
Radiation therapy, especially radiation to the brain, to the base of the skull, and to the neck may result in cognitive problems such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating.
What are the side effects of whole-brain radiation therapy?
Some short-term memory loss and difficulty thinking can occur if you are treated with whole-brain radiation therapy. Brain tissue swelling can develop during treatment. You may get a headache or feel pressure in your head if this occurs.
What are the side effects of radiation to the breast?
Radiation to the breast can cause: 1 Skin irritation, dryness, and color changes. 2 Breast soreness. 3 Breast swelling from fluid build-up (lymphedema).
How does radiation therapy affect the brain?
About Radiation Therapy to the Brain. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to treat cancer. It works by damaging the cancer cells and making it hard for them to reproduce. Your body then is naturally able to get rid of these damaged cancer cells. Radiation therapy also affects normal cells. However, your normal cells are able to repair ...
What happens during a radiation treatment?
During Your Treatment. You will not see or feel the radiation, but you may hear the machine as it moves around you and is turned on and off. You will be in the treatment room for 15 to 90 minutes, depending on your treatment plan. Most of this time will be spent putting you in the correct position.

What are the side effects of radiation treatment on the brain?
Radiation to the brain can cause these short-term side effects:Headaches.Hair loss.Nausea.Vomiting.Extreme tiredness (fatigue)Hearing loss.Skin and scalp changes.Trouble with memory and speech.More items...•
How long does it take to recover from brain radiation?
You may develop fatigue after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment, and it can range from mild to severe. Fatigue may last 6 weeks to 12 months after your treatment ends. There are a lot of reasons why you may develop fatigue during treatment, including: The effects of radiation on your body.
How long can you live after brain radiation?
Survival analysis The median follow-up of patients was 7 months, with a minimum of 2 months and a maximum of 34 months. At the end of the study period, 25 deaths were registered (71%). The median survival with brain metastases was 4.43 months, ranging from 0.73 months to 78.53 months.
What are side effects of having radiation to brain tumors?
What are the possible side effects of radiation therapy for brain cancer?Fatigue and mood changes. Fatigue and mood changes are among the most common side effects of radiation therapy. ... Hair loss. ... Nausea and vomiting.Skin changes. ... Headaches. ... Vision changes.Radiation necrosis.Increased risk of another brain tumor.More items...•
What are 5 harmful effects of radiation?
Here are a few common health effects or harmful effects of radiation on the human body.Hair. Loss of hair fall occurs when exposure to radiation is higher than 200 rems.Heart and Brain. Intense exposure to radiation from 1000 to 5000 rems will affect the functioning of the heart. ... Thyroid. ... Blood System. ... Reproductive Tract.
What are the worst side effects of radiotherapy?
Treatment areas and possible side effectsPart of the body being treatedPossible side effectsBrainFatigue Hair loss Memory or concentration problems Nausea and vomiting Skin changes Headache Blurry visionBreastFatigue Hair loss Skin changes Swelling (edema) Tenderness5 more rows•Jan 11, 2022
Can you recover from whole brain radiation?
The WBRT response rate ranges from 40 to 60%, and the median survival time (MST) ranges from 3 to 6 months [3–9]. Potential risks of WBRT include hair loss, nausea, and neuro-cognitive deficits.
Can brain tumors come back after radiation?
Some brain tumours are cured with the first round of treatment. But unfortunately, it's common for brain tumours to come back some time after they were first treated.
What is the success rate of radiation therapy?
“In fact, based on the literature reviewed, it appears that external-beam radiation therapy is a superior treatment in some cases. “When patients are treated with modern external-beam radiation therapy, the overall cure rate was 93.3% with a metastasis-free survival rate at 5 years of 96.9%.
How do you feel after brain radiation?
Radiotherapy to the brain can cause short term side effects such as tiredness and sickness. These side effects usually improve a few weeks after treatment. You may also have long term side effects which can continue for a lot longer and sometimes might be permanent.
What happens after radiation treatment for brain tumor?
Radiation is a powerful weapon against cancer cells, but sometimes it kills healthy brain tissue as well. This severe side effect is called radiation necrosis. Necrosis (a late effect of high doses of radiation) can cause headaches, seizures, or even death in a small number of cases.
How many times can you have radiation on the brain?
Whole-brain radiation applies radiation to the entire brain in order to kill tumor cells. People undergoing whole-brain radiation usually require 10 to 15 treatments over two to three weeks. Side effects may include fatigue, nausea and hair loss.
