How many wastewater treatment facilities are there in the US?
Sep 28, 2021 · Small communities have 10,000 or fewer people and an average daily wastewater flow of less than 1 million gallons. Wastewater is water that has been used for various purposes around a community, including sewage, stormwater, and all other water used by residences, businesses, and industry. Wastewater requires treatment before it returns to ...
How many houses in Indiana do not have sewage treatment facilities?
Wastewater Collection Systems: Preliminary Treatment Methods of collecting wastewater from individual homes for a community or multiple home (cluster) system Who designs: Qualified Minnesota Professional Engineer. Who regulates: Usually LGU if less than or equal to 10,000 gal. per day flow and subsurface discharge. MPCA if over 10,000 gal. per ...
How much do small communities need to prepare for Clean Water Act?
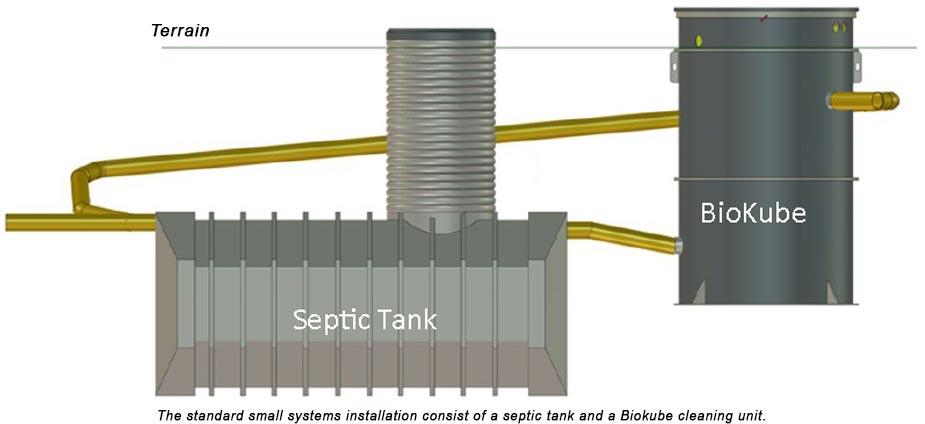
Each bedroom can hold two people, so the standard three-bedroom house could have six people generating household wastewater. Location and Installation The septic tank should be at least 10 feet away from the house. The tank should be aligned straight out from the point where the discharge sewer line leaves the house.
What is the primary level of treatment in wastewater treatment?
Feb 14, 2020 · A good layout can often be helpful in public acceptance of the project. Consider the following: Locate the plant downwind of residences and other concerned neighbors. Keep some buffer between residences and the nearest plant facility (say 500 ft.). Build odorous facilities farthest from residences (i.e. headworks).

How do you size a water treatment plant?
Are wastewater treatment plants profitable?
Building on a survey of the nearly 225 wastewater treatment plants in California, the report finds that many have the existing anaerobic digestion capacity to accommodate diverted food waste.Aug 24, 2020
What is a small waste water system used by a single home or business?
How much wastewater is produced per person per day?
How far should sewage treatment be from house?
Do all houses have a septic tank?
How do I calculate the size of my septic drain field?
- The size of the drainfield is based on the number of bedrooms and soil characteristics, and is given as square feet. ...
- For example, the minimum required for a three bedroom house with a mid range percolation rate of 25 minutes per inch is 750 square feet.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
Why is chlorine added to wastewater?
How many wastewater treatment plants are there in the US?
What is a sewage publication?
It is meant to be a homeowner reference document. An individual sewage system both treats and disposes of household wastewater. If a homeowner understands how the various components of a home sewage system work, then a properly designed and installed system will function for many years with a minimum of maintenance and upkeep.
How does a sewage system work?
An individual sewage system both treats and disposes of household wastewater. If a homeowner understands how the various components of a home sewage system work, then a properly designed and installed system will function for many years with a minimum of maintenance and upkeep.
What are the parts of a sewage disposal system?
The five parts of a sewage disposal system are: (1) the house plumbing, (2) the sewer line from house to septic tank, (3) the septic tank, (4) the septic tank outlet sewer pipe, and (5) the final soil treatment unit, which may be a soil absorption unit or lagoon.
