What is the treatment for erythroblastosis fetalis?
Injections of a medicine called Rh immune globulin can keep your body from making Rh antibodies. It helps prevent the problems of Rh incompatibility. If treatment is needed for the baby, it can include supplements to help the body to make red blood cells and blood transfusions.
What is erythroblastosis fetalis What is the cause who is at risk How is it treated?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is hemolytic anemia in the fetus (or neonate, as erythroblastosis neonatorum) caused by transplacental transmission of maternal antibodies to fetal red blood cells. The disorder usually results from incompatibility between maternal and fetal blood groups, often Rho(D) antigens.
What is the treatment for Rh incompatibility?
Rh incompatibility can be prevented with the use of RhoGAM. Therefore, prevention remains the best treatment. Treatment of an infant who is already affected depends on the severity of the condition. Infants with mild Rh incompatibility may be treated with phototherapy using bilirubin lights.
How do we prevent hemolytic erythroblastosis fetalis?
HDN can be prevented. Almost all women will have a blood test to learn their blood type early in pregnancy. If you're Rh negative and have not been sensitized, you'll get a medicine called Rh immunoglobulin (RhoGAM). This medicine can stop your antibodies from reacting to your baby's Rh positive cells.
What happens when mother is Rh positive and baby is Rh-negative?
If the mother is Rh-negative, her immune system treats Rh-positive fetal cells as if they were a foreign substance. The mother's body makes antibodies against the fetal blood cells. These antibodies may cross back through the placenta into the developing baby. They destroy the baby's circulating red blood cells.
Why are Rh positive mother not at risk for erythroblastosis fetalis?
It is rare for a mother to become sensitized during the course of her first Rh-positive pregnancy because the amount of fetal Rh antigen that enters maternal circulation is insufficient to cause sensitization; usually only during labour will exposure be significant.
How is a Rh negative mother treated?
If the mother is RhD negative, she'll be offered injections of anti-D immunoglobulin at certain points in her pregnancy when she may be exposed to the baby's red blood cells. This anti-D immunoglobulin helps to remove the RhD foetal blood cells before they can cause sensitisation.
Can Rh disease be treated?
Treatment for rhesus disease depends on how severe the condition is. In more severe cases, treatment may need to begin before the baby is born. Around half of all cases of rhesus disease are mild and don't usually require much treatment.
What is RhoGAM and how does it work?
RhoGAM is a medicine that stops your blood from making antibodies that attack Rh-positive blood cells. RhoGAM is a sterilized solution made from human blood that contains a very small amount of Rh-positive proteins. These proteins keep your immune system from making permanent antibodies to Rh-positive blood.
How is hemolytic disease of the newborn treated?
TreatmentFeeding often and receiving extra fluids.Light therapy (phototherapy) using special blue lights to convert bilirubin into a form which is easier for the baby's body to get rid of.Antibodies (intravenous immunoglobulin, or IVIG) to help protect the baby's red cells from being destroyed.More items...•
What are the possible treatments for a Coombs positive new born?
Treatment for Coombs-Positive Babies A significant level of jaundice will be treated with phototherapy. Also known as light therapy, this is a non-invasive medical treatment in which a light source (often from fluorescent, LED, or halogen bulbs) is used to help the baby's body break down bilirubin.
How does a treatment with anti Rh antibodies prevent hemolytic disease of the newborn?
If a mother is Rh-negative and has not been sensitized, she is usually given a drug called Rh immunoglobulin, or RhoGAM. This specially developed blood product prevents an Rh-negative mother's antibodies from reacting to her baby's Rh-positive red blood cells.
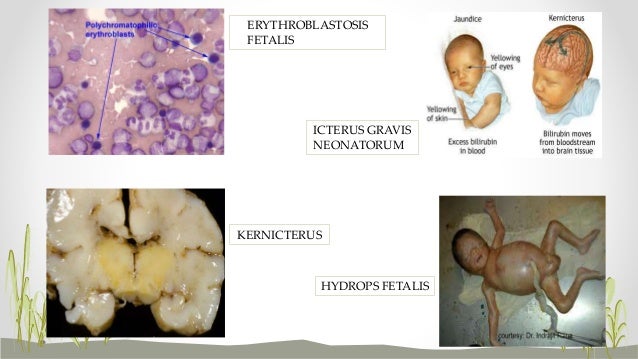
What Is Erythroblastosis Fetalis?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is also called hemolytic disease. Babies develop this condition before they are born. Erythroblastosis fetalis occurs when...
What Causes Erythroblastosis Fetalis?
Certain incompatibilities (differences) in blood type can cause erythroblastosis fetalis. One type of incompatibility happens because you are Rh ne...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Erythroblastosis Fetalis?
