Medication
Mar 19, 2021 · How can I prevent a kidney infection? Drink lots of liquid, especially water. Liquids can help flush bacteria from the urinary system. Water is best. Most healthy people should try to ... Wipe from front to back after using the toilet. Urinate often …
Nutrition
Jul 10, 2021 · The mainstay of treatment of acute pyelonephritis is antibiotics, analgesics, and antipyretics. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) work well to treat both pain and fever associated with acute pyelonephritis. The initial selection of antibiotics will be empiric and should be based on the local antibiotic resistance.
How long should you treat pyelonephritis?
Sep 01, 2011 · for women with acute pyelonephritis who require hospitalization, initial intravenous antimicrobial therapy is recommended ( table 7). 15 options include a fluoroquinolone, an aminoglycoside (with...
What antibiotics are used to treat pyelonephritis?
Jan 24, 2004 · Oral antibiotics, carefully chosen to cover local uropathogens, are as safe and effective as intravenous antibiotics in children with a clinical diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis. This is not surprising given the combination of high bioavailability and renal excretion of orally administered antibiotics.
How to diagnose and treat pyelonephritis?
Mar 01, 2005 · Outpatient oral antibiotic therapy with a fluoroquinolone is successful in most patients with mild uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Other effective alternatives include extended-spectrum penicillins,...
What is the best antibiotic for pyelonephritis?
Jul 01, 2021 · Inpatient admission is warranted for any pregnant patient with pyelonephritis. The treatment of choice during pregnancy includes the use of beta-lactam antibiotics. Intravenous antibiotics should...

What is the first line treatment for pyelonephritis?
Fluoroquinolones (FQ) are the first line empiric treatment for acute pyelonephritis. Fluoroquinolones (FQ) are the first line empiric treatment for acute pyelonephritis. An effective modality along when given IV or IM or given as a first dose in outpatient treatment.Aug 3, 2016
How long is treatment for pyelonephritis?
In the current International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the treatment of acute pyelonephritis, the recommended duration of treatment for pyelonephritis is 7 days for fluoroquinolones, 10–14 days for β-lactams and 14 days for trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.May 21, 2013
Can pyelonephritis be totally cured?
Treating pyelonephritis Although drugs can cure the infection within 2 to 3 days, the medication must be taken for the entire prescription period (usually 10 to 14 days). This is true even if you feel better. The antibiotic options are: levofloxacin.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work for pyelonephritis?
Most patients with uncomplicated cases of pyelonephritis find that their symptoms begin to improve after one to two days of treatment with antibiotics. However, even after symptoms improve, antibiotics are usually prescribed to complete a 10 to 14 day course.May 31, 2021
What are the classic signs of pyelonephritis?
The classic presentation in acute pyelonephritis is the triad of fever, costovertebral angle pain, and nausea and/or vomiting. These may not all be present, however, or they may not occur together temporally. Symptoms may be minimal to severe and usually develop over hours or over the course of a day.Jul 1, 2021
What is the most common cause of pyelonephritis?
The main cause of acute pyelonephritis is gram-negative bacteria, the most common being Escherichia coli. Other gram-negative bacteria which cause acute pyelonephritis include Proteus, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter.Jul 10, 2021
How do you know a kidney infection is getting worse?
You have symptoms that a kidney infection is getting worse. These may include: Pain or burning when you urinate. A frequent need to urinate without being able to pass much urine.
What does pyelonephritis pain feel like?
Frequent, painful urination. Back, side (under the ribs), and groin pain. Chills and high fever. Nausea and vomiting.
Where is pain with pyelonephritis?
Back, side (flank) or groin pain. Abdominal pain. Frequent urination. Strong, persistent urge to urinate.Aug 26, 2020
Does pyelonephritis require hospitalization?
Outpatient Treatment. Most cases of uncomplicated acute pyelonephritis can be managed in the outpatient setting. However, patients who appear ill may have severe pyelonephritis or a complication of acute pyelonephritis and should be considered for hospitalization and further evaluation (Table 514).Sep 1, 2011
Is acute pyelonephritis serious?
