How long does it take to recover from radiation treatment?
Often the side effects are worse at the end of treatment, or even a week or two afterwards, because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Most side effects are temporary and go away in time, usually within a few weeks of treatment finishing.
How long does radiation stay in your body after treatment?
Radiation to the brain can cause these short-term side effects: Headaches. Hair loss. Nausea. Vomiting. Extreme tiredness (fatigue) Hearing loss. Skin and scalp changes. Trouble with memory and speech. Seizures.
What are the long term effects of radiation treatment?
Radiation therapy is associated with harsh side effects, many of which don’t emerge until months or years after treatment. Acute side effects occur and disappear within 14 days of treatment, but long-term effects like bone degeneration, skin ulcers, and …
What are the negative effects of radiation therapy?
"The only long-term side effect of radiation that occurs outside the area that was treated is some lingering mild fatigue, which typically fades within three to six months." He breaks down the most common potential side effects by the body part treated with radiation therapy. Consult your doctor about your individual risk, as each person is unique.

How long does it take to feel normal after radiation?
Radiation therapy is associated with harsh side effects, many of which don't emerge until months or years after treatment. Acute side effects occur and disappear within 14 days of treatment, but long-term effects like bone degeneration, skin ulcers, and bladder irritation take much longer to manifest.
How long does it take radiation to leave your body after cancer treatment?
For most people, the cancer experience doesn't end on the last day of radiation therapy. Radiation therapy usually does not have an immediate effect, and it could take days, weeks or months to see any change in the cancer. The cancer cells may keep dying for weeks or months after the end of treatment.
What is the most common acute side effect of radiation treatment?
Fatigue is the most common acute side effect of radiation therapy. It is believed to be caused by the large amount of energy that is used by the body to heal itself in response to radiation therapy. Most people begin to feel fatigued about 2 weeks after radiation treatments begin.Apr 14, 2022
What are long term side effects of radiation?
What are the most common long-term side effects of radiation?Cataracts.Hair loss.Hearing loss.Memory loss ("It's hard to determine how much memory loss or cognitive dysfunction is related to a tumor and how much is related to radiotherapy," says Dr. Nowlan.
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
Normal cells close to the cancer can also become damaged by radiation, but most recover and go back to working normally. If radiotherapy doesn't kill all of the cancer cells, they will regrow at some point in the future.Jul 6, 2020
What are the worst side effects of radiotherapy?
Treatment areas and possible side effectsPart of the body being treatedPossible side effectsBrainFatigue Hair loss Memory or concentration problems Nausea and vomiting Skin changes Headache Blurry visionBreastFatigue Hair loss Skin changes Swelling (edema) Tenderness5 more rows•Jan 11, 2022
What is the success rate of radiation therapy?
When it comes to early stages of disease, patients very frequently do well with either brachytherapy or external beam radiation. Success rates of around 90% or higher can be achieved with either approach.
Is radiation worse than chemo?
Since radiation therapy is focused on one area of your body, you may experience fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. However, it may still affect healthy cells in your body.Mar 27, 2020
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Brain
People with brain tumors often get stereotactic radiosurgery (radiation given in one large dose) if the cancer is in only one or a few sites in the...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Head Or Neck
People who get radiation to the head and neck might have side effects such as: 1. Soreness (or even open sores) in the mouth or throat 2. Dry mouth...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Breast
If you have radiation to the breast, it can affect your heart or lungs as well causing other side effects.
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Chest
Radiation treatment to the chest may cause side effects such as: 1. Sore throat 2. Swallowing problems 3. Loss of appetite 4. Cough 5. Shortness of...
If You’Re Getting Radiation Therapy to The Abdomen (Belly)
If you are getting radiation to your stomach or some part of the abdomen (belly), you may have side effects such as: 1. Nausea 2. Vomiting 3. Belly...
If You’Re Having Radiation Therapy to The Pelvis
Radiation therapy to the pelvis (for example, as treatment for bladder, ovarian, or prostate cancer) can cause side effects such as: 1. Bladder pro...
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
Does radiation therapy have side effects?
It's very important to remember that every person reacts differently to treatment. Any side effect you might have depends on the type and location of cancer, the dose of radiation being given, and your general health. Some people have few or no side effects, while others have quite a few.
What are the side effects of brachytherapy?
If your treatment includes brachytherapy (internal radiation implants), you might notice breast tenderness, tightness, redness, and bruising. You may also have some of the same side effects that happen with external radiation treatment.
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
Can radiation therapy cause low blood count?
Rarely, radiation therapy can cause changes in your blood count levels. These blood cells help your body fight infection and prevent bleeding. If your blood tests show low blood counts, your treatment might be stopped for a week or so to allow your blood counts to return to normal. This side effect is more likely if you’re also getting chemotherapy.
