What is the recovery time from C diff?
diff again is to:
- Work with your healthcare professional to avoid taking unnecessary antibiotics.
- Tell your healthcare professional if you’ve had a C. diff infection. ...
- Wash your hands with soap and water every time you use the bathroom and before you eat anything.
What is the cure rate for C diff?
difficile culture and microbiome changes - Ph2a trial demonstrated 100% clinical cure and 100% sustained ... diff Conference: Sponsored by the C Diff Foundation, clinical professionals gathered ...
What are the long term effects of C diff?
- PPIs and Clostridium difficile(C. difficile) infection
- PPIs and dementia
- PPIs and pneumonia
- PPIs and antiplatelet agents
- PPIs and kidney disease
- PPIs and micronutrient deficiency
- PPIs and bone mineral density
What is the survival rate for C diff?
The study found the average CHF survival rates were:
- 80-90% after one year, compared to 97% in the general population
- 50-60% by the fifth year, compared to 85% in the general population
- 30% by year 10, compared to 75% in the general population

Can C. difficile go away on its own?
Asymptomatic Clostridium difficile infections usually go away on their own without even being noticed. When a C. diff infection does become symptomatic, research has shown that 1 in 5 infections will resolve without medications.
What happens if C. diff goes untreated?
Left untreated or treated unsuccessfully, Clostridium difficile infection can lead to sepsis, an intestinal perforation, or death. Patients with severe Clostridium difficile infections are typically treated with the antibiotics vancomycin or metronidazole.
How long does it take for C. diff to run its course?
Although in about 20% of patients, CDI will resolve within two to three days of discontinuing the antibiotic to which the patient was previously exposed, CDI should usually be treated with an appropriate course (about 10 days) of treatment, including oral vancomycin or fidaxomicin.
Can C. diff clear up without treatment?
For asymptomatic carriers or patients with antibiotic-associated diarrhea, antibiotics to target C. diff aren't needed. “This will usually resolve on its own,” Dr.
Does C. diff get worse if untreated?
When a C. diff infection is not treated, the inflammation of the colon can get worse. This may result in extreme discomfort, bloating, nausea, and even vomiting and weight loss. If your doctor suspects you may have a C.
How do I know if my C. diff is getting worse?
Severe infection causes: Watery diarrhea 10 or more times a day. Severe abdominal pain or cramping. Nausea....Clostridioides difficile symptoms3 or more watery liquid stools per day, with a very distinct odor.Fever.Abdominal pain or cramping.
How long does C. diff diarrhea last?
Antibiotics for Clostridioides difficile are usually an effective treatment. Fever usually goes away within 2 days, and diarrhea ends in 2 to 4 days. In about 10-20% of patients, symptoms may recur (return) within 1 to 2 weeks of ending treatment. Tell your healthcare provider if your diarrhea returns.
What does C. diff pain feel like?
It felt like a combination of being stabbed and a burning, gnawing sensation of being eaten alive from the inside out. This went on for 10 days before I was diagnosed with a clostridium difficile infection (CDI).
How long does C. diff last?
Clostridium difficile (C diff) infection typically resolves within two weeks of starting antibiotics, however, many people become reinfected one to three weeks afterward.
Can you have a mild case of C. diff?
C. difficile infection can range from mild to life threatening. Symptoms of mild cases include watery diarrhea, three or more times a day for several days, with abdominal pain or tenderness. Symptoms of more severe C.
What does poop with C. diff look like?
The symptoms of C. diff infections include: Diarrhea (loose, watery stools) or frequent bowel movements for several days.
What color is C. diff poop?
Greenish stools were more common among the control cases. Another study correlated nurses' response as to whether a stool was positive or not for C. difficile based on stool odor.
How long does it take for C diff to relapse?
Depends: In most cases, c diff is treated with 2 weeks of antibiotics. This is effective around 85% of the time, but 15% can "relapse" after their antibiotics. ... Read More
How long does Flagyl take to treat C diff?
C. Diff: If you are infected with c. Difficile, which can be treated with a simple course of Flagyl for 10 days. You do not need to recheck the status of c. D ... Read More
How long does it take for colitis to improve?
Long if not treated: C. Difficile can cause a prolonged severe colitis if it is not treated. If treated it usually starts to improve 3-4 days into the 10-14 day treatment ... Read More
How long does gastroenteritis last?
It depends: Normal viral gastroenteritis usually lasts for a day or two. C-difficile enteritis can take much longer, and you need to make sure you take the antib ... Read More
Can C diff be antibiotic resistant?
Yes!: If you have above symptoms and past history of C Diff- sometimes it can be antibiotic resistant strain . You should be retested and seek medical atte ... Read More
How to get rid of C diff?
