
Medication
Sep 10, 2012 · Local anaesthetic blocks of suprascapular nerve are used to treat painful shoulder conditions such as adhesive capsulitis. A double-blinded randomised controlled trial 51 compared three suprascapular blocks with bupivacaine at weekly intervals with placebo.
Procedures
May 10, 2021 · The subacromial space is injected with an anesthetic, typically 5 ml of 1% lidocaine. In patients with adhesive capsulitis, the ROM limitations and pain will persist after the injection. In patients with subacromial pathology (rotator cuff tendinopathy or subacromial bursitis) will show an improvement of pain and improved range of motion.
Therapy
Oct 20, 2010 · You may be given a corticosteroid injection into the shoulder joint or soft tissues. But the cornerstone of treatment is physical therapy, concentrating first on exercises that stretch the joint capsule, and later, on strengthening exercises. A physical therapist can show you how far to push yourself and can teach you the appropriate exercises.
Self-care
Simple treatments, such as use of pain relievers and shoulder exercises, in combination with a cortisone injection, are often enough to restore motion and function within a year or less. Even left completely untreated, range of motion and use of the shoulder continue to get better on their own, but often over a slower course of time.
Nutrition
Apr 21, 2022 · Frozen shoulder (FS), medically known as adhesive capsulitis, is a self-limiting condition characterised by an insidious, progressive onset of symptoms. ... Millar NL. Comparison of Treatments for Frozen Shoulder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Dec 16;3(12):e2029581. Tagged: Shoulder Pain, Frozen shoulder. Older ...
What are the surgical options for adhesive capsulitis?
Adhesive capsulitis embolization is an alternative treatment for frozen shoulder syndrome. The procedure is performed by an interventional radiologist – a doctor specializing in treating vascular issues using minimally invasive methods. One such method is embolization, which is used to block abnormal vascular channels or individual blood vessels.
Why is adhesive capsulitis difficult to define?
Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory medicine that is injected directly into your shoulder joint. Hydrodilatation. If your symptoms are not relieved by other nonsurgical methods, your doctor may recommend hydrodilatation.
How long does adhesive capsulitis last without treatment?
Introduction. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder is characterized by a gradual onset of shoulder pain and limited passive and active range of motions (ROM) with respect to external rotation and forward flexion which affects 2–5% of the general population [].Its incidence increases in systemic diseases, especially in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [].
How effective is Arthroscopic Capsular Release in the treatment of adhesive capsulitis?
Aug 01, 2020 · Treatment for frozen shoulder involves range-of-motion exercises and, sometimes, corticosteroids and numbing medications injected into the joint capsule. In a small percentage of cases, arthroscopic surgery may be indicated to loosen the joint capsule so that it can move more freely.
See more

How do you fix adhesive capsulitis?
TreatmentNon-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. Drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen reduce pain and swelling.Steroid injections. Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory medicine that is injected directly into your shoulder joint.Physical therapy. Specific exercises will help restore motion.
What is the fastest way to heal a frozen shoulder?
Your clinician may recommend an anti-inflammatory medication such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil), or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn, Anaprox). An ice pack or bag of frozen vegetables applied to the shoulder for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day can also help with pain.
Does adhesive capsulitis go away?
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in your shoulder joint. Signs and symptoms typically begin gradually, worsen over time and then resolve, usually within one to three years.Aug 1, 2020
How long does it take to recover from adhesive capsulitis?
In general, frozen shoulder will resolve almost completely with time and consistent compliance with the prescribed treatment program. This process can take up to six to nine months for some patients, although it may take only a few months for others.
How do you unfreeze a frozen shoulder?
How do you "thaw" a frozen shoulder?Doorway stretch. Stand in a doorway and put the hand of your affected shoulder on the top of the door frame, or as high as you can reach. ... Broomstick flexion. Grab a broom, or an item with similar dimensions, like a mop, cane, or long stick. ... Broomstick abduction.Jun 13, 2017
What aggravates frozen shoulder?
For example, it can happen if you can't move your shoulder very well because of an injury or surgery, or if you have diabetes, which can worsen symptoms and make them last longer. Thyroid problems, Parkinson's disease, heart disease, and certain HIV medications also seem to raise your odds of getting frozen shoulder.Jun 24, 2020
What foods should you avoid with frozen shoulder?
People with a frozen shoulder should avoid all vata-aggravating diets and lifestyle practices. Frozen food, carbonated drinks, fast food, stale food, packaged food, chips, popcorn, white flour (refined flour) products, ice cream and any form of stimulant like tea, coffee or alcohol should be avoided.Aug 7, 2018
Is heat or cold better for frozen shoulder?
