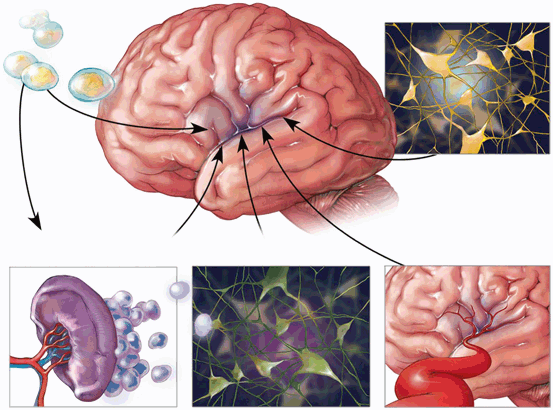
Previous studies have also shown that intravenous infusion of these cultured adipose stem cells can significantly improve smoke exposure-induced emphysema A group of progressive lung disorders characterized by increasing breathlessness.Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
What are the positive effects of stem cell therapy?
- Limitations on ASC ability to differentiate are still uncertain; currently thought to be multi or unipotent.
- Cannot be grown for long periods of time in culture
- Usually a very small number in each tissue making them difficult to find and purify
- Currently there is no technology available to generate large quantities of stem cells in culture
What is the goal of stem cell therapy?
The purpose of Fast Track designation ... CYNK-001 is a cryopreserved allogeneic off-the-shelf cell therapy enriched for CD56+/CD3- NK cells expanded from human placental CD34+ cells.
How effective is stem cell therapy against cancer?
There are several problems:
- Type 1 diabetesis an autoimmune disease. The body is attacking the pancreatic islet cells. ...
- There are no known adult stem cells that reproducibly differentiate into pancreatic islet cells. ...
- Some research has looked into turning ESCs into islet cells. However, the patient would have to be on immunosuppressants fo
How much does stem cell treatment for COPD cost?
There are no plans we know about that cover COPD stem cell therapy. How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy For COPD Cost? Stem cell therapy is quite expensive. The treatment for COPD can cost anywhere between $10,000 and $35,000. There are a few factors that affect the cost of stem cell therapy for COPD.
Do COPD stem cells work?
Stem cells were known to differentiate into a variety of cell types and used to regenerate lung parenchyma and airway structures. Stem cell therapy is a promising therapeutic strategy that has the potential to restore the lung function and improve the quality of life in patients with COPD.
What is the latest treatment for emphysema?
Endobronchial valve surgery This procedure is used to treat people with severe emphysema. With endobronchial valve surgery, the surgeon places tiny Zephyr valves in the airways to block off damaged parts of the lungs. This reduces hyperinflation, allowing healthier sections of your lungs to work more efficiently.
How much does it cost for stem cell treatment for COPD?
Prices are likely to vary among clinics, very few of which, if any, list the treatment costs upfront. A company called DVC Stem offers stem cell therapy in the Cayman Islands and states that the average cost of treatment is between $10,000 and $35,000.
What is the best treatment for emphysema?
Treatment for emphysemastopping smoking immediately and completely – this is the most effective treatment for COPD and emphysema.avoiding other air pollutants.respiratory (pulmonary) rehabilitation programs.oxygen treatment, in advanced cases.medications such as. ... stress management techniques.More items...
Can your lungs heal from emphysema?
Emphysema and COPD can't be cured, but treatments can help relieve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Are they working on a cure for emphysema?
There's no direct cure for emphysema once the lung damage is done, but treatments can relieve symptoms and prevent further lung damage. People with emphysema who smoke should quit smoking immediately.
Can stem cells grow new lungs?
Researchers have revealed that stem cells transplanted into embryonic mice can mature into fully functional lungs, a method which could be developed to grow lungs for humans. Using transplanted stem cells, researchers have grown a pair of fully functional lungs in mouse embryos.
Can lungs regenerate from COPD?
There is no cure for COPD, and the damaged airways don't regenerate. However, there are things you can do to slow progress of the disease, improve your symptoms, stay out of hospital and live longer.
Can lung function be restored with COPD?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease makes it increasingly difficult for a person to breathe. It is not currently possible to cure or reverse the condition completely, but a person can reduce its impact by making some treatment and lifestyle changes.