1. Before your baby is born: 1. Fast heart rate 2. Enlarged organs, such as the heart, liver, or spleen 3. Swelling of your baby's body 2. After yo...
How Is Erythroblastosis Fetalis Diagnosed?
1. Before your baby is born: Healthcare providers will need to know if you have past pregnancies, abortions, miscarriages, or any blood transfusion...
How Is Erythroblastosis Fetalis Treated?
1. Before your baby is born: 1. Blood transfusions: Your unborn baby may need to have blood transfusions while still in the womb. These may be give...
What Are The Risks of Erythroblastosis Fetalis?
1. Your baby may have breathing or other problems if he was born earlier than expected. An IVIG may cause an infection. A reaction to IVIG may caus...
How Can Erythroblastosis Fetalis Be Prevented?
1. Screening tests: Get your blood type checked before you get pregnant. You can also have it checked during your first prenatal visit. You may nee...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. Before your baby is born: 1. You feel your baby is moving less or is not moving at all. 2. You develop a fever. 2. After your baby is born: 1. Y...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care Or Call 911?
1. Your baby has jaundice that does not go away or gets worse. 2. Your baby has shortness of breath. 3. Your baby is having a seizure. 4. Your baby...
What causes erythroblastosis fetalis?
There are two main causes of erythroblastosis fetalis: Rh incompatibility and ABO incompatibility. Both causes are associated with blood type. There are four blood types: In addition, blood can be either Rh positive or Rh negative. For example, if you’re type A and Rh positive, you have A antigens and Rh factor antigens on the surface of your RBCs.
Why do you give blood transfusions to a baby?
If a baby experiences erythroblastosis fetalis in the womb, they may be given intrauterine blood transfusions to reduce anemia. When the baby’s lungs and heart mature enough for delivery, a doctor may recommend delivering the baby early. After a baby is born, further blood transfusions may be necessary.
What is the condition where the mother's blood type isn't compatible with the baby's blood type?
ABO incompatibility. Another type of blood type mismatch that can cause maternal antibodies against her baby’s blood cells is ABO incompatibility. This occurs when the mother’s blood type of A, B, or O isn’t compatible with the baby’s. This condition is almost always less harmful or threatening to the baby than Rh incompatibility.
Why is it bad for a baby to have fluid in the fetus?
This includes spaces in the: This symptom can be harmful because the extra fluid places pressure on the heart and affects its ability to pump.
What blood type causes erythroblastosis?
Another type happens because you and your baby have different major blood types. A, B, and O are the 3 major blood types. Erythroblastosis fetalis is most common when the mother's blood type is O and ...
What is the condition that causes the RBCs to break down?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a condition that causes your unborn baby's red blood cells (RBCs) to break down. This may cause severe anemia (low RBC count). Anemia makes it difficult for the RBCs in your baby's blood to carry enough oxygen to his or her body. This condition is also called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What blood test is used to check a baby's blood type?
You or your baby may need any of the following tests: Blood tests are used to check your blood type and Rh type, and to look for antibodies. Providers may want to test the blood of the baby's father for ABO and Rh type. Your baby's blood type, RBCs, Rh type, and bilirubin levels may also be checked. Bilirubin is made when RBCs break down.
How does phototherapy work?
After your baby is born: Phototherapy uses light to turn bilirubin into a form that your newborn's body can remove.
Can you have your blood tested during your first prenatal visit?
You can also have it checked during your first prenatal visit. You may need more tests if you have been pregnant before or had blood transfusions. Healthcare providers may screen your blood for antibodies to other blood types. Providers may also want to test the baby's father's blood.
What is erythroblastosis fetalis?
It is a blood disorder that occurs when the blood types of a mother and baby are incompatible. It is also called as hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
What is the name of the disease when a mother has Rh negative blood?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis most frequently occurs when a mother with Rh-negative blood becomes pregnant by a Rh-positive father, resulting in a Rh-positive baby. This type of Erythroblastosis Fetalis is often called Rh disease.
Is erythroblastosis fetalis preventable?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis is very preventable. Erythroblastosis Fetalis prevention is easy. Today, nearly all women with Rh-negative blood are identified in early pregnancy through blood tests. If a mother is Rh-negative and has not been sensitized, she is usually given a drug called Rh immunoglobulin, or RhoGAM. This specially developed blood product prevents a Rh-negative mother’s antibodies from reacting to her baby’s Rh-positive red blood cells. Mothers are typically given RhoGAM around the 28th week of pregnancy and again within 72 hours of giving birth.
How often do you have to have a fetal transfusion?