Acute pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of the kidney parenchyma that can be organ- and/or life-threatening and that often leads to scarring of the kidney. The bacteria in these cases have usually ascended from the lower urinary tract, but may also reach the kidney via the bloodstream.Jul 1, 2021
Is pyelonephritis an emergency?
Emphysematous pyelonephritis is a surgical emergency. Most patients are septic, and fluid resuscitation and broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapy are essential. If the kidney is functioning, medical therapy can be considered [5, 6].Jul 6, 2012
What is the treatment for pyelonephritis?
Surgical Treatments for Pyelonephritis. In addition to antibiotics, acute pyelonephritis may also require surgery if it is accompanied by an abscess, calculi (stones), renal papillary necrosis, or xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGP).
How long does it take for pyelonephritis to heal?
All three are treated initially with IV antibiotics for 10 to 14 days, followed by oral antibiotics for two to four weeks. The specific antibiotics are chosen based on which bacteria are found in the urine cultures. Most patients with smaller abscesses (< 3cm) will be cured without surgery. If patients do not respond to antibiotics within a week, a surgeon may drain the abscess, usually using ultrasound or CT imaging to guide a needle into the abscess (es) and drain it (a process called percutaneous drainage). In some cases, the surgeon may insert a catheter through the needle and leave it in to drain the abscess until fever disappears and drain output is minimal.
What is pyelonephritis UTI?
Tweet. Pyelonephritis is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) affecting one or both kidneys. It occurs when bacteria or viruses travel into the kidneys from the bladder or invade the kidneys through the bloodstream. Pyelonephritis is typically diagnosed using urinalysis and other tests, and initial treatment consists of antibiotics.
What is XGP in kidney?
XGP is a rare, serious inflammatory disorder in which a destructive mass invades the main body of the kidney . It is most often associated with Proteus or E. coli -related urinary tract infections. XGP results in a non-functioning kidney that must be removed surgically (nephrectomy) in order to prevent the infection from spreading. If possible, surgery is delayed until the patient is stable.
Can a UTI be removed?
When a UTI is related to kidney or blad der stones, the bacteria can often survive inside the stones despite antibiotic therapy. In cases of acute infection, the stones should be removed immediately. If the stones are small and limited to the bladder, they may be removed during cytoscopy, in which a urologist inserts a small, ...
Can pyelonephritis cause kidney failure?
Rarely, pyelonephritis can threat en the kidney (necessitating removal) or cause permanent kidney scars, which can then lead to high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, and kidney failure.
What should be done for suspected acute pyelonephritis?
All patients with suspected acute pyelonephritis should have a urine culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing to guide possible adjustment of the initial antimicrobial regimen (if there is no improvement) and selection of step-down oral therapy for patients treated initially with intravenous therapy. 15
What antibiotics are used for pyelonephritis?
Initial treatment of women with acute pyelonephritis who require hospitalization should include an intravenous antimicrobial regimen, such as a fluoroquinolone, an aminoglycoside (with or without ampicillin), an extended-spectrum cephalosporin or penicillin (with or without an aminoglycoside), or a carbapenem.*.
How long does ciprofloxacin stay in your system?
Treatment options for women with acute pyelonephritis not requiring hospitalization include 500 mg of oral ciprofloxacin (Cipro) twice per day for seven days; 1,000 mg of extended-release ciprofloxacin once per day for seven days; or 750 mg of levofloxacin (Levaquin) once per day for five days.
When was the pyelonephritis guidelines updated?
In 2010, the Infectious Diseases Society of America updated its 1999 guidelines on the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women. 15 The guidelines include recommendations for antimicrobial regimens in patients with acute pyelonephritis.
What is acute pyelonephritis?
