What is the best treatment for low testosterone?
Dec 08, 2016 · Lack of testosterone, often nicknamed, low-t, can cause unwanted symptoms. Testosterone levels peak by early adulthood and drop as you age—about 1% to 2% a year beginning in the 40s. As men reach their 50s and beyond, this may lead to signs and symptoms, such as impotence or changes in sexual desire, depression or anxiety, reduced muscle mass, …
What medications can lower testosterone levels?
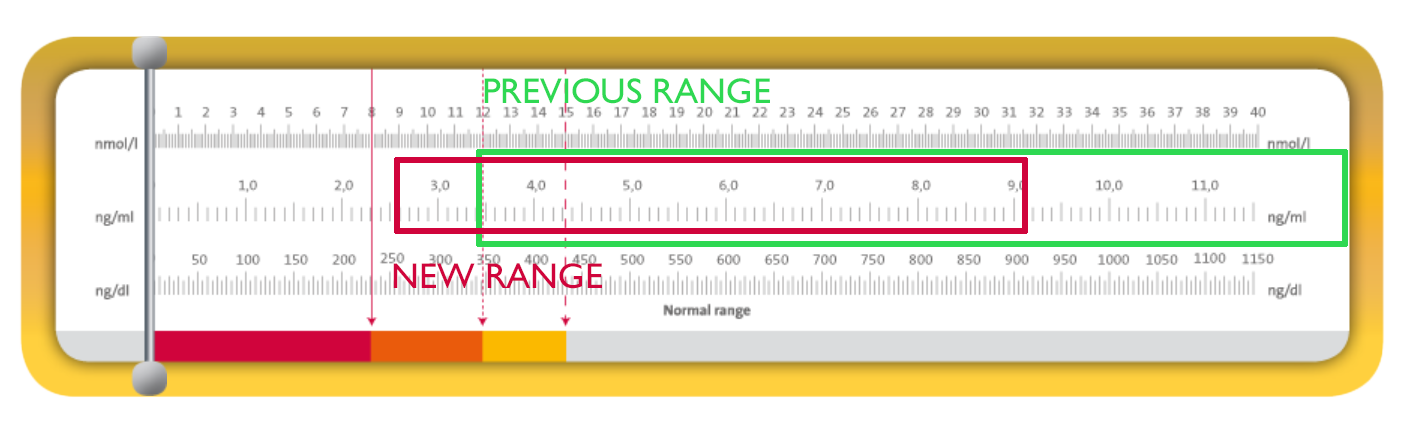
May 07, 2018 · A normal range for testosterone levels is 300 ng/dL to 1,000 ng/dL, with the Endocrine Society considering low testosterone below 263 ng/dL, says Dr. Bhasin. Your doctors should also determine if you (your spouse) shows signs …
What are the risks of low testosterone treatment?
Feb 28, 2022 · The American Urology Association (AUA) defines hypogonadism as total testosterone level of less than 300 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). The diagnosis is only made after two testosterone lab checks are done and the patient has symptoms. 1. Females may also have low testosterone, especially as they age.
What level of testosterone requires treatment?
At what level should low testosterone be treated?
When should I start testosterone treatment?
Does low testosterone require treatment?
Is 400 a low testosterone level?
Is 400 ng dL low testosterone?
How can I help my husband with low testosterone?
What is considered low testosterone by age?
How long does it take for a testosterone shot to work?
What happens if your testosterone is too low?
What is considered extremely low testosterone?
Is low testosterone reversible?
How much does testosterone drop as you age?
As men age, the ability to produce testosterone begins to decline such that testosterone levels begin to drop about 1 to 3 percent a year beginning around age 40 years. This natural decline, however, does not imply that a man is testosterone deficient or a candidate for testosterone therapy.1,2 A deficiency in this hormone only occurs in cases ...
When does testosterone drop?
As men age, the ability to produce testosterone begins to decline such that testosterone levels begin to drop about 1 to 3 percent a year beginning around age 40 years. This natural decline, however, does not imply that a man is testosterone deficient or a candidate ...
What causes testosterone deficiency?