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Brain
People with brain tumors often get stereotactic radiosurgery (radiation given in one large dose) if the cancer is in only one or a few sites in the...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Head Or Neck
People who get radiation to the head and neck might have side effects such as: 1. Soreness (or even open sores) in the mouth or throat 2. Dry mouth...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Breast
If you have radiation to the breast, it can affect your heart or lungs as well causing other side effects.
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Chest
Radiation treatment to the chest may cause side effects such as: 1. Sore throat 2. Swallowing problems 3. Loss of appetite 4. Cough 5. Shortness of...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Abdomen (Belly)
If you are getting radiation to your stomach or some part of the abdomen (belly), you may have side effects such as: 1. Nausea 2. Vomiting 3. Belly...
If You’Re Having Radiation Therapy to The Pelvis
Radiation therapy to the pelvis (for example, as treatment for bladder, ovarian, or prostate cancer) can cause side effects such as: 1. Bladder pro...
How does radiation affect cancer?
The radiation used to destroy cancer cells can also hurt normal cells in the area that is radiated . Side effects from radiation treatment can vary, depending on the area of the body being treated. Side effects are caused by the cumulative effect of radiation on the cells. This means they develop over time and most patients do not experience any side effects until a few weeks into their treatment. Side effects may be unpleasant, but there are treatments to help deal with them. Most side effects are temporary, disappearing bit by bit after therapy is complete.
What are the side effects of radiosurgery?
Side effects of radiosurgery are usually related to sending high doses of radiation to particular areas of the skull. For instance, if you are treated for an acoustic neuroma (a tumor involving the nerve that controls hearing), you might lose some hearing. Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia can lead to tingling or numbness of the face.
How often do radiation oncologists see patients?
Most side effects are temporary, disappearing bit by bit after therapy is complete. Most radiation oncologists see their patients at least once a week while the patient is receiving treatment. This visit with the healthcare team is an opportunity to ask questions, talk about any side effects, and to make a plan to manage side effects. ...
What to do after cancer treatment?
After treatment, talk with your oncology team about receiving a survivorship care plan, which can help you manage the transition to survivorship and learn about life after cancer.
How long does it take for fatigue to go away after radiation?
Talk with your radiation oncologist and health care team about what you can expect from your specific treatment. Fatigue is very common with radiation treatment and tends to begin a few weeks into therapy. Fatigue typically resolves slowly over the weeks and months following treatment.
How long does it take for a syringe to heal?
This typically resolves in 2-4 weeks after finishing treatment. Skin irritation: The skin in the treatment area may become red, irritated, dry, or sensitive. This may start to look like a sunburn. Treat the skin gently to avoid further irritation, and bathe carefully, using only warm water and mild soap.
Can radiation therapy cause memory loss?
Avoid sun exposure, which can worsen the irritation. Some short-term memory loss and difficulty thinking can occur if you are treated with whole-brain radiation therapy. Brain tissue swelling can develop during treatment. You may get a headache or feel pressure in your head if this occurs.
Fatigue and mood changes
Fatigue and mood changes are among the most common side effects of radiation therapy.
Nausea and vomiting
About 50 to 80 percent of people undergoing traditional radiation therapy develop nausea and vomiting during or after treatment. Nausea may come in waves and may appear before vomiting.
Skin changes
Approximately 85 percent of people undergoing modern radiation therapy experience moderate to severe skin reactions around the treatment area. Some people develop dry and peeling patches of skin, while others develop skin that looks sunburned, puffy, red, or swollen.
Headaches
Radiation therapy can cause swelling of the brain that causes headaches. Headaches are a less common side effect than fatigue or irritability but can affect your quality of life. There are several medications that can help the pain from these headaches. Your doctor may also recommend steroids to address headaches.
Vision changes
Some people develop blurry vision or other vision changes because of damage to cells in the eyes or optic nerve. Vision changes due to damage to the optic nerve is a rare side effect but can seriously impact your vision. It’s important to immediately report any visual changes to your doctor.
Radiation necrosis
Radiation necrosis is a rare side effect where a lump of dead tissue forms at the tumor site months or years after the initial treatment. It can often be managed with corticosteroids, but in some cases, you may need surgery.
Increased risk of another brain tumor
Radiation can damage the DNA of your healthy cells, increasing your chances of developing cancer in your brain, surrounding tissue, or skull. The risk is small, and when it happens, tumors usually occur years after radiation.
