
As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
What is the first step in sewage treatment?
- Step 1: Screening and Pumping. The incoming wastewater passes through screening equipment where objects such as rags, wood fragments, plastics, and grease are removed.
- Step 2: Grit Removal.
- Step 3: Primary Settling.
- Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Step 5: Secondary Settling.
- Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
- Sludge Treatment.
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
There are four major processes under the tertiary treatment:
- Solids removal
- Biological nitrogen removal
- Biological phosphorus removal
- Disinfection.
Where does your sewage go and how is it treated?
The answer is yes, but not in the way you might think. In the U.S. sewage first goes to treatment facilities where it’s processed into liquid and solids. After the liquid is cleaned (filtration and chlorine) it can be reintroduced into our rivers and oceans.
How expensive is sewage treatment?
Dolgeville’s wastewater treatment plant’s digester needs an emergency cleaning, and the project will be an expensive one. Village officials estimate the total cost could run to $200,000 or more. “It must be done. We have no other choice but to bond for it,” said Dolgeville Mayor Mary Puznowski.
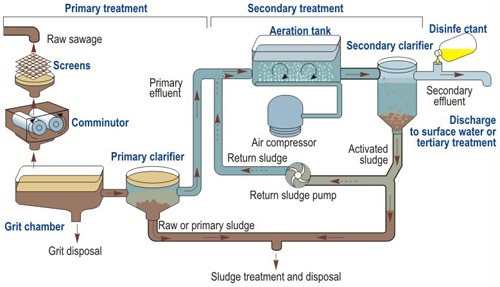
What are the steps in sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
How does a sewage system work?
1:344:14How Do Sewer Systems Work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd chemicals. And when we push it through turbulent environments like pumps it can create dangerousMoreAnd chemicals. And when we push it through turbulent environments like pumps it can create dangerous and deadly gases like hydrogen sulfide.
Where does sewage go after treatment?
What happens to the treated water when it leaves the wastewater treatment plant? The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What happens to poop in the sewer?
From the toilet, your poop flows through the city's sewage system along with all the water that drains from our sinks, showers and streets. From there, it goes to a wastewater treatment plant.
Does shower water and toilet water go to the same place?
That separates water vapor from the solid waste, and then the two part ways. Water vapor travels up and through a cleaning system that uses a cyclo...
What happens when you flush the toilet while showering?
The shower and toilet are connected to the sanitary sewer system. The wastewater from both can be treated at the same facility. Gray water is waste...
What are the methods of sewage treatment?
The Toilet Flush When the toilet flushes while you're showering, the toilet demands a load of cold water, and because it shares a cold water line w...
What happens during the first stage of sewage treatment plant?
Majorly, four methods of sewage water treatment are followed – physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment. By following these metho...
Where does poop go after the sewer?
Primary treatment in sewage treatment involves physical removal of particles (large and small) from the sewage through filtration and sedimentation...
What do sewage plants do with poop?
From the toilet, your poop flows through the city's sewage system along with all the water that drains from our sinks, showers and streets. From th...
What are the 5 stages of sewage treatment?
The wastewater flows through bar screens to remove trash and debris, then slowly moves through a grit tank where sand and heavy particles settle an...
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What is the purpose of screening wastewater?
Screening the wastewater. First, we remove large objects that may block or damage equipment or pollute our rivers. This includes items that should never have been put down the drain in the first place, such as nappies, wet wipes, sanitary items and cotton buds, and sometimes even things like bricks, bottles and rags.
How do we separate waste from water?
We separate the waste from the water by putting it into large settlement tanks, where solids sink to the bottom. We call the settled solids ‘sludge’. Large arms or scrapers help to push the sludge towards the centre, where it’s then pumped away for further treatment.
What is the name of the tank where sewage is put into?
At our larger sewage treatment works, we put the wastewater into rectangular tanks called ‘aeration lanes’ , which pump air into the water. This encourages the useful bacteria to break down and eat ...
Why do we treat sludge?
We treat the sludge we collect at the start of the process so that we can put it to good use. We recycle most of it to agricultural land for farmers to use as fertiliser, but we also use it to generate energy. We do this in several different ways:
What is the process of drying sludge into blocks called?
2. Thermal destruction: We dry the sludge into blocks called ‘cake’ , which are then burned to generate heat. We capture this heat and turn it into electricity.
How to make biogas from sludge?
1. Combined heat and power: We treat the sludge using a process called ‘anaerobic digestion’. This heats the sludge up to high temperatures, encouraging the bacteria inside to break down the waste. This creates biogas that we can then burn to create heat, which in turn creates electricity. 2.
Who regulates the quality of wastewater?
The Environment Agency strictly regulates the quality of the cleaned wastewater, and we test it to make sure that it meets their high-quality standards.
How is wastewater treated?
It is done by putting the wastewater into large settlement tanks for the solids to sink to the bottom. The settled solids are called sludge. At the bottom of these circular tanks, large scrappers continuously scrape the floor of the tank and push the sludge towards the center, where it is pumped away for further treatment. The rest of the water is moved to Secondary treatment.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
Screening is the first stage of the wastewater treatment process. Screening removes large objects like diapers, nappies, sanitary items, cotton buds, face wipes, and even broken bottles, bottle tops, plastics, and rags that may block or damage equipment.
Why is air pumped into sludge scraping water?
These are called aeration lanes. Air is pumped into the water to encourage bacteria to break down the tiny bits of sludge that escaped the sludge scraping process.
Where does liquid waste go?
Wastewater (liquid waste) from flushing the toilet, bathing, washing sinks, and general cleaning goes down the drain and into a pipe, which joins a larger sewer pipe under the road. The sewer pipe goes on to connect to a different sewer pipe that leads to the treatment center.
