What is the optimal duration of treatment for DVT?
Feb 10, 2018 · The pain from DVT will last at least as long as the blood clot remains untreated. After the blood clot resolves, the blood will begin to flow normally and DVT symptoms will usually fade. However, some patients develop a condition known as the post-phlebitic syndrome, which causes continued pain, swelling and changes in skin color even after the clot is gone.
What is DVT and how can you treat it?
All patients with acute venous thromboembolism should receive oral anticoagulant treatment for three months. At the end of this treatment period physicians should decide for definitive withdrawal or indefinite anticoagulation with scheduled periodic re-assessment of the benefit from extending anticoagulation. Publication types Review MeSH terms
What you can do to Prevent DVT?
It usually takes about 3 months to treat a DVT. If you aren’t likely to have another one, you may be able to stop taking blood thinners at that point. People whose chances are higher may need to...
How long do you take Eliquis for DVT?
Apr 29, 2014 · Most patients with DVT or PE recover completely within several weeks to months without significant complications or long-term adverse effects. However, long-term problems can occur, with symptoms ranging from very mild to more severe.

How long does it take for DVT to go away?
It is important to start treatment right away for DVT. It takes about 3 to 6 months for a blood clot to go away. During this time, there are things you can do to relieve symptoms. Elevate your leg to reduce swelling.Sep 10, 2020
How long should you be on blood thinners after a DVT?
After a DVT, you'll take blood thinners for at least 3 to 6 months. Your doctor will tell you exactly how long to take these medications. It might be different based on which drug you use. You may need to take oral blood thinners for a longer time if the reason for your clot is still present in your body.Feb 16, 2021
Can DVT be cured completely?
Articles On What Happens After a DVT? Most people are fully healed from a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) within a few weeks or months.Mar 21, 2022
Will my leg go back to normal after DVT?
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome is when you have the ongoing symptoms of a blood clot, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), in the leg. Some people who have had DVT or blood clots in the leg recover completely, but others still experience symptoms, and these symptoms are called PTS.
How do I know if my DVT is getting better?
The pain and swelling from a DVT usually start to get better within days of treatment. Symptoms from a pulmonary embolism, like shortness of breath or mild pain or pressure in your chest, can linger 6 weeks or more. You might notice them when you're active or even when you take a deep breath.Mar 16, 2020
Can walking dislodge a DVT?
The authors concluded that walking exercise was safe in acute deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and may improve acute symptoms. Exercise training did not acutely increase leg symptoms of previous DVT and may prevent or improve post-thrombotic syndrome.
Can you live a long life with DVT?
Yes, you can die of a deep vein thrombosis. Death in DVT cases typically occurs when the clot or a piece of it travels to the lung (pulmonary embolism). Most DVTs resolve on their own. If a pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs, the prognosis can be more severe.
Is DVT a lifelong condition?
Many people with DVT blood clots will recover completely. But up to 50% will develop post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), a condition that can cause chronic pain, swelling, and discomfort that can permanently affect your quality of life.
Can I exercise with DVT?
Conclusions: Early walking exercise is safe in patients with acute DVT and may help to reduce acute symptoms. Exercise training does not increase leg symptoms acutely in patients with a previous DVT and may help to prevent or improve the postthrombotic syndrome.
What can you not do while on blood thinners?
Because you are taking a blood thinner, you should try not to hurt yourself and cause bleeding. You need to be careful when you use knives, scissors, razors, or any sharp object that can make you bleed. You also need to avoid activities and sports that could cause injury. Swimming and walking are safe activities.
What happens if a DVT does not dissolve?
In addition, when a clot in the deep veins is very extensive or does not dissolve, it can result in a chronic or long-lasting condition called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), which causes chronic swelling and pain, discoloration of the affected arm or leg, skin ulcers, and other long-term complications.
Can a blood clot move while on blood thinners?
Yes. Medications that are commonly called blood thinners — such as aspirin, warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven), dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis) and heparin — significantly decrease your risk of blood clotting, but will not decrease the risk to zero.
Is heparin a good treatment for VTE?
Cancer patients should receive low molecular-weight heparin over warfarin in the long-term treatment of VTE. These patients should be considered for extended anticoagulation at least until resolution of underlying disease. The risk for recurrent venous thromboembolism can be estimated through a two-step algorithm.
Is anticoagulation effective for venous thromboembolism?