So always wash your hands with soap and water before you eat and after you use the bathroom. Showering and washing with soap is the best way to remove any C. diff germs you might be carrying on your body.
Can you spread C diff after treatment?
Can I still spread C. diff after treatment? The risk of spreading C. diff after completing treatment is low. But if you’re colonized (see the “ Your Risk of C. diff ” page), you can still spread it to others. So always wash your hands with soap and water before you eat and after you use the bathroom. Showering and washing with soap is the best way ...
Can you get C diff again?
This can be a relapse of their original infection, or it can happen when they come in contact with C. diff again. The best way to be sure you don’t get C. diff again is to avoid taking unnecessary antibiotics and to wash your hands with soap and water every time you use the bathroom and before you eat anything.
How long does it take for C. difficile to show symptoms?
difficile in their intestines but never become sick, though rarely may still spread the infection. Signs and symptoms usually develop within five to 10 days after starting a course of antibiotics, but may occur as soon as the first day or up to two months later.
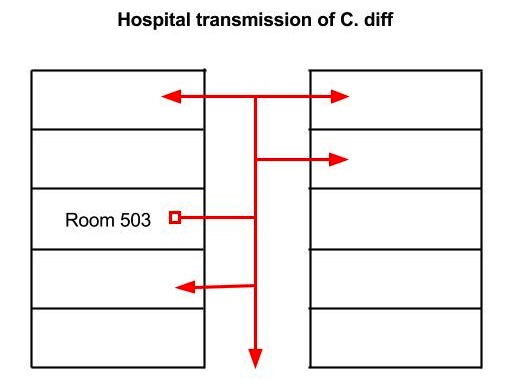
Where does C. difficile affect?
Illness from C. difficile most commonly affects older adults in hospitals or in long-term care facilities and typically occurs after use of antibiotic medications.
How do you know if you have C. difficile?
difficile infection are: Watery diarrhea three or more times a day for two or more days. Mild abdominal cramping and tenderness.
How many people get C. difficile each year?
Each year in the United States, about a half million people get sick from C. difficile, and in recent years, C. difficile infections have become more frequent, severe and difficult to treat. Recurrent C. difficile infections also are on the rise. C. difficile infection care at Mayo Clinic.
Where do C. difficile infections occur?
difficile infections occur in people who are or who have recently been in a health care setting — including hospitals, nursing homes and long-term care facilities — where germs spread easily, antibiotic use is common and people are especially vulnerable to infection.
Can you get C. difficile from chemotherapy?
If you have a serious illness, such as inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer, or a weakened immune system as a result of a medical condition or treatment (such as chemo therapy), you're more susceptible to a C. difficile infection. Your risk of C. difficile infection is also greater if you've had abdominal surgery or a gastrointestinal procedure.
Is C difficile resistant to antibiotics?
difficile has emerged that produces far more toxins than other strains do. The new strain may be more resistant to certain medications and has shown up in people who haven't been in the hospital or taken antibiotics.
How long does it take for C diff to be undetectable?
C. diff toxin is very unstable. The toxin degrades at room temperature and might be undetectable within two hours after collection of a stool specimen. False-negative results occur when specimens are not promptly tested or kept refrigerated until testing can be done.
What is C diff?
C. diff is a spore-forming, Gram-positive anaerobic bacillus that produces two exotoxins: toxin A and toxin B. It is a common. cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD). It accounts for 15 to 25% of all episodes of AAD.
What is a PCR test for C diff?
Molecular tests: FDA-approved PCR assays, which test for the gene encoding toxin B, are same-day tests that are highly sensitive and specific for the presence of a toxin-producing C. diff organism. Molecular assays can be positive for C. diff in individuals who are asymptomatic.
How many CDIs were reported in 2011?
After tremendous increases during 2000 and 2011, CDI rates plateaued at historic highs and have since begun to show some decline. In 2011, an estimated 476,400 CDIs in the United States were reported; C. diff accounted for 12.1% of all healthcare-associated infections. Between 2011-2017, nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT) increased in use. After adjusting for the use of NAAT, the estimated CDI burden decreased by 24% during 2011-2017 with 365,200 cases reported in 2017. The decrease was driven by a 36% decrease in cases of healthcare-associated CDI, while community-associated CDI was unchanged. After adjusting for NAAT use, hospitalized cases of CDI decreased by 24%. There were no changes in estimates of first recurrences and in-hospital deaths during 2011-2017. We have also seen a decline in ribotype 027, an epidemic strain of C. diff that emerged in the 2000s. This decline in ribotype 027 might be partly driven by a decreased use of fluoroquinolone in U.S. hospitals. Continued efforts to improve adherence to recommended infection prevention measures and implement diagnostic and antibiotic stewardship in both inpatient and outpatient settings will further reduce CDI.
