
Medication
They have not spread to distant parts of the body. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy (removal of the bladder and nearby lymph nodes) is …
Procedures
Bladder Cancer Surgery. Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Targeted Therapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer.
Therapy
In general, the main treatment options for bladder cancer are: Surgery. Chemotherapy. Immunotherapy (local and systemic) Targeted therapy. Radiation therapy. To learn more about the basics of each type of treatment, read this guide’s Types of Treatment section. Developing a …
Nutrition
Sep 28, 2021 · BCG is used to stop the growth of bladder cancer and keep it from returning. 1. BCG is actually a vaccine made with a species of weakened mycobacterium, a group of tiny bacteria. The bacteria used in the vaccine is related to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. But in most people, it doesn’t cause serious disease.
What are the treatment options for Stage 1 bladder cancer?
1 day ago · Promising new drugs have begun to transform the treatment of bladder cancer, the fifth most common form of the disease in the U.S., and the fourth most common in men. These two drug classes, checkpoint inhibitors and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), are giving patients much-improved treatment options for various stages of the disease.
How are non-muscle-invasive bladder cancers treated?
Apr 29, 2022 · Fast-growing but noninvasive bladder cancer has a higher likelihood of returning after treatment than other kinds. Speak with your cancer care team about treatment options designed to lower the risk of recurrence. Metastatic bladder cancer: Advanced bladder cancer has spread, or metastasized, to distant sites in the body. This makes the cancer harder to treat, …
What is a radiation therapy regimen for bladder cancer?
Jun 10, 2016 · 1. Intravesical BCG therapy for high-grade T1. If patients with high-grade T1 disease have a low risk of progression, bladder sparing management should be considered. BCG instillation into bladder is the gold standard for conservative treatment for high-grade T1 disease.
What is the best immunotherapy drug for bladder cancer?
This type of cancer is called urothelial carcinoma (also called transitional cell carcinoma). Most urothelial carcinomas are noninvasive. That means the tumor stays within the bladder’s inner lining. Urothelial carcinoma also has rarer subtypes, or “variants.”. These differ depending on how the cells appear under a microscope.

What is the best treatment for T1 bladder cancer?
BCG instillation into bladder is the gold standard for conservative treatment for high-grade T1 disease.Jun 10, 2016
Is first stage bladder cancer curable?
What is the survival rate for stage 1 bladder cancer?
What is the common immunotherapy treatment given at the early stage of urinary bladder cancer?
Does bladder cancer spread fast?
What is the new treatment for bladder cancer?
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
- Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test.
- Frequent urination.
- Painful urination.
- Back pain.
What is stage1 bladder cancer?
Where does bladder cancer spread first?
How many rounds of chemo do you need for bladder cancer?
What is the success rate of immunotherapy for bladder cancer?
Is bladder cancer a terminal?
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv...
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti...
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers...
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical...
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca...
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc...
Which Treatments Are Used For Bladder Cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: 1. Surgery 2. Intravesical th...
Which Doctors Treat Bladder Cancer?
Depending on your options, you can have different types of doctors on your treatment team. The types of doctors who treat bladder cancers include:...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c...
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: Bladder Cancer Surgery. Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Targeted Therapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer.
Can bladder cancer be removed?
Surgery, alone or with other treatments, is used to treat most bladder cancers. Early-stage bladder tumors can often be removed. But a major concern in people with early-stage bladder cancer is that new cancers often form in other parts of the bladder over time.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 Urologists: surgeons who specialize in treating diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive system 2 Radiation oncologists: doctors who treat cancer with radiation therapy 3 Medical oncologists: doctors who treat cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy
How to decide on cancer treatment?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include: 1 Your age and expected life span 2 Any other serious health conditions you have 3 The stage and grade of your cancer 4 The likelihood that treatment will cure your cancer (or help in some other way) 5 Your feelings about the possible side effects from treatment
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What is the number to call for cancer treatment?
Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists. Palliative Care. Find Support Programs and Services in Your Area.
Why is it important to discuss all of your treatment options with your doctor?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include:
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemotherapy is commonly used in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Radical cystectomy and lymph node dissection. A radical cystectomy is the removal of the whole bladder and possibly nearby tissues and organs. For men, the prostate and part of the urethra are usually also removed.
What is radiation therapy for bladder cancer?