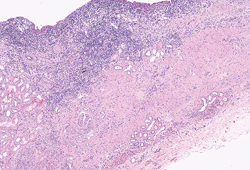
By definition, acute pyelonephritis is an infection of the renal pelvis and kidney that usually results from ascent of a bacterial pathogen up the ureters from the bladder to the kidneys. It is estimated that acute pyelonephritis accounts for approximately 250,000 office visits and 200,000 hospital admissions each year in the United States, and approximately 11 hospitalizations per 10,000 Canadian women each year. 1 – 3 The incidence of acute pyelonephritis is highest in otherwise healthy women 15 to 29 years of age, followed by infants and older persons. 4 Although acute pyelonephritis also occurs in men, children, and pregnant women, these groups account for only a small percentage of cases. Accordingly, this review focuses on diagnosis and treatment of acute pyelonephritis in nonpregnant women.
How long does it take for pyelonephritis to improve?
Therapy with appropriate empiric antibiotics should produce improvement within 48 to 72 hours. If the patient does not improve as expected (i.e., no progressive reduction in, or resolution of, the local and systemic signs and symptoms that led to the diagnosis), strong consideration should be given to a complication of acute pyelonephritis or an alternative diagnosis, and appropriate additional testing should be performed.
Is E. coli a pathogen?
Escherichia coli is the most common pathogen in acute pyelonephritis, and in the past decade, there has been an increasing rate of E. coli resistance to extended-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics.
What is the best antibiotic for pyelonephritis?
Outpatient oral antibiotic therapy with a fluoroquinolone is successful in most patients with mild uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Other effective alternatives include extended-spectrum penicillins, amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium, cephalosporins, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
How long does it take for a UTI to respond to antibiotics?
Men younger than 60 years without obstruction, renal abnormalities, or prostatitis respond well to 14 days of antibiotic therapy. 2 Men who have recurrent UTIs require a six-week regimen.
How many patients have positive blood cultures?
Blood cultures have been recommended for hospitalized patients; up to 20 percent of these patients have positive cultures. 1 In two studies, 24, 25 however, completion of blood cultures did not result in changes in management strategies in patients with acute pyelonephritis.
Is pyelonephritis a mild illness?
The spectrum of acute pyelonephritis is wide, ranging from a mild illness to sepsis syndrome. 1 To diagnose acute pyelonephritis, physicians must rely on evidence of UTI from urinalysis or culture, along with signs and symptoms suggesting upper UTI (fever, chills, flank pain, nausea, vomiting, costovertebral angle tenderness). Symptoms that are suggestive of cystitis (dysuria, urinary bladder frequency and urgency, and suprapubic pain) also may be present.
Can pyelonephritis be treated with antibiotics?
Although patients with acute pyelonephritis traditionally have been hospitalized and treated with intravenous antibiotics, outpatient oral therapy is successful in 90 percent of selected patients with uncomplicated acute pyelonephritis who can tolerate oral intake, will be compliant with the treatment regimen, will return for early follow-up, and have adequate social support 27, 28 ( Figure 2). Patients with complicated acute pyelonephritis who are more ill or have not responded to outpatient therapy should be hospitalized. Using specific hospitalization criteria ( Table 4), 1 up to 70 percent of patients can be selected for outpatient management. Another option is initial therapy with parenteral antibiotics in an inpatient observation unit, followed by oral therapy as an outpatient. 26, 29
What is the sensitivity of leukocyte esterase?
The combination of the leukocyte esterase test and the nitrite test (with either test proving positive) has a sensitivity of 75 to 84 percent and a specificity of 82 to 98 percent for urinary tract infection.
Can pyelonephritis cause renal failure?
Acute pyelonephritis is considered uncomplicated if the infection is caused by a typical pathogen in an immunocompetent patient who has normal urinary tract anatomy and renal function. Misdiagnosis can lead to sepsis, renal abscesses, and chronic pyelonephritis that may cause secondary hypertension and renal failure.
How long does it take to get ciprofloxacin for pyelonephriti
Although the guidelines recommend either 14 days of TMP-SMX or 7 days of ciprofloxacin for the treatment of pyelonephritis, a study in 272 women with susceptible E coli pyelonephritis reported similar clinical outcomes with 7 days of TMP-SMX therapy compared with 7 days of ciprofloxacin.
How long does it take to take ciprofloxacin?