How long does it take for a CDI to go away?
In about 20% of patients, CDI will resolve within two to three days of discontinuing the antibiotic to which the patient was previously exposed. The infection can usually be treated with an appropriate course (about 10 days) of antibiotics, including oral vancomycin or fidaxomicin.
What to do if a patient is positive for CDI?
If the patient is positive for CDI: Continue isolation and contact precautions. Use antibiotics judiciously. Clean room surfaces thoroughly on a daily basis while treating a patient with C. diff and upon patient discharge or transfer using an EPA-approved spore-killing disinfectant.
Why do you wear gloves when treating C. Diff?
Gloves are important because hand sanitizer doesn’t kill C. diff and handwashing might not be sufficient alone. In patient being evaluated for C. diff, reassess correctness of antibiotics. If the patient is positive for CDI:
What's a Virus? Viral Infection Types, Symptoms, Treatment
Is a virus alive? Learn the definition of a virus. Viral infections like COVID-19 can occur in your eyes, mouth, skin, or...
Fungal Skin Infections: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
Fungal skin infections and fungal nail infections produce symptoms like red, itchy, circular rashes and thick, discolored, flaky...
Skin Infections: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Viruses, bacteria, and fungi can all cause skin infections. What is scabies? Learn about golden staph infections, cellulitis,...
Respiratory Illnesses: 13 Types of Lung Infections
Is your cough caused by a cold, flu, pneumonia or something else? Learn causes of respiratory infection like bronchitis,...
Parasitic Infections: Worms People Can Get
Find out about the types of worms that humans can get, how it happens, and what the symptoms and treatments are.
What is the best treatment for C. difficile?
difficile is another antibiotic. These antibiotics keep C. difficile from growing, which in turn treats diarrhea and other complications. Your doctor may prescribe vancomycin ( Vancocin HCL, Firvanq) or fidaxomicin (Dificid).
What age can you take antibiotics for C difficile?
Are older than 65. Are taking other antibiotics for a different condition while being treated with antibiotics for C. difficile infection. Have a severe underlying medical disorder, such as chronic kidney failure, inflammatory bowel disease or chronic liver disease. Treatment for recurrent disease may include:
What test can detect C difficile toxin B?
Several main types of lab tests exist, and they include: Polymerase chain reaction. This sensitive molecular test can rapidly detect the C. difficile toxin B gene in a stool sample and is highly accurate. GDH/EIA. Some hospitals use a glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) test in conjunction with an enzyme immunoassay (EIA) test.
What is the test for C difficile?
difficile infection and look for alternative causes of your symptoms, your doctor may examine the inside of your colon. This test (flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy) involves inserting a flexible tube with a small camera on one end into your colon to look for areas ...
How long does it take to get cytotoxicity test results?
This type of test is sensitive, but it is less widely available, is more cumbersome to do and requires 24 to 48 hours for test results. It's typically used in research settings.
What is the procedure to check for C. difficile?
If your doctor is concerned about possible complications of C. difficile, he or she may order an abdominal X-ray or a computerized tomography (CT) scan, which provides images of your colon. The scan can detect the presence of complications such as thickening of the colon wall, expansion of the bowel or, more rarely, a hole (perforation) in the lining of your colon.
Can probiotics help with C. difficile?
Research hasn't consistently shown that currently available products are helpful in preventing or treating infection with C. difficile. Advanced probiotics are currently being studied for their potential use in C. difficile treatment or prevention but aren't currently available.
How to prevent C diff?
9. 5. Use certain medications that make it easier for C diff to make it past the stomach.
How often does C diff poop?
C. diff poop often appears as severe diarrhea that occurs frequently. It’s not uncommon for those with C. diff to have loose, watery stools at least three times per day. The stools may appear to have blood or pus. Although odor is not the only deciding factor, the C. diff smell is unique.
What are the risk factors for C diff?
Antibiotic Use. Antibiotics lower the number of probiotics (good bacteria) in your gut allowing the opportunity for C. diff to take over your gut. Many healthy people have C diff in their digestive tract. However, after taking antibiotics, C diff can multiply and cause problems.
What happens when you take antibiotics and C diff?
When the antibiotics kill off the good bacteria, C diff can multiply and take over the gut, which lead to many health problems. Once established in the gut, C. diff can secrete toxins that wear down the intestinal lining.
What is C diff infection?
4. Hospitalization or Residing in a Nursing Home. C diff infections acquired from nursing homes and hospitals are called nosocomial infections. C. diff spreads particularly well in nursing homes, which often have the highest concentrations of the bacteria because of the large number of patients treated with antibiotics.
Why is C diff common in nursing homes?
