
Apart from causing different hydraulic conditions in the plant, increased flow due to rain or snow-melting, changes the properties of the incoming wastewater which affects process performance and effluent quality, especially the particle removal efficiency.
Full Answer
How do waste water treatment plants affect the river ecosystem?
Oct 29, 2015 · When a river receives waste water from a treatment plant, the plant's efficiency is revealed. A new study group has observed that the waste water from treatment plants significantly influences the...
How does a wastewater treatment system work?
The primary purpose of the raw water-settling pond is to allow much of the sand and debris to naturally settle out of the water before it is pumped to the water treatment plant. Secondarily, the pond allows for some capacity in the event that the river water is muddy or if an accident on U.S. Highway 50 spills contaminants into the Arkansas River.
What is the main function of a water treatment plant?
Water treatment plants are vulnerable to the impacts of SARS-CoV-2 contaminated wastewater; however, receiving surface water sources with upstream wastewater impacts are the most susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 contamination during and after the COVID-19 outbreak. However, up to date, there is no infectious SARS-CoV-2 case detected from drinking water supplies, thus it can …
Why choose our municipal River and lake water treatment plant?
Jun 18, 2018 · So wastewater-treatment plants are located on low ground, often near a river into which treated water can be released. If the plant is built above the ground level, the wastewater has to be pumped up to the aeration tanks (item 3). From here on, gravity takes over to move the wastewater through the treatment process. 3. Aerating. One of the ...

How do water treatment plants affect rivers?
When a river receives waste water from a treatment plant, the plant's efficiency is revealed. A new study group has observed that the waste water from treatment plants significantly influences the river ecosystem. As the quantity of organic matter is bigger, the activity of the organisms that feed on it increases.Oct 29, 2015
What is the effect of water treatment?
The discharge of effluent from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) has major detrimental effects on the health of aquatic ecosystems. WWTP outfall can deposit large amounts of organic matter and nutrients into receiving waterways.May 1, 2008
What are the negative effects of wastewater treatment?
Effects include reduced reproductive capacity and growth. Acute impacts can also occur with high ammonia levels. The toxic impacts of wastewater discharges can be seen a large distance away from the treatment plant outlets. Toxic effluents can still do harm 10-20 km away from the discharge point.
How do wastewater treatment plants pollute water?
Wastewater contains nitrogen and phosphorus from human waste, food and certain soaps and detergents. Once the water is cleaned to standards set and monitored by state and federal officials, it is typically released into a local water body, where it can become a source of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution.Mar 1, 2021
What happens at a water treatment plant?
As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What are the three main purposes of water treatment?
Water treatment is a process involving different types of operations (physical, chemical, physicochemical and biological), the aim of which is to eliminate and/or reduce contamination or non-desirable characteristics of water.
How does water treatment affect the environment?
Water treatment reduces the volume of waste that is released into the ecosystem. When wastewater is treated, the quantity of waste that is released into the environment is cut down significantly resulting into overall improvement in the environment's status.Oct 3, 2021
Are sewage treatment plants good for the environment?
It removes various solids, which includes everything from rags and sticks to sand and smaller particles found in wastewater. It reduces organic material and pollutants by the controlled action of helpful bacteria and other microorganisms that consume organic matter in wastewater.Apr 13, 2022
Do sewage treatment plants cause pollution?
Treatment of wastewater also releases emissions to air mostly in the form of carbon dioxide and methane.Apr 11, 2014
How is wastewater treated in a wastewater treatment plant?
Primary Treatment As wastewater enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen. This removes large floating objects, such as rags and sticks, which clog pipes or damage equipment. Once the wastewater has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.Mar 6, 2020
What is the importance of wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment protects humans and ecosystem Wastewater contains elements toxic to humans and the ecosystem. Wastewater treatment facilities help to purify the water and eliminate situations like what is currently seen in developing countries.May 26, 2021
What is the purpose of septic systems and wastewater treatment plants?
Septic systems are underground wastewater treatment structures, commonly used in rural areas without centralized sewer systems. They use a combination of nature and proven technology to treat wastewater from household plumbing produced by bathrooms, kitchen drains, and laundry.Jul 2, 2021
What is the Cajon City water treatment plant?
The Cañon City Water Treatment Plant is a conventional surface water treatment plant that diverts water from the Arkansas River to produce drinkable (potable) water, which meets or exceeds all Environmental Protection Agency ( EPA) Safe Drinking Water Act and the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment Primary Drinking Water Standards.
How is potable water run?
Potable water is run backwards through the filters releasing the entrapped particulates that are collected in drain troughs. The backwash water is sent to the Backwash Recovery Pond and, after a settling process, the backwash water is returned to the raw water settling pond for re-use.
What is the process of flocculation?
The flocculation process promotes contact between the floc particles and the particulates (sediment) in the water. Generally, these contacts or collisions between particles result from gentle stirring created by a mechanical or hydraulic means of mixing.
How does sedimentation work?
Sedimentation is accomplished by decreasing the velocity of the water being treated below the point where it can transport settleable suspended material, thus allowing gravitational forces to remove particles held in suspension. When water is almost still in sedimentation basins, settleable solids will move toward the bottom of the basin. This process of sedimentation removes almost ninety percent of the solids in the water. The clearer water on the surface is collected in the launder tubes that direct the water to the filter gallery to remove the remaining ten percent of solids.