Transfusions occur every 1 to 2 weeks, usually until 32 to 35 weeks. During that time period, delivery may be recommended if there is continuing evidence of severe fetal anemia (based on MCA blood flow). The woman may continue to term delivery if there is no evidence of severe fetal anemia based on MCA blood flow.
What is fetal DNA screening?
Cell-free fet al DNA screening. At the first prenatal visit, all women are screened for blood type, Rh type, and anti-Rho (D) and other antibodies that are formed in response to antigens and that can cause erythroblastosis fetalis (reflex antibody screening). If women have Rh-negative blood and test positive for anti-Rho ...
Why should placenta removal be avoided?
Delivery should be as atraumatic as possible. Manual removal of the placenta should be avoided because it may force fetal cells into maternal circulation. Maternal sensitization and antibody production due to Rh incompatibility can be prevented by giving the woman Rho (D) immune globulin.
What is the greatest movement during pregnancy?
Movement is greatest at delivery or termination of pregnancy. Movement of large volumes (eg, 10 to 150 mL) is considered significant fetomaternal hemorrhage; it can occur after trauma and sometimes after delivery or termination of pregnancy.
Does Kell antibody incompatibility suppress RBC?
The mechanism is the same when other antigen systems are involved; however, Kell antibody incompatibility also directly suppresses RBC production in bone marrow.
Is fetal anemia likely if MCA blood flow is elevated?
If fetal blood is Rh positive or status is unknown and if MCA blood flow is elevated, fetal anemia is likely .
Why does erythroblastosis occur in fetal blood?
Erythroblastosis fetalis only occurs when the mother is Rh-. Erythroblastosis fetalis occurs as a result of the sensitization of the mothers Rh- blood due to exposure to Rh-D antigens either by blood transfusion ...
Why do Rh+ babies have erythroblastosis fetalis?
As a result of the production of anti-bodies, subsequent Rh+ babies will be subjected to erythroblastosis fetalis because the body of the synthesized mother will attack the baby’s red blood cell due to the presence of Rh-D antigens.
What is the first step in a pregnancy?
The first step of diagnosis is prenatal maternal blood typing and screening. The blood group and Rhesus factor of the woman is determined. She is also screened for anti-RhD and any other anti-bodies that may have developed due to exposure of any of the antigens that may lead to erythroblastosis fetalis.
What causes erythroblastosis in neonates?
Erythroblastosis fetalis of neonates, also erythroblastosis neonatorum or hemolytic anemia of the newborn is caused by the transmission of antibodies to the red blood cell of the fetus through the placenta in intrauterine life. It is caused by incompatibility of the maternal blood group and the fetal blood group, ...
What happens if the father has no antigens?
If the father has neither of the antigens, then the child will be 100 percent free of these antigens and will be free of erythroblastosis fetalis.
What happens if a mother is Rh+?
If the mother is found to be Rh+, normal pregnancy procedures are carried on. If the mother is Rh- and has any of the anti-bodies caused by erythroblastosis fetalis causing antigens, then the next step will be to test the blood of the father, if the paternity of the child is certain.
When is Rh+ given?
When the Rh- woman is pregnant with her first Rh+ baby and she has not been previously sensitized, she is given Rh-D immune globulin at: 28th week of pregnancy. 72 hours of terminating the pregnancy either by delivery or abortion or treatment of ectopic pregnancy. After any occurrence of vaginal bleeding.
What is the term for a newborn that breaks down red blood cells?
This condition occurs when there is an incompatibility between the blood types of the mother and baby. "Hemolytic" means breaking down of red blood cells. "Erythroblastosis" refers to making of immature red blood cells. "Fetalis" refers to fetus.
What happens to the baby when the mother's antibodies cross the placenta?
As the antibodies destroy the red blood cells, the baby can become sick. This is called erythroblastosis fetalis during pregnancy. In the newborn, the condition is called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What is the term for a baby's organs that are unable to handle anemia?
Hydrops fetalis. This occurs as the baby's organs are unable to handle the anemia. The heart begins to fail and large amounts of fluid build up in the baby's tissues and organs. A fetus with hydrops is at great risk of being stillborn.
What happens when a baby has a Rh negative mother?
HDN most frequently occurs when an Rh negative mother has a baby with an Rh positive father. When the baby's Rh factor is positive, like the father's, problems can develop if the baby's red blood cells cross to the Rh negative mother. This usually happens at delivery when the placenta detaches. However, it may also happen anytime blood cells ...
Does the placenta help with bilirubin?
The placenta helps rid some of the bilirubin, but not all. Severe anemia with enlargement of the liver and spleen. When these organs and the bone marrow cannot compensate for the fast destruction of red blood cells, severe anemia results and other organs are affected. Hydrops fetalis.
