Medication
· A person can reduce the risk of contracting or transmitting pharyngitis and other infections by: washing hands thoroughly and regularly covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing avoiding close contact with people who have contagious viral or bacterial infections avoiding smoking and ...
Self-care
Pharyngitis can be caused by viral, bacterial, or fungal infections. Viral causes are often self-limiting, while bacterial and fungal infections typically require antimicrobial therapy. Rapid antigen detection tests and throat cultures can be used with clinical findings to identify the inciting organism.
Nutrition
· If a virus is causing your pharyngitis, home care can help relieve symptoms. Home care includes: drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration eating warm broth gargling with warm salt water (1...
Is there any cure for pharyngitis?
· Bacterial pharyngitis: Bacterial pharyngitis treatments focus on the eradication of GAS. A 6- to 10-day course of amoxicillin is the mainstay for …
Is dexamethasone helpful for treating pharyngitis?
However, there are a few chronic pharyngitis home remedies you can try to ease your sore throat symptoms: Drink lots of water. Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, naproxen sodium or ibuprofen. Gargle with warm salt water a few times a day. Don’t smoke.
What are the best symptoms of acute pharyngitis?
31 rows · · Current U.S. treatment guidelines recommend erythromycin for patients with penicillin allergy. Gastrointestinal side effects of erythromycin cause many physicians to instead prescribe the...
Should we treat strep pharyngitis with antibiotics?
· Viral pharyngitis will go away on its own without treatment. Your sore throat should start to feel better in 3 to 5 days for both viral and bacterial infections. You may need any of the following: Antibiotics treat a bacterial infection. NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever.

What is the fastest way to cure pharyngitis?
16 Best Sore Throat Remedies to Make You Feel Better Fast, According to DoctorsGargle with salt water—but steer clear of apple cider vinegar. ... Drink extra-cold liquids. ... Suck on an ice pop. ... Fight dry air with a humidifier. ... Skip acidic foods. ... Swallow antacids. ... Sip herbal teas. ... Coat and soothe your throat with honey.More items...•
What is the best medicine for pharyngitis?
Penicillin and amoxicillin are the antibiotics of choice for the treatment of pharyngitis.
How do you permanently cure pharyngitis?
Viral pharyngitis typically clears up on its own within a couple of weeks, but bacterial pharyngitis may require a course of antibiotics to prevent complications. Complications of pharyngitis, such as rheumatic fever, are rare. Anyone with severe, recurring, or persistent symptoms should see a doctor.
How is acute pharyngitis treated?
Rest, oral fluids, and salt-water gargling (for soothing effect) are the main supportive measures in patients with viral pharyngitis. Analgesics and antipyretics may be used for relief of pain or pyrexia. Acetaminophen is the drug of choice. Traditionally, aspirin has been used, but it may increase viral shedding.
What are the symptoms of pharyngitis?
Many conditions and factors cause sore throat, also called pharyngitis. You may feel pain and irritation anywhere in the back of your mouth, on your tonsils, and down your neck. You may also have a fever, swollen lymph nodes in your neck, and a headache or earache.
How do you test for pharyngitis?
Available diagnostic tests include throat culture and rapid antigen detection testing. Throat culture is considered the diagnostic standard, although the sensitivity and specificity of rapid antigen detection testing have improved significantly.
Is vitamin C good for sore throat?
Taking vitamin C supplements regularly may slightly reduce the duration of cold symptoms, like a sore throat. However, there isn't any evidence that vitamin C supplements can help treat sore throat conditions like strep throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and laryngitis.
What causes pharyngitis?
It is usually caused by viral and/or bacterial infections, such as the common cold and flu (both viral infections) or by infection with the Streptococcus bacterium (strep throat). Pharyngitis can also occur with mononucleosis (aka “mono”), a viral infection.
Can pharyngitis last for months?
Chronic pharyngitis is a persistent sore throat that lingers for a few weeks or returns frequently. Chronic pharyngitis may be caused by infection, environmental pollutants, allergies or acid reflux. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause.
Is azithromycin good for pharyngitis?
Conclusions: Treatment with 3-day, once daily 10 mg/kg azithromycin for GAS pharyngitis is associated with similar high levels of clinical efficacy, but lower levels of bacteriologic eradication, than with 10-day 100,000 IU/kg/day penicillin V.
