Medication
Traditionally, therapy for impending neuroblastoma-associated visual loss includes radiation and/or high dose steroids to decompress the optic nerve(s) from an optic neuropathy. High dose steroids have been used empirically to decrease inflammation, lower the perineural pressure, and prevent neuronal injury.
Procedures
The types of treatment used for neuroblastoma can include: Neuroblastoma Surgery. Chemotherapy for Neuroblastoma. Radiation Therapy for Neuroblastoma. High-Dose Chemotherapy/Radiation Therapy and Stem Cell Transplant for Neuroblastoma. Retinoid Therapy for Neuroblastoma. Immunotherapy for Neuroblastoma.
Therapy
Late effects after neuroblastoma treatment can include: Hearing loss Problems with bones and muscles, like scoliosis (curving of the spine) Thyroid problems Problems with growth and development Fertility problems Neurological problems Second cancers, including leukemia Emotional or psychological issues
Nutrition
This means they grow out of control and replicate. Neuroblastoma can affect any part of the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is part of the autonomic nervous system, which the body uses to regulate many of its most crucial functions.
See more
What are the treatment options for neuroblastoma-associated visual loss?
What is the best treatment for neuroblastoma?
What are the late effects of neuroblastoma treatment?
How does neuroblastoma affect the nervous system?

Does neuroblastoma affect the eyes?
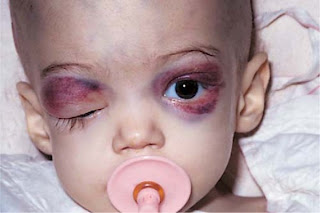
Other signs and symptoms that may indicate neuroblastoma include: Lumps of tissue under the skin. Eyeballs that seem to protrude from the sockets (proptosis) Dark circles, similar to bruises, around the eyes.
Can neuroblastoma cause blindness?
Although neuroblastoma commonly causes blindness by metastasis to the orbit, it rarely causes bilateral blindness from intracranial compression of the optic nerves. This is the first report of bilateral blindness as the presenting feature.
What are the long term effects of neuroblastoma?
Sometimes this syndrome improves or goes away after the neuroblastoma is treated, but some children might have longer-term problems such as learning disabilities, delays in muscle development, language problems, and behavioral problems.
How does cancer affect vision?
Symptoms of eye cancer can include: shadows, flashes of light, or wiggly lines in your vision. blurred vision. a dark patch in your eye that's getting bigger.
Can you go blind from chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy drugs, as well as hormonal and targeted therapies, can indeed cause eye and vision problems. Steroids and other drugs used to manage other treatment side effects can also affect your eyes.
What part of the brain affects eyesight?
Occipital lobe. The occipital lobe is the back part of the brain that is involved with vision.
Can neuroblastoma spread to the brain?
Relapsed neuroblastoma metastasizes to the CNS as one cause of death. The overall incidence of brain metastasis in neuroblastoma after treatment ranges from 1.7% to 11.7% [3].
What are the chances of neuroblastoma coming back?
It is estimated that as many as 50-60% of children with high-risk neuroblastoma will eventually suffer a relapse. In children with intermediate- or low-risk neuroblastoma, relapses occur in only 5-15% of cases.
Does neuroblastoma run in families?
Most cases of neuroblastoma (NBL) occur sporadically, affecting individuals who have no family history of the disease. However, in 1-2 percent of cases, a susceptibility to develop neuroblastoma can be inherited from a parent.
Does blurry vision from chemo go away?
Usually, the effects are temporary and will go away when you stop taking the drug. But some effects may be long term. Changes to your eyesight and eyes can be uncomfortable and upsetting. These changes can make your usual activities hard to do and as a result, affect your quality of life.
Does medication blurred vision go away?
Medications can have a variety of effects on your eyes, ranging from minor, temporary issues such as blurred vision to permanent damage.
What can cause blurred vision?
Blurred vision can be caused by eye conditions, including:difficulty focusing your eyesight, such as with near-sightedness or far-sightedness.astigmatism (when the surface of the eye isn't curved properly)presbyopia (when your eyes find it harder to focus as you age)dry eye syndrome.cataracts.glaucoma.More items...
What to do if your child has neuroblastoma?
Treating Neuroblastoma. If your child has been diagnosed with neuroblastoma, the cancer care team will discuss treatment options with you. It’s important to consider both the benefits of each treatment option and the possible risks and side effects.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is neuroblastoma surgery?
Surgery is used to treat neuroblastoma that has not spread to other parts of the body. As much of the tumor as is safely possible is removed. Lymph nodes are also removed and checked for signs of cancer.
What are the symptoms of neuroblastoma?
Signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma include a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest or bone pain. Tests that examine many different body tissues and fluids are used to diagnose neuroblastoma. A biopsy is done to diagnose neuroblastoma. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
How do you know if you have neuroblastoma?
Signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma include a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest or bone pain. The most common signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma are caused by the tumor pressing on nearby tissues as it grows or by cancer spreading to the bone.
Why do they remove cells during a biopsy?
Cells and tissues are removed during a biopsy so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. The way the biopsy is done depends on where the tumor is in the body. Sometimes the whole tumor is removed at the same time the biopsy is done.
Where does neuroblastoma occur?
Neuroblastoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in neuroblasts (immature nerve tissue) in the adrenal glands, neck, chest, or spinal cord. Neuroblastoma often begins in the nerve tissue of the adrenal glands. There are two adrenal glands, one on top of each kidney in the back of the upper abdomen.
Can radiation therapy help with neuroblastoma?