However, evidence suggests that in young, healthy women who are receiving a fluoroquinolone, including ciprofloxacin, the course of treatment can be shortened to 7 days. Levofloxacin, 750 mg/day, can be given for 5 days. [ 34, 35] Young, healthy males should complete a 14-day course. [ 3]
What are the conditions that are considered a metabolic disease?
Metabolic disease (eg, diabetes, kidney insufficiency) Impaired host defenses (eg, HIV, current chemotherapy, underlying active cancer) Pregnancy. Admission is also indicated for patients with apparent clinically uncomplicated pyelonephritis who have any of the following: Inability to maintain adequate oral hydration.
Can fluoroquinolones cause aneurysms?
An important caveat for the use of fluoroquinolones in the elderly is their potential to cause aortic aneurysm or dissection; hypoglycemia; and a variety of neuropsychiatric symptoms, ranging from seizures to worsening of dementia.
When diagnosis suspected, always obtain urine (via clean-catch, mid-stream sample OR catheterized specimen) for
When diagnosis suspected, always obtain urine (via clean-catch, mid-stream sample OR catheterized specimen) for urinalysis and culture (with antibiotic susceptibility testing).#N#Urine specimen: should be received in the laboratory within 1 h of collection (or stored at 4°C and tested within 18h) to reduce risk of overgrowth of bacteria.#N#Bacterial colony counts typically >100,000 CFU/mL.#N#Absence of pyuria and bacteriuria suggest an alternative diagnosis (unless obstruction present).
What are the symptoms of UTI?
Clinical: signs and symptoms include fever, chills, flank pain, nausea, and vomiting. Patients may or may not have symptoms of a lower tract UTI ( uncomplicated acute bacterial cystitis ). Abdominal and/or pelvic pain may be present. Costovertebral angle tenderness to percussion typical.
Is S. aureus a pathogen?
S. agalactiae and Enterococcus spp. are possible but uncommon pathogens. S. aureus is an uncommon pathogen and should raise concern for other infectious process (e.g., blood stream infection, endocarditis).
What are the causes of pyelonephritis?
A man is more likely to develop the problem if his prostate is enlarged, a common condition after age 50. Both men and women are more likely to develop pyelonephritis if they have any of the following conditions: 1 An untreated urinary tract infection 2 Diabetes 3 Nerve problems that affect the bladder 4 Kidney stones 5 A bladder tumor 6 Abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder to the kidneys, called vesicoureteral reflux 7 An obstruction related to an abnormal development of the urinary tract
How long does pyelonephritis last?
Doctors treat pyelonephritis with antibiotics. In most uncomplicated cases of pyelonephritis, the antibiotic can be given orally (by mouth), and treatment usually lasts for 7 to 10 days. Commonly used oral antibiotics include trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole ( Bactrim and others), ciprofloxacin ( Cipro) or levofloxacin ( Levaquin ), but the choice of antibiotic will depend on your history of allergies and laboratory testing of the bacteria causing the infection.
Why do women have more bladder infections than men?
Women have more bladder infections (also called urinary tract infections) than men because the distance to the bladder from skin, where bacteria normally live, is quite short and direct . However, the infection usually remains in the bladder. A woman is more likely to develop pyelonephritis when she is pregnant.
How do you know if you have pyelonephritis?
The two primary symptoms of pyelonephritis are pain in one flank, the area just beneath the lower ribs in the back, and fever. The pain can travel around the side toward the lower abdomen. There also can be shaking chills and nausea and vomiting. The urine may be cloudy, tinged with blood or unusually strong or foul-smelling.
Can pyelonephritis cause kidney failure?
However, repeated episodes of pyelonephritis can cause chronic (long-lasting) kidney disease in children, people with diabetes, and adults who have structural abnormalities of the urinary tract, or nerve diseases that disrupt bladder function.
Is pyelonephritis more common in women?
A woman is more likely to develop pyelonephritis when she is pregnant. Pyelonephritis and other forms of urinary tract infection increase the risk of premature delivery. A man is more likely to develop the problem if his prostate is enlarged, a common condition after age 50.
