooded animals. It is an indicator of human fecal contamination.
Do you have a septic system?
You may already know you have a septic system. If you do not know, here are tell-tale signs that you probably do:
What is a public owned wastewater treatment system?
Section I.B, National Priority, states “For purposes of this announcement, rural and small wastewater treatment systems are systems that treat up to 1 million gallons per day (MGD) of wastewater or serve a population of less than 10,000 persons and may also serve operations such as, but not limited to hospitals, schools, and restaurants… [and]… For the purposes of this announcement, “publicly owned treatment works” are defined as wastewater systems or treatment facilities that are owned by a public entity (such as a municipality) or not-for-profit entity (such as regional sewer districts), and/or serve tribal communities (with the exception of systems that are owned by U.S. federal entities).“
What is the EPA's purpose in Section III.A?
EPA is soliciting applications from eligible applicants as described in Section III.A to provide training and technical assistance for rural, small, and tribal publicly owned wastewater treatment works and decentralized wastewater treatment systems for the prevention, reduction and elimination of pollution. Clean Water Act (CWA) Section 104 (b) (8) ...
What is EPA priority consideration?
EPA will give priority consideration to applications that describe a thorough, quality, and flexible approach that tailors the training and technical assistance techniques and resources to address the specific needs of the target audience in as many states, tribes and U.S. territories as possible. ”.
How much is the EPA funding?
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is requesting applications for $12 million in competitive funding for projects to provide training and technical assistance for small, rural and tribal wastewater utility systems and onsite septic systems.
When is the EPA application deadline for 2021?
The closing date and time for receipt of application submissions is May 17, 2021, by 11:59 p.m., Eastern Time (ET) in order to be considered for funding. Application packages must be submitted electronically to EPA through Grants.gov (https://www.grants.gov/) no later than May 17, 2021, in order to be considered for funding.
Can EPA staff meet with individual applicants?
However, consistent with the provisions in the announcement, EPA staff cannot meet with individual applicants to discuss draft proposals, provide informal comments on draft proposals, or provide advice to applicants on how to respond to ranking criteria. Applicants are responsible for the contents of their proposals.
Who is eligible for Clean Water Act funding?
Section III.A., Eligible Applicants, states “Eligible applicants under this competition are public or private nonprofit organizations, subject to Clean Water Act (CWA) Section 104 (w), that are qualified and experienced in providing on-site training and technical assistance to small publicly owned treatment works.” Section III.A. also states “For-profit organizations, states, municipalities, tribal governments, and individuals are not eligible to apply. Nonprofit organizations described in Section 501 (c) (4) of the Internal Revenue Code that engage in lobbying activities as defined in Section 3 of the Lobbying Disclosure Act of 1995 are not eligible to apply. EPA may ask applicants to demonstrate that they are eligible for funding under this announcement.”
What is peak flow in sewage treatment?
Peak Flows at Sewage Treatment Plants. Many sewage treatment processes may be used for complying with Clean Water Act (CWA) requirements. Most municipalities use a series of unit processes to treat wastewater prior to discharge including the following: primary clarification (or preliminary sedimentation) to remove floating and settleable solids,
Why do wastewater plants divert?
Under these peak flow conditions, in order to prevent damage to the wastewater treatment plant and maintain future effective operations, some plant operators divert a portion of the flow around biological or advanced treatment units. The diverted flow is then either recombined with flows from the biological treatment units or discharged directly into waterways.
What is disinfection in healthcare?
disinfection to deactivate pathogens. Some facilities also provide more advanced treatment which is designed to reduce constituents, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, that are not removed in any significant quantity by traditional biological treatment processes.
Why upgrade wastewater treatment system?
Enhanced treatment systems enable some wastewater plants to produce discharges that contain less nitrogen than plants using conventional treatment methods . Upgrading wastewater treatment systems is often expensive for municipalities and rate payers, but upgrades can pay for themselves or end up saving a plant money.
How does a septic system contribute to nutrient pollution?
Septic systems can easily become a source of nutrient pollution if not properly maintained. Most homes and businesses send their wastewater to a treatment plant where many pollutants are removed from the water. Wastewater treatment facilities in the United States process approximately 34 billion gallons of wastewater every day.
What is the source of nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater?
Wastewater contains nitrogen and phosphorus from human waste, food and certain soaps and detergents. Once the water is cleaned to standards set and monitored by state and federal officials, it is typically released into a local water body, where it can become a source of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution. Some wastewater treatment plants are able ...
How to maintain a septic system?
Homeowners are responsible for maintaining their septic systems in most cases. To protect and maintain their system, homeowners should: 1 Have their system inspected regularly and pump their tank as necessary 2 Use water efficiently 3 Not dispose of household hazardous waste in sinks or toilets 4 Avoid driving vehicles or placing heavy objects on their drainfield 5 Visit EPA's decentralized wastewater (septic) systems webpage to learn more about septic systems and EPA's SepticSmart Week Program 6 Consult EPA's guide on maintaining septic systems for more information: Homeowner's Guide to Septic Systems (PDF) (9 pp, 3 MB, About PDF)
What causes a septic system to fail?
