
Ionizing radiation and cancer risk
| Procedure | Average effective dose (mSv) | Range reported in the literature (mSv) |
| Bone density test+ | 0.001 | 0.00–0.035 |
| X-ray, arm or leg | 0.001 | 0.0002–0.1 |
| X-ray, panoramic dental | 0.01 | 0.007–0.09 |
How is radiation used to treat cancer?
Systemic radiation: Radioactive drugs given by mouth or put into a vein are used to treat certain types of cancer. These drugs then travel throughout the body. The type of radiation you might get depends on the kind of cancer you have and where it is. In some cases, more than one type is used.
How is radiation used in radiopharmaceutical imaging?
The radiation that comes from the radiopharmaceutical is used for treatment or is detected by a camera to take pictures of the corresponding body organ, region or tissue. What happens during a nuclear medicine imaging procedure?
Do imaging tests that use radiation cause cancer?
Because radiation exposure from all sources can add up over a lifetime, and radiation can, indeed, increase cancer risk, imaging tests that use radiation should only be done for a good reason. In many cases, other imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be used.
How has Medical Imaging changed the use of ionizing radiation?
The use of ionizing radiation for cancer treatment has undergone extraordinary development during the past hundred years. The advancement of medical imaging has been critical in helping to achieve this change. The invention of computed tomography (CT) was pivotal in the development of treatment planning.

How is radioactivity used in cancer treatment?
How radiation therapy works against cancer. At high doses, radiation therapy kills cancer cells or slows their growth by damaging their DNA. Cancer cells whose DNA is damaged beyond repair stop dividing or die. When the damaged cells die, they are broken down and removed by the body.
Which radioactive element is used for treatment of cancer?
Cobalt therapy or cobalt -60 therapy is the medical use of gamma rays from the radioisotope cobalt -60 to treat conditions such as cancer.
Is radioactivity used for diagnosis of cancer?
Nuclear Medicine for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Nuclear medicine can help diagnose and treat different conditions, including some forms of cancer. In nuclear medicine, doctors put small amounts of radioactive material into your body so they can see your organs and tissues, as well as how well they work.
How are radioisotopes used in radiation therapy for cancer?
Radioisotope therapy is a procedure in which a liquid form of radiation is administered internally through infusion or injection. RIT's ultimate purpose is to treat cancerous cells with minimal damage to the normal surrounding tissue. These therapies are not normally the first approach used to fight a patient's cancer.
What is used in the treatment of cancer?
Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and hormone therapy can all be used to relieve symptoms. Other medications may relieve symptoms such as pain and shortness of breath. Palliative treatment can be used at the same time as other treatments intended to cure your cancer.
How does radiation cause cancer?
High-energy radiation, such as x-rays, gamma rays, alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons, can damage DNA and cause cancer. These forms of radiation can be released in accidents at nuclear power plants and when atomic weapons are made, tested, or used.
What is the role of radioactivity in the diagnosis of disease?
Since Rontgen's discovery over 100 years ago, radiation has been used to create visual images of the inside of the body to diagnose medical conditions. Medical professionals use ionizing radiation in specific imaging procedures to help diagnose injuries or illness within the body.
What radiation is used in medical treatments?
X-rays, gamma rays, and other forms of ionizing radiation are used to diagnose and treat some medical conditions. This can be in the form of radiation that penetrates from outside the body, or radioactive particles that are swallowed or inserted into the body.
How radioactive isotopes are used for medical diagnosis and treatment?
Radioisotopes are an essential part of medical diagnostic procedures. In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can be used for imaging to study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body.
How are radioisotopes used in medical treatment?
Radioisotopes in medicine. Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radiation to provide information about a person's body and the functioning of specific organs, ongoing biological processes, or the disease state of a specific illness. In most cases the information is used by physicians to make an accurate diagnosis.
What Is Radiation Therapy?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves, such as x-rays, gamma rays, electron beams, or protons, to destroy or damage cancer cells.Yo...
Who Gets Radiation Therapy?
More than half of people with cancer get radiation therapy. Sometimes, radiation therapy is the only cancer treatment needed.
What Are The Goals of Radiation Therapy?
Most types of radiation therapy don’t reach all parts of the body, which means they’re not helpful in treating cancer that has spread to many place...
How Is Radiation Therapy given?