Currently available anticoagulants are effective in reducing the recurrence rate of venous thromboembolism (VTE). However, anticoagulant treatment is associated with an increased risk for bleeding complications. Thus, anticoagulation has to be discontinued when benefit of treatment no longer clearly outweigh its risks.
How to keep a DVT from getting bigger?
You probably take medicine that makes your blood slower to clot. These drugs, called anticoagulants or blood thinners, can keep a DVT from getting bigger while your body breaks it down. They also can help keep another clot from forming. Some are given as shots, and some are pills.
How long does it take for a blood clot to heal?
Most people are fully healed from a deep vein thrombosis ( DVT) within a few weeks or months. But if you’re recovering from this type of blood clot (which happens in a large vein, most often in your leg), you might be worried about how it will change your life and whether it will happen again. Learning about the condition and taking charge ...
Why do people with DVT have long term complications?
Up to half of people with DVT will have long-term complications because of damage to the leg vein (post-thrombotic syndrome), where blood remains too long (chronic venous insufficiency).
What does it feel like to have blood in your urine?
Blood in your urine or stool. Unusually heavy vaginal bleeding. Low blood pressure symptoms like weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath. It may be hard to tell if your symptoms are related to the first clot or if you have a new one.
How to help yourself after a DVT?
In addition to taking your medication as your doctor instructed, you can do a few other things to make another DVT less likely. Get up and around as soon as you safe ly can after an injury or surgery. Staying active helps your blood flow like it should.
How long does it take to get a blood thinner for DVT?
Some are given as shots, and some are pills. It usually takes about 3 months to treat a DVT. If you aren’t likely to have another one, you may be able to stop taking blood thinners at that point. People whose chances are higher may need to stay on them for years. Talk with your doctor about what’s best for you.
How to get rid of leg pain?
On long trips, get up and walk the aisle of the plane or stop the car to take a walk every hour or two. If you can’t move around, flex and point your toes, or tighten and release your leg muscles. Stay a healthy weight. Don’t smoke.
What happens when blood thickens?
Usually this happens in the lower leg or thigh. One or more clumps may break off and travel through the blood stream. If the clots block the lungs, this may cause a serious problem and can result in death.
What is the treatment for clots?
The goal of treatment is to prevent additional clotting, bigger clots forming and breaking off. Blood thinners , called anticoagulants, are the primary treatment. Heparin, given by injection, usually begins treatment. Heparin is a fast-acting medication used to thin your blood.
How long does warfarin treatment last?
The goal of treatment is to prevent additional clotting, bigger clots forming and breaking off. Treatment with warfarin usually lasts from three to six months, during which blood tests for its level are done periodically.
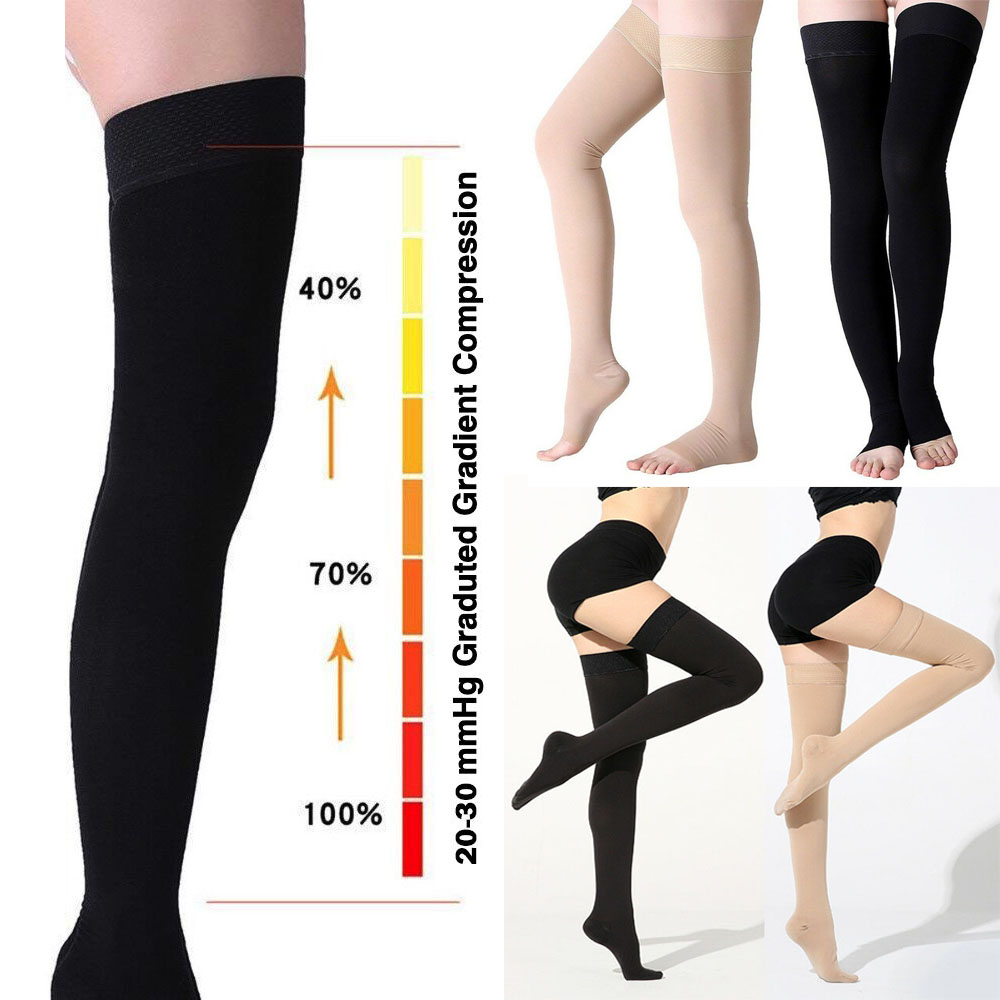
How long do compression stockings last?