Outside of age, there are “myriad causes for testosterone deficiency,” Dr. Mulhall adds. “They include testicular dysfunction, chemotherapy or radiation to testes, or loss of the testes,” he said. Then there are secondary testosterone deficiencies, genetic disorders, Kleinfelter syndrome, pituitary disorders, steroid use, opioid use, diabetes, and obesity.
Is low testosterone a risk factor for cardiovascular disease?
For example, low testosterone is a risk factor for cardiovascular events, but “giving a patient [supplemental] testosterone cannot be said to definitively raise or lower the risk for cardiovascular issues,” Dr. Mulhall says.
Why is it important to monitor T levels during treatment?
Both sets of guidelines stress the importance of monitoring T levels during treatment to make sure the hormone falls within a desired range and to check the status of other health conditions such as sex, heart and bone health.
Is testosterone good for hypogonadism?
Despite some controversy, testosterone therapy has been established as a safe and effective principal treatment for hypogonadism for nearly 70 years. In the last decade, studies have improved our understanding of hypogonadism and have helped clarify its prevalence and associated comorbid illnesses. [ 1-3] Causes.
Does testosterone affect mood?
Generally, this symptom complex is more often associated with hypogonadism, and mood in fact improves with restoration of the eugonadal state. [ 9 ]
How many men are diagnosed with hypogonadism?
Hypogonadism affects approximately 40% of men aged 45 or older, [ 1] although less than 5% of these men are actually diagnosed and treated for the condition. Despite some controversy, testosterone therapy has been established as a safe and effective principal treatment for hypogonadism for nearly 70 years.
What are the symptoms of hypogonadism?
Symptoms of hypogonadism can include mood changes such as irritability or increased sadness, reduced libido, low energy, fatigue, decreased muscle bulk, decreased muscle strength, muscle aches, hot flushes, decreased ability to concentrate on tasks, lack of morning erections or less rigid erections, decreased volume of ejaculate, and infertility.
How do you know if you have hypogonadism?
Symptoms of hypogonadism can include mood changes, reduced libido, low energy, decreased muscle bulk and strength, hot flushes, decreased ability to concentrate, lack of morning erections, decreased volume of ejaculate, and infertility. To confirm a diagnosis of hypogonadism physicians should look for:
What is the ICMJE?
The ICMJE created the Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals to help authors and editors create and distribute accurate, clear, easily accessible reports of biomedical studies.
Is testosterone level normal?
On average, a testosterone level of 300–1,000 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL) of blood is normal. But a healthy level really depends on your age, lifestyle, and bioavailable testosterone level – the unbound testosterone your body isn't using for daily functions. If you listen to sports radio, it seems as if every other ad is pushing ...
How many men have low testosterone?
An estimated 1 in 50 men have low-T and experience symptoms such as less energy, decreased libido (sex drive), erectile dysfunction, lack of concentration, or trouble sleeping. Around age 30, a man's testosterone levels may slowly begin to decline. Approximately 35% of men in their 70s have low-T, according to the American Urological Association. ...
When does testosterone drop?
Around age 30, a man's testosterone levels may slowly begin to decline. Approximately 35% of men in their 70s have low-T, according to the American Urological Association. But we're beginning to see more men in their 20s with low-T at the UT Southwestern male urology clinic.
Can testosterone supplements be over the counter?
Avoid supplements over the counter. None are regulated or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which means you can't verify what they're made with or whether they're safe, even if they come with a celebrity endorsement. Some testosterone supplements have been shown to cause health conditions such as erectile dysfunction or kidney failure.
Can testosterone cause kidney failure?
Some testosterone supplements have been shown to cause health conditions such as erectile dysfunction or kidney failure. Low-T clinics tend to overtreat, making blanket recommendations around the patient's total testosterone and not their individual health needs.
Does testosterone cause infertility?
Unfortunately, some doctors prescribe testosterone to treat infertility, and inad vertently make the problem worse. Natural testosterone and sperm production is fueled by two hormones created in the pituitary gland of the brain: luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
What does it mean when your testicles aren't stimulated?
Little to no LH and FSH production, means no stimulation of the testicles. If the testicles aren't stimulated by these hormones, they may atrophy, or shrivel up . Testicular atrophy has been associated with long-term use of exogenous testosterone or over-the-counter steroids.