People often think that applying heat to a frozen shoulder is a good idea, but in fact the reverse is true. The frozen shoulder will respond better to cold than heat.
Is it OK to massage a frozen shoulder?
Massage and stretching are extremely beneficial for treating frozen shoulder pain. Massage helps to relieve tension and tightness so your muscles can relax. This helps to restore mobility and improve function. It also may help improve blood flow to the affected area and reduce inflammation.Sep 29, 2020
What supplements help frozen shoulder?
What are the Best Supplements for Frozen Shoulder? Some over-the-counter supplements like turmeric, Omega-3 fatty acids, and glucosamine and chondroitin may help relieve joint pain and reduce inflammation.
Can a frozen shoulder be permanent?
Without aggressive treatment, a frozen shoulder can be permanent. Diligent physical therapy to treat a frozen shoulder can include ultrasound, electric stimulation, range-of-motion exercises, ice packs, and strengthening exercises.
Can a frozen shoulder heal on its own?
Medical experts refer to frozen shoulder as a “self-limiting” condition, meaning it will eventually go away on its own. However, people with frozen shoulder may not regain their full range of motion.
What is the best treatment for adhesive capsulitis?
The most effective treatment for adhesive capsulitis is still uncertain. Nonsurgical treatments include physiotherapy, oral or intra-articular corticosteroids, acupuncture, and hydrodilatation. Arthroscopic capsular release and manipulation under anesthesia are options in patients who do not improve with nonsurgical treatments.
How long does acupuncture help with shoulder pain?
There is limited evidence that shows that acupuncture can improve pain and function for two to four weeks in patients with shoulder pain. 14 A 2017 randomized controlled trial demonstrated an immediate improvement in pain scores in patients with adhesive capsulitis who received acupuncture with physiotherapy.
How old is the average person with adhesive capsulitis?
Most patients diagnosed with adhesive capsulitis are women between 40 and 60 years of age. 2
What is a frozen shoulder?
Adhesive capsulitis, also known as “frozen shoulder,” is a common shoulder condition characterized by pain and decreased range of motion, especially in external rotation. Adhesive capsulitis is predominantly an idiopathic condition and has an increased prevalence in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism.
Can corticosteroids help with adhesive capsulitis?
4 A 2006 Cochrane review concluded that oral corticosteroids may produce a small short-term benefit (less than six weeks) in pain relief and improved range of motion, but it was not maintained in the long-term. 8 Given the risks associated with extended oral corticosteroid usage, and the lack of long-term benefit, oral corticosteroids should not be used routinely to treat adhesive capsulitis.
Can MRI confirm adhesive capsulitis?
However, the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis is a clinical diagnosis and the use of MRI should be reserved for the evaluation of other sources of shoulder pathology, not to confirm a diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis.
Is fasting glucose a test for adhesive capsulitis?
References. A fasting glucose or A1C level, or a thyroid-stimulating hormone measurement may be considered for patients at risk of or with signs and symptoms of diabetes and thyroid disease, respectively. 4, 6 Additional blood tests are not indicated to support a diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis.
What happens when you move your shoulder?
When the shoulder becomes immobilized in this way, the connective tissue surrounding the glenohumeral joint — the joint capsule — thickens and contracts, losing its normal capacity to stretch. Trying to avoid the pain caused by moving the shoulder leads to further contraction of the capsule.
What is the best treatment for a frozen shoulder?
Your clinician may recommend an anti-inflammatory medication such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil), or naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox).
How long does it take for a frozen shoulder to develop?
In advanced cases, bands of scar tissue (adhesions) form between the joint capsule and the head of the humerus. A frozen shoulder may take two to nine months to develop.
How to assess shoulder range of motion?
To assess your shoulder's range of motion, the clinician will ask you to perform various movements with your arm, such as reaching across your chest to touch the opposite shoulder or down your back to touch the opposite shoulder blade (the Apley scratch test).
How to strengthen rotator cuff?
After your range of motion improves, you can add rotator cuff–strengthening exercises. Be sure to warm up your shoulder and do your stretching exercises before you perform strengthening exercises. Outward rotation. Hold a rubber exercise band between your hands with your elbows at a 90-degree angle close to your sides.
How long does it take to recover from a frozen shoulder?