Radiation therapy for children whose disease has gotten worse after chemotherapy and second-look surgery. Treatment for recurrent neuroblastoma that comes back in other parts of the body may include the following: Treatment as for newly diagnosed high-risk neuroblastoma, for children older than 1 year.
Can neuroblastoma be passed on to a child?
Gene mutations that increase the risk of neuroblastoma are sometimes inherited (passed from the parent to the child). In children with a gene mutation, neuroblastoma usually occurs at a younger age and more than one tumor may form in the adrenal glands or in the nerve tissue in the neck, chest, abdomen, or pelvis.
What is the stage of neuroblastoma?
The INRG stages of neuroblastoma are: Stage L1: This is the stage with the lowest risk.
What causes neuroblastoma to grow?
The cells become abnormal and continue growing and dividing, forming a tumor. A genetic mutation (a change in the neuroblast’s genes) causes the cells to grow and divide uncontrollably.
How to diagnose neuroblastoma in unborn baby?
Sometimes, providers diagnose neuroblastoma in unborn babies during a prenatal ultrasound. To diagnose neuroblastoma, your child’ s provider will do a physical and neurological examination. A neurological exam checks your child’s nerve function, reflexes and coordination.
How many children are diagnosed with neuroblastoma every year?
Every year in the United States, about 800 children are diagnosed with neuroblastoma. Neuroblastoma almost always develops before age 5. It can occur in babies before they are born. Neuroblastoma is very rare in children over age 10.
What is the name of the cancer that develops in the nerves?
Neuroblastoma . Neuroblastoma is a rare cancer that develops in nerve tissue. It usually affects kids under age 5. Symptoms include fatigue, decreased appetite and a lump in the chest, neck or belly. Treatment can include chemotherapy, surgery and radiation. The outlook varies depending on the stage of the disease, ...
Where does neuroblastoma occur?
Neuroblastoma is a type of pediatric cancer that develops in the nervous system of babies and young children. Neuroblastoma grows in immature nerve tissue (neuroblasts). It usually affects neuroblasts in the adrenal glands (small organs that sit on top of the kidneys). The adrenal glands make hormones that control automatic body functions, ...
Is neuroblastoma inherited?
But about 98% to 99% of the time, neuroblastoma is not inherited (or, passed down in families). Children born with other congenital anomalies (birth defects) may have a higher risk of developing neuroblastoma.
What are the side effects of neuroblastoma?
Depending on the treatment and other factors, late effects after neuroblastoma treatment might include: 1 Hearing loss 2 Problems with bones and muscles, like scoliosis (curving of the spine) 3 Thyroid problems 4 Problems with growth and development 5 Fertility problems 6 Neurological (nervous system) problems 7 Second cancers, including leukemia 8 Emotional or psychological issues
What are the symptoms of neuroblastoma?
In very rare instances and for unknown reasons, in some children with neuroblastoma the body’s immune system attacks the child’s normal nerve tissue, which can lead to symptoms such as rapid eye movements, muscle spasms, and lack of coordination.
What is the term for neuroblastoma that goes away?
This is called opsoclonus myoclonus syndrome. Sometimes this syndrome improves or goes away after the neuroblastoma is treated, but some children might have longer-term problems such as learning disabilities, delays in muscle development, language problems, and behavioral problems.
What are the effects of neuroblastoma on children?
Depending on the treatment and other factors, late effects after neuroblastoma treatment might include: Hearing loss.
Can neuroblastoma be treated into adulthood?
Because of major advances in treatment, most children treated for neuroblastoma are now surviving into adulthood.
Is neuroblastoma a late effect?
Neuroblastoma survivors are at risk for several possible late effects from their treatment. It’s important to discuss what these possible effects might be with your child’s medical team. After treatment, the cancer care team will create a Survivorship Care Plan describing the treatments given and what that tells you about your child's risk ...
What happens after neuroblastoma treatment?
Sometimes, after treatment for neuroblastoma has ended, children may experience other health issues as a result . The risk of developing certain late effects varies depending on a variety of factors, including the specific drugs used during treatment, the dose of those drugs, and the age of the child during treatment.
How to treat neuroblastoma in children?
Treatment for neuroblastoma may include: Surgery: This involves an operation to remove as much of the tumor as possible. If the tumor has not spread through the body, surgery could be the only treatment a child may need. Chemotherapy: This involves using a mixture of drugs to kill the cancer cells.
What part of the nervous system does neuroblastoma affect?
Neuroblastoma can affect any part of the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is part of the autonomic nervous system, which the body uses to regulate many of its most crucial functions. Learn about the autonomic and sympathetic nervous systems here. Most neuroblastomas start in the abdomen.
How rare is neuroblastoma?
Neuroblastoma is a very rare type of cancer, but it most commonly affects children. It makes up approximately 6% of all cancers in children. According to the American Cancer Society, there are about 800 new cases of neuroblastoma each year in the United States.
How old is a child when they get neuroblastoma?
Neuroblastoma mostly affects babies or very young children. It usually does not affect children over the age of 10. Most cases involve children between 1 and 2 years old. This cancer has usually begun to spread by the time doctors diagnose it. However, in younger children, the cancer cells can sometimes die by themselves.
Can neuroblastoma cells die by themselves?
However, in younger children, the cancer cells can sometimes die by themselves. At times, the cells can also become benign, and therefore no longer harmful. This article will explain what neuroblastoma is and describe its symptoms, stages, causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
Can neuroblastoma cause late effects?
The risk of developing certain late effects varies depending on a variety of factors, including the specific drugs used during treatment, the dose of those drugs, and the age of the child during treatment. A neuroblastoma diagnosis can be a very distressing experience for a child and caregiver.