How long does it take for brain tumors to show up?
Side effects depend on where the radiation is aimed. Some side effects might show up quickly, but others might not show up until 1 to 2 years after treatment.
How does radiation affect the bladder?
Just like radiation harms cells in your bones, it also affects the cells in your bowel and bladder. You might experience blood in your urine, reduced bladder control, sexual dysfunction, and interruptions to your daily routine.
Can radiation cause burns?
The concentrated exposure of X-rays during radiation therapy often causes painful burns across the skin. As X-rays pass through the skin, they produce dangerous free radicals that damage DNA, injure skin tissue, and trigger inflammation. This side effect is so common that about 85% of radiation patients experience moderate to severe burns during and after treatment
Does radiation weaken bones?
Radiation is so potent that it can weaken the bones and cause osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Since bones are living and growing organisms, radiation harms their active cells and stunts their strength. The ribs in your chest or bones in your leg may become far more vulnerable to fractures and breaks.
What is radiation oncology?
Radiation oncologists are trained to deliver the right dose of radiation to the right body part on the correct schedule. They work to minimize side effects and limit overall radiation exposure so you can receive the correct dose of radiation to sterilize cancer cells while minimizing the effects on your normal, healthy cells.
Can radiation cause long term side effects?
Your risk of long-term side effects may increase with the amount of radiation you receive. Some people have a rare inherited disease that causes them to heal poorly from radiotherapy.
Is radiation therapy bad for cancer?
Long-term side effects of radiation therapy. If you have undergone radiation therapy (radiotherapy) for cancer treatment, it is normal to have concerns about potential long-term side effects. Fortunately, not everyone experiences side effects and for those who do, side effects are rarely serious.
Can radiation therapy help cancer patients?
We can treat cancer cells that remain even after chemotherapy or surgery, or shrink tumors before surgery or chemotherapy. Radiation therapy is capable of helping someone who could have died from cancer and giving them their life back.".
Who is Adam Nowlan?
Adam Nowlan, M.D., a radiation oncologist at Piedmont, shares the overall benefits of radiotherapy, the most common signs to watch for after treatment and when to see your doctor.
What are the side effects of radiation?
Several variables can increase or decrease your risk of developing long-term side effects of radiotherapy. Some of these are: 2 1 Your age at the time of radiation 2 The dose of radiation you receive 3 The number of treatment sessions 4 The type of cancer treated 5 The area of the body that receives radiation 6 Other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy 7 Other health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes
What is radiation fibrosis?
Radiation Fibrosis Syndrome. Radiation fibrosis can be thought of simplistically as the loss of elasticity in tissues after radiation, due to permanent scarring. Many of the side effects below are caused by this fibrosis, which can occur in nearly any region of the body. 7 .
When was radiation therapy first used?
Despite possible long-term side effects of radiation treatment, it's essential to point out that radiation therapy has come a long since it was introduced in 1903 , especially in recent years. With more precise dosing and newer methods of delivery, older studies may overestimate the risks.
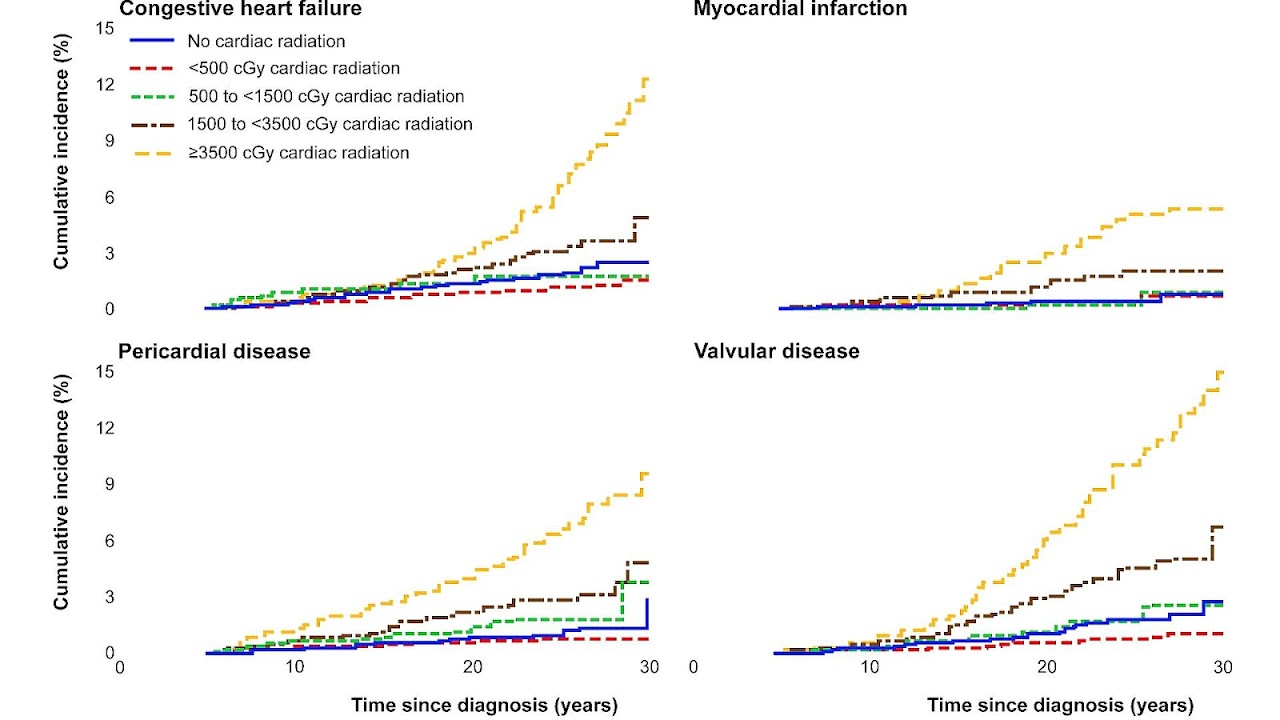
Can radiation therapy cause heart problems?
