This measurement is made by observing the sump levels when the pumps on and cycles off and calculating the volume contained between the two levels. This volume times the number of pump cycles provides an estimate of the daily wastewater flow.
Full Answer
How should a wastewater treatment plant's hydraulic flow be used to calculate effluent?
· Nonparametric 80% exceeded measured daily flow ( Q80) in a year. 1. DWF formula DWF = PG + I DWF + E Where: DWF = total dry weather flow (l/d) P = catchment population (number) G = per capita...
How should a wastewater treatment plant's capacity be determined?
· Wastewater Treatment Math Formulas Wastewater Treatment Formulas 3 Flow Conversions cfs = cubic feet per second gps = gallons per second cfm = cubic feet per minute gpm = gallons per minute cfd = cubic feet per day gpd = gallons per day
Should effluent limits be measured on streams or on treatment plants?
· The basic principle of this method is that the flow in a channel (cubic feet/second) is equal to the average velocity (feet/second) times the cross-sectional area (square feet) of the channel. LSASD has two methods for determining flow using the area velocity method.
What is the average load of wastewater in a day?
The average sewage flow rate is usually about the same as the average water use in the community. In a lateral sewer, short-term peak flow rates can be roughly four times the …

How do you calculate daily flow?
0:453:01How to calculate flowrate - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey're asking for the flow rate so let's write down that formula flow rate equals velocityMoreThey're asking for the flow rate so let's write down that formula flow rate equals velocity multiplied by area the area is the cross-sectional area of the pipe hatched.
How is peak daily flow calculated?
The peak daily flow for determining equalization tank volume shall be calculated as follows: Peak Daily Flow (gpd)= 3 1/3 × Average daily flow (gpd)× 24 (hrs.) Run-off period (hrs.)
How do you calculate daily sewage flow?
Daily Sewage Flow. Multiply the ultimate population by per capita average daily sewage flow to obtain the average daily sewage flow e.g.
How do you calculate peak flow in wastewater?
The peak flow per household (qh, l/s) is given by equation 2.2 as: qh = 1.8 × 10-5 P w = 1.8 × 10-5 × 5 × 100 = 0.009 l/s per household.
What is peak flow in wastewater?
A “peak” flow may be simply defined as a sudden and/or sustained increase in the hydraulic and/or contaminant loading into a wastewater treatment plant. Peak flows can be further delineated into “instantaneous” (duration of about one hour), or “sustained” (duration of about 24 hours).
What is the minimum daily flow?
Min daily flow= 2/3 * avg daily flow. Max hourly flow= 3 * avg daily flow. Min belt flow= 1/3 * avg daily flow.
Calculate the current DWF
There are 2 ways to calculate the current DWF: DWF formula. Nonparametric 80% exceeded measured daily flow (Q80) in a year. 1. DWF formulaDWF = PG...
Calculate DWF for new discharges
Use the DWF formula for new discharges.Base the values, such as population, on predictions that will take account of any expected increases up to t...
Calculate future DWF for existing discharges
For existing discharges, you can use either the DWF formula or the Q80 method to determine DWF permit limits at the design horizon. You must take i...
How is wastewater capacity determined?
The size and capacity of wastewater treatment systems are determined by the estimated volume of sewage generated from residences, businesses, and industries connected to sewer systems as well as the anticipated inflows and infiltration (I&I). The selection of specific on-lot, clustered, or centralized treatment plant configurations depends upon factors such as the number of customers being served, the geographical scenario, site constraints, sewer connections, average and peak flows, influent wastewater characteristics, regulatory effluent limits, technological feasibility, energy consumption, and the operations and maintenance costs involved.
What are the three levels of wastewater treatment?
There are three levels of wastewater treatment: primary, secondary, and tertiary (or advanced). Primary treatment removes about 60 percent of total suspended solids and about 35 percent of BOD; dissolved impurities are not removed. It is usually used as a first step before secondary treatment. Secondary treatment removes more than 85 percent of both suspended solids and BOD. A minimum level of secondary treatment is usually required in the United States and other developed countries. When more than 85 percent of total solids and BOD must be removed, or when dissolved nitrate and phosphate levels must be reduced, tertiary treatment methods are used. Tertiary processes can remove more than 99 percent of all the impurities from sewage, producing an effluent of almost drinking-water quality. Tertiary treatment can be very expensive, often doubling the cost of secondary treatment. It is used only under special circumstances.