Radiation therapy can be given in 3 ways: 1. External radiation (or external beam radiation): uses a machine that directs high-energy rays from out...
Who Gives Radiation Therapy Treatments?
During your radiation therapy, a team of highly trained medical professionals will care for you. Your team may include these people: 1. Radiation o...
Does Radiation Therapy Cause Cancer?
It has long been known that radiation therapy can slightly raise the risk of getting another cancer. It’s one of the possible side effects of treat...
Does Radiation Therapy Affect Pregnancy Or Fertility?
Women: It’s important not to become pregnant while getting radiation – it can harm the growing baby. If there’s a chance you might become pregnant,...
Questions to Ask About Radiation Therapy
Before treatment, you’ll be asked to sign a consent form saying that your doctor has explained how radiation therapy may help, the possible risks,...
Will I Be Radioactive During Or After External Radiation Treatment?
External radiation therapy affects cells in your body only for a moment. Because there’s no radiation source in your body, you are not radioactive...
How much radiation is in a CT scan?
A CT scan of the abdomen (belly) and pelvis exposes a person to about 10 mSv. A PET/CT exposes you to about 25 mSv of radiation. This is equal to about 8 years of average background radiation exposure. Keep in mind that these are estimates for an average-sized adult.
What to do if you have concerns about radiation?
If you have concerns about the radiation you may get from a CT scan, PET scan, or any other imaging test that uses radiation, talk to your health care provider. Ask whether the test is needed and if it’s the best one to use in your case. You may also want to know what you and your health care provider can expect to learn from it.
How much radiation does the average American get?
The average American is exposed to about 3 mSv ( millisieverts) of radiation from natural sources over the course of a year. (A millisievert is a measure of radiation exposure.) But background radiation exposure varies throughout the United States, and the world. The largest source of background radiation (typically about 2 mSv per year) is radon, ...
How much radiation is exposed to a chest xray?
For instance: A single chest x-ray exposes the patient to about 0.1 mSv. This is about the same amount of radiation people are exposed to naturally over the course of about 10 days.
What is the best way to look for cancer?
But if there’s a reason to believe that an x-ray, CT scan, or nuclear medicine scan (such as a PET scan) is the best way to look for cancer or other diseases, the person will most likely be helped more than the small dose of radiation can hurt.
Why does radon vary from one part of the country to another?
Radon levels vary greatly from one part of the country to another. Location also plays a role because the earth’s atmosphere blocks some cosmic rays. This means being at a higher altitude increases a person’s exposure.
How much exposure is normal for a mammogram?
A mammogram exposes a woman to 0.4 mSv, or about the amount a person would expect to get from natural background exposure over 7 weeks. Some other imaging tests have higher exposures, for example: A lower GI series using x-rays of the large intestine exposes a person to about 8 mSv, or about the amount expected over about 3 years.
How does radiation help cancer?
When radiation is combined with surgery, it can be given: 1 Before surgery, to shrink the size of the cancer so it can be removed by surgery and be less likely to return. 2 During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation. With this technique, doctors can more easily protect nearby normal tissues from radiation. 3 After surgery to kill any cancer cells that remain.
Why do people with cancer need radiation?
Why People with Cancer Receive Radiation Therapy. Radiation therapy is used to treat cancer and ease cancer symptoms . When used to treat cancer, radiation therapy can cure cancer, prevent it from returning, or stop or slow its growth. When treatments are used to ease symptoms, they are known as palliative treatments.
What is intraoperative radiation therapy?
During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation.
What is brachytherapy with liquid source?
Learn more about brachytherapy. Internal radiation therapy with a liquid source is called systemic therapy. Systemic means that the treatment travels in the blood to tissues throughout your body, seeking out and killing cancer cells.
What is the best radiation treatment for thyroid cancer?
A systemic radiation therapy called radioactive iodine, or I-131, is most often used to treat certain types of thyroid cancer.
What is the treatment for cancer that has spread to the bone called?
Pain from cancer that has spread to the bone can be treated with systemic radiation therapy drugs called radiopharmaceuticals.
What is external beam radiation therapy?
External Beam Radiation Therapy. External beam radiation therapy comes from a machine that aims radiation at your cancer. The machine is large and may be noisy. It does not touch you, but can move around you, sending radiation to a part of your body from many directions.
Why is radiotherapy effective?