But full recovery from a frozen shoulder takes time — from several months to two or three years. If you don't improve steadily or if you reach a plateau, go back to your clinician or consult a shoulder expert. Rarely, recalcitrant cases require surgery.
Why does my shoulder freeze?
Sometimes freezing occurs because the shoulder has been immobilized for a long time by injury, surgery, or illness. In many cases the cause is obscure. Fortunately, the shoulder can usually be unfrozen, though full recovery takes time — and lots of self-help.
What is frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, is a painful condition in which the movement of the shoulder becomes limited. Frozen shoulder occurs when the strong connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint (called the shoulder joint capsule) become thick, stiff, and inflamed. (The joint capsule contains the ligaments ...
Why is my shoulder frozen?
The condition is called "frozen" shoulder because the more pain that is felt, the less likely the shoulder will be used. Lack of use causes the shoulder capsule to thicken and becomes tight, making the shoulder even more difficult to move -- it is "frozen" in its position. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How long does it take for a shoulder to become stiff?
The pain slowly increases. It may worsen at night. Inability to move the shoulder increases. This stage lasts 6 weeks to 9 months. The "frozen" stage: In this stage, pain may lessen, but the shoulder remains stiff.
How long does it take to recover from shoulder surgery?
Full or near full recovery occurs as normal strength and motion return. The stage lasts 6 months to 2 years. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is the physical exam of your arms and shoulders?
Conduct a physical exam of your arms and shoulders: The doctor will move your shoulder in all directions to check the range of motion and if there is pain with movement. This type of exam, in which your doctor is moving your arm and not you, is called determining your “passive range of motion.”.
What happens when you have shoulder surgery?
Manipulation under anesthesia: During this surgery, you will be put to sleep and your doctor will force movement of your shoulder. This will cause the joint capsule to stretch or tear to loosen the tightness. This will lead to an increase in the range of motion.
What is TENS in medical terms?
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Use of a small battery-operated device that reduces pain by blocking nerve impulses. If these simple treatments have not relieved pain and shoulder stiffness after about a year trial, other procedures may be tried.
How long does it take for adhesive capsulitis to resolve?
In most cases, the symptoms begin gradually, get worse over time, and then resolve – on their own or with treatment – in one to three years.
How long does it take for capsulitis to heal after ACE?
Most patients experience dramatic and long-lasting pain relief within just a few days after their ACE procedure. Improved quality of life. Peoplewho undergo capsulitis embolization usually report a significant reduction in the use of pain medications and a significant increase in joint function scores.
How to treat a frozen shoulder?
The standard frozen shoulder treatment protocol typically involves a combination of: 1 Applying heat and ice to the affected area, which can help reduce the pain and swelling. 2 Physical therapy, including gentle stretching and range-of-motion exercises. 3 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which may help reduce inflammation. 4 Corticosteroids, a broad spectrum of drugs that decrease inflammation in the body and help reduce immune system activity. 5 Numbing medications that are usually injected directly into the joint capsule to relieve shoulder pain. 6 Arthroscopic surgery, which is only prescribed in a small percentage of the most severe cases. These are typically patients with refractory pain or pain that cannot be controlled with less invasive means. If the surgery goes well, it can help loosen the joint capsule, allowing it to move more freely.
What is the best treatment for inflammation?
Physical therapy, including gentle stretching and range-of-motion exercises. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which may help reduce inflammation. Corticosteroids, a broad spectrum of drugs that decrease inflammation in the body and help reduce immune system activity.
Does ACE help with shoulder pain?
Both clinical studies and real-world data indicate the procedure can deliver long-lasting, highly effective pain relief and improve joint stiffness and range of mobility.
Can you use adhesive capsulitis embolization for frozen shoulder?
However, many patients do not know that they can now try a minimally invasive alternative treatment for frozen shoulder called adhesive capsulitis embolization (ACE). This procedure has already shown excellent results in successfully relieving capsulitis shoulder pain.
What is the procedure to cut through a shoulder capsule?
This releases the tightening and increases range of motion. Shoulder arthroscopy. In this procedure, your doctor will cut through tight portions of the joint capsule.
What is the best treatment for frozen shoulder?
Physical therapy, with a focus on shoulder flexibility, is the primary treatment recommendation for frozen shoulder. Frozen shoulder most commonly affects people between the ages of 40 and 60, and occurs in women more often than men.
What is the goal of frozen shoulder surgery?
Surgery for frozen shoulder is typically offered during "Stage 2: Frozen.". The goal of surgery is to stretch and release the stiffened joint capsule.