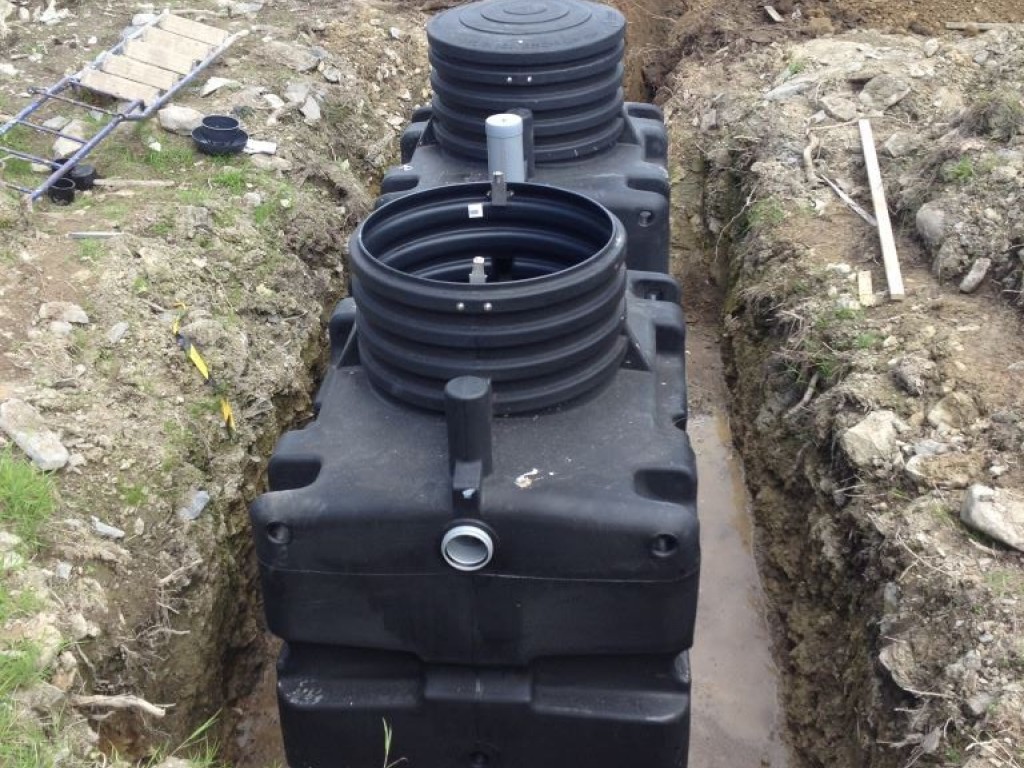
What is a septic tank?
The septic tank is a “bioreactor” where microorganisms break down organic matter in the wastewater to liquids, gases and solids. Gases are vented off through the house vent stack. Solids are composed of both scum and sludge. Scum is lighter than water and floats to the surface in the septic tank.
How long have septic tanks been used?
Septic Tanks. S eptic tanks have been used for on-site wastewater treatment for more than 120 years. A septic tank can have single or multiple compartments. Single- and two-compartment septic tanks generally are used with individual home sewage treatment systems.
How far away should a septic tank be from the house?
The septic tank should be at least 10 feet away from the house. The tank should be aligned straight out from the point where the discharge sewer line leaves the house. Installing the tank so it is level, with no slope in any direction, is important. For pumping and cleaning, the septic tank should be situated near a driveway or other access road. Most septic pump trucks carry between 50 and 100 feet of hose, so the tank should be accessible from this distance. Select a location away from high vehicle traffic areas. Never locate septic tanks under sidewalks or patios where the tank is inaccessible for pumping.
Where should a septic tank be located?
For pumping and cleaning, the septic tank should be situated near a driveway or other access road. Most septic pump trucks carry between 50 and 100 feet of hose, so the tank should be accessible from this distance. Select a location away from high vehicle traffic areas.
How to build a plant?
A good layout can often be helpful in public acceptance of the project. Consider the following: 1 Locate the plant downwind of residences and other concerned neighbors. 2 Keep some buffer between residences and the nearest plant facility (say 500 ft.). 3 Build odorous facilities farthest from residences (i.e. headworks). 4 Cover and/or house the odor causing facilities, provide necessary ventilation and air scrubbing.
How tall are chemical scrubbers?
The chemicals oxidize hydrogen sulfide and other odorous compounds producing innocuous byproducts. If the owners prefer chemical scrubbers, they usually will be tall (10 to 15 ft.), but can be hidden behind an architecturally designed wall facing the neighbors. In exceptional cases, the wall can have a nice mural painted on it to enhance appearance. [See Figure 1]
How to reduce pressure on septic system?