When do you need antibiotics for pharyngitis?
Only sore throats caused by bacteria need antibiotic treatment. People with fever and sore throat are more likely to need antibiotic treatment. Some helpful remedies for sore throat include over-the-counter pain medication, cold and warm fluids, and throat sprays and lozenges.
How long does it take for pharyngitis to go away?
Viral pharyngitis often goes away in five to seven days. If you have bacterial pharyngitis, you will feel better after you have taken antibiotics for two to three days. You must take your antibiotic even when you are feeling better. If you don't take all of it, your sore throat could come back.
What is the best treatment for pharyngitis?
For bacterial infections, a doctor may prescribe a person a course of oral antibiotics, such as amoxicillin or penicillin. The antibiotics help reduce symptoms and prevent complications, such as rheumatic fever.
How long does it take for pharyngitis to clear up?
Pharyngitis is rarely a serious condition and often occurs alongside colds and the flu. Viral pharyngitis typically clears up on its own within a couple of weeks, but bacterial pharyngitis may require a course of antibiotics to prevent complications.
How long does it take for a viral infection to go away?
People usually recover from viral infections, such as the common cold, within 7-10 days. However, due to the viral incubation period, people may be contagious before any symptoms appear.
Do antibiotics help with pharyngitis?
The antibiotics help reduce symptoms and prevent complications, such as rheumatic fever. It is essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics to ensure the infection has cleared and to prevent reinfection. Viral pharyngitis does not respond to antibiotics and will typically clear up on its own.
How do you know if you have pharyngitis?
A doctor will usually begin diagnosing pharyngitis by performing a physical examination. They will review the person’s current symptoms and check their throat, ears, and nose for signs of infection. When an individual has clear signs of a viral infection, the doctor will likely not perform further testing.
Is tonsillitis a subset of pharyngitis?
Symptoms of tonsillitis and pharyngitis are similar. Tonsillitis is effectively a subset of pharyngitis. Symptoms of both include:
What are the symptoms of pharyngitis?
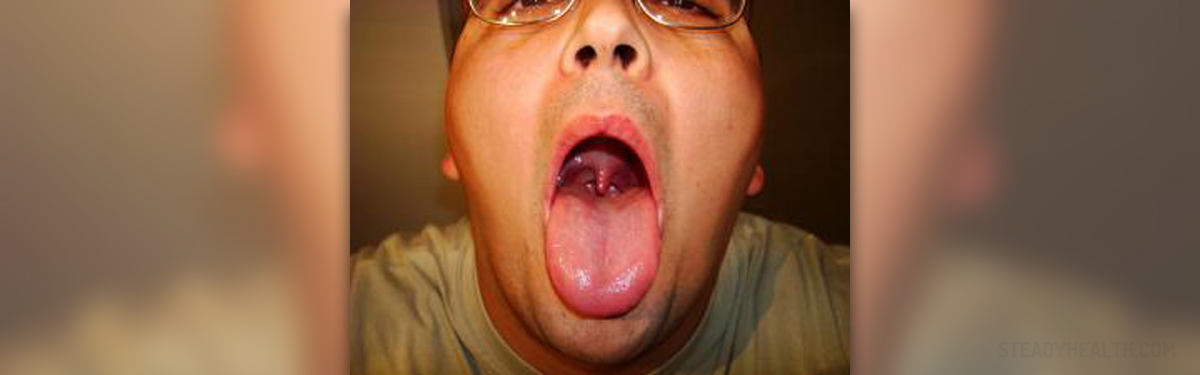
The main symptom of pharyngitis is a sore, dry, or itchy throat. Additional symptoms may appear depending on the type of infection, such as cold or flu symptoms. abdominal pain, especially on the upper left side. visible white patches or pus on the back of the throat.
What is the importance of a thorough history of pharyngitis?
A thorough history is key to diagnosing pharyngitis. Rapid antigen detection tests should be reserved for concerns about antibiotic initiation. Physicians should exercise restraint in antibiotic initiation for pharyngitis, as restraint does not delay recovery or increase the risk of <i>S pyogenes</i> …
Should rapid antigen testing be reserved for pharyngitis?