Types of Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors
There are 2 main types of therapy. You may get both types. They include:
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT)
There are several types of EBRT. The goal is to target the tumor and limit damage to nearby healthy brain cells. To limit the harm, your healthcare provider may use special types of EBRT such as:
Brachytherapy
For this treatment, the radiation is placed very close to or inside the tumor. This is done during surgery. The radiation the implants give off travels a very short distance. This helps limit the effect on nearby healthy tissue.
Brain Radiation Side Effects
Generally, side effects from radiation treatment are grouped into two categories:
Radiation necrosis
Sometimes dead brain tissue forms at the site of the radiation. This is called radiation necrosis. The mass of dead brain tissue comes from both cancer cells and healthy cells. Radiation necrosis can take anywhere from months to years to develop.
Risk of future cancer
Radiation can damage the DNA in healthy cells. As a result, you have a small risk of a second brain cancer after brain radiation. This second cancer usually occurs many years later. Talk to your radiation oncologist about the risks and benefits of radiation therapy.
The Radiation Team
Treatment planning for radiation therapy includes mapping to pinpoint the exact location of the brain tumor using X-rays or other images.
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
How long does it take for radiation to show up in the brain?
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later – usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function.
What is the most common drug used for radiation therapy?
The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy. Not all doctors agree on how these drugs should be used in radiation therapy. These drugs have their own side effects, too, so be sure you understand what to look for.
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
What are the side effects of brachytherapy?
If your treatment includes brachytherapy (internal radiation implants), you might notice breast tenderness, tightness, redness, and bruising. You may also have some of the same side effects that happen with external radiation treatment.
How to take care of your mouth during radiation?
Here are some tips that may help you manage mouth problems: Avoid spicy and rough foods, such as raw vegetables, dry crackers, and nuts.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Common side effects include fatigue, hair loss and memory problems.
What are the side effects of stereotactic radiosurgery?
Common side effects include fatigue, hair loss and memory problems. Stereotactic radiosurgery is a more focused therapy that aims a very high dose of radiation at only the tumor itself. Sometimes, it can be completed in a single day. The more focused dose minimizes radiation exposure to the rest of the brain.
What is the best treatment for metastatic brain tumors?
There are two main types of radiation therapy used at the Comprehensive Brain Tumor Center to treat metastatic brain tumors: 1 Whole-brain radiation therapy targets the entire brain, treating even microscopic tumors that can’t be seen on an MRI scan. Common side effects include fatigue, hair loss and memory problems. 2 Stereotactic radiosurgery is a more focused therapy that aims a very high dose of radiation at only the tumor itself. Sometimes, it can be completed in a single day. The more focused dose minimizes radiation exposure to the rest of the brain. That also means the potential for fewer side effects.
Where is proton therapy used?
Proton therapy is used to treat certain tumors in children and adults. Our treatment center, located at Sibley Memorial Hospital in Washington, D .C., combines advanced proton therapy technology, the latest research and caring specialists.
Does radiation kill brain tumors?
Here’s what he wants you to know about radiation therapy for brain metastases: 1. Radiation kills cancer. There’s a reason radiation therapy is one of the main ways doctors treat metastatic brain tumors today — it works. Radiation therapy is effective in destroying cancer cells.
Do you need follow up appointments for radiation?
With either type of radiation therapy, you will probably need follow-up appointments. This is the best way to detect any new disease early so it can be treated effectively right away. 3. Decide if radiation therapy is right for you.
Is radiation therapy effective?
Radiation therapy is effective in destroying cancer cells. Lim says radiation therapy has been shown to be as effective as surgery in several studies, and it could even reduce your chances of a tumor recurrence (the tumor coming back). As radiation therapies become more advanced, people who undergo treatments for brain metastases are living longer ...
How long does radiation treatment last?
What Happens During Radiation. The treatment is normally Monday through Friday and lasts about 45 minutes. A lot of time is spent getting your body in the right position, so the radiation hits its desired locations. You lay down on a custom-molded table. A technician positions your body using lasers and measurements.
How long does it take for radiation to hit your body?
This may seem scary, but this ensures the radiation does not hit healthy areas. The radiation takes a couple of minutes. You can sense when the radiation hits your body if you receive radiation to your brain.
Does radiation cause hair loss?
Radiation to your brain causes hair loss, but over time it grows back. As your hair grows again, so will you. Remember, during and after radiation treatment, listen to your body, ask questions, acknowledge side effects and adjust.