Following some water conservation practices can greatly reduce pressure on your septic system. For more information about conserving water, see the fact sheet about Water Consumption. Here are a few things that you can do to care for your septic system: 1 Do not use your drain or toilet as a garbage disposal; avoid putting dental floss, diapers, coffee grounds and paper towel down the drain, as they can clog up your septic system. 2 Spread your loads of laundry out over the week. When too much water is added to the septic tank, it does not have time to treat wastes, and you could be flooding your drainfield with wastewater. 3 Plant grass on your drainfield, but keep trees and shrubs away from it, because roots can clog the system and cause damage. 4 Do not drive on your drainfield, because this can compact the soil and damage the septic system components.
What are the different levels of wastewater treatment?
There are several levels of wastewater treatment; these are primary, secondary and tertiary levels of treatment. Most municipal wastewater treatment facilities use primary and secondary levels of treatment, and some also use tertiary treatments.
Why is oxygen important in wastewater treatment?
The oxygen helps the bacteria to digest the pollutants faster. The water is then taken to settling tanks where the sludge again settles, leaving the water 90 to 95 percent free of pollutants. The picture below shows the settling tanks in the Winnipeg Wastewater Treatment Plant.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment?
Tertiary (or advanced) treatment removes dissolved substances, such as colour, metals, organic chemicals and nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary (or advanced) treatment removes dissolved substances, such as colour, metals, organic chemicals and nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen. There are a number of physical, chemical and biological treatment processes that are used for tertiary treatment.
What is wastewater in water?
Wastewater is water that has been used and must be treated before it is released into another body of water, so that it does not cause further pollution of water sources. Wastewater comes from a variety of sources. Everything that you flush down your toilet or rinse down the drain is wastewater. Rainwater and runoff, along with various pollutants, ...
What is the Canadian Environmental Protection Act?
The Canadian Environmental Protection Act governs the release of toxic substances into the environment and allows the federal government to develop regulations for the use of toxic substances. Most provincial and territorial governments have legislation regarding wastewater treatment standards and requirements.
What is a package plant?
Package plants are pre-manufactured treatmentfacilities used to treat wastewater in smallcommunities or on individual properties .Accordingto manufacturers, package plants can bedesigned to treat flows as low as 0.002 MGD or ashighas 0.5 MGD,although they more commonlytreatflows between 0.01 and 0.25 MGD (Metcalfand Eddy, 1991).
Where is the Aldie Wastewater Treatment Plant located?
The Aldie Wastewater Treatment Plant, located inAldie , Virginia, is an extended aeration facilitywhich treats an average of 0.0031 MGD with adesign flow of 0.015 MGD. This technology waschosen because it would allow the area to meetpermit requirements while minimizing land use.The plant consists of an influent chamber whichdirects the flow to two parallel aeration basins,parallel clarifiers, and a UV disinfection system.
What is extended aeration?
The extended aeration process is one modificationof the activated sludge process which providesbiological treatment for the removal ofbiodegradable organic wastes under aerobicconditions. Air may be supplied by mechanical ordiffused aeration to provide the oxygen required tosustain the aerobic biological process. Mixing mustbe provided by aeration or mechanical means tomaintain the microbial organisms in contact withthe dissolved organics. In addition, the pH must becontrolled to optimize the biological process andessential nutrients must be present to facilitatebiological growth and the continuation of biologicaldegradation.
What is sequencing batch reactor?
sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a variation ofthe activated sludge process. As a fill and draw orbatch process, all biological treatment phases occurin a single tank. This differs from the conventionalflow through activated sludge process in that SBRsdo not require separate tanks for aeration andsedimentation (Kappe, 1999). SBR systems containeither two or more reactor tanks that are operated inparallel, or one equalization tank and one reactortank. The type of tank used depends on thewastewater flow characteristics (e.g. high or lowvolume). While this setup allows the system toaccommodate continuous influent flow, it does notprovide for disinfection or holding for aeratedsludge.
Where are package treatment plants used?
They are most often used inremote locations such as trailer parks, highway restareas, and rural areas.
What are the components of an oxidation ditch?
Key components of a typical oxidation ditchinclude a screening device, an influent distributor(with some systems), a basin or channel, aerationdevices (mechanical aerators, jet mixers, ordiffusers, depending on the manufacturer), asettling tank or final clarifier (with some systems),and an RAS system (with some systems).Typically , the basin and the clarifier areindividually sized to meet the specific requirementsof each facility. These components are often builtto share a common wall in order to reduce costs andsave space (Lakeside, 1999).Concrete tanks are typically used when installingpackage plant oxidation ditches. This results inlower maintenance costs as concrete tanks do notrequire periodic repainting or sand blasting.Fabricated steel or a combination of steel andconcrete can also be used for construction,depending on site conditions (Lakeside, 1999).