Primary treatment of sewage basically involves the physical removal of large and small particles, through filtration and sedimentation. This is done in many stages. Initially, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration and then the grit i.e. soil and small pebbles, is removed by sedimentation.
What is primary treatment of sewage?
· Primary TreatmentnAs sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.,
How do primary secondary and tertiary wastewater treatment work?
The process of treating sewage is broadly classified as primary; secondary and tertiary (see Figures 8.3, 8.4 and 8.5). 1. Primary Treatment: Primary treatment consists of removing floating and suspended solids by mechanical means. More than half of the suspended solids can be removed by primary treatment as shown in Figure 8.4.
What are the first stages of waste water treatment?
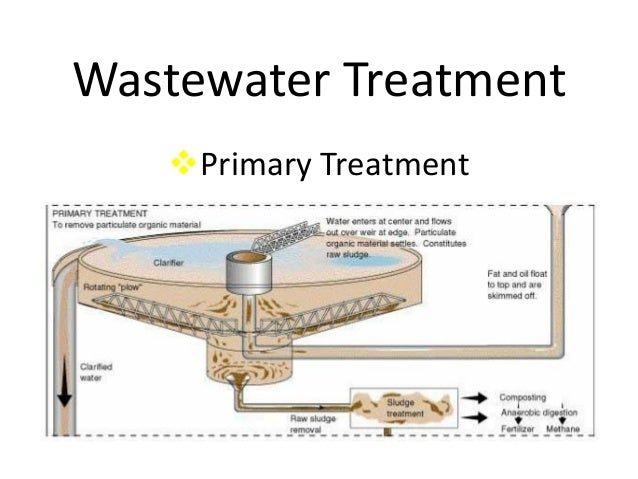
· Primary Treatment Process of Sewage In the primary treatment process, various suspended; floating and oily substances are removed from the sewage. The units of primary treatment are: Screens. Grit chamber. Detritus tank. Skimming tank. Primary sedimentation tank. Flow diagram of Primary Treatment Process of Sewage 1) Screens
What are the main components of wastewater treatment?
Primary treatment of sewage basically involves the physical removal of large and small particles, through filtration and sedimentation. This is done in many stages. Initially, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration and then the grit i.e. soil and small pebbles, is removed by sedimentation. All the solids that settle down, form the primary sludge and the supernatant …

What happens in primary sewage treatment?
In primary treatment, sewage is stored in a basin where solids (sludge) can settle to the bottom and oil and lighter substances can rise to the top. These layers are then removed and then the remaining liquid can be sent to secondary treatment. Sewage sludge is treated in a separate process called sludge digestion.
What is targeted in primary sewage treatment?
One component of the sewage that is targeted for removal by primary treatment is human waste. One component of the sewage that is targeted for removal by secondary treatment is pathogens.
What happens to sewage solids during primary treatment?
Primary wastewater treatment usually involves gravity sedimentation of screened, degritted wastewater to remove settleable solids; slightly more than one-half of the suspended solids ordinarily are removed. BOD in the form of solids removable by sedimentation (typically about one-third of total BOD) is also removed.
What is the purpose of primary treatment?
The objective of primary treatment is the removal of settleable organic and inorganic solids by sedimentation, and the removal of materials that will float (scum) by skimming.
What is primary and secondary treatment of sewage?
Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.
What happens in secondary sewage treatment?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What happens to sewage sludge after primary treatment?
Once treated, sludge can be recycled or disposed of using three main routes: recycling to agriculture (landspreading), incineration or landfilling.
Which of the following is a primary treatment?
Which of the following is a primary treatment? Explanation: Primary treatment includes physical and chemical methods like sedimentation, coagulation, etc. It will considerably reduce the Biochemical Oxygen Demand of the resulting effluent.
What happens to sewage water after treatment?
Treating sewage produces a lot of solid matter called 'sludge'. This has to be treated before we can recycle it to farmland. We use large tanks (known as digesters) where bacteria break the sludge down and release methane gas.
What are the preliminary and primary treatment of wastewater?
