
Medication
The most serious and deadly form of skin cancer is malignant melanoma. It is the leading cause of death from skin cancer because it is aggressive and fast growing and readily spreads (metastasizes) to other parts of the body, often quickly.
Procedures
This means 92 of every 100 people diagnosed with melanoma will be alive in 5 years. In the very early stages the 5-year survival rate is 99%. Once melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the 5-year survival rate is 63%.
Therapy
almost all people (almost 100%) will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed; around 90 out of every 100 people (around 90%) will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis; more than 85 out of every 100 people (more than 85%) will survive their melanoma for 10 years or more after they are diagnosed
Nutrition
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Is melanoma a deadly cancer?
How long do you have to live with melanoma?
What is the life expectancy of melanoma?
Why is melanoma so deadly?

What is the success rate of melanoma treatment?
5-year relative survival rates for melanoma skin cancerSEER stage5-year relative survival rateLocalized99%Regional68%Distant30%All SEER stages combined93%Mar 1, 2022
Can melanoma be successfully treated?
During its early stages, melanoma can be successfully treated with surgery alone. Other types of cancer treatment are effective for more advanced stages of melanoma.
What percentage of people with melanoma survive?
Survival for all stages of melanoma almost all people (almost 100%) will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed. around 90 out of every 100 people (around 90%) will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Is melanoma a death sentence?
Metastatic melanoma was once almost a death sentence, with a median survival of less than a year. Now, some patients are living for years, with a few out at more than 10 years.
What happens after melanoma is removed?
After you finish treatment, your dermatologist (or oncologist) will still want to see you regularly. Melanoma can return or spread after treatment. If this happens, it's most likely to occur within the first 5 years. During the first 5 years, you'll need thorough check-ups.
Can you live 10 years with melanoma?
This means 92 of every 100 people diagnosed with melanoma will be alive in 5 years. In the very early stages the 5-year survival rate is 99%. Once melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the 5-year survival rate is 63%. If melanoma spreads to other parts of the body, the 5-year survival drops to just 20%.
Is melanoma always fatal?
Melanoma is usually curable when detected and treated early. Once melanoma has spread deeper into the skin or other parts of the body, it becomes more difficult to treat and can be deadly. The estimated five-year survival rate for U.S. patients whose melanoma is detected early is about 99 percent.
Are melanoma survival rates improving?
Overall, the melanoma mortality rate declined by 17.9% during the 4-year period. The reduction in deaths was seen in nearly every age group, but was greatest in men aged 50 and older.
What are the treatment options for melanoma?
Options include: Surgical removal of the melanoma. Immunotherapy. Targeted therapy. Chemotherapy. Radiation.
How to treat melanoma early?
Tumors discovered at an early stage are confined to the upper layers of the skin and have no evidence of spread. These melanomas are treated by excisional surgery. Usually, this is the only treatment required.
How does immunotherapy help with cancer?
Immunotherapies boost the body’s ability to fight melanoma and other cancers by using synthetic versions of natural immune system proteins, or by enabling the release of cells that attack tumors. These therapies are effective when used alone or in combinations.
What is advanced melanomas?
Advanced melanomas are those that have spread beyond the original tumor, most often reaching the lymph nodes and/or distant organs and becoming more difficult to treat. In recent years, new immunotherapies and targeted therapies have achieved positive results in many patients with stage III and stage IV melanoma.
What to do if you have melanoma in your lymph node?
If melanoma is found in the sentinel node, your physician may examine the rest of the nodes in this lymphatic basin and remove any that contain cancer cells. After surgery, additional treatment may be recommended, including immunotherapy or radiation to decrease the chance that the melanoma will come back.
How long does it take for a melanoma to be removed?
Surgeons may, under certain circumstances, recommend removal of melanoma by Mohs surgery. The procedure is done in stages over a few days to remove all of the cancer cells in layers while sparing healthy tissue and leaving the smallest possible scar. One layer at a time is removed and examined until the margins are cancer-free. New advances in this technique make it easier for the surgeon to spot melanoma cells in the margins.
What is the use of immunotherapy to destroy cancer cells?
Pioneering breakthroughs in immunotherapy — the use of medicines to stimulate a patient’s immune system to destroy cancer cells — have led to significant progress in treating patients with advanced melanoma.
What is the best treatment for stage IV melanoma?
Chemotherapy can help some people with stage IV melanoma, but other treatments are usually tried first. Dacarbazine (DTIC) and temozolomide (Temodar) are the chemo drugs used most often, either by themselves or combined with other drugs. Even when chemotherapy shrinks these cancers, the cancer usually starts growing again within several months.
How to treat melanoma on arm?
