
In fetuses with anti-Ro/La, bradycardia secondary to second-degree (Mobitz type II) or complete AV block may lead to congestive heart failure, hydrops, and, eventually, fetal demise. Although no standard approach to treatment exists, fluorinated steroids have been used.
Full Answer
What causes second degree AV block?
Second-degree AV heart block happens when the electrical signals that tell your heart to contract don't always pass between the top and bottom chambers of your heart like they should. This causes an abnormal heart beat (arrhythmia).
What is 2nd degree AV block?
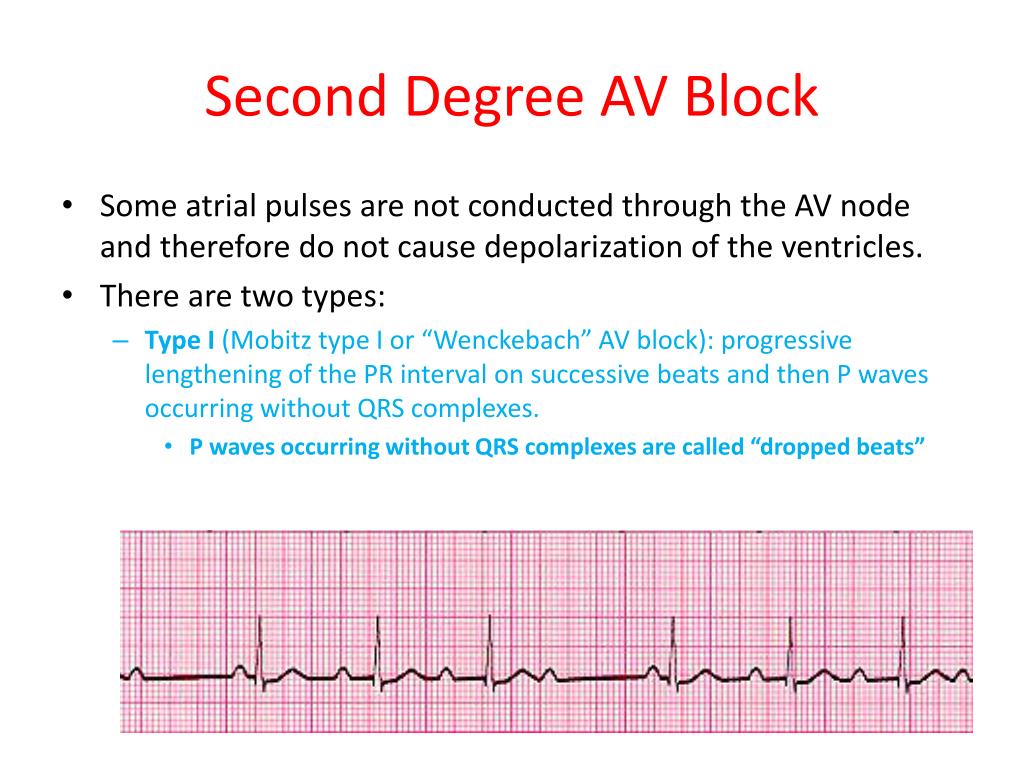
Second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, or second-degree heart block, is a disorder characterized by disturbance, delay, or interruption of atrial impulse conduction to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node (AVN) and bundle of His. Electrocardiographically, some P waves are not followed by a QRS complex.
What is the treatment for 2nd degree heart block?
Treatments for second-degree heart block with symptoms include:
- Taking medicines to increase your heart rate in the short-term (acutely) to relieve symptoms
- Stopping medicines, if they are causing the heart block
- Getting a pacemaker
What medications cause second degree heart block?
- Mechanism. This is usually a result of a reversible conduction block at the level of the AV node. ...
- Causes. There are multiple causes of second-degree Mobitz type 1 (Wenckebach) AV block, including reversible ischemia, myocarditis, increased vagal tone, status post-cardiac surgery, or even medications that slow AV nodal ...
- Clinical significance. ...

Is second degree type 2 heart block serious?
Most people who have the second type of second-degree heart block will need a pacemaker even if they have no symptoms. This type of heart block often can progress to more serious type of heart block that can be potentially dangerous.
What is the treatment for second degree heart block type 2?
Treatment for a Mobitz type II involves initiating pacing as soon as this rhythm is identified. Type II blocks imply structural damage to the AV conduction system. This rhythm often deteriorates into complete heart block. These patients require transvenous pacing until a permanent pacemaker is placed.
Does second-degree AV block type 2 require emergency treatment?
Second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block in the asymptomatic patient does not require any specific therapy in the prehospital setting. If the patient is symptomatic, standard advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) guidelines for bradycardia, including the use of atropine and transcutaneous pacing, are indicated.
Under which conditions does a type II AV block have a very serious prognosis?