How does the pre sedimentation process work?
The raw water is delivered to the headworks of the water treatment plant where the first of 5 major unit water treatment processes start the treatment to make the water safe to drink. The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What is the first chemical added to water?
The first chemical added is chlorine dioxide and it is an oxidant used to break down naturally occurring organic matter such as decaying leaves and other plant material. A chemical coagulant known as aluminum sulfate is used as the primary coagulant. A polymer, a long chain of synthetic organic compounds, is also added to the water as a coagulant aid to help in strengthening the primary coagulant’s bonding chains. The coagulants are added at the rapid mix unit; this is a unit that creates turbulent mixing energies to help thoroughly disperse the chemical coagulants into the raw water and to begin the coagulation process. The coagulants that cause very fine particles to clump together into larger particles that can then be removed later in the treatment process by settling, skimming, draining or filtering.
What is a PLC in water treatment?
Devices known as programmable logic controllers ( PLCs) that are networked together with other PLCs control the water treatment plant and the treatment processes. The PLCs track over 1,500 signals or data points to ensure optimized treatment. The computer signals and data are collected by the Supervisory Collection and Data Acquisition ( SCADA) system and provide information to the Operator on shift whenever any item requires Operator intervention.
When was the first potable water treatment plant?
Already in 2001, the first potable water treatment plant using a MIEX® -DOC process was launched in Australia. In this plant, the MIEX ® -DOC step was introduced prior to conventional treatment, and a significant improvement in water quality was observed.
What is centralized water treatment?
Centralized water treatment plants are based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water.
What is the water district in Orange County?
Orange County Water District (OCWD). OCWD located between Los Angeles and San Diego counties in southern California manages the groundwater basin that supplies about 3.0 × 10 8 m 3 per year potable water to a population of more than 2 million.
What is the water used in CMF-S?
Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals.
What is the Bendigo water treatment plant?
I. Bendigo water treatment plant (BWTP). The 12.54 × 10 4 m 3/day (33 MGD) BWTP has been producing drinking water for nearly 1 million people in central Victoria, Australia since 2002. It is one of the largest if not the largest MF plant in the world. The plant combines submerged microfiltration (CMF-S), ozonation and biological activated carbon (BAC) to treat a variable and difficult raw water. Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals. The coagulant dosage is typically 5–6 mg/l. The coagulant precipitate is removed by MF. The coagulant/CMF-S process removes up to 15% of the dissolved organic carbon.64
What is water treatment automation?
Automation of water treatment plant involves the control system opening and closing valves and starting and stopping equipment in predefined sequences to complete specific tasks or to provide the desired process plant output. To achieve these results the automation system relies on signals from correctly selected and placed instruments, devices such as actuators and motor control circuits and reliable control logic. The degree of automation to be used is fundamental to developing an automation system.
What is make up water treatment?
Make up water treatment. Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.
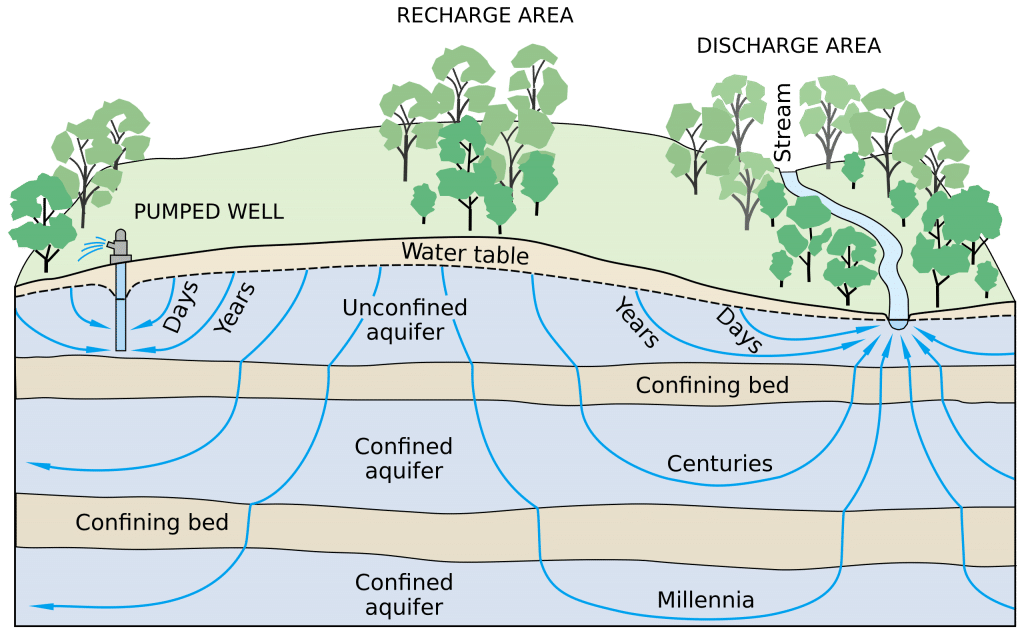
Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
Household Water Treatment
- Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1. Remove specific contaminants 2. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3. Improve the taste of drinking water Household water treatment systems are composed of two categories: point...