What are the main causes of disparities in care?
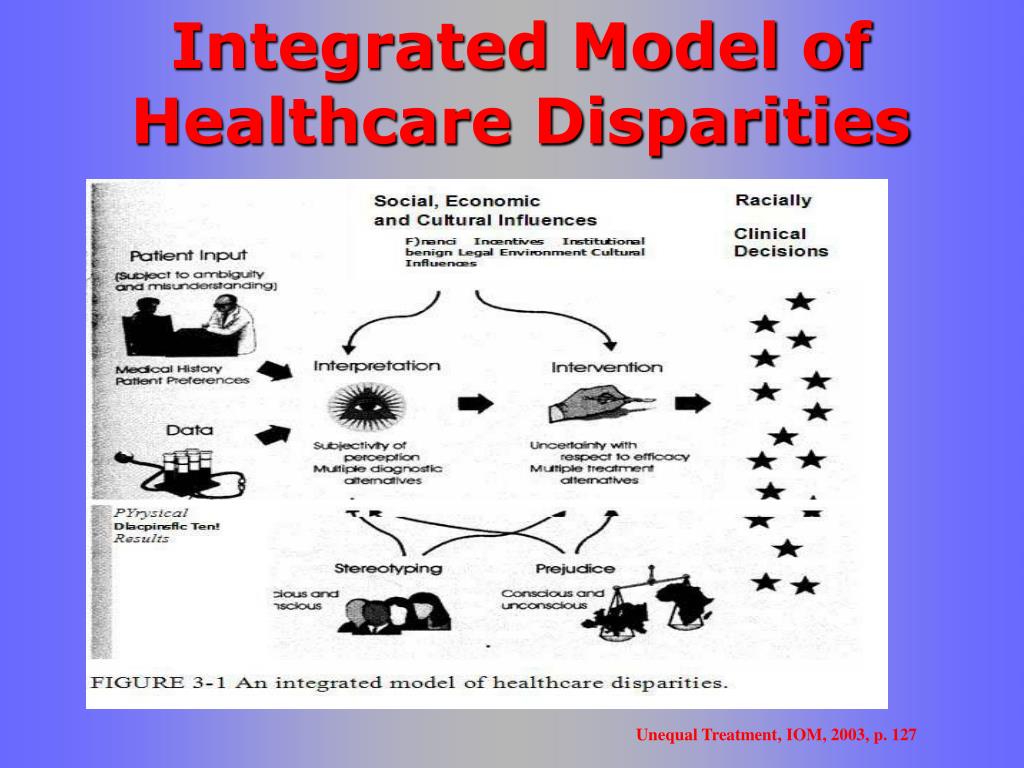
There are many sources across health systems, providers, patients and managers that contribute to disparities. Bias, stereotyping, prejudice and clinical uncertainty contribute to disparities. A small number of studies suggest that racial and ethnic minority patients are more likely to refuse treatment.
How can we reduce racial and ethnic disparities in healthcare?
Increase awareness of racial and ethnic disparities in health care among the general public. Strengthen patient-provider relationships in publicly funded health plans. Apply the same managed care protections to publicly funded HMO participants that apply to private HMO participants.
What are the antecedents of health disparities?
The antecedents of such differences involve such “drivers” as cost and access to the healthcare system, primary care physicians, and preventive health services. In addition, the subtle role of bias in creating and/or exacerbating health disparities is well documented in the literature.
What does the IOM report say about disparities in health care?
A 2002 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report confirmed that there are significant disparities in the quality of health care received according to a patient’s socioeconomic status, access to health care, and use of health care services. 7

How do health disparities affect health care?
Health disparities lead to approximately $93 billion in excess medical care costs and $42 billion in lost productivity per year as well as economic losses due to premature deaths. For example, as of 2018, Latinx individuals are two-and-a-half times more likely to be uninsured than whites (19% vs. 7.5%).
