Top10homeremedies.com
1. Salt Water...
2. Coffee...
3. Raisins...
4. Holy Basil...
5. Licorice Root...
6. Beetroot Juice...
7. Almonds and Milk...
8. Rosemary...
Learn More...Trueremedies.com
1. Adjust Positions...
2. Ginger...
3. Raisins...
4. Caffeinated Drinks...
5. Salt Water...
6. Basil Leaves...
7. Ginseng...
8. Licorice Root...
Learn More...Allremedies.com
1. Salt Water...
2. Ginger...
3. Caffeinated Beverage...
4. Water, Juices Or Teas...
5. Licorice...
6. Carrot Honey...
7. Lemon, Salt Sugar...
Learn More...How can one get rid of orthostatic hypotension?
- Use more salt. Experts usually recommend limiting salt in your diet because sodium can raise blood pressure, sometimes dramatically. ...
- Drink more water. Fluids increase blood volume and help prevent dehydration, both of which are important in treating hypotension.
- Wear compression stockings. ...
- Medications. ...
What qualifies as orthostatic hypotension?
Orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension)
- Diagnosis. You begin by lying flat on a table. ...
- Treatment. Compression stockings, also called support stockings, compress your legs, promoting circulation. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
How can orthostatic hypotension be prevented?
There are several ways of managing or preventing orthostatic hypotension, most of which do not involve the use of medication. Keep hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids. Fluids lost from diarrhea or vomiting should be replaced immediately. Avoid or limit alcohol intake because alcohol can worsen orthostatic hypotension. Use more salt in meals.
What are some nursing diagnosis for orthostatic hypotension?
To Diagnose Orthostatic Hypotension (OH) Criteria for the diagnosis of OH: The basic or classic OH is defined as a decrease in the blood pressure (BP) when the person stands up. 1 The blood pressure (BP) goes down in the first 3 minutes after the person stands up. To be "classic OH", the systolic blood pressure (top number) has to go down by at ...
Explore

What is the best medicine for orthostatic hypotension?
The most commonly used agents are midodrine, droxidopa (Northera, Lundbeck), fludrocortisone and pyridostigmine (see Table below). Midodrine, an alpha-1 agonist, was the first medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of OH.
Can orthostatic hypotension be cured?
This condition has no cure, symptoms vary in different circumstances, treatment is nonspecific, and aggressive treatment can lead to marked supine hypertension. This review focuses on the prevention and treatment of neurogenic causes of orthostatic hypotension.
How do you fix orthostatic hypotension naturally?
Lifestyle and home remediesDrink more water, less alcohol. Alcohol is dehydrating and can lower blood pressure, even if drinking in moderation. ... Pay attention to body positions. Gently move from lying flat or squatting to a standing position. ... Eat small, low-carb meals. ... Exercise regularly.
What is the first line treatment for hypotension?
Fludrocortisone is recommended as first-line drug therapy. This is a drug that prevents dehydration by causing the kidneys to retain water. This drug boosts the blood volume, which raises the blood pressure.
How do I take my blood pressure standing up?
Take the blood pressure and pulse, recording the numbers and identifying them as “lying down.” 3. Next, have the resident stand upright, or sit upright if unable to stand. Wait one minute, and then take the blood pressure and pulse again. Record the results as “standing/sitting.”
What is the most common cause of orthostatic hypotension?
Loss of fluid within the blood vessels is the most common cause of symptoms linked to orthostatic hypotension. This could be due to dehydration brought about by diarrhea, vomiting, and the use of medication, such as diuretics or water pills.
Is orthostatic hypotension life threatening?
In people with orthostatic hypotension, hypoperfusion to other organs contributes to an increased risk of life-threatening health problems, including heart attack or heart failure, a heart rhythm abnormality called atrial fibrillation , stroke, or chronic kidney failure.
Can orthostatic hypotension cause brain damage?
“The most apparent explanation for our findings is that orthostatic hypotension causes brain damage due to recurrent transient cerebral hypoperfusion,” the authors write.
What is the most common cause of orthostatic hypotension?
Loss of fluid within the blood vessels is the most common cause of symptoms linked to orthostatic hypotension. This could be due to dehydration brought about by diarrhea, vomiting, and the use of medication, such as diuretics or water pills.
Is orthostatic hypotension a disability?
