
What to do if exposed to TB?
Tuberculosis: Post-Exposure Testing and Management
- Urgent message: Patients who present after exposure to tuberculosis test the clinician’s ability to assimilate broad and generalized information, including a unique set of historical, clinical, and laboratory data required ...
- Testing Options. ...
- Special Considerations. ...
- Window Period Prophylaxis. ...
- Current Treatment for LTBI. ...
- Conclusion. ...
How long can you Survive with TB?
The average duration of tuberculosis from the time of implantation to the fatal termination, when it terminates fatally, is about ten years. The severe symptoms often last from six months to two years. The dying period is usually about two months. Is tuberculosis always fatal?
How do you get infected with TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person. It mainly affects the lungs, but it can affect any part of the body, including the tummy (abdomen), glands, bones and nervous system. TB is a potentially serious condition, but it can be cured if it's treated with the right antibiotics.
How to tell if you have tuberculosis?
- Usually has a skin test or blood test result indicating TB infection
- May have an abnormal chest x-ray, or positive sputum smear or culture
- Has active TB bacteria in his/her body
- Usually feels sick and may have symptoms such as coughing, fever, and weight loss
- May spread TB bacteria to others
- Needs treatment to treat TB disease
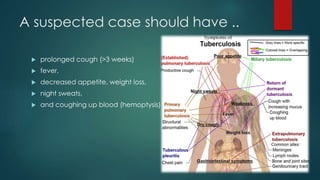
How long does TB stay infectious after starting treatment?
After taking antibiotics for 2 weeks, most people are no longer infectious and feel better. However, it's important to continue taking your medicine exactly as prescribed and to complete the whole course of antibiotics. Taking medication for 6 months is the best way to ensure the TB bacteria are killed.
Is TB still infectious when on treatment?
A person with TB disease may remain contagious until he/she has been on appropriate treatment for several weeks. It is important to note that a person with TB infection, but not disease, cannot spread the infection to others, since there are no TB bacteria in the sputum.
Do TB patients have to be quarantined?
Individuals who are latently infected with TB pose no risk of transmission; therefore, quarantine is not an appropriate disease control measure for TB.
When can a TB patient be considered noninfectious?
Patients can be considered noninfectious when they meet all of the following three criteria: They have three consecutive negative AFB sputum smears collected in 8- to 24-hour intervals (one should be an early morning specimen); They are compliant with an adequate treatment regimen for two weeks or longer; and.
How long does it take to cure TB?
Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured.
How does TB spread?
The TB germs are spread into the air when a person with infectious TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs, speaks, or sings. People nearby may breathe in these TB germs and become infected. When a person breathes in TB germs, the TB germs can settle in the lungs and begin to grow.
How many people with LTBI will develop TB?
While not everyone with LTBI will develop TB disease, about 5–10% will develop TB disease over their lifetimes if not treated. Progression from untreated LTBI to TB disease is estimated to account for approximately 80% of U.S. TB cases. Some people who have LTBI are more likely to develop TB disease than others.
What does a negative TB test mean?
A negative TB blood test means that your blood did not react to the test and that you likely do not have TB infection. TB blood tests are the recommended TB test for: People who have received the bacille Calmette–Guérin (BCG) TB vaccine.
What is the cause of TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). The bacteria, or germ, usually attack the lungs. TB germs can attack any part of the body, such as the kidney, spine, or brain. There is good news. People with TB can be treated if they seek medical help.
What does it mean when you have a positive TB test?
May feel sick and may have symptoms such as a cough, fever, and/or weight loss. Usually has a positive TB skin test or TB blood test indicating TB infection. Usually has a positive TB skin test or TB blood test indicating TB infection. Has a normal chest x-ray and a negative sputum smear.
Where are people born with TB?
You were born in or frequently travel to countries where TB disease is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, and other countries where TB is common.
How does TB spread?
TB is spread through the air. The droplets containing the bacteria must be inhaled for the infection to spread from one person to another. This means that being near someone with TB disease when they cough, sneeze, or even talk close to your face for an extended period of time puts you at risk for infection.
How long does it take for a bacterial infection to show?
If you’ve been infected with the bacteria, you may develop symptoms within a few weeks, or it could be years before you see signs of infection.