What is meant by healthcare disparities and why does it exist?
Health disparities are preventable differences in the burden of disease, injury, violence, or in opportunities to achieve optimal health experienced by socially disadvantaged racial, ethnic, and other population groups, and communities. Health disparities exist in all age groups, including older adults.
How does racial bias affect healthcare?
Racial bias in healthcare can lead to Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC) having a harder time accessing healthcare. This can mean a Person of Color has delays in treatment, leading to worse outcomes.
How can we fix healthcare disparities?
Raising public and provider awareness of racial/ethnic disparities in care; Expanding health insurance coverage; Improving the capacity and number of providers in underserved communities; and. Increasing the knowledge base on causes and interventions to reduce disparities.
What is the cause and effect of health disparity?
Health disparities are the result of systemic conflict, as well as lack of resources and distribution of these resources to accommodate the population that is in need (10 facts on health inequities and their causes, 2017).
What are some examples of healthcare disparities?
Some populations can have higher rates of cancer, for example, while others might be more likely to be obese or use tobacco. These differences in health or medical conditions are called health disparities, and they can have a profound impact on the public health of a community.
How does discrimination affect healthcare?
Racial and ethnic discrimination has a significant impact on the health of people of color, affecting mental health and contributing to high blood pressure, negative health behaviors, and early aging.
Why Do racial disparities exist in healthcare?
The sources of racial and ethnic health care disparities include differences in geography, lack of access to adequate health coverage, communication difficulties between patient and provider, cultural barriers, provider stereotyping, and lack of access to providers.
What role does racism play in healthcare?
Racial Underrepresentation in Healthcare Discrimination and bias leads fewer people of color to enter the healthcare profession and affects the lives of those who do. For example, a 2019 study by the Journal of the American Medical Association looked at 15 years' worth of U.S. medical school students.
How can nurses eliminate health disparities?
One of the most powerful things nurses can do to reduce health disparities is to advocate for their patients. This may include advocating for patient rights, appropriate resources, interpreters, distress screening or even cultural-competence training in your workplace.
What are current challenges to addressing disparities?
Beyond coverage, there are an array of other challenges to addressing disparities, including limited capacity to address social determinants of health, declines in funding for prevention and public health and health care workforce initiatives, and ongoing gaps in data to measure and understand disparities.
What are the 5 health disparities?
Health disparities include the following:Mortality.Life expectancy.Burden of disease.Mental health.Uninsured/underinsured.Lack of access to care.
What is health disparity?
HEALTH DISPARITIES DEFINED. Health disparities are differences and/or gaps in the quality of health and healthcare across racial, ethnic, and socio-economic groups. It can also be understood as population-specific differences in the presence of disease, health outcomes, or access to healthcare.
What are the consequences of being uninsured?
The consequences of being uninsured are significant and include use of fewer preventive services, poorer health outcomes, higher mortality and disability rates, lower annual earnings because of sickness and disease, and the advanced stage of illness ( i.e., many are “sicker” when diagnosed).
What is culturally competent emergency care?
Culturally competent emergency care providers also possess the skills to identify and manage racial and ethnic differences in health values, beliefs, and behaviors with the ultimate goal of delivering quality health services to all patients cared for in EDs.
What is the Institute of Medicine's landmark report?
The Institute of Medicine's landmark report, "Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care," documents the pervasiveness of racial and ethnic disparities in the U.S. health care delivery system, and provides several recommendations to address them.
What is disparity in health care?
A health care disparity is defined as unequal treatment or variations in the care quality we provide to populations with equal access to care, after taking into account clinical need and patient preferences.
How does unconscious bias affect health care?
Unconscious bias can influence a health care provider’s assessments and decisions regarding a patient’s care, creating disparities in treatment. Bias and discrimination may also negatively impact provider-patient communication and lead to disparate outcomes and treatment.
What can influence your decisions and actions without you realizing it?