What is the life expectancy of someone with emphysema?
Because most patients aren't diagnosed until stage 2 or 3, the prognosis for emphysema is often poor, and the average life expectancy is about five years.
How do you reverse emphysema?
Once developed, emphysema can't be reversed. If you have emphysema, your doctor will likely diagnose the condition as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This is an umbrella term for lung diseases that get worse over time.
At what stage of emphysema do you need oxygen?
Stage 4 means your emphysema is advanced and that your breathing is very severely affected. At this stage, smoking or other pollutants have destroyed many of the 300 million tiny air sacs, or alveoli, that help bring oxygen into your body and get rid of carbon dioxide.
What are the two types of stem cells?
There are two types of stem cells. 1. Those that come from a human embryo – obtained by in-vitro fertilization in a laboratory. They cells can take on the function of any part of the body including cells in the lung. 2. Those that come from developed organs and tissues in the human. They are used by the body to repair and replace damaged areas.
What happens when a stem cell divides?
When a stem cell divides, each new cell has the potential either to remain a stem cell or become another type of cell with a more specialized function, such as a muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a lung cell. Types of Stem Cells There are two types of stem cells. 1.
How much does stem cell therapy cost for COPD?
Stem cell therapy for COPD can cost anywhere from $10000 - $35,000 depending on the nature of the treatment and the clinic. When researching stem cell clinics for COPD, it is essential to ask how many cells are included in the treatment protocol and what type of cells the patient will be receiving. Studies have shown that expanded cord tissue-derived mesenchymal cells have incredibly high anti-inflammatory properties and tissue regeneration capabilities. When delivered, intravenously MScs (mesenchymal stem cells) will travel to the lungs (or any area of inflammation) and combat the issue. Currently, Medicare does not cover the cost of stem cell therapy for COPD.
What causes mucus to rise in the bronchial tubes?
Inhaling smoke or other airborne irritants or pollutants can increase mucus production in one's bronchial tubes (bronchi), this can cause inflammation in the form of thickening bronchi walls. Symptoms of increased mucus production in the bronchial tubes include; frequently coughing, resulting in raising mucus (phlegm).
Why does COPD develop?
COPD can develop over long periods or a short period when pollutants are inhaled in excess. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD or Lung Disease) may also be caused by other environmental factors such as; exposure to dust, air pollution, and airborne chemicals. .
Can stem cells help with COPD?
When used in regards to COPD patients, stem cells can repair damaged lung tissue to combat emphysema or chronic bronchitis. Stem cells have natural anti-inflammatory properties, which can clear airways for those with chronic bronchitis. Completed studies have shown the ability to quantify the effects of stem cell therapy.
Can mesenchymal stem cells be used for pulmonary disease?
It is possible to help patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with Mesenchymal Stem Cells. When administered intravenously stem cells have the ability to promote healing and regeneration by excreting messenger cells called "cytokines".
Does Medicare cover mesenchymal stem cells?
When delivered, intravenously MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) will travel to the lungs (or any area of inflammation) and combat the issue. Currently, Medicare does not cover the cost ...
Is there a cure for multiple sclerosis?
Multiple Sclerosis can be managed with treatment, but there is currently no cure for the disease. For that reason, David came to DVC Stem years ago to use the regenerative and anti-inflammatory attributes of stem cells to aid in his fight for fitness.
How do stem cells help with COPD?