What are the two types of TB?
There are two main types of TB: latent TB infection (LTBI) and active TB disease (sometimes just referred to as TB disease).
What is the best medicine for TB?
The most frequent combination for active TB includes the antibiotics isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide.
How long does a cough last?
When symptoms are present, they usually include coughing that lasts for more than a few weeks. The coughs tend to produce phlegm, and it may be flecked with blood at times or be pink, suggesting bleeding and irritation. Chest pain, especially when breathing deeply or coughing, is also a common symptom.
How to avoid TB?
Other ways to reduce your exposure include: Keeping your room well-ventilated . TB bacteria tend to spread faster in more confined spaces with less outside air.
Where is TB more common?
TB is also more common in certain parts of the world, including Russia, South America, and Africa. You may be at increased risk if you live in areas with more incidences of TB or if you travel to these areas.
How long does it take for TB to be noninfectious?
These observations made it clear that anti-TB therapy rendered patients virtually noninfectious within 2 weeks or so; it also persuaded most jurisdictions to eliminate compulsory segregation of subjects being treated for TB and removed the need for sanatoria.
How is TB spread?
Tuberculosis (TB) is spread by the coughing up of minute droplets smaller than 2 μ%m. Suspension of these droplets as droplet nuclei necessitates the evaporation of any moisture in less than a fraction of a second. This causes the droplet nucleus to shrink to less than a thousandth of its original size. The concentration of anti-TB drugs in the saliva and bronchial secretions is the same as it is in the blood. With the evaporation of the moisture the dried-out tubercle bacillus in the droplet nucleus is exposed to a thousand-fold increase in the concentration of the drugs.
What to do if you think you have been exposed to TB?
If you think you have been exposed to someone with TB disease, you should contact your doctor or local health department about getting a TB skin test or a special TB blood test. Be sure to tell the doctor or nurse when you spent time with the person who has TB disease. It is important to know that a person who is exposed to TB bacteria is not able ...
Can TB spread to others?
Only persons with active TB disease can spread TB bacteria to others. Before you would be able to spread TB to others, you would have to breathe in TB bacteria and become infected. Then the active bacteria would have to multiply in your body and cause active TB disease.
How will I know if I am cured of tuberculosis? What is the contagious period for TB?
Treatment for tuberculosis, both active infections and latent TB infections, involves the use of several different anti-TB medications (for example, isoniazid [Nydrazid, Laniazid, INH], rifampin [ Rifadin ], rifapentine [ Priftin ], ethambutol [ Myambutol ], pyrazinamide ), often in combination, for up to a total of six to nine months. A physician will determine the best treatment for you on an individual basis, since some strains of the bacteria are resistant to certain drugs. Some people are probably noncontagious after two weeks while on medication or during treatment but some researchers suggest that others may take longer (months) until they are not able to spread the disease. Reduction or absence of symptoms and signs suggests that a person on antibiotics is unlikely to be contagious, but this is not always true.
How long does it take for TB to cure?
Tuberculosis (TB) is 100% curable if treated with the approved four drug combination for a minimum of six months.
What is tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that can be cured with antibiotics.
How will I know if I have tuberculosis?
People may suspect they have tuberculosis if they have spent any length of time around coughing or sneezing individuals known to have tuberculosis . Symptoms and signs of TB include the following:
When should I contact a medical caregiver about tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis, like many diseases, is best treated early in the infection. Consequently, you should contact a physician if
What is XDR TB?
Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB) Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR TB) is a rare form of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) that's transmitted when TB germs are expelled into the air by sneezing, speaking, singing, or coughing.
How does TB spread?
TB spreads when the organisms are coughed up or aerosolized by sneezing, speaking, or singing. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that TB is not spread by handshakes, sharing food, drinks, or toothbrushes, touching items like toilet seats, clothing, or bedsheets, or kissing.
How long does tuberculosis treatment last?
But unlike other times you’ve probably been on antibiotics for another type of infection, the treatment regimen for tuberculosis can last for a few months (anywhere between six to nine months depending on how well the treatment appears to be working).