Rapid antigen detection tests should be reserved for concerns about antibiotic initiation. Physicians should exercise restraint in antibiotic initiation for pharyngitis, as restraint does not delay recovery or increase the risk of S pyogenesinfections. Copyright© the College of Family Physicians of Canada.
What is the best medicine for pharyngitis?
For pain and fever relief, consider taking over-the-counter medication such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil). Throat lozenges may also be helpful in soothing a painful, scratchy throat. Alternative remedies are sometimes used to treat pharyngitis.
What is the most common cause of pharyngitis?
Bacterial infections require antibiotics. The most common bacterial infection of the throat is strep throat, which is caused by group A streptococcus. Rare causes of bacterial pharyngitis include gonorrhea, chlamydia, and corynebacterium. Frequent exposure to colds and flus can increase ...
What is the best medicine for strep throat?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Trusted Source. (CDC), amoxicillin and penicillin are the most commonly prescribed treatments for strep throat. It’s important that you take the entire course of antibiotics to prevent the infection from returning or worsening.
How to test for strep throat?
This involves using a cotton swab to take a sample of the secretions from your throat. Most doctors are able to do a rapid strep test in the office. This test will tell your doctor within a few minutes if the test is positive for streptococcus. In some cases, the swab is sent to a lab for further testing and results are not available for at least 24 hours.
Can you take antibiotics for pharyngitis?
Medical treatment. In some cases, medical treatment is necessary for pharyngitis. This is especially the case if it’s caused by a bacterial infection. For such instances, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
How to tell if you have pharyngitis?
If you’re experiencing symptoms of pharyngitis, your doctor will look at your throat. They’ll check for any white or gray patches, swelling, and redness. Your doctor may also look in your ears and nose. To check for swollen lymph nodes, they will feel the sides of your neck.
Can mononucleosis cause a sore throat?
In addition to a sore throat, the symptoms of mononucleosis include: Strep throat, another type of pharyngitis, can also cause: The length of the contagious period will also depend on your underlying condition. If you have a viral infection, you will be contagious until your fever runs its course.
What is the best way to diagnose viral pharyngitis?
History and clinical examination can be used to diagnose viral pharyngitis when clear viral symptoms are present. Viral symptoms include:
What is the most common cause of pharyngitis in all age groups?
The differential diagnosis of acute pharyngitis includes multiple viral and bacterial pathogens. Viruses are the most common cause of pharyngitis in all age groups. Experts estimate that group A strep, the most common bacterial cause, causes 20% to 30% of pharyngitis episodes in children. In comparison, experts estimate it causes approximately 5% to 15% of pharyngitis infections in adults.
How does group A strep pharyngitis work?
Shortens the duration of symptoms. Reduces the likelihood of transmission to family members, classmates, and other close contacts. Prevents the development of complications, including acute rheumatic fever. When left untreated, the symptoms of group A strep pharyngitis are usually self-limited.
How old do you have to be to get antibiotics for strep pharyngitis?
Clinicians should confirm group A strep pharyngitis in children older than 3 years of age to appropriately guide treatment decisions. Giving antibiotics to children with confirmed group A strep pharyngitis can reduce their risk of developing sequela (acute rheumatic fever). Testing for group A strep pharyngitis is not routinely indicated for:
Can a rapid antigen test be used to differentiate strep pharyngitis?
However, clinicians cannot use clinical examination to differentiate viral and group A strep pharyngitis in the absence of viral symptoms. Clinicians need to use either a rapid antigen detection test (RADT) or throat culture to confirm group A strep pharyngitis.
What is the most common risk factor for group A strep pharyngitis?
The most common risk factor is close contact with another person with group A strep pharyngitis. Adults at increased risk for group A strep pharyngitis include:
How long does it take for strep pharyngitis to develop?
The incubation period of group A strep pharyngitis is approximately 2 to 5 days.
How to manage pharyngitis?
Management of pharyngitis focuses on deciding whether to watch and wait, provide symptomatic treatment, or initiate antimicrobial therapy. This relies on accurate differentiation between bacterial and viral infections. Cultures effectively identify pathogens but should not delay or guide initial treatment in atypical presentations, as results have a 5- to 10-day latency and fail to distinguish those with acute infections from carriers. Alternatively, RADT technology is specific but equally should not guide management in isolation, as its sensitivity can be variable and RADT lacks high-quality evidence in the pediatric population.23Negative RADT results in patients aged 5 to 15 should be verified with a throat culture.34Moreover, children younger than 3 should not be tested unless there is a high chance of GAS exposure, as incidence within this population is less than 14% and infection rarely causes acute rheumatic fever.35
What is the generalized approach to pharyngitis?