When radiation therapy is given using implants, it is called internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. However, brachytherapy is not used in bladder cancer. A radiation therapy regimen, or schedule, usually consists of a specific number of treatments given over a set period of time.
What is standard of care for cancer?
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for cancer. “Standard of care” means the best treatments known so far. When making treatment plan decisions, you are encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option.
What is bladder surgery?
Surgery is the removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue during an operation. There are different types of surgery for bladder cancer. Your health care team will recommend a specific surgery based on the stage and grade of the disease.
Can you live without a bladder?
Living without a bladder can affect a patient’s quality of life. Finding ways to keep all or part of the bladder is an important treatment goal. For some people with muscle-invasive bladder cancer, treatment plans involving chemotherapy and radiation therapy after optimal TURBT (see "Bladder preservation" in Treatments by Stage) may be used as an alternative to removing the bladder.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy, also called biologic therapy, is designed to boost the body’s natural defenses to fight the cancer. It uses materials made either by the body or in a laboratory to improve, target, or restore immune system function. It can be given locally or throughout the body.
Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
For bladder cancer, side effects most commonly occur in the pelvic or abdominal area and may include bladder irritation, with the need to pass urine frequently during the treatment period, and bleeding from the bladder or rectum; other side effects may occur less commonly.
What is the best treatment for bladder cancer?
In general, the main treatment options for bladder cancer are: Surgery. Chemotherapy. Immunotherapy (local and systemic) Targeted therapy. Radiation therapy. To learn more about the basics of each type of treatment, read this guide’s Types of Treatment section.
Is bladder cancer recurrent?
This will then be followed with long-term surveillance. People with high-grade, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer are at higher risk for the tumor returning, called a recurrent tumor. Sometimes a tumor comes back at a more advanced stage, with a risk of developing into metastatic bladder cancer.
What is a multidisciplinary team in cancer?
In cancer care, different types of doctors often work together to create a patient’s overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team . This team is usually led by a urologist, a doctor who specializes in the genitourinary tract, or a urologic oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating cancers of the genitourinary tract. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, and others.
What is the first line of treatment for urothelial cancer?
The first treatment a person is given for advanced urothelial cancer is called first-line therapy . If that treatment stops working, then a person receives second-line therapy.
Can bladder cancer come back?
People with high-grade, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer are at higher risk for the tumor returning, called a recurrent tumor. Sometimes a tumor comes back at a more advanced stage, with a risk of developing into metastatic bladder cancer.
What is stage IV bladder cancer?
Metastatic urothelial cancer (stage IV) If bladder cancer has spread to another part of the body, doctors call it metastatic bladder cancer. If this happens, it is a good idea to talk with doctors, usually medical oncologists, who have experience in treating it.
What is it called when bladder cancer spreads?
If bladder cancer has spread to another part of the body, doctors call it metastatic bladder cancer. If this happens, it is a good idea to talk with doctors, usually medical oncologists, who have experience in treating it. Doctors can have different opinions about the best standard treatment plan.
What is the treatment for stage IV bladder cancer?
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following: Chemotherapy with or without local treatment ( surgery or radiation therapy ). Immunotherapy ( immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy ).
What is bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys.
Does smoking cause bladder cancer?
Smoking can affect the risk of bladder cancer. Signs and symptoms of bladder cancer include blood in the urine and pain during urination. Tests that examine the urine and bladder are used to help diagnose bladder cancer. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Where is the bladder located?
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low- grade or high-grade: Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs (comes back) after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
What is it called when you have cancer in your bladder?
Cancer that is in the lining of the bladder is called superficial bladder cancer. Cancer that has spread through the lining of the bladder and invades the muscle wall of the bladder or has spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes is called invasive bladder cancer. See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
What happens after bladder cancer diagnosis?
After bladder cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the bladder or to other parts of the body.
Is bladder cancer invasive?
Almost all squamous cell carcinomas of the bladder are invasive. Adenocarcinoma of the bladder closely resembles the gland-forming cells seen in colon cancers, and accounts for about 1 percent of bladder cancers in the United States.
What is the name of the tumor that grows out of the bladder?
Papillary carcinoma: Grows out from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center in finger-like projections. Often, these tumors are called noninvasive papillary cancers, meaning they don’t grow into the deeper layers of the bladder wall.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
The most common type of bladder cancer is transitional cell (urothelial) carcinoma (TCC). This type accounts for about 95 percent of bladder cancers.