How does mycobacterium tuberculosis spread?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a bacteria that mainly affects the respiratory system (lungs). It can only be spread by air droplets from speaking, coughing, sneezing, and singing —as opposed to shaking hands or other plain physical contact.
What Is Tuberculosis?
What is tuberculosis (TB)? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that is caused by a bacteria called mycobacterium tuberculosis. While it mainly infects the lungs, tuberculosis can affect other parts of the body. Most tuberculosis infections don’t have symptoms (referred to as latent tuberculosis). Tuberculosis gained the alternative name of “consumption” due to the amount of weight loss that its sufferers would usually have.
Why is tuberculosis called consumption?
Tuberculosis gained the alternative name of “consumption” due to the amount of weight loss that its sufferers would usually have.
How to check for TB?
The first step will be for the doctors to listen to your lungs and check for swelling in the lymph nodes. The doctor may follow that up with a number of questions about your medical history, as well as where you’ve recently been. If everything is sounding like TB to the doctor, they will probably proceed with a skin test. The doctor will inject an injection of PPD tuberculin, which is made with the bacteria that makes up tuberculosis. After a few minutes, if a hard bump appears, TB is more than likely in your system, and further tests like x-rays will be scheduled.
What are the side effects of latent tuberculosis?
Side effects can include the following: Jaundice. Loss of appetite.
How to tell if you have tuberculosis?
Night sweats and a fever. Swelling in the neck (when lymph nodes in the neck are infected) Shortness of breath and chest pain (in rare cases) It should be noted that tuberculosis may affect other systems beyond the respiratory system.
How long does it take for a TB patient to become smear negative?
Patients became smear-negative a median of 18 days after starting TB therapy, and culture-negative after a median of 41 days. However, it took a median of 48 days for 90% of patients to become smear-negative, and median of 93 days for 90% to attain culture-negativity.
How long does it take to culture TB?
Among patients with drug-sensitive TB, the median time to culture-negativity was 36.5 days
How long does it take for a TB smear to be positive?
Although prolonged smear and/or culture positivity during treatment was associated with the presence of drug-resistant TB, the majority of patients with drug-sensitive TB also took longer than two weeks to test culture-negative, and 10% of patients with drug-sensitive TB were still culture-positive at least 2 months after starting treatment.
Where was the study of TB conducted?
The study was conducted in Lima, Peru, and involved 93 patients with both culture and smear-positive TB who were provided with DOTS.
Is MDR TB a predictor of delayed time to attaining negative cultures?
In statistical analysis, MDR-TB was shown to be a significant predictor of delayed time to attaining negative cultures (p = 0.007).
Is TB smear positive or negative?
Moreover, the researchers found that many patients were TB culture-positive despite being smear-negative.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
What is drug resistant TB?
Drug-resistant TB is caused by TB bacteria that are resistant to at least one first-line anti-TB drug. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB) is resistant to more than one anti-TB drug and at least isoniazid (INH) and rifampin (RIF).
How long does pyrazinamide last?
pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment). Drug Susceptible TB Disease Treatment Regimens. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, ...
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
How long does it take for TB to develop?
Some people develop TB disease soon after becoming infected (within weeks) before their immune system can fight the TB bacteria. Other people may get sick with TB disease when their immune system becomes weak for another reason. Latent TB infection can be treated to prevent the development of TB disease.
How long does it take to treat latent TB?
Short-course latent TB infection treatment regimens are effective, safe, and have higher completion rates than longer 6 to 9 months of isoniazid monotherapy.
How long does rifamycin last?
Four months of daily rifampin (4R) Three months of daily isoniazid plus rifampin (3HR) Shorter, rifamycin-based treatment regimens generally have a lower risk of hepatotoxicity than longer 6 to 9 months of isoniazid monotherapy (6H/9H, respectively).
What is the best treatment for latent TB?
Rifampin (RIF) In 2020, CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) published new guidelines for the treatment of latent TB infection. CDC and NTCA preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid monotherapy.
Why is latent TB important?
Why is treatment of latent TB infection important? Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
What is a latent TB test?
A diagnosis of latent TB infection is made if a person has a positive tuberculin skin test (TST) or TB blood test (interferon-gamma release assays, or IGRA) result and a medical evaluation does not indicate TB disease.