Why do we need a treatment break for radiation?
Therefore, a treatment break may be needed to prevent the possibility of infection and bleeding if these counts get too low.
How long does it take for hair to grow after radiation?
The hair loss will occur about two weeks after treatment has started. Hair will usually begin to grow again 2 to 3 months after treatment is over.
What is the best medicine for a tumor?
MEDICATIONS#N#While you are receiving treatment, you may be taking a medicine called Decadron (dexamethasone). This medicine decreases the swelling and inflammation caused by the tumor and radiation. You need to know the following about Decadron: 1 Decadron may cause an increase in appetite, increased urination, fluid retention (swelling), leg cramps, and mood changes. These are expected and temporary effects of the drug, but should be reported to your nurse or doctor 2 DO NOT take this medicine on an empty stomach. DO take it with food or milk, or prescribed antacid medication During treatment, your doctor will, over a period of time, decrease the amount of Decadron. 3 DO NOT decrease or stop this medicine without being instructed to do so by your doctor.
How to stop sunburn reaction?
There are several things you can do to minimize this. Wash hair and scalp very gently with baby shampoo, brush or com b very gently . Apply pure Aloe Vera gel to forehead and around ears to diminish sunburn reaction.
Does radiation cause fatigue?
During radiation therapy, the body uses a lot of energy. Stress related to your illness, daily trips for treatment, and the effects of radiation on normal cells all contribute to fatigue. The amount of fatigue varies with each person and generally will go away when your treatment is completed.
Does Decadron cause swelling?
This medicine decreases the swelling and inflammation caused by the tumor and radiation. You need to know the following about Decadron: Decadron may cause an increase in appetite, increased urination, fluid retention (swelling), leg cramps, and mood changes.
What is the treatment for cancer of the brain?
Cancer that spreads to the brain is usually treated with radiosurgery - highly focused radiation with a tool such as the Gamma Knife, followed by less intense radiation to the whole brain. The latter treatment can cause hair loss, dry mouth, fatigue and thinking problems.
Does radiation help cancer?
Radiation helped control the cancer, "but at the cost of cognitive decline.". For patients, the study is not necessarily the bad news it may seem. It shows that in this case, quality of life is better with less treatment, and many people can be spared the expense and side effects of futile care.
Does radiation therapy help with brain cancer?
Contrary to conventional wisdom, radiation therapy to the whole brain did not improve survival, and it harmed memory, speech and thinking skills, doctors found.
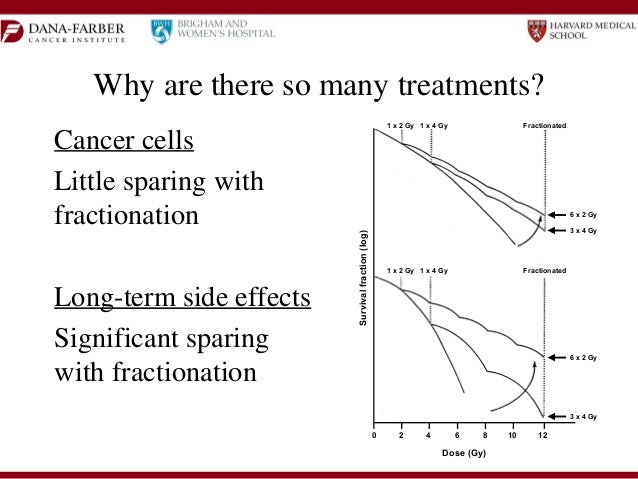
Acute (Short-Term) Side Effects
- The following list includes some of the most common side effects of radiation therapy for brain tumors. Remember that the treatment can affect each patient differently, and you may not experience these particular side effects. Side effects can also be different depending on your dose and treatment schedule. Talk with your radiation oncologist about what side effects you ca…
Chronic (Long-Term) Side Effects
- The side effects mentioned above tend to occur during or shortly after treatment. Long-term effects can happen months to years after treatment has ended. The risks of long-term effects vary depending on the treatment area, the total dose that is given, and the radiation techniques that were used, as these continue to develop and improve. Though the risk is low, you should be …
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Srs) Side Effects
- Side effects of radiosurgeryare usually related to sending high doses of radiation to particular areas of the brain. For instance, if you are treated for an acoustic neuroma (a tumor involving the nerve that controls hearing), you might lose some hearing. Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia can lead to tingling or numbness of the face. Talk to your ...