Radiotherapy is effective against cancer because cancer cells reproduce rapidly and, consequently, are more sensitive to radiation. The central problem in radiotherapy is to make the dose for cancer cells as high as possible while limiting the dose for normal cells.
What is nuclear radiation used for?
What makes nuclear radiation so useful? First,#N#γ#N#γ radiation can easily penetrate tissue; hence, it is a useful probe to monitor conditions inside the body. Second, nuclear radiation depends on the nuclide and not on the chemical compound it is in, so that a radioactive nuclide can be put into a compound designed for specific purposes. When that is done, the compound is said to be tagged. A tagged compound used for medical purposes is called a radiopharmaceutical. Radiation detectors external to the body can determine the location and concentration of a radiopharmaceutical to yield medically useful information. For example, certain drugs are concentrated in inflamed regions of the body, and their locations can aid diagnosis and treatment as seen in Figure 22.37. Another application utilizes a radiopharmaceutical that the body sends to bone cells, particularly those that are most active, to detect cancerous tumors or healing points. Images can then be produced of such bone scans. Clever use of radioisotopes determines the functioning of body organs, such as blood flow, heart muscle activity, and iodine uptake in the thyroid gland. For instance, a radioactive form of iodine can be used to monitor the thyroid, a radioactive thallium salt can be used to follow the blood stream, and radioactive gallium can be used for cancer imaging.
How effective is radiation therapy?
Radiotherapy is effective against cancer because cancer cells reproduce rapidly and , consequently, are more sensitive to radiation. The central problem in radiotherapy is to make the dose for cancer cells as high as possible while limiting the dose for normal cells. The ratio of abnormal cells killed to normal cells killed is called the therapeutic ratio, and all radiotherapy techniques are designed to enhance that ratio. Radiation can be concentrated in cancerous tissue by a number of techniques. One of the most prevalent techniques for well-defined tumors is a geometric technique shown in Figure 22.41. A narrow beam of radiation is passed through the patient from a variety of directions with a common crossing point in the tumor. The technique concentrates the dose in the tumor while spreading it out over a large volume of normal tissue.
What is the radiation dose unit?
To quantitatively discuss the biological effects of ionizing radiation, we need a radiation dose unit that is directly related to those effects. To do define such a unit, it is important to consider both the biological organism and the radiation itself. Knowing that the amount of ionization is proportional to the amount of deposited energy, we define a radiation dose unit called the rad. It 1/100 of a joule of ionizing energy deposited per kilogram of tissue, which is
How sensitive are cancer cells to radiation?
Cancer cells are particularly sensitive to radiation-induced DNA damage. Depending on the type of radioactive compound used, the resulting energy can penetrate the cell bound to the radiopharmaceutical as well as about 10 to 30 cells surrounding that cell.
What is radiopharmaceutical?
Radiopharmaceuticals consist of a radioactive molecule, a targeting molecule, and a linker that joins the two. The past two decades have brought a sea change in the way many types of cancer are treated. Targeted therapies shut down specific proteins in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread. Immunotherapies stimulate ...
What are the three building blocks of radiopharmaceuticals?
They envisioned engineered radiopharmaceuticals that consist of three main building blocks: a radioactive molecule, a targeting molecule (that recognizes and latches specifically onto cancer cells), and a linker that joins the two.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
The resulting side effects of radiation therapy depend on the area of the body treated but can include loss of taste, skin changes, hair loss, diarrhea, and sexual problems. Now, researchers are developing a new class of drugs called radiopharmaceuticals, which deliver radiation therapy directly and specifically to cancer cells.
How does cancer treatment work?
Immunotherapies stimulate or suppress the body’s immune system to help fight cancer. But long-used treatments — surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy — remain the backbone of treatment for most cancers.
How many cancer patients still receive radiation?
About half of all cancer patients still receive it at some point during their treatment. And until recently, most radiation therapy was given much as it was 100 years ago, by delivering beams of radiation from outside the body to kill tumors inside the body.
What is the drug that is used to treat prostate cancer?
A similar natural affinity was later exploited to develop drugs to treat cancer that has spread to the bones, such as radium 223 dichloride ( Xofigo), which was approved in 2013 to treat metastatic prostate cancer. When cancer cells grow in the bone, they cause the bone tissue they invade to break down.