Concern over long-term side effects of radiation therapy is becoming more common, as survival rates improve. Just as there can be long-term side effects of chemotherapy, radiation therapy may result in side effects that may begin and linger far after treatment has been completed. These can include heart problems, lung problems, thyroid problems, ...
Can radiation cause hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is one of the more common late effects of radiation therapy when radiation treatment involves the neck, head, and chest. 5 . Immunotherapy drugs also increase the risk of hypothyroidism, so that those who have received both of these treatments should be extra aware of the possibility. 6 .
What happens if you get radiation on your head?
Radiation to the head and neck region can damage to the salivary glands and tear ducts. This damage may result in permanent dry mouth or dry eyes. 16 Cataracts and dental decay may also be problems.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy works by damaging DNA in cells. This damage isn't isolated to cancer cells, though; normal cells can be damaged as well. While radiation therapy has improved significantly such that less damage occurs to healthy cells than in the past, some healthy tissues are inevitably exposed. 2

Mechanism of action
Risks
- Several variables can increase or decrease your risk of developing long-term side effects of radiotherapy. Some of these include: The following are some possible long-term side effects of radiation treatment but it's essential to point out that radiation therapy has improved in recent years; and a very long way since it was introduced to treat cancer in 1903. With more precise do…
Prognosis
- At the same time, as people are living longer with cancer, the long-term effects of radiation will become increasingly important. It's estimated that 50 percent of people diagnosed with cancer will receive radiation therapy at some point in their journey.
Pathophysiology
- Radiation fibrosis can be thought of simplistically as the loss of elasticity in tissues after radiation, due to permanent scarring. Many of the side effects below are caused by this fibrosis which can occur in nearly any region of the body.
Overview
- Lung fibrosis is a permanent scarring of the lungs which can result from untreated radiation pneumonitis. Radiation pneumonitis is an inflammation of the lungs which occurs one to six months after completing radiation therapy to the chest and happens in roughly a fourth of people treated with radiation for lung cancer. Since the symptoms can mimic symptoms due to cancer, …
Prevention
- Thankfully, newer techniques such as respiratory gating (controlled breathing designed to minimize the exposure of the heart to radiation) are becoming available, which may lower the risk of this complication. There are a number of things you can do yourself in addition to precautions taken by your doctor to reduce your risk of long term complications related to radiation therapy.
Adverse effects
- Radiation therapy, especially radiation to the brain, to the base of the skull, and to the neck may result in cognitive problems such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating. Radiation oncologists now frequently treat people with a medication (one ordinarily used for Alzeimers) during radiation therapy and this has been found to reduce cognitive problems later on.
Effects
- Osteoporosis/Fractures: Radiation may result in weakening of the bones, osteoporosis, and osteonecrosis. For example, radiation to the chest may result in the ribs becoming fractured more easily.
Symptoms
- Muscles/joints/nerves/ligaments: Radiation can affect the muscles and supporting structures of the musculoskeletal system resulting in restricted mobility, pain, and numbness.
Signs and symptoms
- Soft tissue: Permanent darkening of the skin, telangiectasias (spidery red marks) and permanent hair loss may occur with radiation. Radiation may also result in lymphedema, swelling that occurs as the result of damage to the lymph channels, for example, the arm swelling seen in some women who have had breast cancer.
Safety
- Damage to the salivary glands and tear ducts from radiation to the head and neck region may result in permanent dry mouth or dry eyes.