Generalized approach to pharyngitis: Antimicrobial therapy should be initiated in patients who are severely ill or who are highly suspected of having streptococcal infections. Modified Centor and FeverPAIN scores of < 3 should be treated symptomatically with possible follow-up for worsening symptoms or delayed prescription if there are concerns about loss to follow-up. Those at risk of complications (elderly, frail, immunocompromised) might benefit from RADT to rule out bacterial causes. Severely ill patients should be referred immediately to the hospital or urgent care for immediate management and workup.
How long does it take for pharyngitis to resolve?
Clinical differentiation of viral, bacterial, and fungal pharyngitis is challenging owing to similarities in presentation. Sore throat, odynophagia, and fever are all common features. These symptoms typically peak within 3 to 5 days and resolve by day 10.8Although some pathogen-specific symptoms have been reported, predictive values have only been formulated for GAS pharyngitis (Table 2).2,3,9–14
What percentage of pharyngitis cases are caused by viral agents?
Sore throat and pharyngitis represent more than 2% and 5% of all outpatient primary care visits for adult and pediatric populations, respectively.1It is characterized by inflammation of the pharynx, nasopharynx, and tonsillar tissues.2Incidence peaks between late winter and early spring. Eighty percent of cases are caused by viral agents, while the remaining are bacterial and, rarely, fungal infections3(Table 1). Herein, we provide an updated clinical review of pharyngitis for Canadian family physicians.
What is the importance of a thorough history of pharyngitis?
A thorough history is key to diagnosing pharyngitis. Rapid antigen detection tests should be reserved for concerns about antibiotic initiation. Physicians should exercise restraint in antibiotic initiation for pharyngitis, as restraint does not delay recovery or increase the risk of S pyogenesinfections.
What is the sensitivity of a throat culture?
Throat culture remains the criterion standard for bacterial pharyngitis diagnosis, with 97% to 100% specificity20and 90% to 95% sensitivity.10Unfortunately, culture of throat samples is difficult and can delay antibiotics.21Cultures rarely influence antibiotic selection, as prescribing practices currently cover for GAS. Rather, they can rule out atypical infections such as non-GAS and fungal pharyngitis that require alternate antimicrobial regimens.22
What is the best treatment for pharyngitis?
Penicillin is the treatment of choice for GABHS pharyngitis in persons who are not allergic to penicillin.
What are the symptoms of pharyngitis?
Palatal petechiae and scarlatiniform rash are highly specific but uncommon; a swollen uvula is sometimes noted. Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and diarrhea are more common with viral pharyngitis.
Is amoxicillin a substitute for penicillin?
Oral amoxicillin suspension is often substituted for penicillin because it tastes better. The medication is also available as chewable tablets. Five of eight trials (1966 to 2000) showed greater than 85 percent GABHS eradication with the use of amoxicillin. 29 [ corrected] Ten days of therapy is standard; common dosages are provided in Table 3. 2, 17 - 20, 28 - 34 Amoxicillin taken once per day is likely as effective as a regimen of three times per day. One randomized controlled trial (RCT) demonstrated comparable symptom relief with once-daily dosing, although like almost all studies of pharyngitis treatment, the trial was not powered to detect nonsuppurative complications. 30 A recent study of children three to 18 years of age showed that once-daily dosing of amoxicillin was not inferior to twice-daily dosing; both regimens had failure rates of about 20 percent. 31 It should be noted that once-daily therapy is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Can a septic plaque cause a jugular vein thrombus?
Untreated Fusobacterium infections may lead to Lemierre syndrome, an internal jugular vein thrombus caused by inflammation. Complications occur when septic plaques break loose and embolize. Empiric antibiotic therapy may reduce the incidence of complications.
Can non-group A streptococci cause pharyngitis?