Common causes of septic system failure include aging infrastructure, inappropriate design, overloading with too much wastewater in too short a period of time and poor maintenance.
Who is responsible for septic system maintenance?
Homeowners are responsible for maintaining their septic systems in most cases. To protect and maintain their system, homeowners should: Have their system inspected regularly and pump their tank as necessary. Use water efficiently. Not dispose of household hazardous waste in sinks or toilets.
What percentage of homes in the US have septic systems?
Septic Systems. Approximately 20 percent of homes in the United States use septic systems that locally treat their wastewater. When a septic system is improperly managed, elevated nitrogen and phosphorus levels can be released into local water bodies or ground water.
Why is sewage important?
The collection and treatment of domestic sewage and wastewater is vital to public health and clean water. It is among the most important factors responsible for the general level of good health enjoyed in the United States. Sewers collect sewage and wastewater from homes, businesses, and industries and deliver it to wastewater treatment facilities ...
What is separate sanitary sewer?
Separate Sanitary Sewers. The other major type of domestic sewer design is sanitary sewers (also known as separate sanitary sewers). Sanitary sewers are installed to collect wastewater only and do not provide widespread drainage for the large amounts of runoff from precipitation events.
What is combined sewer?
Combined sewers are designed to collect both sanitary sewage and stormwater runoff in a single-pipe system. These systems were designed to convey sewage and wastewater to a treatment plant during dry weather. Under wet weather conditions, these combined sewer systems would overflow during wet weather conditions when large amounts of stormwater would enter the system. State and local authorities generally have not allowed the construction of new combined sewers since the first half of the 20th century.
What is the national pretreatment program?
National Pretreatment Program - The national pretreatment program identifies specific discharge standards and requirements that apply to sources of nondomestic wastewater discharged to a POTW.
What is NPDES permit?
NPDES permits establish discharge limits and conditions for discharges from municipal wastewater treatment facilities to waters of the United States . Resources for discharge requirements include:
Why are sewers not watertight?
Sanitary sewers that are not watertight due to cracks, faulty seals, and/or improper connections can receive large amounts of infiltration and inflow (I/I) during wet weather.
What causes sewage overflows?
In addition, sewage overflows can be caused by other problems such as blockages, equipment failures, broken pipes, or vandalism. Resources for overflows and peak flows at treatment plants include: Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs) Sanitary Sewer Overflows (SSOs)
What is the EPA?
EPA's compliance and enforcement program monitors compliance with Effluent Guidelines and other Agency regulations with the help of states and tribes and takes enforcement actions when necessary. EPA provides information, environmental management tools and incentives to assist businesses in complying with the law.
What is the EPA's strategic plan?
Enforcing environmental laws is a central part of EPA's Strategic Plan to protect human health and the environment. When warranted, EPA will take civil or criminal enforcement actions against violators of environmental laws. Water Enforcement Policy, Guidance and Publications. Compliance Assistance Centers.
What is discharge monitoring tool?
The Discharge Monitoring Report (DMR) Pollutant Loading Tool is designed to help you determine who is discharging, what pollutants they are discharging and how much, and where they are discharging. It uses data from ICIS-NPDES and PCS.
What is indirect discharger?
Indirect dischargers to a municipal treatment plant ( publicly owned treatment works publicly owned treatment works A treatment works , as defined by Section 212 of the CWA, that is owned by the state or municipality.

New Request For Applications 2021 Grant Funding
- EPA is soliciting applications to provide training and technical assistance to rural, small, and tribal municipalities, publicly owned wastewater treatment works, and decentralized wastewater treatment systems for the prevention, reduction, and elimination of pollution. EPA’s Fiscal Year 2021 appropriation directed the Agency to competitively award up to $18 million to public and/o…
Grant Program Overview
- The Training and Technical Assistance for Rural, Small and Tribal Municipalities and Wastewater Treatment Systems for Clean Water Act Prevention, Reduction, and Elimination of Pollution Grant Program was established by the America’s Water Infrastructure Act of 2018. The program aims to provide training and tools to improve small wastewater system operations and management pra…
Request Training and Technical Assistance
- Communities and systems may directly contact the awarded grantees requesting training and technical assistance, as eligible. The current grantees awarded for the FY2020 Training and Technical Assistance for Small, Rural, and Tribal Wastewater Systems are: 1. Rural Community Assistance Partnership 2. National Rural Water Association 3. University of New Mexico – Envir…
Historical Funding
- FY 2020 Training and Technical Assistance for Small Wastewater Systems
On September 15, 2021, EPA announced the selection of $12 million in grant funding to provide training and technical assistance to serve small, rural and tribal community wastewater systems. This funding will improve public health and environmental protection by helping to ensure that w…