Your background, personal experiences, societal stereotypes, and cultural context can influence your decisions and actions without you realizing it. Unconscious bias happens when our brains make incredibly quick judgments and assessments of people and situations without us realizing.
What are the causes of health disparities?
There are many sources across health systems, providers, patients and managers that contribute to disparities. Bias, stereotyping, prejudice and clinical uncertainty contribute to disparities. A small number of studies suggest that racial and ethnic minority patients are more likely to refuse treatment.
What is the Health Disparities Toolkit?
Health Disparities Toolkit. This kit focuses on the theme of “Working Together to End Racial and Ethnic Disparities: One Physician at a Time.” Access DVD interviews with physicians, nurses and patients, and a CD of information on topics such as cultural competence and literacy. Use the facilitation guide to work with other health care providers and physicians.
What is the AMA policy?
AMA’s policy to reduce health care disparities. AMA has enacted policies that support the research findings from the IOM and support the goals of reducing disparities in health care. These policies aim to: Increase awareness of racial and ethnic disparities in health care among the general public.
What is the goal of Healthy People?
Department of Health and Human Services launched Healthy People 2010, which had two broad goals: to improve the overall health status of Americans and to eliminate racial and ethnic health care disparities.
What is the importance of review in ensuring a health care facility not only meets required standards, but provides a
Review the important considerations in ensuring a health care facility not only meets required standards, but provides a safe, accessible and comfortable environment for patients with disabilities. AMA’s work to reduce health care disparities .
Do minorities have a lower quality of health care?
Recent studies have shown that despite the improvements in the overall health of the country, racial and ethnic minorities experience a lower quality of health care—they are less likely to receive routine medical care and face higher rates of morbidity and mortality than nonminorities. The American Medical Association (AMA) encourages physicians ...
What is health disparity?
The U.S. government defines health disparity as “a particular type of health difference that is closely linked with social or economic disadvantage.” These disparities negatively impact whole groups of people that already face significantly more obstacles to maintaining good health, often because of specific social or economic factors, such as:
What are the social factors that contribute to health disparities?
There are dozens of social factors exacerbating health disparities, but the Healthy People 2020 objectives have put just five front and center: economic stability, education, social and community context, health and health care, and neighborhood and built environment.
What are the things that can be done to improve the environmental health of a community and reduce health disparities?
Improving access to healthy foods, supporting healthy eating behaviors, improving the quality of housing, reducing crime and violence, and protecting the environment are all things that can be done to improve the environmental health of a community and reduce health disparities as a result.
What are some examples of health disparities?
Here are just a few examples: Infant mortality: Babies born to Black women in the United States die at more than double the rate of babies born to white women.
How much money would the state save if the health disparities were eliminated?
Persistent gaps in health-related outcomes can also have economic consequences. One study in North Carolina estimated that the state could save $225 million a year if disparities in diabetes could be eliminated.
What are the economic stability issues?
Economic stability refers to things like food security, income or wealth, housing stability, and employment opportunities, and research shows addressing some of these issues could help reduce disparities associated with a whole range of health issues. Providing housing assistance, for example, has been shown to improve both the psychological and physical health of individuals. Similarly, providing influenza vaccination in poorer neighborhoods could help reduce gaps in hospitalization due to flu. And increasing economic opportunities for financially insecure women might help prevent the disproportionately high number of cases of HIV in that population.
How do social forces perpetuate inequalities?
Social drivers—like racism, sexism, ableism, classism, or homophobia—can perpetuate inequities by prioritizing one group over another. These forces are so deeply ingrained in cultural practices and norms that many people might not realize they’re happening. Oftentimes, these forces are the result of past inequities that still affect communities today. Take, for example, mid-20th-century discriminatory housing practices. These policies forced many minority families into neighborhoods without nearby access to community resources, like public transportation, quality education, or job opportunities—all of which affect a family’s financial stability and, therefore, long-term health .