What is the radiation that comes from a radiopharmaceutical used for?
The radiation that comes from the radiopharmaceutical is used for treatment or is detected by a camera to take pictures of the corresponding body organ, region or tissue.
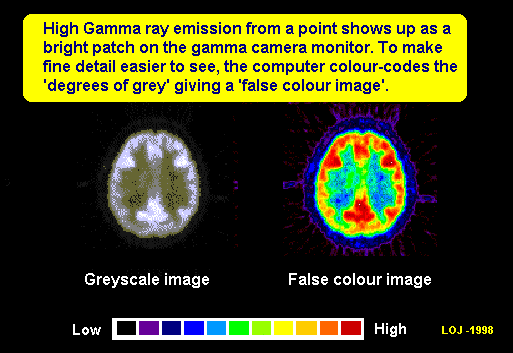
What is the purpose of a computer in a radiotherapy patient?
A computer is used to show where the body concentrates the radioactive material.
What is nuclear medicine?
Nuclear medicine procedures are used in diagnosing and treating certain illnesses. These procedures use radioactive materials called radiopharmaceuticals. Examples of diseases treated with nuclear medicine procedures are hyperthyroidism, thyroid cancer, lymphomas, and bone pain from some types of cancer. The amount of radioactive materials used in ...
What is the test used to diagnose heart disease?
Heart disease can be diagnosed with a stress test using Sestamibi that contains technetium-99m or through the use of positron emission tomography (PET) scans. See more information about how PET scans are used in nuclear medicine in the section below.
Why do doctors use PET scans?
Doctors use PET scans to get more data about how body organs are functioning. PET scans may be performed together with a computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan that provides an image of the organ. PET scans provide a clear view of how the organs are working at the cellular level and if they have been damaged.
What agency regulates the use of radioactive materials for nuclear medicine?
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and states regulate the use of radioactive materials for nuclear medicine to make sure patients, medical personnel, and the public are safe.
Can radioactive materials be man made?
Radioactive materials can be natural or they can be man-made. They can be solids (like some rocks on earth) or liquids or they can also be gases that people can breathe (like radon). Each radioactive material has a unique half-life, which tells how quickly it stops being radioactive.
What is the use of ionizing radiation for cancer?
The use of ionizing radiation for cancer treatment has undergone extraordinary development during the past hundred years. The advancement of medical imaging has been critical in helping to achieve this change. The invention of computed tomography (CT) was pivotal in the development of treatment planning.
What is radiation therapy?
There are two, general classes of radiation therapy: brachytherapy and teletherapy. “Brachy,” a Greek word, means short distance and “tele” means long distance. Brachytherapy is treatment performed by placing the radioactive source near or in contact with a tumor, that is, the use of intracavitary or intraluminal placement of the treatment source.
What is fusion imaging?
In medical applications, these points are the same anatomical regions of the body, such as bone and organs, for the same patient. Fusion is the ability to display different types of registered images anatomically overlain on one another in a single, composite image [ 33#N#A. Ardeshir Goshtasby and S. Nikolov, “Image fusion: advances in the state of the art,” Information Fusion, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 114–118, 2007. View at: Publisher Site | Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#]. Fusion provides the best information for each image, that is, geometric definition and tissue density from the CT image, soft-tissue contrast from the MR image, and metabolic information from the PET image. The combined information reduces the uncertainty regarding the tumor definition for geometric localization as well as determining the size and spread of the disease. By improving the accuracy of the target definition, image fusion can potentially improve the treatment outcome and decrease complications as less normal tissue is irradiated.
How does image fusion improve radiation treatment?
By improving the accuracy of the target definition, image fusion can potentially improve the treatment outcome and decrease complications as less normal tissue is irradiated. Currently, most radiation treatment planning systems support image registration and fusion. There are several fusion algorithms.
What are the three main aspects of cancer treatment?