C. diff is common in nursing homes and long-term care facilities due to the higher number of elderly patients combined with the communal living situation. The prevalence of recurrent infections and carriers who are asymptomatic increases the risk.
How do you get C. Diff?
You can become colonized by C. diff by consuming C. diff spores, which are spread through contact with fecal matter or contact with a contaminated object, including phones, door handles, and keyboards. Once colonized, you are at a higher risk for C. diff infection.
How long does it take for C diff to go away?
This is effective against mild to moderate strains. For many people this c diff treatment works and it goes away after 7-14 days. About 20% of the patients are not cured and more powerful drugs must be used.
What is the treatment for C diff?
C Diff Treatment – Vancocin. This is the oral form of the common vancomycin drug used for many other conditions. It takes the medication directly to the infected area and is effective for many patients.
What is a CDI guideline?
This clinical practice guideline is a focused update on management of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) in adults specifically addressing the use of fidaxomicin and bezlotoxumab for the treatment of CDI. This guideline was developed by a multidisciplinary panel representing the Infectious Dis …
What antibiotic is used for Clostridioides difficile?
Fidaxomicin should be the antibiotic of choice when treating adults with Clostridioides difficile infection, according to new guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Is fidaxomicin good for Clostridioides difficile?
Fidaxomicin should be the antibiotic of choice when treating adults with Clostridioides difficile infection, according to new guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. ·.
Does Bezlotoxumab help with Clostridioides difficile?
Bezlotoxumab significantly reduced the incidence of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection among solid-organ transplant and hematopoietic-cell transplant recipients, according to a study published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases.“Solid-organ and hematopoietic-cell transplant recipients are at high-risk for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection and poor outcomes associated
Is fidaxomicin a CDI?
Fidaxomicin is an effective and well-tolerated CDI treatment in a real-world setting in France, which included patients at high risk of adverse outcome s.Trial registration: Description of the use of fidaxomicin in hospitalised patients with documented Clostridium difficile infection and the m …
How to protect yourself from C diff?
While you may not have a severe diarrhea infection, protect yourself and others by staying home. Take a sick day at work or keep your child home from school so that the infection does not spread.
How many times a day can you get diarrhea from C diff?
Mild cases of a C. diff infection involve watery diarrhea at least 3 times per day for multiple days and some minor abdominal cramping or pain. More severe cases may involve frequent diarrhea (as much as 10 to 15 times per day), fever, intense abdominal cramping and pain, weight loss, dehydration and blood or pus in the stool.
Can you have diarrhea with C diff?
You may be experiencing diarrhea and not know if it is caused by C. diff. Keeping track of your symptoms and self-monitoring how your illness progresses is essential. Severe forms of a C. diff infection will need immediate medical attention.
Can diarrhea get out of hand?
Diarrhea is a common gastrointestinal occurrence, but it can get out of hand pretty quickly. While most diarrhea clears up on its own, there are certain instances in which diarrhea can be deadly. Depending on the source of diarrhea, there are treatment options that you can take to treat it at home. However, more serious cases can develop ...
Can Clostridium difficile cause diarrhea?
Clostridium difficile is a bacterium that can aggravate the colon and cause a wide array of issues. Sometimes C. diff only causes diarrhea and goes away on its own, whereas other people can develop life-threatening colitis, dehydration, organ failure, bowel perforation, bowel rupture and/or death. C. diff is no little stomach bug!
Overview
Symptoms
- Some people carry C. difficile bacteria in their intestines but never become sick. These individuals are carriers of the bacteria and may spread infections. Signs and symptoms usually develop within 5 to 10 days after starting a course of antibiotics. However, they may occur as soon as the first day or up to three months later.
Causes
- C. difficile bacteria enter the body through the mouth. They can begin reproducing in the small intestine. When they reach the large intestine (colon), they can release tissue-damaging toxins. These toxins destroy cells, produce patches of inflammatory cells and cellular debris, and cause watery diarrhea. When the bacteria are outside the colon — virtually anywhere in the environmen…
Risk Factors
- Although people who have no known risk factors have gotten sick from C. difficile, certain factors increase the risk.
Complications
- Complications of C. difficile infection include: 1. Dehydration.Severe diarrhea can lead to a significant loss of fluids and electrolytes. This makes it difficult for your body to function normally and can cause blood pressure to drop to dangerously low levels. 2. Kidney failure.In some cases, dehydration can occur so quickly that kidney function rapidly deteriorates (kidney failure). 3. Tox…
Prevention
- To help prevent the spread of C. difficile, hospitals and other health care facilities follow strict infection-control guidelines. If you have a friend or family member in a hospital or nursing home, follow recommended practices. Ask questions if you observe caregivers or other people not following guidelines. Preventive measures include: 1. Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics.Antib…