However, some clots may remain for life. Your physician may prescribe compression stockings to wear for six months to a year after medication is halted. The design of the stockings prevents blood from pooling in your legs.
What does a dye X-ray show?
There are several ways in which DVT is diagnosed, but two are most often used. A concentration of dye on the X-ray may indicate a clot.
How long does it take for Coumadin to work?
When warfarin reaches the proper level, the other medication is stopped. Treatment with warfarin usually lasts from three to six months, during which blood tests for its level are done periodically.
How do you know if you have blood clots?
If you notice a sudden onset of shortness of breath, pain with deep breathing, a fast heart rate or you begin coughing up blood, you need to seek immediate medical attention.
What is a blood clot in the leg called?
When a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the body, it is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs most commonly in the leg; however, it can occur anywhere in the body, such as the veins in the arm, abdomen, pelvis, and around the brain. A complication of DVT in legs and arms is pulmonary embolism (PE).
What is the complication of DVT in legs and arms?
A complication of DVT in legs and arms is pulmonary embolism ( PE). A PE occurs when a blood clot breaks off from a DVT and travels through the blood stream, traversing the right atrium and right ventricle, and lodging in the lung.
How long does it take for a DVT to go away?
Symptoms typically improve within a few days of starting the anticoagulant. Most patients with DVT or PE recover completely within several weeks to months without significant complications or long-term adverse effects. However, long-term problems can occur, with symptoms ranging from very mild to more severe.
What is the best combination of warfarin and anticoagulant?
If you take warfarin, the ideal combination may be to have (1) a health care professional (most likely a pharmacist or a nurse) in a formal anticoagulation clinic (to manage your blood thinning medication) and (2) a physician with special expertise in blood clots (thrombosis).
How long does it take for a blood clot to heal?
This is long enough for the present clot to heal. However, if the risk for developing another clot is high, then treatment for >3 months may be appropriate.
How long does it take for warfarin to work?
Warfarin takes ≥5 days after starting to reach its full blood thinning effect. Therefore, patients who start warfarin need to be treated with an additional blood thinner (typically injections underneath the skin) during those first 5 or more days. Full blood thinning effect is achieved within 2–3 h.
Where is Beth Waldron?
Beth Waldron From the Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (B.W.), and the Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine (S.M.), Chapel Hill, NC.
What does a DVT do to your veins?
Your leg veins have tiny valves inside them. These valves help blood move back up your legs to your heart. A DVT blood clot in your vein can damage and weaken these valves. They can become leaky or weak. Blood can move in the wrong direction and then pool inside your leg.
How to prevent blood clots after surgery?
Prevent blood clots after surgery. Use compression stockings or compression devices as directed after any procedure, especially while you’re in bed at the hospital or at home. Get up and move around as soon as you’re able. Stop clots from coming back.