Meanwhile, the mechanism of stem cells in the regulation of COPD has been extensively studied. [ 38] First of all, stem cells are cells with multidirectional differentiation potential. Studies have shown that MSCs can differentiate into type I and/or type II alveolar epithelial cells and participate in the repair of lung tissue structure. [ 39] In addition to promoting lung structural repair by differentiating into alveolar epithelial cells, stem cell transplantation also inhibits the apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells. [ 40, 41] Specially, cytokines secreted by MSCs interfere the expression level of apoptotic gene Bax, cleaved-caspase 3, and the antiapoptotic gene Bcl-2 in alveolar epithelial cells. [ 42, 43] It is noted that COPD is the result of an abnormal and persistent inflammatory process that damages the lung architecture. [ 44] Especially, cigarette smoke activates macrophages, neutrophils, and lymphocytes in the lung, causing the release of a variety of inflammatory cytokines that result in COPD progression. [ 45, 46] MSCs have shown the ability to slow the progression of COPD by effectively decreasing the inflammatory response with attenuated classic activated macrophage cytokine release including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 and promoting the release of anti-inflammatory mediators, like IL-10, transforming growth factor-β, indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase 1. [ 18, 35] Another equally important factor for the pathogenesis of COPD is the balance of proteases and antiproteases. The imbalance of protease/antiprotease will cause the degradation of extracellular matrix, [ 47] promote the apoptosis of alveolar wall structure cells, increase the high secretion of mucus and finally lead to the destruction of alveolar wall and the expansion of air space. [ 48] Previous data have shown that stem cells reversed the up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases induced by cigarette smoke. [ 49] Indeed, MSCs can effectively inhibit the progression of COPD by regulating the balance between proteases and antiproteases. [ 50] Additionally, stem cell transplants can also reduce oxidative stress in the lung tissue. [ 51] Excessive oxidative stress will cause cell damage and further aggravate the inflammatory response in the lung by inducing the release of inflammatory cytokines. [ 52]
What are the diseases that stem cells are used for?
At present, stem cells therapies have been applied to numerous diseases like cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, endocrine system diseases, autoimmune system diseases, malignant tumors, hematopoietic system diseases, neurological diseases, and medical cosmetology industry . [ 26 – 29] Of course, many latest findings of stem cells research have also provided new insights into the potential of stem cells to treat a variety of lung diseases, and the stem cell therapy for COPD has gradually become a hot spot.
What is COPD in health?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common respiratory disease that is characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The airway or alveolar abnormalities are usually caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases. [ 1, 2] COPD represents an important public health challenge that is preventable and treatable, but there are still many people who die prematurely from it. COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world and is projected to be the third leading cause of death by 2020. [ 3, 4] The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) defines and classifies COPD based on the severity of airflow obstruction. First, the patients are featured by forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV 1 )/forced vital capacity (FVC) <0.70 and the airflow limitation is not fully reversible. [ 5] Then, according to the percentage of FEV 1 in the estimated value, COPD was classified into four stages. If FEV 1 is ≥80% of the predicted value, the stage is defined as mild; if FEV 1 is ≥50% and <80% of the predicted value, the stage is defined as moderate; if FEV 1 is ≥30% and <50% of the predicted value, the stage is defined as severe; if FEV 1 is <30% of the predicted value, the stage is defined as very severe. [ 6]
What causes COPD in the lung?
The pathogenesis of COPD was extremely complicated, which mainly includes airway inflammation, alveolar structure destruction, and excessive expansion mediated by a variety of causes. [ 7] In general, cigarette smoke and other inhaled particles stimulate the epithelial cells to produce reactive oxygen species, which may induce inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and eosinophils, [ 8] to infiltrate around the airway and cause the imbalance of protease/antiprotease. [ 9] Given that elastin is the main component of connective tissue in the lung parenchyma, [ 10] the imbalance between protease and antiprotease will further cause lung overinflation, expansion, and loss in lung elasticity, thus resulting in emphysema. [ 11, 12]
What is the function of stem cells?
[ 14, 15] The most important function of stem cells is to maintain cell regeneration. Stem cells exist in most tissues of the body from early embryogenesis all the way throughout adult life and are thought to contribute to tissue maintenance and repair. [ 16] In particular, stem cells could give rise to subsequent generations with variable degrees of differentiation capacities, which offers significant potential for the generation of tissue that could potentially replace diseased and damaged areas in the human body. [ 17, 18] According to different differentiation potential, stem cells can be divided into totipotent stem cells, pluripotent stem cells, and unipotent stem cells. [ 19] Totipotent stem cells are a kind of cells that have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into any cell types. They have the potential to differentiate into any of the components of a complete individual, such as embryonic stem cells (ESCs). [ 20] Pluripotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into many types of cells of a specific organ system, without the ability to develop into complete individual. Unipotent stem cells are unidirectionally differentiated stem cells in many tissues that normally produce only one type of cell. [ 21] Currently, pluripotent stem cells are most widely used in clinical research due to their broadly acting anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties, [ 22, 23] such as hematopoietic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and human lung stem cells (hLSCs). [ 24] Among them, MSCs are the most widely studied. MSCs exist in a variety of tissues, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cords. According to the different sources, they are respectively named as bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-MSCs), adipose-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs), and umbilical cords-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs). [ 25]
What are the best treatments for COPD?