Preliminary treatment will have little effect on pathogens in the liquid wastestream. Primary treatment (also called primary sedimentation) is a sanitation technology that removes suspended solids and floating organic material (called scum) to reduce the suspended solids load for subsequent treatment processes.
What is the first step in primary sewage treatment plant?
Primary treatment in sewage treatment involves physical removal of particles (large and small) from the sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Initially floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Then the grit (soil and small pebbles) are removed by sedimentation.
What is the treatment of sewage?
The treatment of sewage is one of the important measures, which aims in the removal of BOD, phosphorous, nitrogen, solids and bacteria. The composition of sewage is complex, and it differs depending upon the sources, the type of treatment or lack of it. The process of treating sewage is broadly classified as primary;
What is secondary treatment of waste?
Secondary treatment of waste involves the biological degradation of organic material by micro-organisms under controlled conditions. The usual method is to bring about the biological oxidation of the organic material under aerobic conditions, in which the waste is aerated to supply oxygen for the micro-organisms.
How is sand removed from water?
Sand and other coarse material is removed by grit chambers . After screening and removal of grit, the waste water is run directly into settling or sedimentation tanks, the process by which the suspended solids are removed by gravitational setting. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What are the methods of tertiary treatment?
The number of methods used for tertiary treatment is: (iii) Chemical oxidation. (v) Oxidation ponds. However, there is a growing need for advanced procedures that will provide a product capable of being reused for various purposes.
What is primary treatment?
Primary treatment consists of removing floating and suspended solids by mechanical means. More than half of the suspended solids can be removed by primary treatment as shown in Figure 8.4.
Why is sludge a problem?
Primary sludge is a problem because it is bulky and must be removed. It also contains 94 to 99 per cent water. In some cases, sludge is dried in beds with some water removed by filtration. A report of the American Chemical Society indicates that primary treatment reduces 60 per cent suspended solids, 35 per cent BOD, 30 per cent COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand), 20 per cent nitrogen and 10 per cent phosphorus.
What is secondary treatment of wastewater?
Secondary treatment of wastewater makes use of oxidation to further purify wastewater. This can be done in one of three ways:
How is wastewater treated?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants. The resulting “sludge” is then fed into a digester, in which further processing takes place. This primary batch of sludge contains nearly 50% of suspended solids within wastewater.
What is the third step in wastewater management?
This third and last step in the basic wastewater management system is mostly comprised of removing phosphates and nitrates from the water supply. Substances like activates carbon and sand are among the most commonly used materials that assist in this process.
How long does it take for a wastewater solution to be aerated?
The resulting mixture is then aerated for up to 30 hours at a time to ensure results.
What is the primary treatment process of sewage?
Primary Treatment Process of Sewage. In the primary treatment process, various suspended; floating and oily substances are removed from the sewage. The units of primary treatment are:
What is the first unit of a primary treatment plant?
The screen is the first unit of the primary treatment plant.
Where is the sludge removal pipe?
A sludge removal pipe is provided at the bottom of the tank.
What is the angle of a sewage screen?
Screens are usually placed in an inclined position with an angle 30° to 60° with the direction of flow. Comminutors: Comminutors is the patented devices which break the larger sewage solids into small solids particles when the sewage is screened through them.
What is the purpose of a detritus tank?
The function of detritus tank is to remove finer particles than those removed by a grit chamber.
What is the first stage of sewage treatment?
The first stages of waste water ( sewage ) treatment are commonly physical and aimed to remove larger suspended solids from waste water, primarily using gravity to allow larger (heavy) particles to settle while allowing the remaining liquid to continue through the plant.
What is mechanical cleaning arrangement?
In mechanical cleaning arrangement a horizontal rake on a toothed gear drive rakes the bars and removes the captured material to a conveyor that deposits the material into a dumpster for removal to the sanitary landfill. The Fig. shows the arrangement of mechanically cleaned bar screen. Mechanical cleaning arrangements are provided in larger capacity waste water treatment plants (> 20 MLD capacity). In smaller waste water treatment plants, the screens are manually raked.
What happens when wastewater enters the secondary clarifier?
When the wastewater enters the two Secondary Clarifiers, it still contains lots of microorganisms from the Aeration Basins and looks brown and murky. The Secondary Clarifiers are identical to the Primary Clarifiers; materials in the wastewater sink and float and rotating arms remove this material from the water.