Non–group A beta-hemolytic streptococci ( groups C and G) also can cause acute pharyngitis; these strains are usually treated with antibiotics, although good clinical trials are lacking. Fusobacterium necrophorum causes endemic acute pharyngitis, peritonsillar abscess, and persistent sore throat. Untreated Fusobacterium infections may lead to Lemierre syndrome, an internal jugular vein thrombus caused by inflammation. Complications occur when septic plaques break loose and embolize. Empiric antibiotic therapy may reduce the incidence of complications.
Can streptococcal titers be used for pharyngitis?
Streptococcal antibody titers are not useful for diagnosing streptococcal pharyngitis and are not routinely recommended. They may be indicated to confirm previous infection in persons with suspected acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis or rheumatic fever.
How common is pharyngitis?
1 Most episodes are viral. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS), the most common bacterial etiology, accounts for 15 to 30 percent of cases of acute pharyngitis in children and 5 to 20 percent in adults. 2 Among school-aged children, the incidences of acute sore throat, swab-positive GABHS, and serologically confirmed GABHS infection are 33, 13, and eight per 100 child-years, respectively. 3 Thus, about one in four children with acute sore throat has serologically confirmed GABHS pharyngitis. Forty-three percent of families with an index case of GABHS pharyngitis have a secondary case. 3 Late winter and early spring are peak GABHS seasons. The infection is transmitted via respiratory secretions, and the incubation period is 24 to 72 hours.
How long does it take for pharyngitis to go away?
Viral pharyngitis will go away on its own without treatment. Your sore throat should start to feel better in 3 to 5 days for both viral and bacterial infections. You may need any of the following:
How to get rid of swollen throat?
Manage your symptoms: Gargle salt water. Mix ¼ teaspoon salt in an 8 ounce glass of warm water and gargle. This may help decrease swelling in your throat. Drink liquids as directed. You may need to drink more liquids than usual. Liquids may help soothe your throat and prevent dehydration.
How to get rid of cough and sneezing?
Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Use a cool-steam humidifier to help moisten the air in your room and calm your cough. Soothe your throat with cough drops, ice, soft foods, or popsicles.
How long does it take for a lump in the throat to go away?
Contact your healthcare provider if: Your throat pain gets worse. You have a painful lump in your throat that does not go away after 5 days. Your symptoms do not improve after 5 days. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
What causes a sore throat?
Pharyngitis is most often caused by bacteria. It may also be caused by a cold or flu virus. Other causes include smoking, allergies, or acid reflux.
How to stop a sneeze?
Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze. Do not share food or drinks. Wash your hands often. Use soap and water. If soap and water are unavailable, use an alcohol based hand sanitizer.
What to do if your throat is sore?
Treating bacterial infections. If your or your child's sore throat is caused by a bacterial infection, your doctor or pediatrician will prescribe antibiotics. You or your child must take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed even if the symptoms are gone.
How to help a child with a sore throat?
Regardless of the cause of your sore throat, these at-home care strategies can help you ease your or your child's symptoms: Rest. Get plenty of sleep. Rest your voice, too. Drink fluids. Fluids keep the throat moist and prevent dehydration. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can dehydrate you.
Can antibiotics help with a sore throat?
If you or your child needs an antibiotic for a bacterial infection, don't rely on alternative treatments alone.
Can you give a child candy for a sore throat?
Consider lozenges or hard candy. Either can soothe a sore throat, but don't give them to children age 4 and younger because of choking risk.
How to get rid of sore throat from a humidifier?
Humidify the air. Use a cool-air humidifier to eliminate dry air that may further irritate a sore throat, being sure to clean the humidifier regularly so it doesn't grow mold or bacteria. Or sit for several minutes in a steamy bathroom.
How to cure a sore throat from drinking alcohol?
Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can dehydrate you. Try comforting foods and beverage. Warm liquids — broth, caffeine-free tea or warm water with honey — and cold treats such as ice pops can soothe a sore throat. Don't give honey to children younger than age 1. Gargle with saltwater.
Can antibiotics cause rheumatic fever?
Not completing the full course of antibiotics to treat strep throat can increase a child's risk of rheumatic fever or serious kidney inflammation. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about what to do if you forget a dose.

Etiology
Clinical Features
Transmission
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Diagnosis and Testing
Special Considerations
Treatment
Carriage
Prognosis and Complications
Prevention