The three most important aspects of cancer treatment are surgery, chemotherapy (in earlier times referred to simply as medicine), and radiation therapy . Of these, surgery is the oldest with records discovered by Edwin Smith, an American Egyptologist, and describing the surgical treatment of cancer in Egypt circa 1600 B.C. [ 1#N#R. E. Pollock and D. L. Morton, “Principles of surgical oncology,” in Cancer Medicine, D. W. Kufe and R. E. Pollock, Eds., B. C. Decker, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, 2000. View at: Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#]. Medicines were also used in ancient Egypt at the time of the pharaohs, although the use of chemotherapy in cancer was first used in the early 1900s by the German chemist, Paul Ehrlich [ 2#N#V. T. de Vita Jr. and E. Chu, “A history of cancer chemotherapy,” Cancer Research, vol. 68, no. 21, pp. 8643–8653, 2008. View at: Publisher Site | Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#]. In contrast, radiation therapy, the therapeutic use of ionizing radiation, is by far the most recent technique used to treat cancer. X-rays, a kind of ionizing radiation, were discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen and within months were used to treat tumors. This use of ionizing radiation has undergone extraordinary development during the past century. As we will discuss, the advancements in medical imaging have been critical to the evolution of modern radiation therapy.
When were X-rays created?
X-rays are produced when these accelerated electrons collide with a high-atomic-number target. In 1953, the first isocentric linac was installed at the Christie Hospital in Manchester, United Kingdom, and these units continue to be the mainstay of modern radiation therapy.
When was X-rays first used?
X-rays, a kind of ionizing radiation, were discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen and within months were used to treat tumors. This use of ionizing radiation has undergone extraordinary development during the past century. As we will discuss, the advancements in medical imaging have been critical to the evolution of modern radiation therapy.
What is the role of imaging?
Physicians use imaging tests to help detect and diagnose disease, make appropriate treatment recommendations, and monitor your response to therapy. Some imaging tests, like x-rays and computed tomography (CT), use radiation to capture images of the body. Others, like ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), do not.
What is the oldest form of medical imaging?
X-ray. X-rays are the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. This noninvasive test involves exposing an area to a small dose of radiation to create pictures of the inside of the body.
What is the best way to detect breast cancer?
Breast tomosynthesis is a mammography system that creates a series of three-dimensional images of the breast that improves the physician’s ability to detect breast cancer and results in fewer patients having to undergo additional imaging. X-ray. X-rays are the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging.
How does bone scan index help prostate cancer?
A small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein. It travels through the bloodstream, collects in the bones, and is detected by a scanner, which creates images of the bones on a computer screen. Bone Scan Index May Help Determine Response to Prostate Cancer Treatment.
What is the purpose of a PET scan?
A scanner then takes detailed, computerized pictures of areas inside the body where the glucose is being used. Because cancer cells often use more glucose than normal cells, the pictures can help physicians find cancer cells in the body.
What is CAD in mammography?
For example, digital mammography captures images of the breast that can be seen on a computer screen, and computer-aided detection (CAD) software can search digitized mammographic images for abnormal areas of the breast that require further analysis.
What is nuclear medicine?
Nuclear medicine tests use small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose disease. The radioactive substance is injected into the body, locates specific cells or tissues ― including cancer cells ― and binds to them.
Building on A Natural Affinity
Adapting Drugs from Imaging Compounds
- Researchers are now designing and testing radiopharmaceuticals for a range of cancers as diverse as melanoma, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and leukemia, said Dr. Capala. Any tumor that has a targetable molecule on the surface of its cells and a good blood supply—sufficient to deliver drugs—could potentially be treated with radiopharmaceuticals, added Dr. Chauhan. Man…
Moving to Combination Therapies
- While radiopharmaceuticals have shown promise in early studies, they are also, as is the case with other types of cancer drugs, unlikely to wipe out a tumor on their own. For example, lutetium Lu 177-dotatate more than doubled the number of people who had their neuroendocrine tumors shrink after treatment, but that number was still modest: about 17%, up from 7% without the dru…
Challenges and Cautions
- The field of radiopharmaceuticals is still in its early days. One challenge the approach will need to overcome before it can be used more widely is the shortage of doctors trained to administer such drugs. “The number of nuclear medicinephysicians in the US is small,” said Dr. Lin, who has training in both nuclear medicine and medical oncology. “And I think we only train maybe 70 or 8…
Smoothing Collaborations
- Because these drugs are relatively new, even with the trials underway, “we’re just scratching the surface of drug development for radiopharmaceuticals,” Dr. Chauhan said. In 2019, to further boost trials of promising new radiopharmaceuticals, NCI launched the Radiopharmaceutical Development Initiative (RDI) to speed promising new drugs into clinical testing. One thing NCI ho…