How is wastewater drained?
Waste water is drained through pipe systems and thus enters the public sewerage system . Here we differentiate between two types of drainage. In the combined sewer system, domestic and commercial wastewater is fed into a sewer together with rainwater that accumulates on sealed surfaces (e.g. streets and roofs).
Where does wastewater end up in a combined sewer system?
The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer systems, the sewage treatment plant has more work to do, as all the surface water has to be cleaned as well.
What happens after raking a sand filter?
After rakes comes a sand filter basin throug flow equalization. Here the wastewater is settled and through sedimentation sand, glass splinters and smaller solids sink to the bottom.
How does a separate sewer system work?
The separate sewer system divides the media. Dirty water is fed into one sewer, surface water into another. Because of the low dirt load, the collected surface water is usually discharged into neighbouring waters (lakes or rivers). The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer ...
What is the process of metabolising organic compounds in wastewater?
This process is called Biological nutrient removal.
What is the process of cleaning a toilet called?
Rakes filter everything that is not permeable as solid matter in the wastewater. This can be toilet paper, wet wipes, but also a toothbrush or other things that do not belong in a toilet. This process is called pretreatment.
What happens to clarified water?
In the end, the clarified water is returned to the natural water cycle, usually lakes or streams. Very modern sewage treatment plants have additional treatment stages for further phosphorus elimination or the killing of pathogens.
What is sewage treatment system?
Sewage treatment systems are a special device that treats wastes water in an environmentally sustainable way. The water produced from a sewage treatment system is able to be used on gardens and grass to keep them luscious and green all year round all while not adding to your water bill.
What is the first stage of sewage treatment?
The first stage in the sewage treatment is the Primary chamber. This chamber contains all of the grey and black water from the home and holds it until the heavy materials fall to the bottom and the lighter material floats to the top. Once this process has occurred the left over water (effluent) then leaves the tank and proceeds into the secondary chamber which is known as a pre-treatment chamber.
How long has sewage treatment been around?
Although it may not be something you have considered before, the history of sewage treatment actually goes back almost 12,000 years. From wells to copper drainage pipes to the wastewater systems we know today, sewage treatment has (thankfully) come a long way. Keep reading to learn more!Prehistor...
What is the final stage of wastewater?
The forth and final stage is when your wastewater is pumped out of your hose or irrigation system onto your garden or lawn.
What is the third stage of the water cycle?
The third stage of the process allows for the waste water to settle. The water within the chamber at this point is now lighter and less dense than what is was when it entered the system. The aerobic bacteria will settle to the bottom if not disturbed. Chlorine or UV light will be introduced at this point to remove any unwanted bacteria from the water.
What is the process of sewage treatment?
Because there is ammonia now, the sewage treatment is going to include biological nitrification to remove the ammonia, which gives you nitrates. And after all the ammonia is converted to nitrates, bacteria—either anaerobic or anoxic—reduce all the nitrate and create nitrogen gas, which dissipates into the atmosphere.
What Is a Biological Sewage Treatment System and How Does It Work?
In the United States, these local municipal facilities must follow both federal and local regulations in terms of the purity requirements for the treated effluent, and although they are treating roughly the same types of human waste, their methods for treating these wastes and to what degree are what varies.
What is activated sludge?
Simply speaking, the activated sludge process is a secondary treatment method that occurs after untreated wastewater is collected from throughout the city, travels through all the sewers, and enters pump stations and transfer stations that funnel wastes to the treatment plants. Here, it enters a series of pretreatments of primarily solids removal (screening, clarifying, grit removal, etc.) before it comes to the reactor basin, which is where the biological portion of the sewage treatment, or activated sludge process, takes place.
Why is nitrification used in sewage treatment?
Because there is ammonia now, the sewage treatment is going to include biological nitrification to remove the ammonia, which gives you nitrates. And after all the ammonia is converted to nitrates, bacteria—either anaerobic or anoxic—reduce all the nitrate and create nitrogen gas, which dissipates into the atmosphere.
How does the water flow in a reactor?
The treated water then flows through another clarifier where the biosolids (all the solids made after the biological work is complete) are separated out while the microorganisms are retained. In this clarifier, they settle to the bottom of a cone-shaped base and are either returned back to the basin as activated sludge or wasted as solids whereby they are dewatered and taken to an anaerobic digestor or farm.
What is MLSS in reactors?
In short, they’re managing MLSS (which is the bacterial concentration in the reactor basin) by how many clarified solids are returned and how many clarified solids are wasted.
How does a reactor system manage bacteria?
These systems manage the concentration of bacteria in the reactor basin by how much of the activated sludge becomes RAS or is wasted as WAS. These levels keep the number of suspended solids (which act as a catalyst) at a fixed point designated by the plant operators by essentially controlling how much food the microorganisms get.
How does the municipal wastewater treatment process work?
1. Firstly, wastewater is drained to the WWTP by gravity through the main sewer system of the size of a car. Having such size, objects you could hardly imagine reach the WWTPs, ranging from mattresses, fridges, tree branches to wallets disposed of by thieves in order to get rid of the evidence.
What is the final step of wastewater treatment?
10. The final step of wastewater treatment is the deep inspection of service water. Aim of this inspection is to analyse the contamination level and ensure that the treated water complies with the highest standards, defining its release or reuse for domestic and/or industrial purposes.
What happens during the biological stage of a sludge treatment?
6. During the biological stage, the excess sludge (i.e. excess bacteria) is pumped out and moved before the settling tanks. Here, the sludge settles and is transported to digestion tanks for further treatment.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
What happens to wastewater pollution after primary treatment?
This is the point where primary pre-treatment ends and secondary wastewater treatment starts. After the primary treatment, level of wastewater pollution drops to 60%.