For melanomas on an arm or leg, another option might be isolated limb perfusion or isolated limb infusion (infusing just the limb with chemotherapy ). Other possible treatments might include targeted therapy (for melanomas with a BRAF or C-KIT gene change), immunotherapy, or chemotherapy.
What to do if SLNB found cancer?
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant (additional) treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs (if the melanoma has a BRAF gene mutation) might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back.
What is stage 0 melanoma?
It is usually treated by surgery (wide excision) to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope.
What is the best treatment for cancer at the edges of the sample?
Some doctors may consider the use of imiquimod cream (Zyclara) or radiation therapy instead of surgery, although not all doctors agree with this.
Can stage 3 melanoma be cured?
Other possible treatments might include targeted therapy (for melanomas with a BRAF or C-KIT gene change), immunotherapy, or chemotherapy. Some people with stage III melanoma might not be cured with current treatments, so they may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial of newer treatments.
Does melanoma spread to lymph nodes?
The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
How is melanoma skin cancer treated?
Based on the stage of the cancer and other factors, your treatment options might include:
How to learn more about clinical trials?
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Depending on your options, you may have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors may include: 1 A dermatologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the skin 2 A surgical oncologist (or oncologic surgeon ): a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer 3 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy 4 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures . Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
What are the things to consider when making a decision about cancer treatment?
Some important things to consider include: Your age and overall health. The stage (extent) of your cancer.
What is the treatment for melanoma?
Because surgery (aka surgical removal) tends to be the most effective way to do this, a patient who has melanoma will often have surgery.
Can melanoma spread to the brain?
Melanoma can behave differently on the head and neck. Here’s what a treatment plan may look like. When melanoma spreads to the brain. Attacking the cancer with different types of treatment can improve how well each works.
Why should personalized treatment be considered for melanoma patients?
Depending on the molecular features of the patients and tumors, as well as the responses to therapy, personalized treatment should be considered for melanoma patients, in order to achieve better clinical benefits. Further research is necessary to explore oncogenic pathways and the TME potential in the treatment of melanomas.
What was the first drug approved for melanoma?
FDA-approved drugs for melanoma treatment. Dacarbazine was the first drug approved, in 1974, followed by interferon α-2b, interleukin-2, and ontak in the 1990s. Between 2011 and 2015, 10 therapies were approved, including selective inhibitors, antibodies, and combined targeted therapies.
What are Tregs in melanomas?
Tregs suppress activated Teffs and can inhibit antitumoral immune responses. 66, 67 In melanomas, Tregs appear in peripheral circulation and in the TME and seem to be associated with poor clinical outcome. 68 The therapeutic strategy consists in the suppression of Tregs, thus increasing the antitumoral immunity. Ontak, approved by the FDA in 1999, 69 is the fusion of IL-2 protein with diphtheria toxin that selectively eliminates Tregs expressing IL-2 receptor from the peripheral blood. 70 A Phase II trial in stage IV melanoma patients showed 16.7% of partial responses, 5.0% stable disease, and 15.0% mixed responses. 71 Conversely, another study reported that metastatic melanoma patients administered with ontak showed no objective clinical response, no regression of the disease, and no elimination of regulatory T lymphocytes. 72
What are the mutations in melanoma?
These oncogenic mutations may be associated with melanoma cell proliferation and a malignant phenotype. 118 The targeted therapy approach uses small molecule inhibitors or antibodies that affect these mutated proteins, which are important for the progression of the disease ( Figure 3 ).
What is the most aggressive form of skin cancer?
Melanoma represents the most aggressive and the deadliest form of skin cancer. Current therapeutic approaches include surgical resection, chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, immunotherapy, biochemotherapy, and targeted therapy. The therapeutic strategy can include single agents or combined therapies, depending on the patient’s health, stage, and location of the tumor. The efficiency of these treatments can be decreased due to the development of diverse resistance mechanisms. New therapeutic targets have emerged from studies of the genetic profile of melano cytes and from the identification of molecular factors involved in the pathogenesis of the malignant transformation. In this review, we aim to survey therapies approved and under evaluation for melanoma treatment and relevant research on the molecular mechanisms underlying melanomagenesis.
What is nivolumab used for?
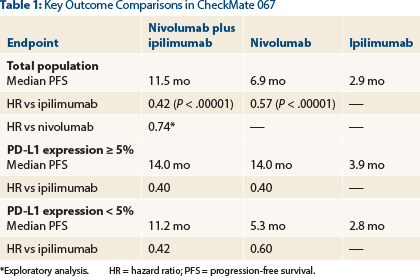
82 Nivolumab was approved (2014) by the FDA for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. 83 The blockade of the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands mediates immune responses and induces (preclinical) antitumor activity that reduces tumor progression. 84 Nivolumab, with a PFS of 6.9 months, seems to be more efficient than monotherapies with ipilimumab, which display a median PFS of 2.9 months, or chemotherapy, with a median PFS of 2.2 months. 84 The combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab achieved a median PFS of 11.5 months, superior than monotherapies, especially in patients with PD-L1 negative tumors. 84, 85
What is ECT treatment?