Mobitz type 2 AV block can be associated with severe bradycardia and hemodynamic instability. It has a greater risk of progressing to third-degree (complete) heart block or asystole.
Which heart block is the most serious?
Third-degree heart block is the most severe. Electrical signals do not go from your atria to your ventricles at all with this type. There is a complete failure of electrical conduction. This can result in no pulse or a very slow pulse if a back up heart rate is present.
What is the most likely cause of a second-degree type 2 heart block?
Second-degree heart block type 2 is usually caused by structural damage to the conduction system of the heart.
Is AV block an emergency?
New-onset third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block (complete heart block) is a medical emergency.
Is AV block curable?
There is no heart-block-specific treatment. Most people with bundle branch block have no symptoms, and they do not require treatment. However, any underlying causes, such as hypertension, will need treatment. Share on Pinterest Patients with second- or third-degree heart block may need a pacemaker.
How long can you survive with complete heart block?
A follow-up study of the survival rate of 164 patients with complete heart block treated with permanent pacemaker showed 87% survival after one year, 76 after two, and 50% after five years.
Is AV block serious?
You might not have symptoms or need treatment. But if you do, a doctor can help you manage your condition. Without the right care, serious AV block can be life threatening.
How common is second-degree heart block?
Mobitz type 2 heart block is rare in the general population, but it is more common in people with certain heart conditions. For example, it is estimated that 1 in 30 people with heart failure will develop Mobitz type 2 heart block.
Is second-degree heart block sinus rhythm?
Sinus rhythm with 2 : 1 AV block is usually considered as a “special” category of second-degree block and may be due to nodal or infranodal conduction abnormalities.
What is the treatment for AV block type 2?
Second-degree AV block (Type 2) should be treated with immediate transcutaneous pacing or transvenous pacing because there is risk that electrical impulses will not be able to reach the ventricles and produce ventricular contraction.
What causes heart block type 2?
Second-degree heart block type 2 is usually caused by structural damage to the conduction system of the heart. Causes of the structural damage to the conduction system include the following:
Can you take atropine if you have TCP?
Atropine may be attempted if immediate TCP is not available or time is needed to initiate TCP. Atropine should not be relied upon and in the case of myocardial ischemia it should be avoided. Below is a short video which will help you quickly identify second-degree heart block type 2 on a monitor.
What are the two types of atrioventricular blocks?
There are two types of second-degree atrioventricular blocks: Mobitz type I, also known as , Wenckebach and Mobitz type II .[1][2][3][4][5] An electrical impulse from the sinoatrial node has to travel through the atria, to the atrioventricular node, and down the His-Purkinje system to reach the ventricles and create a ventricular contraction.
Why does Mobitz type 1 occur?
Mobitz type I occurs because each depolarization results in the prolongation of the refractory period of the atrioventricular (AV) node. When an atrial impulse comes through the AV node during the relative refractory period, the impulse will be conducted more slowly, resulting in a prolongation of the PR interval.
Can Mobitz block cause death?
The mobitz type ll block does have the potential to progress to a complete heart block and if unrecognized, can lead to death. Etiology. Mobitz type I (Wenckebach) is often a normal variant and seen in individuals with a high vagal tone without evidence of structural heart disease.
Does Mobitz cause AV block?
Recently the immunosuppressant agent, fingolimod, used to treat relapsing multiple sclerosis was also found to cause AV block. Mobitz type II is rarely seen in patients without structural heart disease. It is often associated with myocardial ischemia and fibrosis or sclerosis of the myocardium.
Can AV block cause syncope?
In general, patients with second degree AV block may have no symptoms or may experience symptoms like syncope and lightheadedness.The second degree heart block may be temporary or permanent, depending on the impairment of the conduction system.
Can type 1 block cause hypotension?
Occasionally type I blocks may result in bradycardia leading to hypotension. If hypotension and bradycardia occur, type I blocks respond well to atropine. If unresponsive to atropine, pacing (transcutaneous or transvenous) should be initiated for stabilization.
Is Mobitz type II a high degree AV block?
Be aware that if more than one P wave is not conducted this is no longer a Mobitz type II and is considered a high degree AV block.
What is dysfunctional AV node?
The AV node is dysfunctional, such that it will not be able to repolarize adequately by the time the next impulse arrives, which is why the conduction will be slower than the previous and the PR interval becomes prolonged. The AV node becomes more and more exhausted (i.e more and more refractory) each time until it is completely refractory and blocks the atrial impulse. This manifests on the ECG with gradual prolongation of the PR interval until a P-wave is blocked and thus not followed by a QRS complex. The AV node then recovers (after the complete block), only to repeat the cycle again. These cycles are often referred to as Wenckebach periods.
What is the most common P wave block?
If every third P-wave is blocked, then there is 3-to-2 block (which is the most common). If every fourth P-wave is blocked, it is classified as 4-to-3 block, which is less common. 5-to-4 block is even more uncommon.