Although the standard pharmacological therapies, including bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids and the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, roflumilast, showed modest efficacy in improving pulmonary function, [ 13] to date, no conclusive clinical evidence was found to show that any existing medications for COPD could modify the long-term decline in pulmonary function as well as the mortality. Therefore, the development of novel effective treatments to reverse the decline in pulmonary function and reduce the clinical symptoms of the COPD patients is urgently needed.
Is stem cell transplantation safe?
No matter what type of MSCs, which would be transplanted into the lungs of COPD patients, in what mode of administration, it has been proved to be safe. There were no adverse events associated with stem cell transplantation. In terms of the effect of stem cells on pulmonary function, only 2 clinical trials reported that MSCs could improve pulmonary function (autologous BM-MCs 1 × 10 8 and allogeneic UC-MSCs [1–2] × 10 6 /kg), and the remaining six clinical trials all showed that MSCs had no effect on it. In view of the small number of patients (4 and 5, respectively) enrolled in the two clinical trials that showed a therapeutic effect of stem cells on pulmonary function, further research is needed to see whether MSCs can improve it. In eight clinical trials, six studies suggested that MSCs transplantation could improve patients’ quality of life, while the other two studies on BM-MSCs showed no effect on it. We believe that stem cell transplantation may have the ability to improve patients’ quality of life, perhaps because of the placebo effect, the inhibition of systemic inflammatory response or other extra-cognitive effects. In addition, stem cell transplantation would disrupt the CRP level, which rises briefly 1 to 2 days after transplantation, followed by persistent low expression for several months.
Why are stem cells important?
Due to their regenerative power and ability to function as different types of cells, stem cells can help repair or replace damaged tissue. Scientists are interested in using stem cell therapy in the treatment of several chronic diseases.
What is stem cell?
Stem cells are cells from either embryos or adults that can divide and renew. Although they are not specialized, they can become specialized and ultimately function as cells in various body parts.
What are the best treatments for COPD?
The American Thoracic Society states that people can try several alternative or complementary therapies for COPD. These include: 1 yoga, tai chi, and other breathing exercises 2 acupuncture 3 natural supplements 4 mindfulness training and meditation
What is the purpose of phase 1?
Phase 1: Researchers use this phase to judge the side effects of the treatment and often recruit a small group of healthy people. Phase 2: This phase usually involves a larger group of participants and focuses on the efficacy of the treatment.
Does Thailand have stem cell therapy?
Finally, the Regeneration Center of Thailand offers and supports the use of stem cell therapy to treat COPD and other lung disease s. However, to receive treatment, a person would need to travel to Thailand, adding to the costs of an already potentially expensive procedure.
Is stem cell therapy approved for COPD?
Currently, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved the use of stem cell therapy for the treatment of lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The American Lung Association says that this lack of approval is due to the fact that these treatments have high costs, unproven benefits, ...
Can you get stem cell therapy without insurance?
A person can seek stem cell therapy from unapproved clinics, but the treatment often has high costs with no insurance coverage .
What is the function of stem cells?
The primary function of adult stem cells is to heal and maintain the health of the tissues they are found in. Existing throughout the body, stem cells can renew themselves through cell division, as well as differentiate into specialized cell types.
Why do COPD patients need additional infusions?
After having been exposed to stem cell therapy, many COPD patients are often willing “to receive additional cell infusions if possible, due to a feeling of well-being associated with the injection.”.
Can stem cells reverse COPD?
There is no current cure for the disease, yet recent studies suggest that adult stem cells may have the ability to reverse the effects of diseases involving inflammatory or degenerative parts, like COPD.
What are the regenerative approaches to COPD?