In summary, the evidence supports the assignment of a separate 10 percent disability rating for orthostatic hypotension as a distinct disability from hypertension.
How long does it take for a doctor to diagnose orthostatic hypotension?
Your doctor can diagnose orthostatic hypotension if your systolic blood pressure drops by 20 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), or your diastolic blood pressure drops by 10 mm Hg within 3 minutes of standing up. To find the underlying cause, your doctor may also: The tests your doctor may order include:
How to raise blood pressure in a dehydrated person?
Stand up slowly when getting out of a chair or bed. Perform isometric exercises before getting up to help raise your blood pressure. For example, squeeze a rubber ball or a towel with your hand.
What is the term for a sudden fall in blood pressure that occurs when you stand up quickly?
Orthostatic hypotension, also called postural hypotension, is a sudden fall in blood pressure that occurs when you stand up quickly. Hypotension is the term for low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of your blood against the walls of your arteries.
Can drugs cause orthostatic hypotension?
Many drugs can affect these normal reflexes and lead to orthostatic hypotension. These reflexes may also begin to weaken as you age. For this reason, orthostatic hypotension is more common in older adults. According to a 2011 study, about 20 percent of people older than 65 experience orthostatic hypotension. People with orthostatic hypotension may ...
Can orthostatic hypotension be treated?
In most cases, treating the underlying condition will cure orthostatic hypotension. With treatment, people who experience orthostatic hypotension can reduce or eliminate symptoms. Last medically reviewed on November 18, 2019.
What is the most important factor in the proper control of orthostatic hypotension?
Education is probably the single most important factor in the proper control of orthostatic hypotension. A number of issues should be considered. Patients should be taught, in simple terms, the mechanisms that maintain postural normotension and how to recognize the onset of orthostatic symptoms.
What drugs cause orthostatic hypotension?
Common drugs that cause orthostatic hypo tension are diuretics, alpha-adrenoceptor blockers for prostatic hypertrophy, antihypertensive drugs, and calcium channel blockers. Insulin, levodopa, and tricyclic antidepressants can also cause vasodilation and orthostatic hypotension in predisposed patients. Poon and Braun,6in a retrospective study in ...
How to lower intracranial blood pressure?
Elevate the head of the bed to lower intracranial blood pressure. Try a bedtime snack with a glass of warm fluid (to induce nighttime postprandial hypotension) Try a glass of wine at bedtime (for vasodilator effects) Remove abdominal binder before bedtime. Anemia in orthostatic hypotension. (can exacerbate symptoms)
How to reduce nocturia?
Elevate the head of the bed (reducing nocturia) Drink two cups of cold water 30 minutes before arising. Shift from supine to an erect position in gradual stages. Postprandial orthostatic hypotension. (common in patients with diabetic neuropathy) Tell patients to take frequent, small meals and reduce alcohol intake.
How to know if your blood pressure is falling?
Recognize symptoms that indicate your standing blood pressure is falling. Recognize the conditions that lower blood pressure, such as a heavy meal, positional changes, heat, exercise, or a hot bath. Learn the things you can do to raise your blood pressure. E (continued): Exercise.
Can orthostatic hypotension cause recurrent falls?
Recurrent or unexplained falls in older adults may be a manifestation of syncope due to orthostatic hypotension. PROGNOSIS DEPENDS ON CAUSE. Orthostatic hypotension is a syndrome, and its prognosis depends on its specific cause, its severity, and the distribution of its autonomic and nonautonomic involvement.
Is orthostatic hypotension a neurologic condition?
Orthostatic hypotension is a chronic, debilitating illness associated with common neurologic conditions (eg, diabetic neuropathy, Parkinson disease). It is common in the elderly, especially in those who are institutionalized and are using multiple medications. Treatment can be challenging, especially if the problem is neurogenic.
What is orthostatic hypotension?