What percentage of bladder cancer is squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 1 percent to 2 percent of bladder cancers diagnosed in the United States. Squamous cells look similar to the flat cells on the surface of the skin. Almost all squamous cell carcinomas of the bladder are invasive.
Where does bladder cancer start?
This type of bladder cancer begins in neuroendocrine cells, which are similar to nerves. Sarcoma is another very rare type of bladder cancer that begins in the muscle layer of the bladder wall.
What is flat carcinoma?
If a flat carcinoma is confined to the urothelium, it is called noninvasive flat carcinoma or flat carcinoma in situ. Rarer forms of bladder cancer include: Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 1 percent to 2 percent of bladder cancers diagnosed in the United States.
What is the cancer of the bladder called?
Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder. Most bladder cancers — about 90 percent — begin in the cells on the surface of the bladder’s inner lining. This type of cancer is called urothelial carcinoma (also called transitional cell carcinoma). Most urothelial carcinomas are noninvasive.
What is the name of the cancer that starts on the surface of the bladder?
Most bladder cancers — about 90 percent — begin in the cells on the surface of the bladder’s inner lining. This type of cancer is called urothelial carcinoma (also called transitional cell carcinoma). Most urothelial carcinomas are noninvasive.
What are the different types of urothelial carcinoma?
Urothelial carcinoma also has rarer subtypes, or “variants.” These differ depending on how the cells appear under a microscope. The variant of urothelial carcinoma affects the treatment. The variants are called: 1 plasmacytoid 2 nested 3 micropapillary 4 lipoid cell 5 sarcomatoid 6 microcystic 7 lymphoepithelioma-like 8 inverted papilloma-like 9 clear cell
Where does bladder cancer start?
Most bladder cancers — about 90 percent — begin in the cells on the surface of the bladder’s inner lining. This type of cancer is called urothelial carcinoma (also called transitional cell carcinoma). Most urothelial carcinomas are noninvasive. That means the tumor stays within the bladder’s inner lining.
What is the most common form of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is by far the most common form of bladder cancer in the United States. Other types of bladder cancer are rarer, although they may have a higher frequency in other parts of the world. These types include:
What percentage of cases of bladder cancer are adenocarcinoma?
This rare form of bladder cancer accounts for about 1 percent of cases. Adenocarcinoma can be associated with certain bladder defects at birth, as well as with chronic infection and inflammation.
Is urothelial carcinoma noninvasive?
Most urothelial carcinomas are noninvasive. That means the tumor stays within the bladder’s inner lining. Urothelial carcinoma also has rarer subtypes, or “variants.”. These differ depending on how the cells appear under a microscope. The variant of urothelial carcinoma affects the treatment. The variants are called:
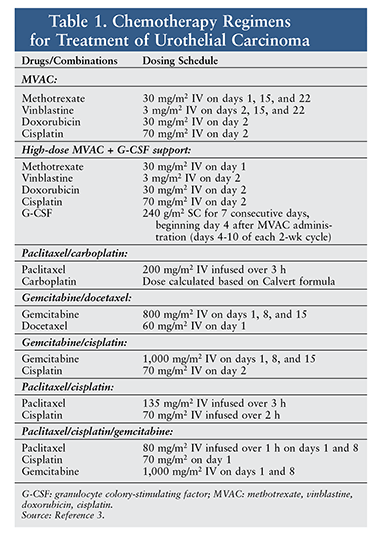
Treatment Overview
Surgery
Therapies Using Medication
Radiation Therapy
Specialist to consult
Physical, Emotional, and Social Effects of Cancer
Remission and The Chance of Recurrence
- Surgery is the removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue during an operation. There are different types of surgery for bladder cancer. Your health care team will recommend a specific surgery based on the stage and grade of the disease. Transurethral bladder tumor resection (TURBT). This procedure is used for diagnosis and staging, as...
If Treatment Does Not Work
- Systemic therapy is the use of medication to destroy cancer cells. This type of medication is given through the bloodstream or from the mouth to reach cancer cells throughout the body (the "system" in "systemic therapy"). Systemic therapies are generally prescribed by a medical oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating cancer with medication. Common ways to give s…