Novel regenerative therapeutic approaches have been investigated with the aim of repairing or replacing the injured functional structures of the respiratory system. We summarized the progress made by regenerative therapies for COPD by analyzing results from both pre-clinical studies and completed clinical trials. These approaches include the application of exogenous stem cells or small molecules to stimulate the regeneration by endogenous lung stem/progenitor cells. Exogenous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been reported to repair the structure and improve the function of the injured respiratory system in COPD models. However, the studies that used MSCs in patients with moderate-to-severe COPD patients did not lead to clear respiratory functional improvements. Exogenous human lung stem cells applied to cryo-injured (CI) lungs of mice have been shown to organize into human-like pulmonary structures, indicating a new property of stem cells that is potentially capable of curing COPD patients. Small molecules like retinoic acid has been shown to lead to regeneration and repair of the damaged lung structures in COPD mouse models probably by activation of endogenous lung stem/progenitor cells. However, retinoic acid or agonists of retinoic acid receptor administered to moderate or severe COPD patients did not improve the density and function of the damaged lung. These novel regenerative approaches have failed in preliminary clinical trials, possibly due to the advanced severity of the disease. Further work should be done to develop the current regenerative approaches for curing patients at different stages of COPD. We suggest that some modifications of the approach in the clinical studies may lead to more successful outcomes of regenerative therapy for COPD.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
The current mainstream medication for COPD are bronchodilators, which are either used on their own or in combination with inhaled corticosteroids. These bronchodilators transiently relieve the symptoms of dyspnea; however, they do not ameliorate the deterioration in lung function (6). According to the “Towards a Revolution in COPD Health” (TORCH) phase III clinical trial, the combined application of bronchodilators, including beta2-agonists and glucocorticosteroids, slightly improved the function of the lung (FEV1increased by 0.092 liter) in moderate-to-severe COPD patients (18). The recently reported phase III clinical trial “TRILOGY” was designed to combine corticosteroids, muscarinic antagonists and beta2-agonists in a single inhaler for moderate-to-severe COPD patients. This therapy was reported to improve the FEV1by 0.081 liter (19). To sum up, no drug is yet available that can stop the deterioration of functional structures and improve significantly the function of respiratory system in COPD patients (4).
How many people will die from COPD in 2020?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major chronic respiratory disease affecting over 380 million people worldwide (1). It has been estimated that COPD will be the third highest cause of global death by 2020 (2,3). Lung parenchymal damage (emphysema) and severe airflow obstruction are the typical pathophysiological features of COPD ...
What is regenerative therapy?
The regenerative approaches have included extrinsic cell therapy such as the infusion of exogenous stem cells to repair the damaged structure of the respiratory system and intrinsic cell therapy such as the administration of small molecules to stimulate the endogenous lung stem/progenitor cells for regeneration and replacement of the damaged structures) (21). This is the first comprehensive review aimed to discuss more effective stem cell treatment solutions to COPD based on the experience learnt from current completed pre-clinical studies and clinical trials.
What are the pathological changes in COPD?
The pathological changes in COPD include chronic inflammation in the respiratory system and alveolar structural degeneration or destruction (4,6). Chronic inflammation was shown as a high count of inflammatory cell types like neutrophils in sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid (7), and macrophages in lung parenchyma (8). Increased neutrophils in sputum was associated with greater airflow obstruction in advanced COPD patients (9). Neutrophils and macrophages can release inflammatory mediators (such as cytokines and oxygen radicals) and enzymes (like protease) in the airways and lung parenchyma (10). Interleukin (IL)-1β is one major cytokine which involves in initiation and persistence of inflammation (11). Sputum neutrophils and alveolar macrophages from smokers can produce more IL-1β than those from non-smokers (12). IL-1β chronically produced in the respiratory system of mice caused lung inflammation and enlargement of airspaces (13). Protease like matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) can mediate destruction of elastin which is the connective structure in lung parenchyma, and lead to airspace enlargement (14,15). Oxidative stress in COPD may amplify inflammatory response, impair the function of protease inhibitor like secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI), and enhance elastin-breakdown by protease in lung parenchyma (16). In sum, inflammatory mediators together with enzymes which were produced by inflammatory cells caused the pathological changes in COPD (17).
How long after transplantation did AD-MSCs decrease mean linear intercept?
One week after transplantation, the AD-MSCs group had decreased mean linear intercept, and reduced caspase-3 activity
How many injections in the last 8 weeks of CS exposure?
3×105; i.v.; four injections in the last 8 weeks of CS exposure; once every 2 weeks