What is the process of aeration of wastewater?
From the Primary Clarifiers, the wastewater flows into large, rectangular tanks called Aeration Basins, where a biological treatment called the “activated sludge process” occurs. The wastewater flows slowing through a series of chambers as large volumes of air are bubbled up through the water. There is so much air added that it looks as if the water is boiling. In these basins, the wastewater is mixed with the “activated sludge;” hundreds of millions of actively growing single-celled microorganisms (mostly bacteria and protozoa) referred to as “bugs.”
How much water does a secondary clarifier hold?
The Secondary Clarifiers each hold 800,000 gallons of water.
How long does it take for wastewater to leave the aeration basin?
When all of the food (waste) is gone, after about eight hours, the wastewater leaves the Aeration Basins.
How many primary clarifiers are there at Soscol?
Large paddles rotate slowly over the surface and floor of the Primary Clarifier, removing these materials from the wastewater. There are two Primary Clarifiers at Soscol Water Recycling Facility. The clarifiers are covered to reduce odors!
How many gallons of water can a primary clarifier hold?
Primary Clarifiers: Physical. From the Headworks, the wastewater flows into two huge circular tanks called Primary Clarifiers. These tanks can hold 600,000 gallons of water each. Here the wastewater slows down and remains in the tanks for about two hours.
What is considered preliminary treatment?
Preliminary Treatment: Physical. When wastewater arrives at the treatment plant, it contains many solids that cannot be removed by the wastewater treatment process. This can include rags, paper, wood, food particles, egg shells, plastic, and even toys and money.
What is sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater, primarily from household sewage to produce water suitable to return to the environment.
What is the purpose of the Safe Drinking Water Act?
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) is the main federal law that ensures the quality of Americans' drinking water.Under SDWA, EPA sets standards for drinking water quality and oversees the states, localities, and water suppliers who implement those standards. Sets maximum contamination levels for microorganisms, disinfectants, inorganic and organic chemicals and radionuclides, does not apply to private wells
What is considered waste?
Waste from residences and businesses that includes durable good, non-durable goods, containers and packaging, food wastes and yard trimmings, and miscellaneous inorganic wastes, construction and demolition waste, rocks & dirt
What is tertiary biological waste?
Tertiary- biological wastes are neutralized, then disposed or reused, the treated water is disinfected chemically or physically
What is the purpose of the Superfund?
set maximum permissible amounts of water pollutants that can be discharged into waterways. Aim: to make surface waters swimmable and fishable. Covered by the Superfund, does not address groundwater contamination
Screening – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
Flow Equalisation – Primary Treatment For Waste Water
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- Under uniform flow rates, clarifiers and mechanised secondary treatment are more efficient.
- Equalization basins store diurnal or wet-weather flow peaks temporarily and make the water flow rate uniform.
- Basins serve as a temporary holding area for the incoming wastewater during temporary plant shut down and maintenance.
- It acts as a means of diluting and distributing hazardous or high-strength waste into batches.
Sedimentation – Primary Treatment For Wastewater
- The wastewater, then moves to sedimentation ponds, settling tanks, or clarifiers after the removal of settled grit. The sedimentation process removes the settleable solids by gravitational settling under quiescent conditions. On proper adjustment of water flow in the sedimentation tank, the suspended particles begin to fall to the bottom and form a solid mass. Raw primary biosolids, al…
Flocculation
- Flocculation is a water treatment process to remove small suspended solids which don’t settle in the sedimentation tank. In this process solids form larger clusters, or flocs on the addition of a flocculent like aluminium sulphate. The coagulant molecules have a positive charge. Hence, they can neutralize the negatively charged solid particles that are suspended in the water. Neutralizat…
Scum Removal
- Lighter materials rise to the surface as sludge settles to the bottom of the sedimentation tanks. The constituents of ‘scum’ are grease, oils, plastics, and soap. Scum is skimmed off the surface of the wastewater by slow-moving rakes. Scum is thickened before being poured into the digesters with the sludge. Primary treatment removes about 60% of the total suspended solids and nearly …