How to restore shoulder motion?
Physical therapy. Specific exercises will help restore motion. These may be done under the supervision of a physical therapist or via a home program. Therapy includes stretching or range of motion exercises for the shoulder. Sometimes heat is used to help loosen the shoulder up before stretching.
How to loosen shoulder muscles before stretching?
Sometimes heat is used to help loosen the shoulder up before stretching. Below are examples of some of the exercises that might be recommended. External rotation — passive stretch. Stand in a doorway and bend your affected arm's elbow to 90 degrees to reach the doorjamb.
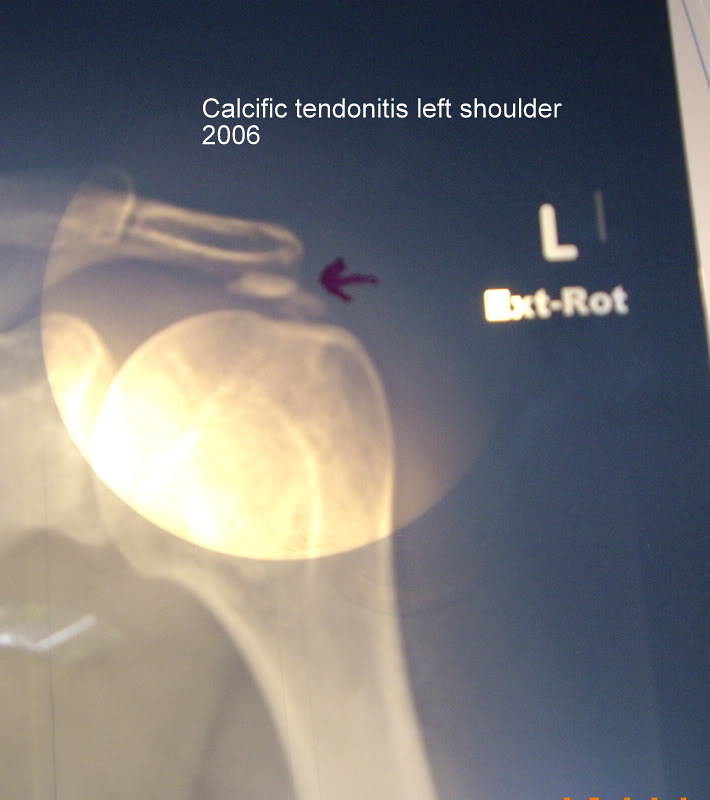
Treatment
Epidemiology
Prognosis
Signs and symptoms
Specialist to consult
Symptoms
- Adhesive capsulitis, also known as frozen shoulder, is a common shoulder condition characterized by pain and decreased range of motion, especially in external rotation. Adhesive capsulitis is predominantly an idiopathic condition and has an increased prevalence in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism. Although imaging is not necessary to make the diag…
Diagnosis
- The prevalence of adhesive capsulitis is estimated at 2% to 5% of the general population. Most patients diagnosed with adhesive capsulitis are women between 40 and 60 years of age.2 Evidence supports an association of adhesive capsulitis with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism. A 2016 meta-analysis found that patients with diabetes were five times more lik…
Medical uses
- Traditionally, the natural history of frozen shoulder has been described as a progression through three phases: painful, stiffness, and recovery. Full resolution of symptoms without treatment has been the expected outcome for most patients over one to two years. However, recent clinical evidence of persistent functional limitation, lasting for years, has challenged this theory. A 2017 …
Research
- Shoulder pain accompanied by a marked decrease in range of motion is the chief characteristic of adhesive capsulitis. Pain is described as a poorly localized, dull ache, and may radiate into the biceps. Reaching overhead or behind the back may stimulate the sensation of pain and stiffness. Symptoms such as fever, night sweats, malaise, or unexplained weight loss should prompt the p…
Overview
- Impaired range of motion with forward flexion, abduction, and external and internal rotation is the cardinal clinical finding for adhesive capsulitis. In advanced disease, observation of a patient's gait may reveal a loss in the natural arm swing that occurs with walking. Further examination of the affected shoulder may reveal muscular atrophy. Palpation may produce vague tenderness o…
Literature
- A fasting glucose or A1C level, or a thyroid-stimulating hormone measurement may be considered for patients at risk of or with signs and symptoms of diabetes and thyroid disease, respectively.4,6 Additional blood tests are not indicated to support a diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. Radiography may be useful in ruling out other pathologies of the shoulder joint such a…