Why is sewage flow higher?
Although sewage flows depend upon residential, commercial, and industrial connections, sewage flow rates potentially can become higher as a result of inflows and infiltration (I&I) into the sanitary sewer system. Inflows correspond to storm water entering sewers from inappropriate connections, such as roof drains, storm drains, ...
What is inflow in sewer system?
Inflows correspond to storm water entering sewers from inappropriate connections, such as roof drains, storm drains, downspouts and sump pumps. High amounts of rainwater runoff can reach the sewer system during precipitation and stormflow events or during seasonal spring flooding of rivers inundated with melting ice.
What are the factors that determine the effluent standards?
The factors controlled under these standards usually include biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), suspended solids, acidity, and coliforms.
How long does it take to disinfect a water tank?
Disinfection is usually accomplished by mixing the effluent with chlorine gas or with liquid solutions of hypochlorite chemicals in a contact tank for at least 15 minutes. Because chlorine residuals in the effluent may have adverse effects on aquatic life, an additional chemical may be added to dechlorinate the effluent.
Why is wastewater treated?
In either case, wastewater must be purified or treated to some degree in order to protect both public health and water quality. Suspended particulates and biodegradable organics must be removed to varying extents. Pathogenic bacteria must be destroyed.
What is SWMM in sewer?
As part of the planning process, a collection system model using EPA Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) Version 5.0, Build 5.0.011 was developed to simulate the flow conditions experienced within the service area. The model was refined and calibrated to simulate the existing collection system based on recent sewer rehabilitation efforts, flow monitoring, and historic pump station and treatment facility flow data. This calibrated model was used to estimate the 5-year, 24-hour and 5-year peak hour wet weather flow events for the existing and build-out conditions.
What is the BOD5 in wastewater?
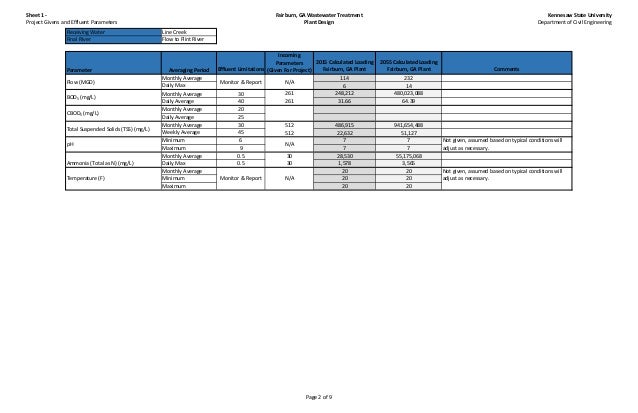
BOD5 is a measure of the amount of oxygen required to biologically oxidize the organic material in the wastewater over a specific time period. A 5-day BOD test is conventionally used for domestic wastewater testing. TSS is a measure of the particulate material suspended in the wastewater. The loading parameters of interest are the annual average loading, maximum month loading, maximum week loading, and peak day loading for BOD5 and TSS load.
When was the WRF based on operating data?
The following assessment of current flow conditions for the WRF is based on operating data from January 1996 through September 2007.
What is the DO of a 50 ml sample of wastewater?
A 50 mL sample of wastewater influent is found to have an initial DO reading of 10.2 mg/L and a final DO reading of 7.5 mg/L. The sample does not need to be seeded for BOD calculation. Using the given information, determine the BOD in mg/L for the influent.
What is the surface loading rate of a wastewater tank?
Plant designs generally use a surface loading rate of 300 to 1200 gpd/ft 2. The surface loading rate can be determined by:
What is the flow to a secondary clarifier?
The flow to a secondary clarifier is 1.2 MGD. If the influent BOD concentration is 220 mg/L and the effluent BOD concentration is 85 mg/L, how many pounds of BOD are removed daily?
How long does it take for a clarifier to detach?
The expected range of hydraulic detention time for a primary clarifier is 1 to 3 hours with an expected range of surface loading/settling rate of 300 to 1200 gpd/ft 2. The expected range of weir overflow rate for a primary clarifier is 10,000 to 20,000 gpd/ft.