Some Facts First
Because requests for testosterone treatment have tripled in the last decade, the AUA, or American Urological Association, has issued guidelines for diagnosis and management of testosterone deficiency. Testosterone is a hormone produced in the testicles of men and is necessary for physical, sexual, cognitive, and many metabolic functions.
Confirmed Symptoms Of Low Testosterone in Men
In order to be clinically diagnosed as having low T, a man must have low testosterone levels and exhibit the following signs or symptoms: low sex drive, low sperm count, trouble getting an erection, hair loss, hot flashes and low bone density. In addition, men must also exhibit the following signs or conditions:
Monitoring Low Testosterone Treatment
The guidelines emphasize the importance of checking T levels during the treatment process to make sure the hormone eventually falls within the desired range. It is also important to monitor sexual issues, plus heart and bone health. Treatments can be a gel, an adhesive pellet, or injections.
Risks Of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
It is important to talk to McIver Clinic about your specific risks, but common risk factors include the following:
How long does testosterone enanthate last?
IM INJECTION:#N#-Testosterone Enanthate: 50 to 200 mg every 2 to 4 weeks for 4 to 6 months#N#IMPLANT:#N#-2 pellets (each pellet contain 75 mg of testosterone) implanted subcutaneously every 3 to 6 months#N#-Duration of therapy: 4 to 6 months#N#Comments:#N#-The chronological and skeletal ages should be taken into consideration when determining the initial dose and when adjusting the dose.#N#-An X-ray of the hand and wrist to determine bone age should be obtained every six months to assess the effect of treatment on the epiphyseal centers.#N#-Report frequent or persistent erections.#N#-Androgen therapy should be used very cautiously in children and only by specialists who are aware of the adverse effects on bone maturation.#N#Use: To stimulate puberty in selected males with clearly delayed puberty
What is the FDA's REMS?
The US FDA requires a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) medication guide for Testosterone. For Testosterone Undecanoate, REMS includes elements to assure safe use and implementation system . For additional information: www.fda.gov/REMS#N#US BOXED WARNINGS:#N#Pulmonary Oil Microembolism (POME) Reactions And Anaphylaxis:#N#-Serious POME reactions, involving urge to cough, dyspnea, throat tightening, chest pain, dizziness, and syncope; and episodes of anaphylaxis, including life-threatening reactions, have been reported to occur during or immediately after the administration of testosterone undecanoate injection. These reactions can occur after any injection of testosterone undecanoate during the course of therapy, including after the first dose.#N#-Following each injection of testosterone undecanoate observe patients in the healthcare setting for 30 minutes in order to provide appropriate medical treatment in the event of serious POME reactions or anaphylaxis.#N#Secondary Exposure To Topical Testosterone:#N#-Virilization has been reported in children who were secondarily exposed to topical testosterone products.#N#-Children should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using testosterone topical.#N#-Healthcare providers should advise patients to strictly adhere to recommended instructions for use.#N#Safety and efficacy have not been established in patients younger than 18 years.#N#Testosterone Enanthate and Testosterone Implant are indicated for delayed puberty in adolescent patients.#N#Testosterone Cypionate: Safety and efficacy have not been established in patients younger than 12 years.#N#Consult WARNINGS section for additional precautions.
Can TRT be used for low testosterone?
Above-normal red blood cell counts. TRT is also not advised to be used for treating those with low testosterone caused by aging.
Does TRT help with testosterone?
If you have an abnormally low T, boosting your testosterone levels with TRT can help bring your energy levels back to normal. It can also restore your sex drive. You may notice a drop in body fat and a buildup of muscle mass after TRT.
Does TRT help with ED?
If you have low testosterone, TRT may help restore your ability to have healthy erections and can boost your sex drive. But ED has many other possible causes. Low testosterone may not be the whole story behind your ED. Talk to your doctor to determine what's at the root of your erection problems.
What are the symptoms of TRT?
Patients taking TRT should call 911 immediately if they have symptoms which include: 1 Chest pain 2 Shortness of breath or trouble breathing 3 Weakness in one side of the body 4 Slurred speech