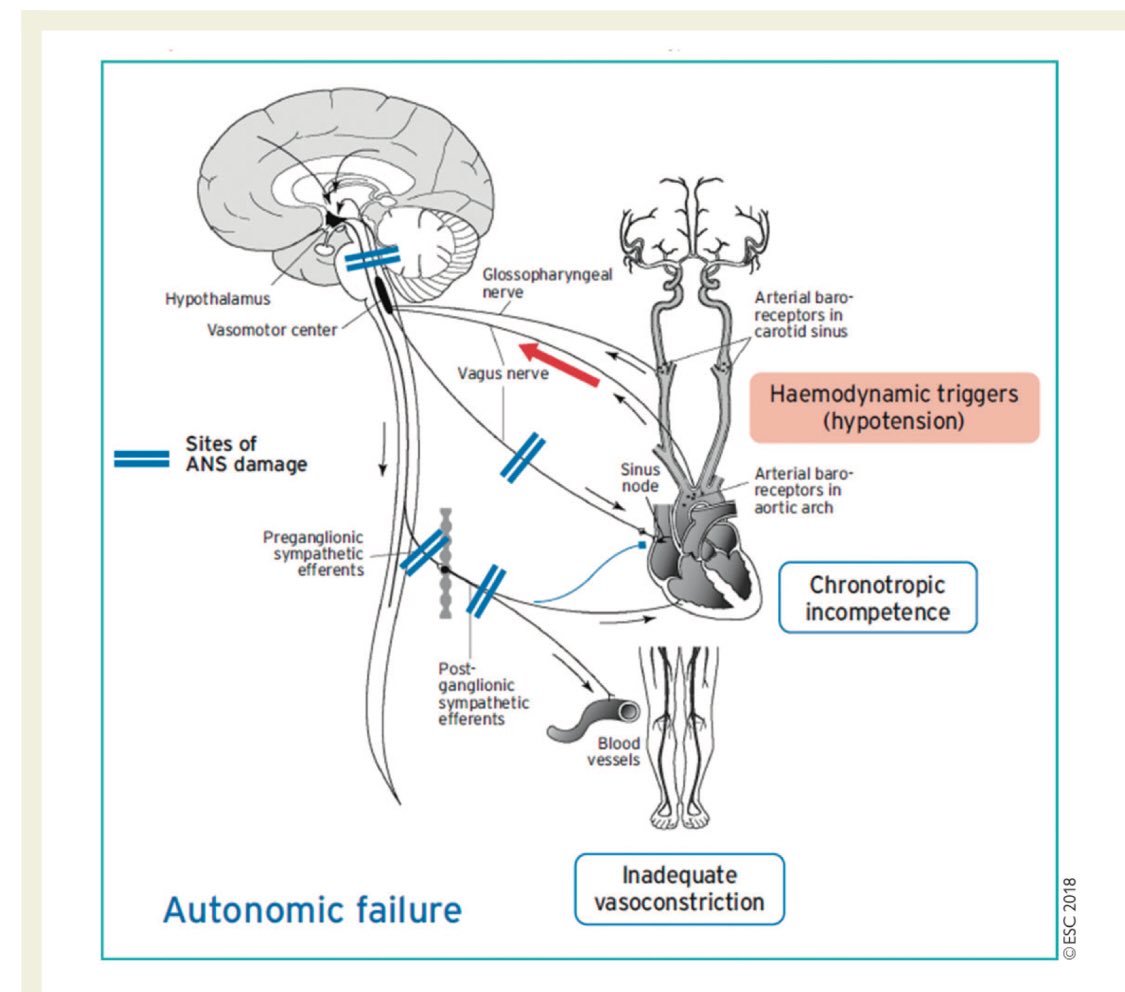
Orthostatic hypotension is the most incapacitating symptom of autonomic failure. This disorder occurs with both central autonomic neurodegenerative disorders, such as multiple system atrophy and Parkinson's disease, and peripheral autonomic disorders, such as the autonomic peripheral neuropathies and pure autonomic failure. The hallmark of both central and peripheral causes of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is the failure to release norepinephrine appropriately upon standing. Patient education is the cornerstone of management. There are several measures that can be implemented to improve orthostatic tolerance prior to pharmacological intervention. Plasma volume expansion is essential to improve orthostatic tolerance, and fluid and sodium chloride intake should be increased. Most patients can be treated successfully with volume expansion or fludrocortisone or both in combination with a sympathomimetic agent. Desmopressin acetate and erythropoietin are useful supplementary agents in patients with more refractory symptoms. There are rare patients who will require additional agents to treat their symptoms. A small group of patients remain refractory to all therapeutic modalities.
What is the hallmark of both central and peripheral causes of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension?
The hallmark of both central and peripheral causes of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is the failure to release norepinephrine appropriately upon standing. Patient education is the cornerstone of management.