Can you repeat bilirubin transfusion?
Exchange transfusions may need to be repeated if the bilirubin levels remain high. Intravenous immunoglobin (IVIG). IVIG is a solution made from blood plasma that contains antibodies to help the baby's immune system. IVIG may help reduce the breakdown of red blood cells and lower bilirubin levels.

Description
- Red blood cells (RBCs) carry several types of proteins, called antigens, on their surfaces. The A, B, and O antigens represent the classification of an individual's blood as type A, B, AB, or O. Depending on the genetic predisposition of the parents, an A, B, or O antigen gene can be passed to a child. How the genes are paired determines the person's blood type.A person who inherits a…
Treatment
- Negative antibody titers can consistently identify the fetus that is not at risk; however, the titers cannot reliably point out the fetus which is in danger because the level of titer does not always correlate with the severity of the disease. For example, a severely sensitized woman may have antibody titers that are moderately high and remain at the same level while the fetus is being mo…
Diagnosis
- 1. Rh system antibodies. 2. ABO system antibodies. 3. Kell system antibodies. 4. Duffy system antibodies (rare). 5. MNS and s system antibodies (rare).
- Erythroblastosis fetalis can be predicted before birth by determining the mother's blood type. If she is Rhnegative, the father's blood is tested to determine whether he is Rh-positive. If the father is Rh-positive, an antibody screen is done to determine whether theRh-negative woman is sensitized to the Rh antigen (developed isoimmunity). The indirect Coombs test measures the n…
Causes
- Erythroblastosis fetalis is also called hemolytic disease. Babies develop this condition before they are born. Erythroblastosis fetalis occurs when you and your baby have different blood types. When your baby's blood mixes with your blood during pregnancy, your immune system reacts by making antibodies against it. Antibodies are a part of the body's immune system that fight germs and su…
- Rh disease and ABO incompatibility disease are caused when a mother's immune system produces antibodies against the red blood cells of her unborn child. The antibodies cause the baby's red blood cells to be destroyed and the baby develops anemia. The baby's body tries to compensate for the anemia by releasing immature red blood cells, called erythroblasts, from th…
Prognosis
- Overall survival has been noted to be 84-90%.Reversal of hydrops as a result of intrauterine treatment is associated with improved perinatal outcome but, when it does not reverse, the survival rate is only 39%. Neurodevelopment is usually normal (for >90%).
- In many cases of blood type incompatibility, the symptoms of erythroblastosis fetalis are prevented with careful monitoring and blood type screening. Treatment of minor symptoms is typically successful, and the baby does not suffer long-term problems.Nevertheless, erythroblastosis is a very serious condition for approximately 4,000 babies annually. In about 15 …
Prevention
- Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis (RAADP) using anti-D immunoglobulin should be given to all rhesus-negative women who have not already been sensitised. It can be given as two doses of anti-D immunoglobulin of at least 500 IU at 28 and 34 weeks or as a large single dose of 1500 IU at 28 weeks gestation. Treatment is also indicated after other sensitising events such as abortio…
- With any pregnancy, whether it results in a live birth, miscarriage, stillbirth, or abortion, blood typing is a universal precaution against blood compatibility disease. Blood types cannot be changed, but adequate forewarning allows precautions and treatments that limit the danger to unborn babies.
History
- HDN was first described by a French midwife, in a set of twins in 1609. It was later termed erythroblastosis fetalis when Louis K Diamond and his co-workers recognised the relationship between erythroblasts in the circulation, anaemia, fetal hydrops and jaundice. The rhesus blood group system was identified in 1940 and the link between rhesus haemolytic disease and alloim…
Definition
- Erythroblastosis fetalis, also known as hemolytic disease of the newborn or immune hydrops fetalis, is a disease in the fetus or newborn caused by transplacental transmission of maternal antibody, usually resulting from maternal and fetal blood group incompatibility. Rh incompatibility may develop when a woman with Rh-negative blood becomes pregnant by a man with Rh-positiv…
Epidemiology
- The incidence of haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) depends on the proportion of the population who are RhD negative. This varies within ethnic minorities but, in the UK, it is highest in the Caucasian population (approximately 16%). Before immunoprophylaxis was available, HDN affected 1% of all newborns and was responsible for the death of one baby in every 2,200 births.…
Management
- As soon as the blood samples confirm anaemia, transfusion should be commenced with group O negative packed cells cross-matched with maternal blood. This is best done at 18 weeks but samples can be taken at 16 weeks if necessary. Intravenous transfusion under ultrasound guidance via the umbilical vein is to be preferred to the intraperitoneal route, as the latter is mor…