ECT is a technique that combines the use of cytotoxic drugs, bleomycin and cisplatin, with high-intensity electric pulses, which facilitates drug delivery into the cells. 24, 25 ECT was reported to be effective for the treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous nodules of melanoma. 26, 27 A study of the European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy reported an overall response of 85% and no major negative AEs were observed. 27 Another remarkable aspect of ECT is that usually the treated nodules do not recur in the treated area, possibly because the treatment destroys the lymphatic stream; however, more studies are needed in this regard. 24
What is the best treatment for melanoma?
The currently approved schedule is first to surgically remove the melanoma tumors, and then give targeted therapy or immunotherapy post-operatively (known as adjuvant therapy). This approach halves the risk of melanoma recurrence. However it's impossible to tell on an individual level whether the drug treatment is working.
Which country has the highest melanoma rate?
This study is the first large analysis of immunotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting in any cancer, results of which should pave the way for the use of immunotherapy pre-operatively in many other cancer types. Australia has the highest melanoma rates in the world with one person diagnosed every 30 minutes, and it is estimated 1300 people will die from the disease in Australia this year.
Why is neoadjuvant therapy important?
In addition to training the immune system to work more effectively against melanoma, neoadjuvant therapy also enables a clinician to assess early on if a patient is responding to a particular treatment and decide on an alternative plan if needed. It can also make surgery less complex.
How long does it take for stage 3 immunotherapy to work?
Researchers found that giving Stage III patients a short course of pre-operative targeted immunotherapy was effective, and the stronger a patient's response to that treatment in the first six to nine weeks, the greater the likelihood their disease would not recur after surgery.
Why is immunotherapy more effective than surgery?
Data from the study suggests that immunotherapy may work more effectively when given before, rather than after surgery, due to the presence of the bulky tumor provoking an immune response. The concept is similar to sniffer dogs being trained by exposure to illegal drugs—if they know what they're searching for, the more effective they are at detection.
Is it safe to take melanoma medication before surgery?
In what is being hailed as one of the biggest breakthroughs in melanoma treatment since the advent of immunotherapy, a new study has revealed that drug treatment before surgery is effective in prevent ing deadly spread of the disease.
Is neoadjuvant therapy for stage III patients currently approved?
Associate Professor Alex Menzies, MIA Oncologist and study first author, said; "Although neoadjuvant therapy for Stage III patients is not currently an approved standard of treatment, we anticipate that this will ultimately change following the very promising clinical trial results."
How has survival improved for people with melanoma?
In the past decade, survival rates for people with advanced-stage melanoma have dramatically improved, in large part because of targeted therapies and immunotherapy. These treatments are the new standards of care for advanced stages of melanoma. However, researchers are still trying to learn which therapies are most likely to help which patients.
How do scientists prevent melanoma resistance?
Scientists are working to prevent that resistance by finding new ways to give and combine existing treatments. Studies are also underway to develop therapies that target other genes and proteins associated with melanoma cells.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapies are designed to identify and target cancer cells, mostly without harming normal cells. Many melanoma cancer cells have mutations in the BRAF gene that help the cancer grow.
What is it called when melanoma spreads?
When that happens, it’s known as advanced-stage melanoma. To treat advanced-stage melanoma, doctors often prescribe other treatments with or instead of surgery.
What is the purpose of immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy helps your natural immune system to attack cancer cells.
Do T cells help with melanoma?
They help the immune system’s T cells recognize and attack melanoma cells. Studies have found these medications improve survival rates for people with advanced-stage melanoma, report the authors of a review article in the American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
Does immunotherapy work for everyone?
But immunotherapy doesn’t work for everyone. According to a research letter published in the journal Nature Medicine, only a portion of people with melanoma benefit from treatment with checkpoint inhibitors. More research is needed to learn which people are most likely to respond well to this treatment.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Treatment
- The best treatment for your melanoma depends on the size and stage of cancer, your overall health, and your personal preferences.
Terminology
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Prevention
- A cancer diagnosis can change your life forever. Each person finds his or her own way of coping with the emotional and physical changes cancer brings. But when you're first diagnosed with cancer, sometimes it's difficult to know what to do next. Here are some ideas to help you cope: 1. Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care.Ask your doctor about your c…
Medical uses
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you notice any skin changes that concern you. Depending on your situation and the outcome of any tests, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in skin diseases (dermatologist) or to a doctor who specializes in cancer treatment (oncologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea t…
Prognosis
Benefits
Research
Advantages
Clinical significance
Example