How many feet of weir is in a sedimentation basin?
A sedimentation basin has a total of 125 ft of weir. What is the weir overflow rate, in gpd/ft, when the flow is 2,055,000 gpd?
What is the diameter of a circular clarifier?
A circular clarifier has a diameter of 100 ft and has a weir along its circumference. The effluent flow rate is 2.22 MGD. What is the weir overflow rate in gallons per day per foot (gpd/ft)?
How wide is a sedimentation basin?
A sedimentation basin has a length of 120 ft and a width of 50 ft. If the primary effluent flow is 3.25 MGD, what is the surface loading, or overflow rate, in gpd/ft2?
When was the Village wastewater treatment plant built?
A Village's wastewater treatment plant originally was constructed in 1926. The tributary collection system allows more than "normal" inflow and infiltration (I/I), according to the court. When the plant was upgraded in 1977-78, it was decided to treat the excess flow rather than reduce it.
What is untreated waste load?
The Village argued that the term "untreated waste load" used in the regulation dictating effluent limits means the amount of wastewater a plant is designed to treat, not the total flow to the plant. Therefore, the Village urged, it was an error to use hydraulic capacity instead of organic loading to calculate "untreated waste load."
What are the limits for NPDES?
The first NPDES permit, issued in 1977, provided for effluent limitations of 30 mg/l BOD, and 30 mg/l suspended solids . In 1986, the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed a new NPDES permit (National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System) reducing the limits to 20 mg/l BOD, and 25 mg/l suspended solids. The Village objected on the ground that the state regulations required the more stringent limits only for untreated waste loads of 10,000 P.E. or more. The Village pointed out that its plant design was for untreated waste loads up to 10,000 P.E. and that the present loading was under that level. The Village and the Illinois EPA compromised. The plant was re-rated at a 9,900 P.E. design organic load and an NPDES permit was issued at 30/30. In 1992, the permit was renewed at 25 mg/l CBOD, and 30 mg/l suspended solids.
How is treated wastewater discharged?
The treated wastewater effluent shall be discharged to the drip disposal system through a dosing tank that has sufficient volume to provide flow equalization. Storage requirements within the treatment and dispersal system shall be at least one full day-storage located between the treatment and dispersal systems.
What is missing from a wastewater pumping station?
The wastewater pumping station is missing one of the four essential items: a telemetering alarm system, a standby pump unit, a stationary auxiliary power source, or a pump-around connection.
What is forward flush residual?
All filter flush and tubing network forward flush residuals are to return to the head of the pre-treatment system, or be treated by an acceptable side-treatment system before returning to the dosing station .
How many gallons per capita per day should be used for design flow?
Actual flow data should be used to determine design flow when possible. At a minimum, 100 gallons per capita per day should be used. Include the following information with design flow calculations.
What is the most important thing to consider when planning a new wastewater treatment facility?
Determination of design flow and loadings is one of the most important items when planning a new or expanded wastewater treatment facility. Sound engineering judgement along with these minimum guidelines will determine the hydraulic and pollutant load capacity required by the proposed facility to meet all permitted limits.
How to find peak instantaneous wet weather flow?
Part B of Table 2 determines the peak instantaneous wet weather flow. The present peak hourly inflow adjusted for a five-year one-hour rainfall event [see part A row (8)] is subtracted from the peak hourly wet weather flow [see part A row (19)]. To this number, add the present peak hourly inflow adjusted for a twenty-five year one- hour storm event. The resulting number is the peak instantaneous wet weather flow.
What is flow data used for?
Existing flow data for critical low and peak wet weather events are used to estimate the following flow conditions critical to the design of wastewater treatment plants.
What is peak instantaneous flow?
flow is the peak instantaneous flow during the day at a time when the ground water is high and a twenty-five year one-hour storm event is occurring. To determine the twenty-five year one- hour storm event for a specific location, please refer to Map Number 2.
What is peak month flow?
or peak month flow is the daily average flow for the wettest 30 consecutive days for mechanical plants or for the wettest 180 consecutive days for controlled discharge pond systems. The 180 consecutive days for pond systems should be based on either the storage period from approximately November 15 through May 15 or the storage period from approximately May 15 through November 15.
How long should a measured flow be plotted?
The measured flow should be plotted for a twenty-four hour period when