How to stop a clot from coming back?
Stop clots from coming back. If you have more than one clot in the same vein, it raises your risk of PTS. Take blood thinners as your doctor tells you so a new clot doesn’t form. Take your blood thinners until your doctor says you can stop. Lose weight if you’re overweight.
What is it called when you have a blood clot in your leg?
It’s a condition called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS). It usually affects veins in your leg, but it’s also possible in your arm.
What is the best way to relieve swelling in the leg?
Your doctor may prescribe an intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) device to wear on your leg to apply pressure to your veins. It helps improve blood flow to ease pain and swelling. Skin care. Keep your skin moistened with a lubricant like petroleum jelly.
What to do if you have a leg ulcer?
Your doctor may also prescribe steroid cream or ointments. Leg ulcer treatments. If you develop leg ulcers, you might need to see a specialist, such as a dermatologist (skin doctor) or vascular surgeon, or work with a wound-care nurse. Continued.
How common is PTS?
PTS is common. It affects approximately 330,000 Americans. About 20%-40% of people who have had a bout of DVT in one of their lower limbs will get it later on. About 10% of people who get it have serious signs, such as leg ulcers.
How common is DVT?
Without intervention, as many as 40-80% of surgerical cancer patients will develop DVT in the calf , while 10-20 % will develop DVT in a proximal vein- according to a report published by the Surgeon General regarding DVT and PE.
What is CDT treatment?
CDT is the gold standard of treatment for chronic, peripheral edema- such as that found by those with DVT or with PTS.
How to reduce edema in patients with DVT?
Exercise will actually reduce the symptoms of acute DVT, and may help to reduce or prevent the occurrence of PTS with patients. Exercise combined with wearing non-elastic compression will also greatly reduce the edema and swelling experienced by your patients.
How long does manual drainage last?
The acute stage of DVT lasts up to 28 days, when the clot has formed but has not yet hardened/attached itself to the walls of the vessels.
How long does it take for a DVT to form?
A DVT is a blood clot, or a lump of solidified blood, which has formed in a vein. They can take as little as 3 or 4 hours to form… but can really complicate your patient’s rehab stay. As therapists/nurses, we should be aware of the risks, the signs (when there are signs) and the most effective treatments.
What is PTS in medical terms?
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) is a form of chronic venous insufficiency (link to 7 types article), which develops in approximately 20 to 50% those who have had a DVT. PTS presents with leg pain, leg heaviness, vein dilation, skin discoloration, venous ulcers, and edema.
What is DVT in medical?
Clinicians like physical therapists, occupational therapists and nurses are all too familiar with the way that developing a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) can slam your patient’s progress to a halt. Whether you are working with a patient in acute inpatient rehab, outpatient therapy, a sub acute setting, or in home-care, ...

Description
- Clots occur when the blood thickens at one or more places and clumps of cells form. Usually this happens in the lower leg or thigh. One or more clumps may break off and travel through the blood stream. If the clots block the lungs, this may cause a serious problem and can result in death. Clots in the lower leg are less likely to break off than clots in the thighs. While clots in a leg are …
Signs and Symptoms
- Only about half the people who develop deep vein thrombosis will exhibit symptoms. The clots may never cause a problem for some unaware of their condition. If the clots break off and travel in the blood stream to lodge in the lungs or heart, noticeable symptoms will appear. If you notice a sudden onset of shortness of breath, pain with deep breathing, a fast heart rate or you begin cou…
Diagnosis
- There are several ways in which DVT is diagnosed, but two are most often used. A physician will examine your affected leg and determine if what she sees is likely to be the result of DVT. She will refer you to an ultrasound technician for an examination. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of blood flow. Clumped blood can be detected with this device. Another method is ven…
Treatment
- The goal of treatment is to prevent additional clotting, bigger clots forming and breaking off. Blood thinners, called anticoagulants, are the primary treatment. Heparin, given by injection, usually begins treatment. Heparin is a fast-acting medication used to thin your blood. Warfarin (trade name Coumadin) takes several days to become effective. When warfarin reaches the pro…
Preventive Treatment
- Clots are not removed by medication. Over time, your body will usually dissolve some or all of the clots. However, some clots may remain for life. Your physician may prescribe compression stockings to wear for six months to a year after medication is halted. The design of the stockings prevents blood from pooling in your legs. This helps reduce the incidence of further clotting.