Is Mobitz type 1 block good?
It is also common among athletes due to their high vagal tone. It is more common in older individuals. The prognosis is good, even in the elderly. Mobitz type 1 block generally does not progress to more advanced blocks. Should it progress to more advanced blocks, which typically is due to a more distal location of the block, an artificial pacemaker is needed.
Does Mobitz block progress to advanced blocks?
The prognosis is good, even in the elderly. Mobitz type 1 block generally does not progress to more advanced blocks. Should it progress to more advanced blocks, which typically is due to a more distal location of the block, an artificial pacemaker is needed.
Is Mobitz type 2 block a sporadically block?
Mobitz type 2 block implies that some atrial impulses are blocked sporadically. The PR interval is constant (although it may be prolonged). Mobitz type 2 is more serious, because it is usually chronic and tends to progress to third-degree AV block. Moreover, cardiac output may be reduced if many impulses are blocked.
Can atropine be used for a vagal block?
If a vagal mechanism is suspected as the cause of acute symptomatic heart block, atropine may also be used. Arrangements for a stable temporary pacing system are necessary because drug therapy is usually only a temporizing measure for symptomatic heart block. Previous. Next: Pharmacologic Therapy.
Can a second degree AV block be reversible?
If the cause of the symptomatic second-degree AV block is unlikely to be reversible, permanent pacing can be initiated. However, in most patients, permanent pacing is reserved for those who do not demonstrate resolution of their conduction disorder after a reasonable period of observation.
Can Mobitz block be reversible?
Patients with Mobitz type II AV block may have a reversible cause (ie, myocarditis, transplant rejection) and thus they may respond after treating the baseline disease. However, if no reversible cause can be found or if medications fail to control symptoms, pacemaker therapy is required.
Is Mobitz I asymptomatic?
In general, patients with Mobitz I (Wenckebach) AV block are asymptomatic; if it is thought to be a normal finding, such as in highly trained athletes or during sleep, no treatment is necessary. However, when symptomatic bradycardia is present, intravenous medications such as isoproterenol and atropine may be helpful.
Does isoproterenol cause AV block?
However, isoproterenol may exacerbate the condition by accelerating the atrial rate, which results in a higher grade of AV block by increasing myocardial oxygen demand, by reducing diastolic and coronary perfusion pressure, or by initiating ventricular dysrhythmias.
Do wenckebach patients need pacemaker therapy?
Temporary and Permanent Pacing Systems. Asymptomatic patients with Wenckebach or non-Wenckebach AV block do not require immediate pacemaker therapy. However, they should be monitored periodically because of the possibility of cardiovascular syncope or Stokes-Adams attacks in cases of a very slow escape rhythm.
What Are The ECG Characteristics of A Second-Degree Av Block Type II?
- Atrial rate is regular, ventricular rate is bradycardic (< 60 beats per minute)
- Consistent, regular P waves
- More P waves than QRS complexes
- Uniform PR intervals
- Atrial rate is regular, ventricular rate is bradycardic (< 60 beats per minute)
- Consistent, regular P waves
- More P waves than QRS complexes
- Uniform PR intervals
What Signs Or Symptoms May Be present?
- A patient with a second-degree AV block type II may exhibit: 1. Shortness of breath 2. Fatigue 3. Diaphoresis 4. Pallor 5. Chest pain 6. Altered mental status 7. Loss of consciousness 8. Bradycardia 9. Hypotension
What Causes A Second-Degree Av Block Type II?
- This type of heart block may be attributed to structural damage within the AV conduction system of the heart. Patients exhibiting this heart dysrhythmia often have underlying heart disease. Potential causes of this rhythm include: 1. Myocardial ischemia 2. Myocardial infarction 3. Infiltrative cardiomyopathies (such as hemochromatosis, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis) 4. Idiopathi…
FAQs
- What is the difference between type I and type II second-degree AV blocks?
A second-degree AV block type I occurs at the AV node. Each impulse is gradually prolonged until one is unsuccessful at being conducted to the ventricles. With this rhythm, the PR interval lengthens gradually until a QRS complex is dropped; there are more P waves than QRS complexe… - What is the difference between a second-degree AV block type II and a third-degree AV block?
In a second-degree AV block type II, AV conduction is irregularly blocked below the AV node. There are more P waves than QRS complexes, P waves are consistent and regular, PR intervals are uniform, and QRS complexes drop unexpectedly. QRS complexes in this rhythm tend to be wi…
Preparing For Your Acls Or Pals Exam
- Mastery of rhythms such as this are key to passing your ACLS or PALS exam, and being prepared to respond effectively when a patient is experiencing a cardiac emergency. That’s why the American Medical Resource Institute (AMRI) incorporates a multidisciplinary teaching approach that utilizes clinical scenarios through an expansive library of case studies to provide meaningfu…